bi107 quiz 3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/128
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
129 Terms
1
New cards
common ancestor
all of life is related through a _______________
2
New cards
homologous structures
most synapomorphies are also
3
New cards
lineage
series of ancestor and descendant populations
4
New cards
phylogeny
Evolutionary history of a species or group of species.
5
New cards
phylogenetic tree
A family tree that shows the evolutionary relationships thought to exist among groups of organisms
6
New cards
- all life forms
- major evolutionary groups
- small groups of closely related species
- individuals
- populations
- genes
- major evolutionary groups
- small groups of closely related species
- individuals
- populations
- genes
phylogenetic trees are hypotheses of the evolutionary relationships of...
7
New cards
root
the common ancestor of all the organisms in the tree forms the ______ of the tree
8
New cards
node
indicate timing of splitting events
9
New cards
splits
in a tree of species this represents a speciation event
10
New cards
splits
in a tree of genes this represents a genetic duplication event
11
New cards
no
if you rotate around a node does the layout of the tree change
12
New cards
false
T or F vertical distances between branches have a meaning
13
New cards
taxon
any group of species designated with a name
14
New cards
clade
any taxon that consists of all the evolutionary descendants of a common ancestor
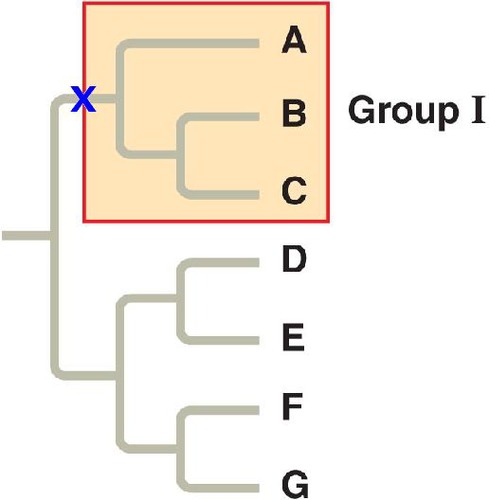
15
New cards
...
evolution can be defined as descent w modification
16
New cards
biological classification
evolutionary relationships form the basis for....
17
New cards
homologous feature
similar features that originated in a shared ancestor
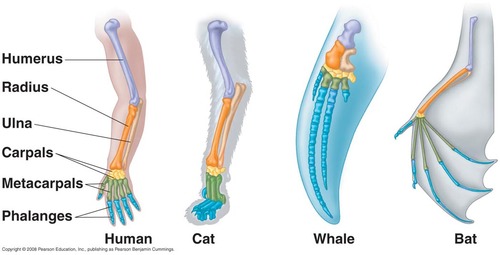
18
New cards
- DNA sequences
- protein structures
- anatomical structures
- behavior patterns
- protein structures
- anatomical structures
- behavior patterns
homologous features can be heritable traits in the form of ...
19
New cards
character
a general category for which species manifest different staes
20
New cards
- wings
- floral nectar
- leaves
- eye color
- floral nectar
- leaves
- eye color
types of characters
21
New cards
- A, G, C, T
- hairy/not hairy
- present/absent
- brown, blue, green
- hairy/not hairy
- present/absent
- brown, blue, green
types of character traits
22
New cards
derived trait
newly evolved features that do not appear in the fossils of common ancestors
23
New cards
ancestral trait
A trait shared by all members of a group through a common ancestor.
24
New cards
Synapomorphy
shared derived traits that provide evidence of the common ancestry of a group
25
New cards
convergent evolution
when superficially similar traits evolve independently in different lineages
26
New cards
wings evolving in bats and birds but not in other ancestors between them
example of convergent evolution
27
New cards
analagous structures
Similar function but different structure - does not show common ancestry
28
New cards
example of analagous structures
Bat, insect, and bird wings
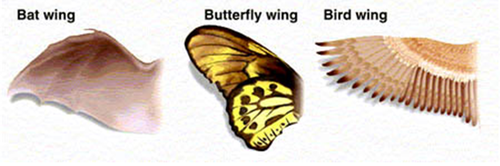
29
New cards
evolutionary rehearsal
when a character reverts from a derived state back to an ancestral state
30
New cards
homplasy
similar traits gained (convergent evolution) or lost (evolutionary rehearsals) in separate lineages over time
31
New cards
Birds have wings to fly and bats have wings to fly but they evolved differently as bats are mammals
example of homoplasy
32
New cards
point of reference
a trait may be ancestral or derived depending on the...
33
New cards
ancestral trait
in a phylogeny of all living vertebrates, feathers are a derived trait, but in a phylogeny of only modern birds they are an
34
New cards
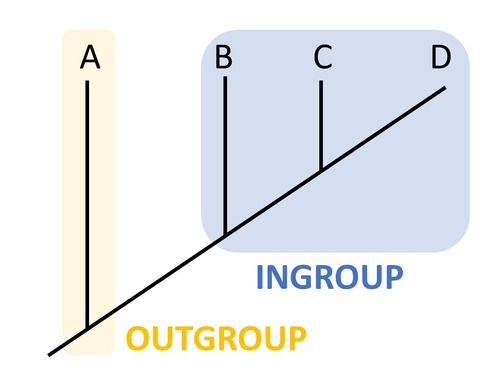
ingroup (phylogenetic tree)
the group of organisms of primary interest
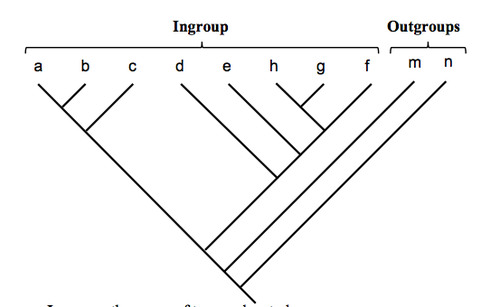
35
New cards
outgroup (phylogenetic tree)
species/ group known to be closely related to, but phylogenetically outside of, the group of interest ( 1 individual who is phylogenetically separate from the ingroup)
36
New cards
more closely related than taxa who have less shared traits
taxa who share derived character traits should be
37
New cards
character matrix
an array of taxa (at left) and characters (at top) that contains the character states for the taxa

38
New cards
parsimony principle
the simplest explanation of observed data is the preferred explanation
39
New cards
minimized
in phylogenies, the number of evolutionary changes that need to be assumed over all characters in all groups is....
40
New cards
fewest
the best hypothesis is the one that requires the __________ homoplasies
41
New cards
- morphology
- developmental traits
- fossil record
- behavioral traits
- molecular traits
- developmental traits
- fossil record
- behavioral traits
- molecular traits
traits that are genetically determined that can be used in a phylogenetic analyses
42
New cards
- reconstructing past events
- forensic investigations that involve viral transmission
- compare and contrast living organisms
- reveal convergent evolution and reconstructing ancestral states
- forensic investigations that involve viral transmission
- compare and contrast living organisms
- reveal convergent evolution and reconstructing ancestral states
why is a phylogenetic tree useful?
43
New cards
divergences
molecular clocks can provide information on timing of
44
New cards
lineage splits
rates of molecular clocks are constant enough to predict the timing of ....
45
New cards
they use the average rate at which a given gene/protein accumulates changes
how do molecular clocks gauge the time of divergence
46
New cards
calibrated using independent data
molecular clocks must be
47
New cards
binomial nomenclature
Classification system in which each species is assigned a two-part scientific name (genus species)
48
New cards
kingdom
phylum
class
order
family
genus
species
phylum
class
order
family
genus
species
taxonomy (king phillip came over for good soup)
49
New cards
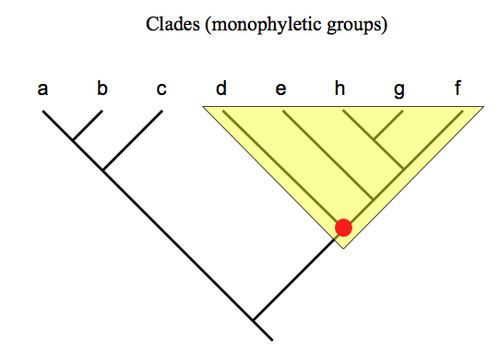
monophyletic group
the group that consists of a single ancestral species and all its descendants and excludes any organisms that are not descended from that common ancestor
50
New cards
cut
a true monophyletic group can be remove from a phylogenetic tree by a single _____
51
New cards
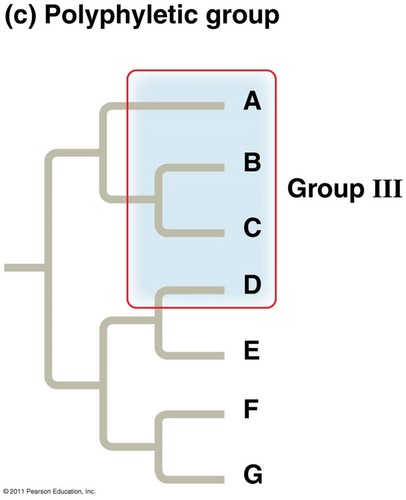
polyphyletic group
a group that doesn't include its common ancestor
52
New cards
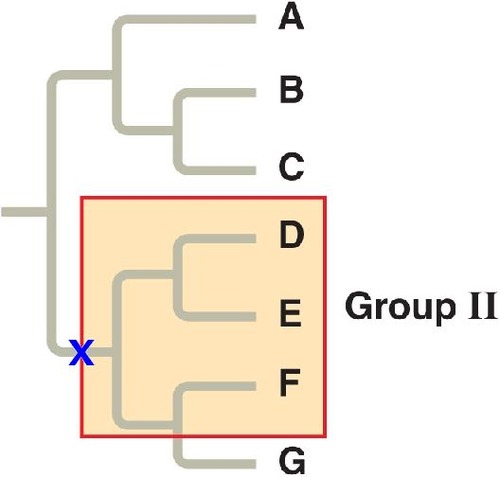
paraphyletic group
a group that doesn't include all the descendants of a common ancestor
53
New cards
stratigraphy
much of Earth's history is recorded in rocks
54
New cards
progressively younger
in sedimentary rock layers, the oldest layers are at the bottom and the higher strata are ....
55
New cards
The oldest of the Precambrian eons; no life on earth (4.5-4.6 bya)
hadean eon
56
New cards
origin of life (3.8 bya)
Archean eon
57
New cards
evolution of photosynthesis (2.5 bya)
proterozoic
58
New cards
beginning of the paleozoic era
cambrian period
59
New cards
phanerazoic
name of our present day eon
60
New cards
anaerobic
all early life forms must have had what type of metabolism?
61
New cards
the great oxygenation
2.5-1.8 bya
when the first aerobic bacteria came to life
- shift in metabolic pathway
when the first aerobic bacteria came to life
- shift in metabolic pathway
62
New cards
cyanobacteria, it Split water as a source of hydrogen ions for photosynthesis
what first released oxygen during the great oxygenation
63
New cards
the slow rise of O2 levels
1.8- 0.8 bya
- atmospheric oxygen rose because of a balance of photosynthesis and respiration
- ozone layer formed which allowed for life on land
- atmospheric oxygen rose because of a balance of photosynthesis and respiration
- ozone layer formed which allowed for life on land
64
New cards
it reduced radiation from the sun hitting the planet
how did the ozone layer allow for expansion of life on land?
65
New cards
anaerobes in most of Earth's environment
as oxygen accumulated, organisms with aerobic metabolisms replaced _______
66
New cards
1.5 bya, a cyanobacteria-like ancestor became symbiotic within eukaryotic cells
how did chloroplasts develop
67
New cards
the rapid rise of O2 levels
850-500 mya
burial of organic matter due to tectonic shifts
burial of organic matter due to tectonic shifts
68
New cards
highest o2 values
320-275 mya
diversification of large land plants
diversification of large land plants
69
New cards
rapid drop of o2 levels
250 mya
96% of multicellular species went extinct
largest mass extinction event
massive volcanic eruptions caused climate cooling
swamps dried up (used atmospheric o2)
96% of multicellular species went extinct
largest mass extinction event
massive volcanic eruptions caused climate cooling
swamps dried up (used atmospheric o2)
70
New cards
permian extinction
largest mass extinction event
71
New cards
radiation-
rapid speciation event
72
New cards
cambrian explosion
rapid diversification of life, evolutionary radiations
73
New cards
ethology
study of animal behavior
74
New cards
1. Causation
2. Development
3. Function
4. Evolution
2. Development
3. Function
4. Evolution
Tinberg's Four Questions
75
New cards
Causation
what is the mechanism underlying the behavior?
how can mechanisms be modified by learning?
how can mechanisms be modified by learning?
76
New cards
development
what experiences are necessary for a behavior to be displayed?
- imprinting, learning, environmental effects, changes with age
- imprinting, learning, environmental effects, changes with age
77
New cards
function
how does the behavior affect the animal's chances of survival and reproduction?
78
New cards
function
Does dispersal increase reproductive success in mice? is an example of what type of question
79
New cards
evolution
how might have the behavior evolved?
similarities to related species?
- phylogenetic history of the behavior
similarities to related species?
- phylogenetic history of the behavior
80
New cards
immediate mechanisms that underlie behavior
(ie: causation and development)
(ie: causation and development)
proximate questions
81
New cards
evolutionary processes that produced the behavior
(ie: function and evolution)
(ie: function and evolution)
ultimate questions
82
New cards
receives info from the environment and coordinates a response
in animals, the nervous system
83
New cards
species-species instinctive behaviors
- performed without learning
- performed the same way every time
- not typically modified by learning
- performed without learning
- performed the same way every time
- not typically modified by learning
fixed action patterns
84
New cards
mother goose chasing after the egg and going back to the nest even though it rolled away
example of a fixed action pattern
85
New cards
biological determinism
an individual's behaviors are fixed by their genetic makeup
86
New cards
behaviors
gene expression can change at certain stages in an organism's life which can lead to differences in
87
New cards
to what extent is behavior shaped by genetic variation vs past experience, learning, or other environmental influences
nurture vs nature
88
New cards
multiple genes have to be expressed and interact in order for a given behavior to be performed
what leads to a specific behavior being performed
89
New cards
for the first 3 weeks, they are nurse bees (caring for the young), and then from day 23-42 the gene expression changes and they become foraging bees
example of behavioral genetics
90
New cards
epigenetics
DNA methylation and histone modification can change gene expression without changing the underlying DNA sequences
91
New cards
Learning
acquired changes in. behavior during one's lifetime
92
New cards
innate learning
fixed action patterns are an example of
93
New cards
1. conditional reflex
2. imprinting
3. cognitive learning
2. imprinting
3. cognitive learning
three types of learned behaviors
94
New cards
conditioned reflex
A simple relation between a specific conditioned stimulus and a conditioned involuntary response.
95
New cards
pavlov's dog salivating at a metronome when no food's around because he heard a metronome at mealtimes
example of conditioned reflex
96
New cards
imprinting
the process by which certain animals form attachments during a critical period very early in life
97
New cards
conservation biologists dressed as whooping cranes to not affect the imprinting of cranes in their labs
- the number of cranes went from 30 to 800
- the number of cranes went from 30 to 800
example of imprinting
98
New cards
Emlen Funnel
funnel with ink pad on bottom, paper on funnel walls, use in planetarium; radial patterns on funnel indicate direction animal is trying to fly
99
New cards
1. prevented from seeing night sky at all
2. recreated the natural sky
3. portray an incorrect sky (different axis of rotation
2. recreated the natural sky
3. portray an incorrect sky (different axis of rotation
three ways the emlen funnel modified the sky
100
New cards
anywhere. they had no directional information
the indigo buntings that didnt see the night sky in the emlen funnel ended up going ...