Biology Lecture 20 Respiratory & Digestive Systems
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Explain how the partial pressures of O2 and CO2 varies across different tissue beds in the body.
Lungs: high O₂, low CO₂
Resting tissues: lower O₂, higher CO₂
Active tissues: very low O₂, very high CO₂
Explain why the O2 saturation curve for hemoglobin (i) is S-shaped, and (ii) peaks at an O2 partial pressure of 100 mm Hg.
Cooperativity - the binding of O2 to hemoglobin increases the affinity of the other sides for oxygen
At this point, oxygen saturation is nearly 100% and hemoglobin molecules are already almost full
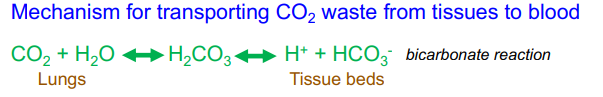
Describe the mechanism for transporting CO2 wastes from tissues to blood
Via three mechanisms:
10% dissolves in plasma
20% binds to hemoglobin to form carbaminohemoglobin
70% is converted to bicarbonate ions within red blood cells
Describe the mechanism for transporting CO2 wastes from the blood to the alveoli
Some of the bicarbonate in the blood plasma combines with H+ to form CO2 and water
Most of the bicarbonate is transported into CO2 and water and diffuses from blood into the alveolar air
Describe the Bohr-shift and its functional significance.
The Bohr shift ensures that oxygen goes where it’s needed the most.
Resting tissues → hemoglobin holds onto O₂ more tightly
Active tissues → hemoglobin releases O₂ more easily
This helps your body match oxygen delivery to oxygen demand.
Indicate which blood gas is most important in controlling breathing rate in humans.
PCO2
Contrast the numbers of ATP yielded by the metabolism of glucose and fatty acids under aerobic versus anaerobic metabolism.
Aerobic - 34
Anaerobic - 2
Explain why glucose is the primary energy substrate at high exercise intensities.
Because the body cannot supply adequate amounts of oxygen for oxidative metabolism. Without oxygen, only glycolysis is possible.
Describe the swallowing reflex and esophageal peristalsis.
Swallowing Reflex:
1. Tongue pushes food back
2. Food touches back of throat
3. The brain “locks down” the airway
4. Food is pushed into the esophagus
Esophageal peristalsis: a wave of muscle contractions that pushes food down into the stomach.
Explain the chemical and mechanical digestive processes that occur in the stomach.
Mechanical digestion: stomach muscles churn food into chyme.
Chemical digestion: acid and enzymes break down proteins and start fat digestion.
Discuss how the stomach protects itself against the high acidity and enzymatic actions of its secretions.
Mucus Layer
Tight Junctions
Rapid Cell Turnover
Inactive Digestive Enzyme (Pepsinogen):
Indicate which macronutrients are digested in the mouth, stomach, small intestinal lumen, and small intestinal brush border.
Mouth - Carbs
Stomach - Proteins
Lumen - Carbs, Proteins, Fats
Brush Border - Carbs, Proteins, Fats
Explain how fats are digested and absorbed
Bile breaks up fat.
Pancreatic lipase digests it into fatty acids + monoglycerides.
Micelles carry them to the intestinal cells.
Cells rebuild fats and package them into chylomicrons.
Chylomicrons enter lymphatic vessels, then the bloodstream.
Explain which nutrients are transported through the hepatic portal versus lymphatic vessels.
Water-soluble stuff → blood → hepatic portal → liver first.
Fat-soluble stuff → lymph vessels → bloodstream later → liver later.
Indicate what is digested in and absorbed by the large intestine.
Water, electrolytes, vitamins
Explain the differences between the intestinal tract of carnivores and herbivores.
Carnivores: short gut, simple cecum, strong acids, fast digestion.
Herbivores: long gut, big cecum or multi-stomach, heavy fermentation, slow digestion.