Chapter 5 : The Muscular System
Function of Muscles
Produce movement,
Maintain posture
Stabilize joints
Generate heat
Types of Muscles
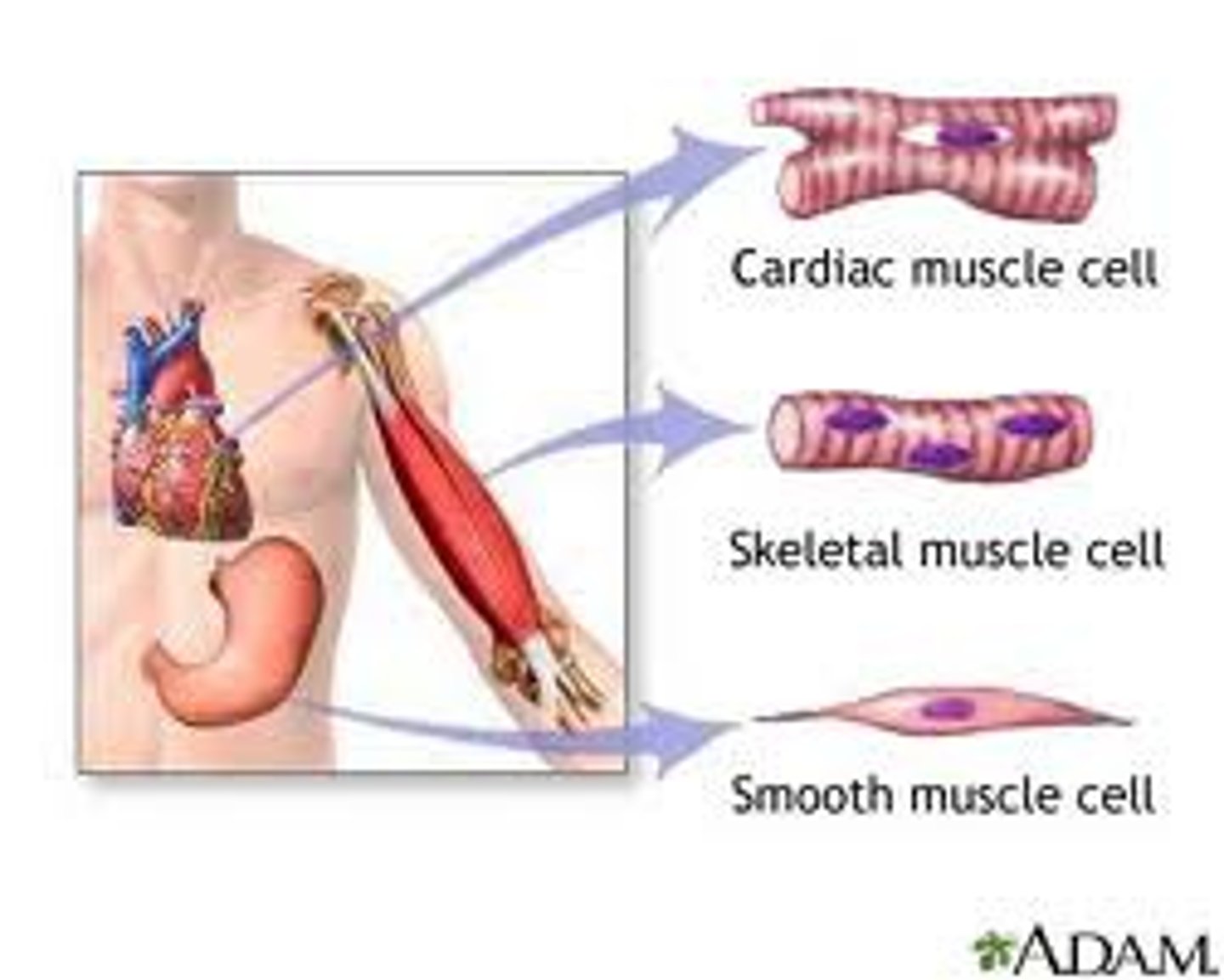
Skeletal muscle, Cardiac muscle, Smooth muscle
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Function of Muscles
Produce movement,
Maintain posture
Stabilize joints
Generate heat
Types of Muscles
Skeletal muscle, Cardiac muscle, Smooth muscle

Prefix myo and mys
Refers to muscle
Prefix sarco
Refers to flesh
Skeletal Muscle Characteristics
- Cells are multinucleate,
- Striated - have visible banding,
- Voluntary control,
- Cells surrounded and bundled by connective tissue
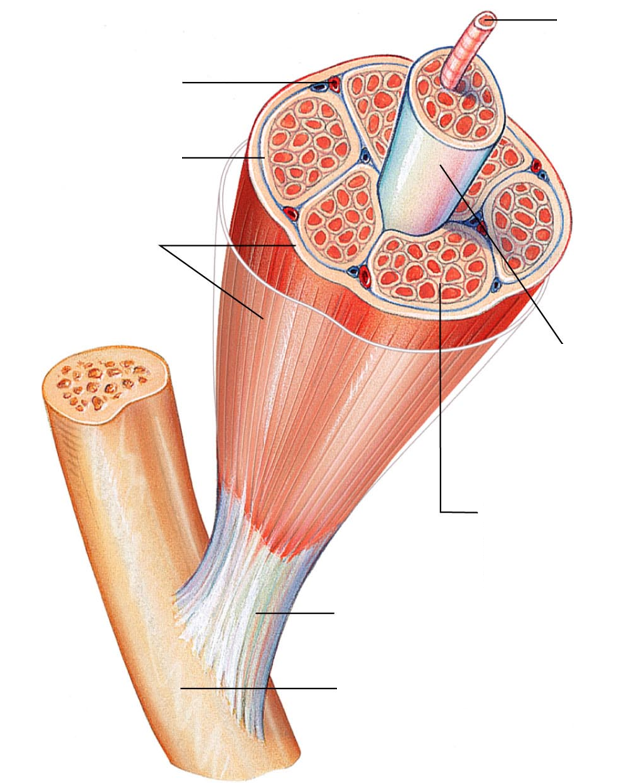
Connective tissue for muscle
Endomysium
Perimysium
Epimysium
Fascia
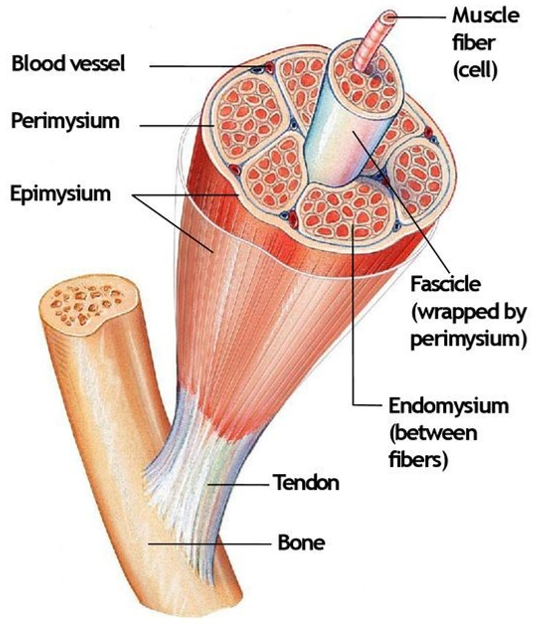
Endomysium
Surrounds individual muscle fibers
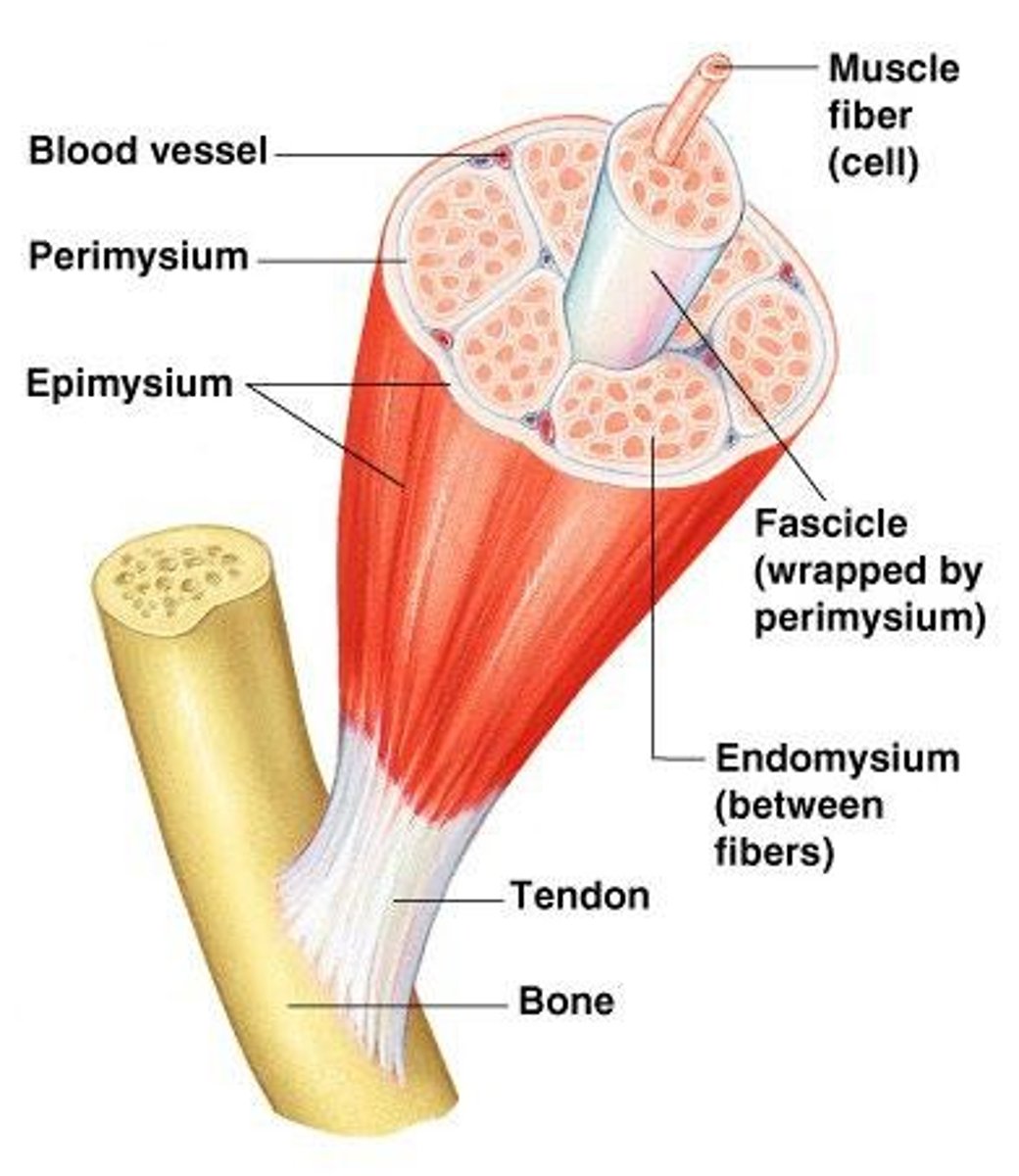
Perimysium
Surrounds fascicles
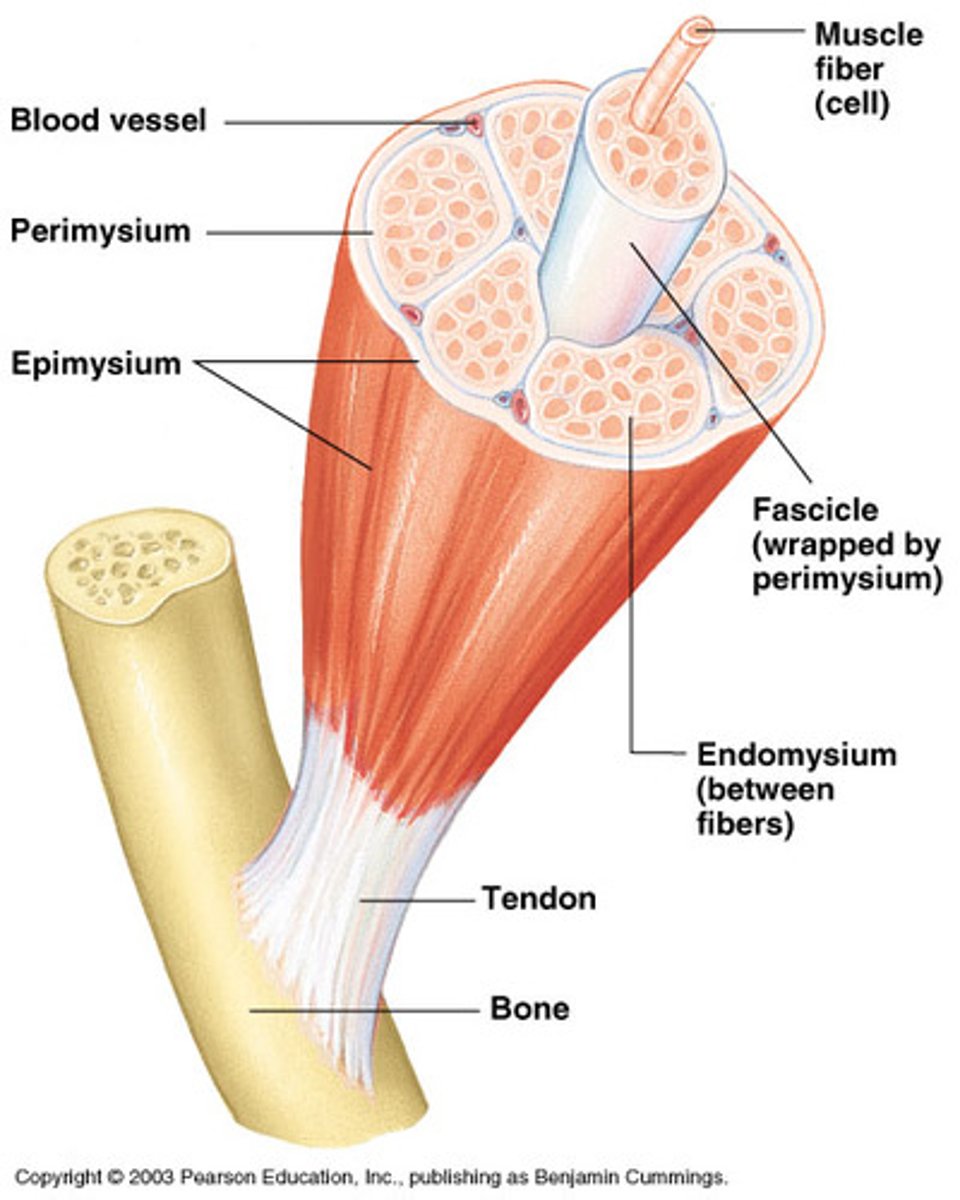
Epimysium
Covers the entire skeletal muscle
Fasciae
On the outside of the epimysium
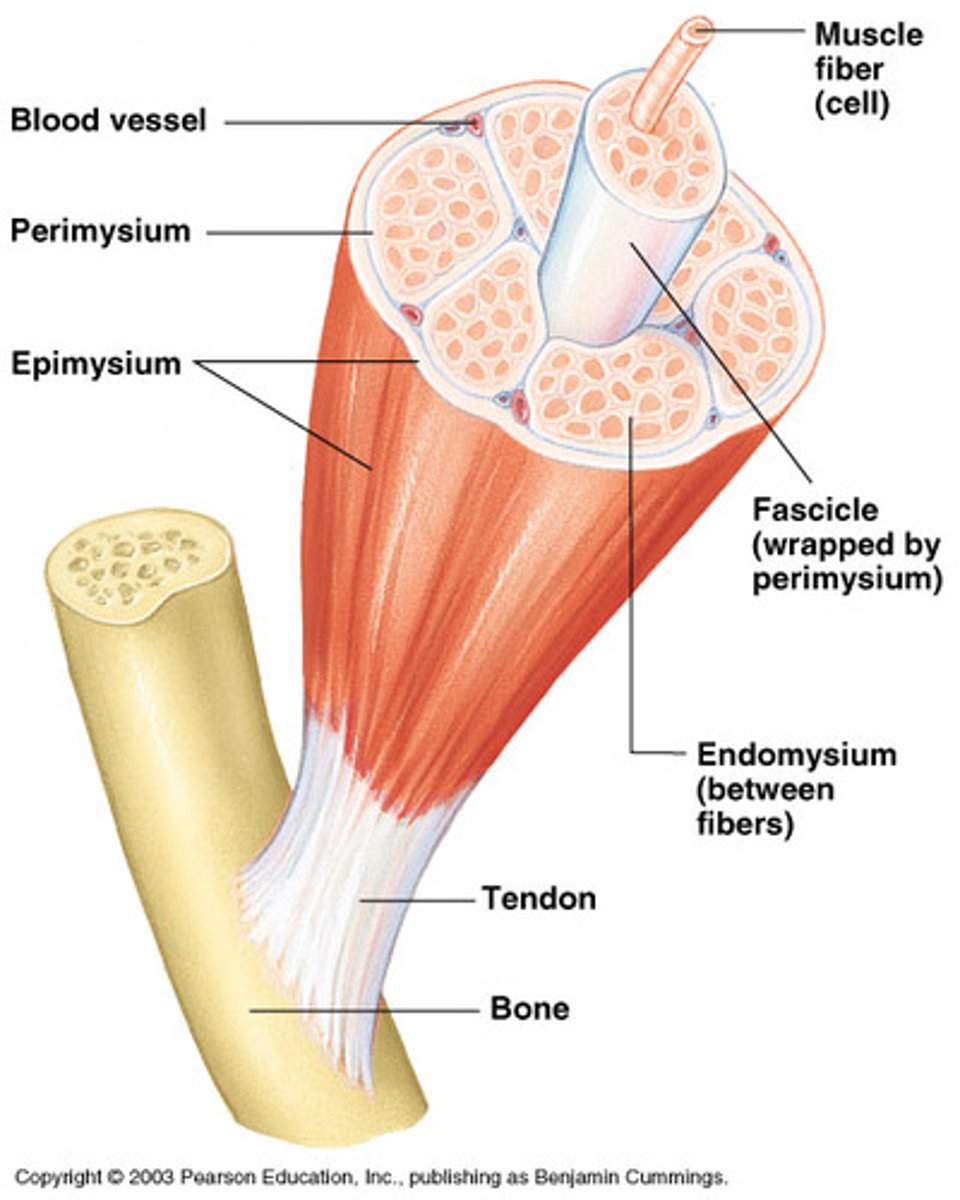
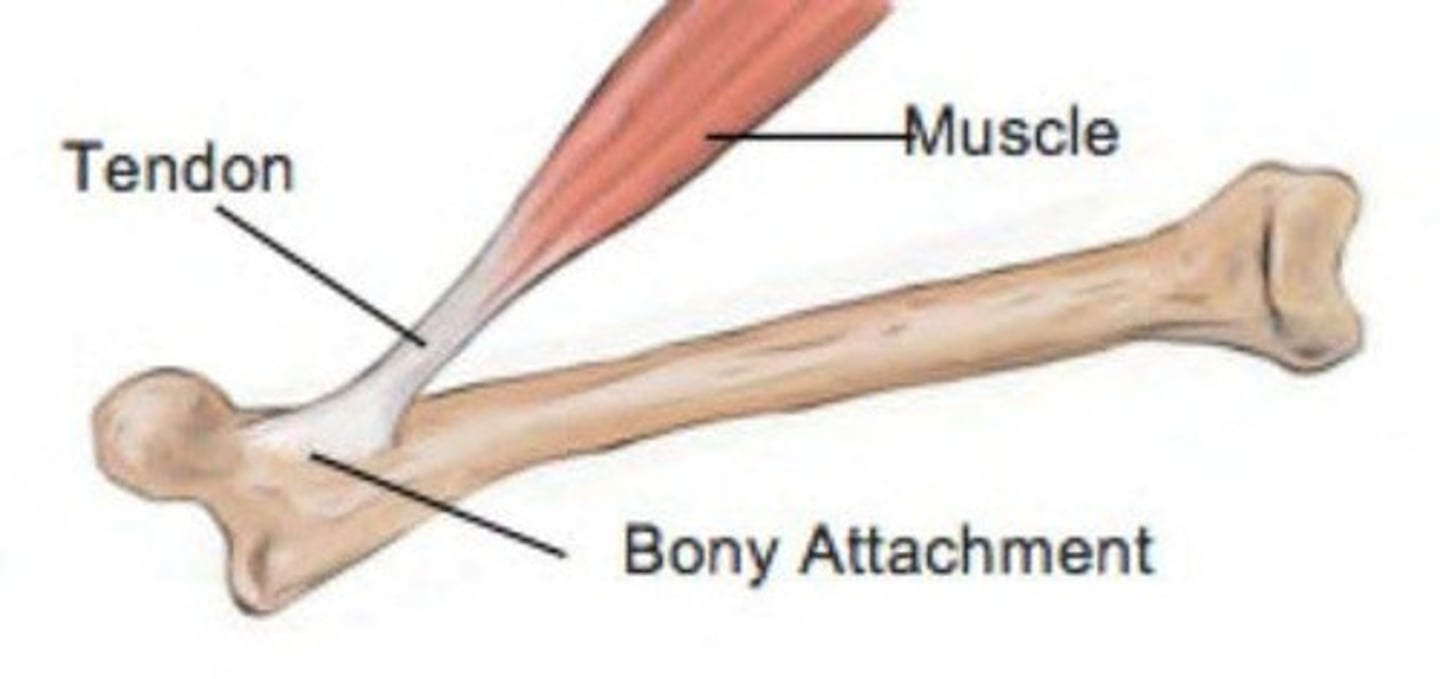
Tendon
Cord-like structure that links skeletal muscles to bones
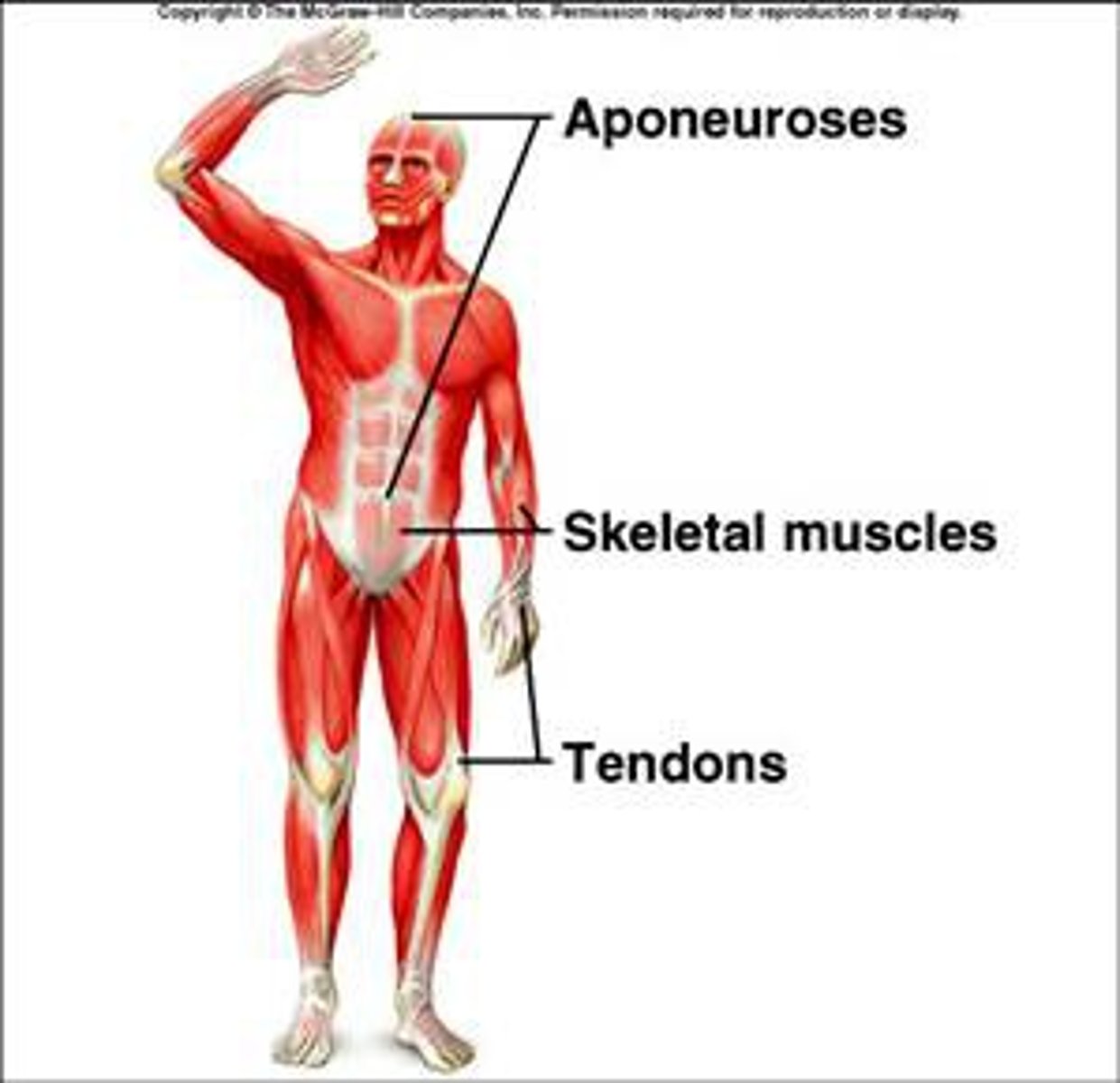
Aponeuroses
Sheet-like structure for muscle attachment
Smooth Muscle Characteristics
Has no striations
Spindle-shaped cells
Single nucleus
Involuntary - no conscious control
Found mainly in the walls of hollow organs
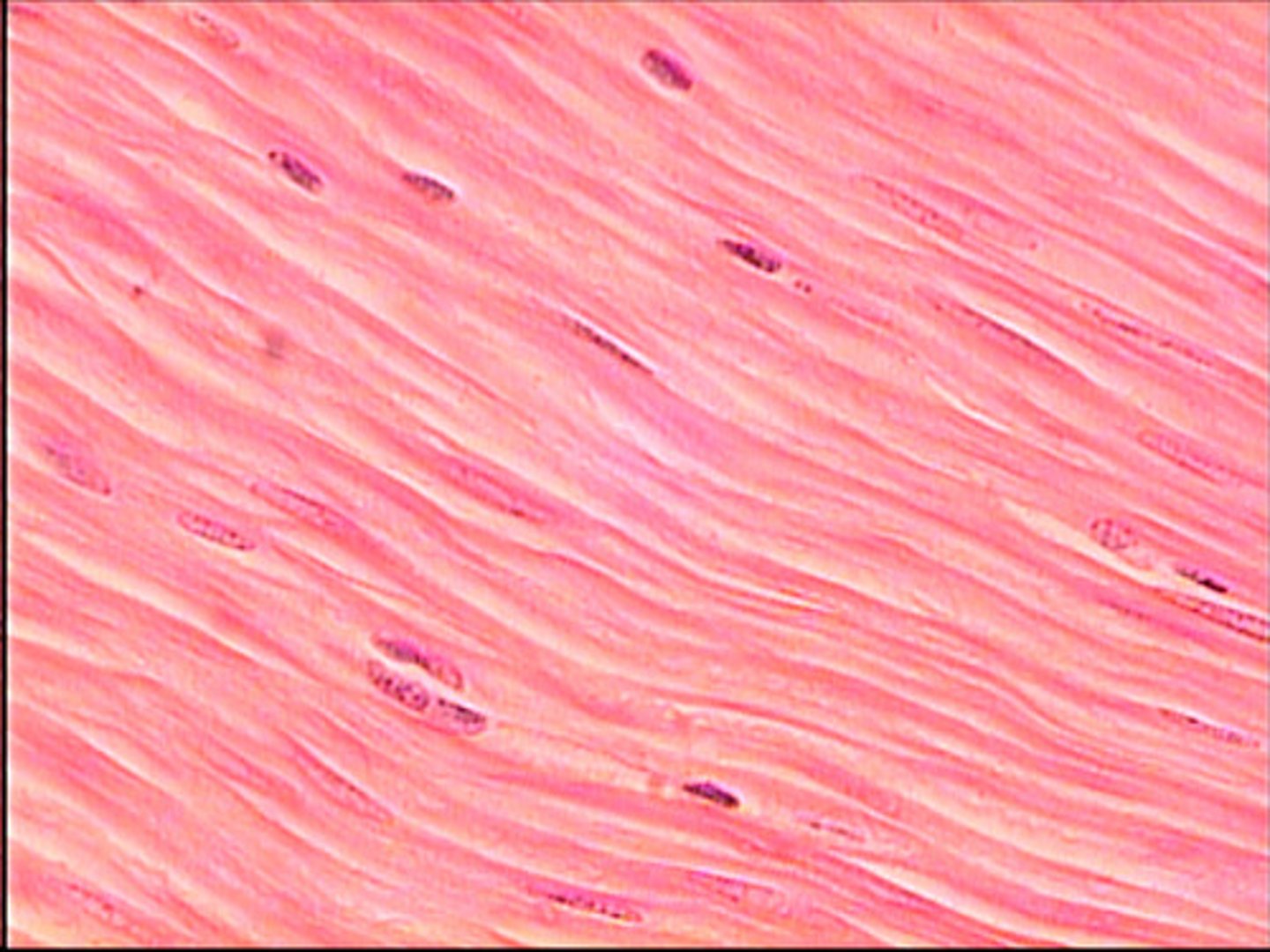
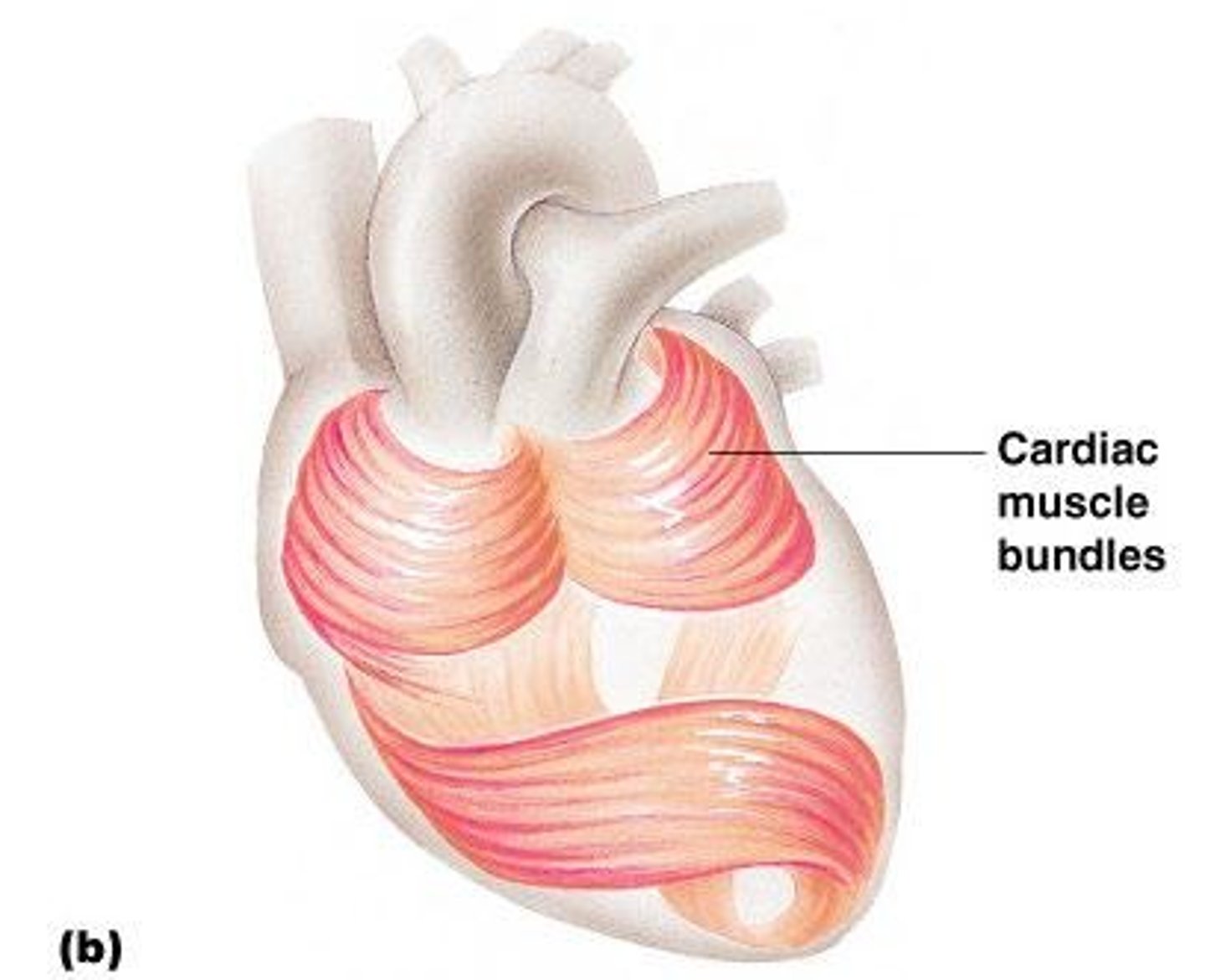
Cardiac Muscle Characteristics
Has striations,
Usually has a single nucleus,
Joined to another muscle cell at an intercalated disc
Involuntary
Found only in the heart
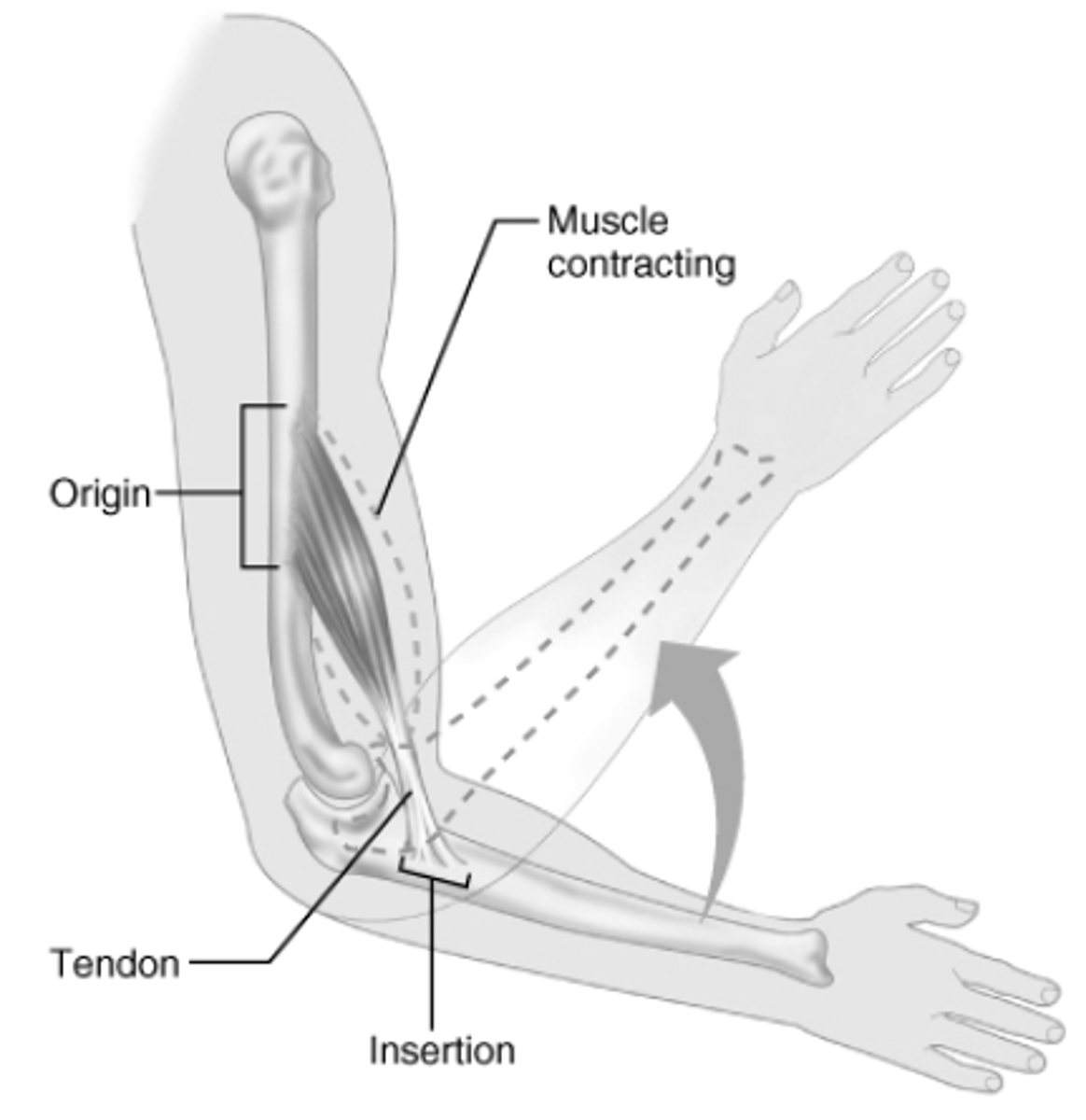
Origin
Attachment to bone that does NOT move
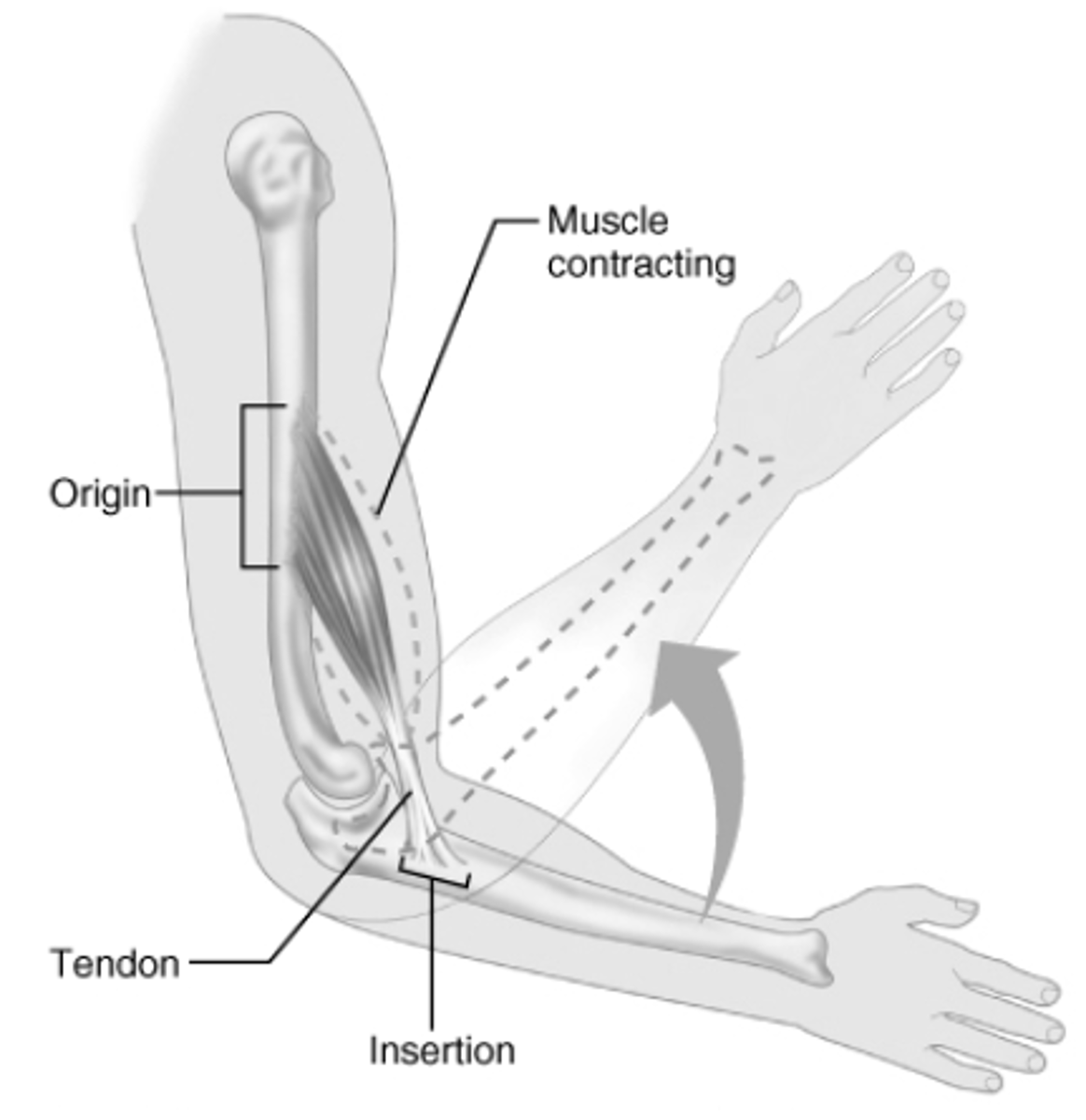
Insertion
Attachment to bone that MOVES
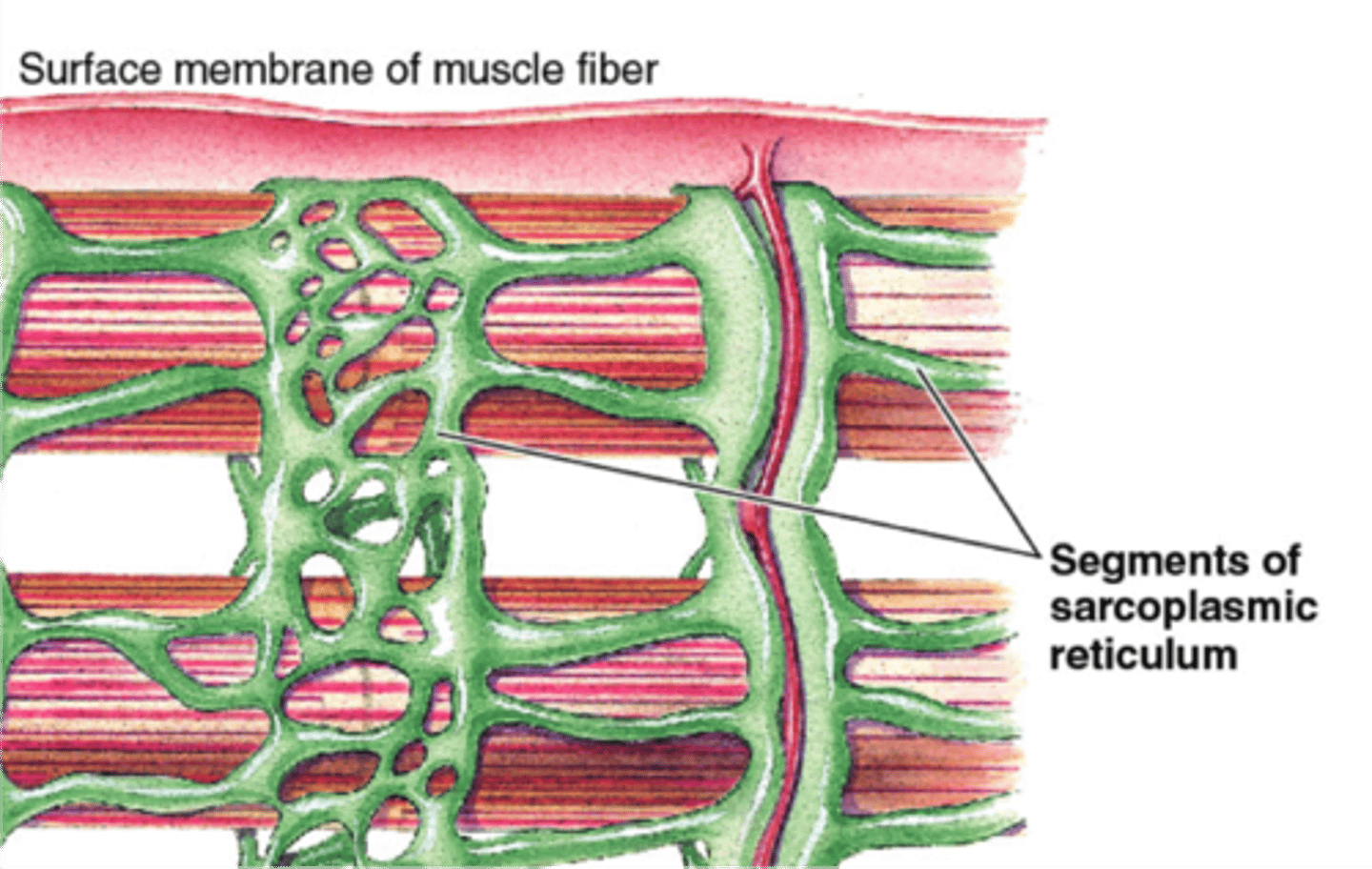
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Specialized smooth endoplasmic reticulum in muscle cells. Used for the storage of calcium in muscle cells.
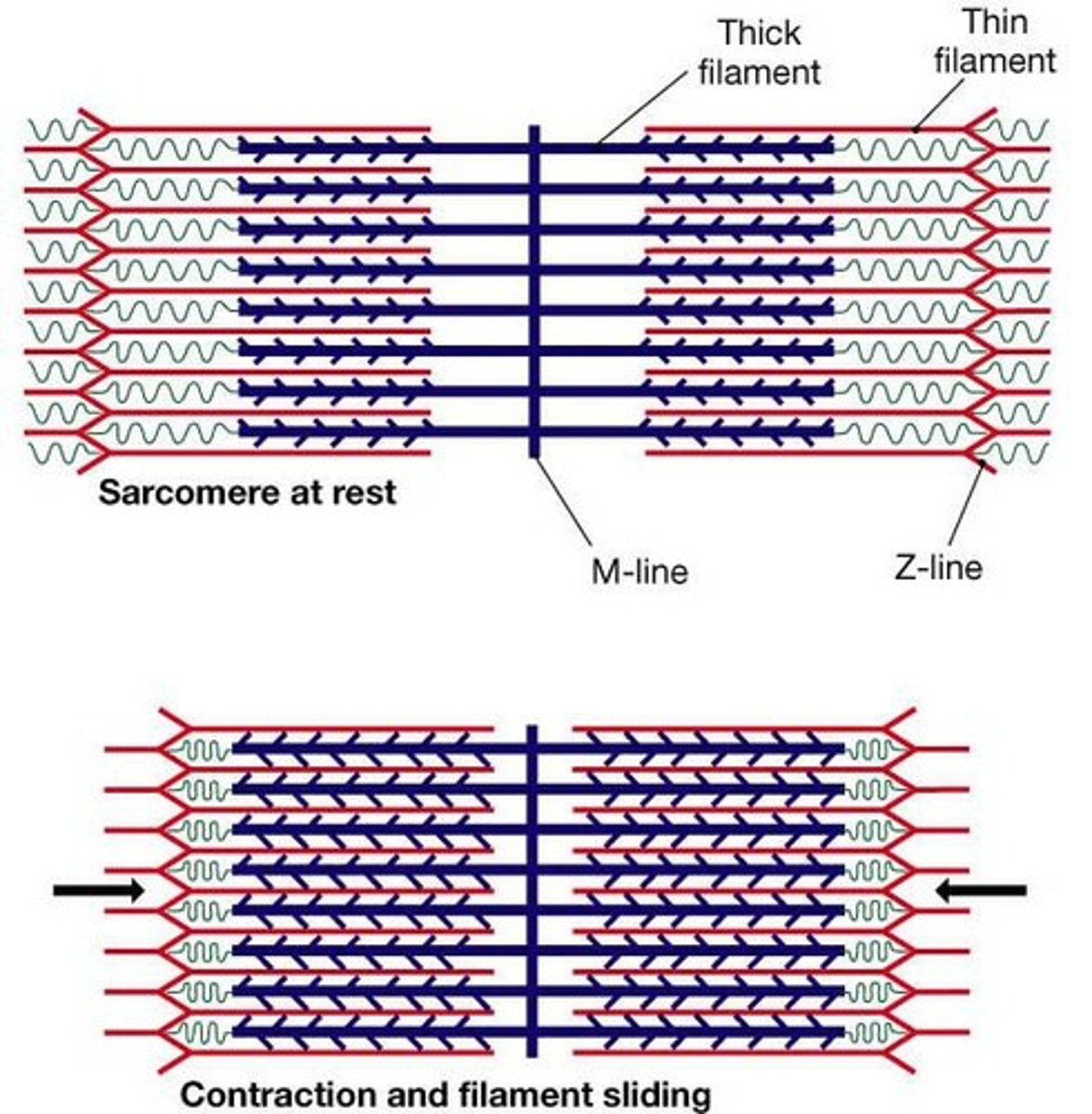
Myofibril
Bundles of myofilaments that are aligned to give distinct bands.
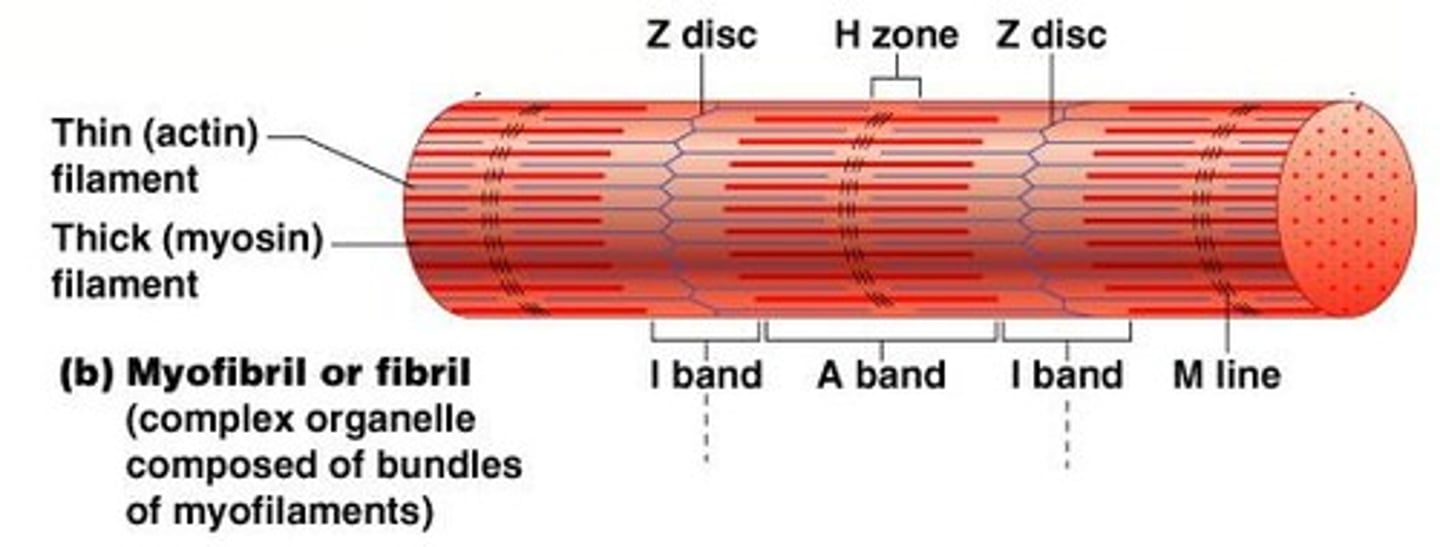
I band
Light band in muscle fibers.
A band
Dark band in muscle fibers.
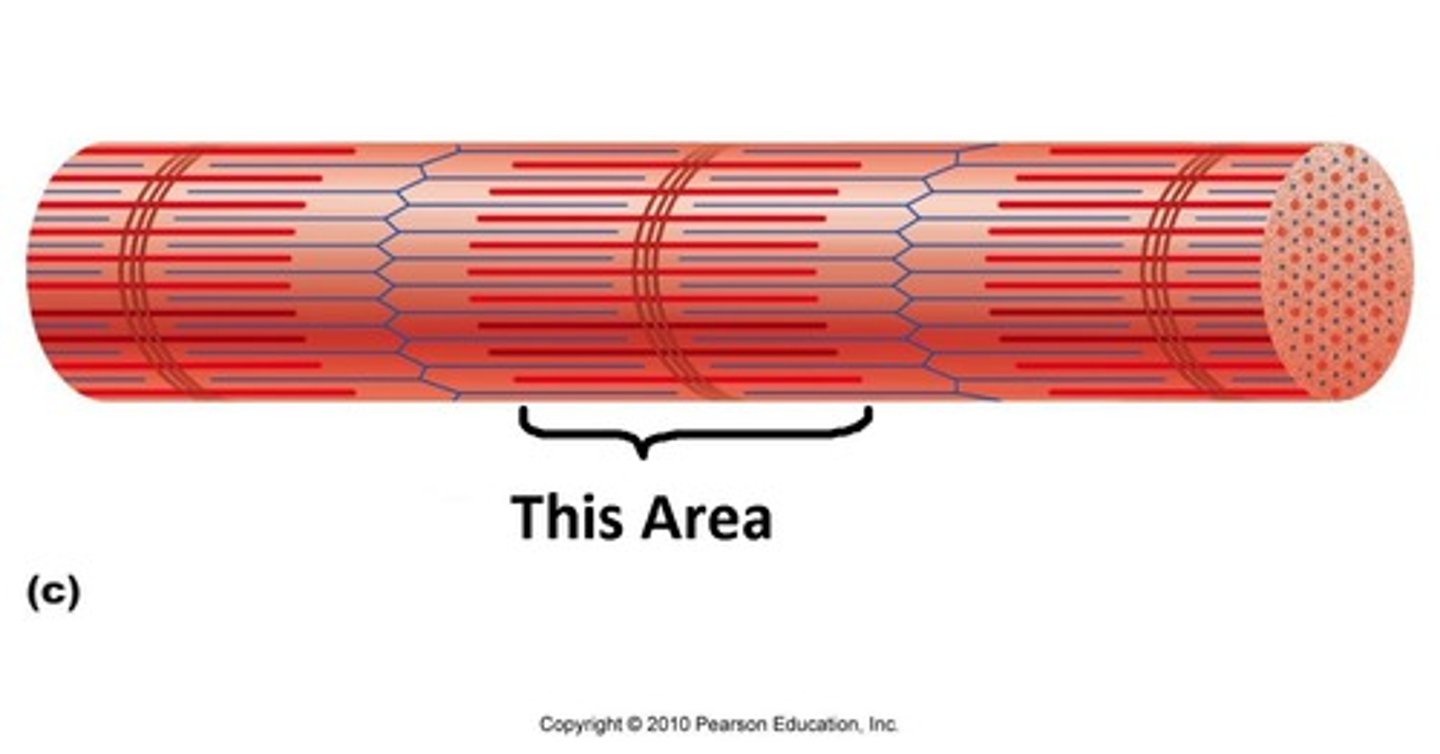
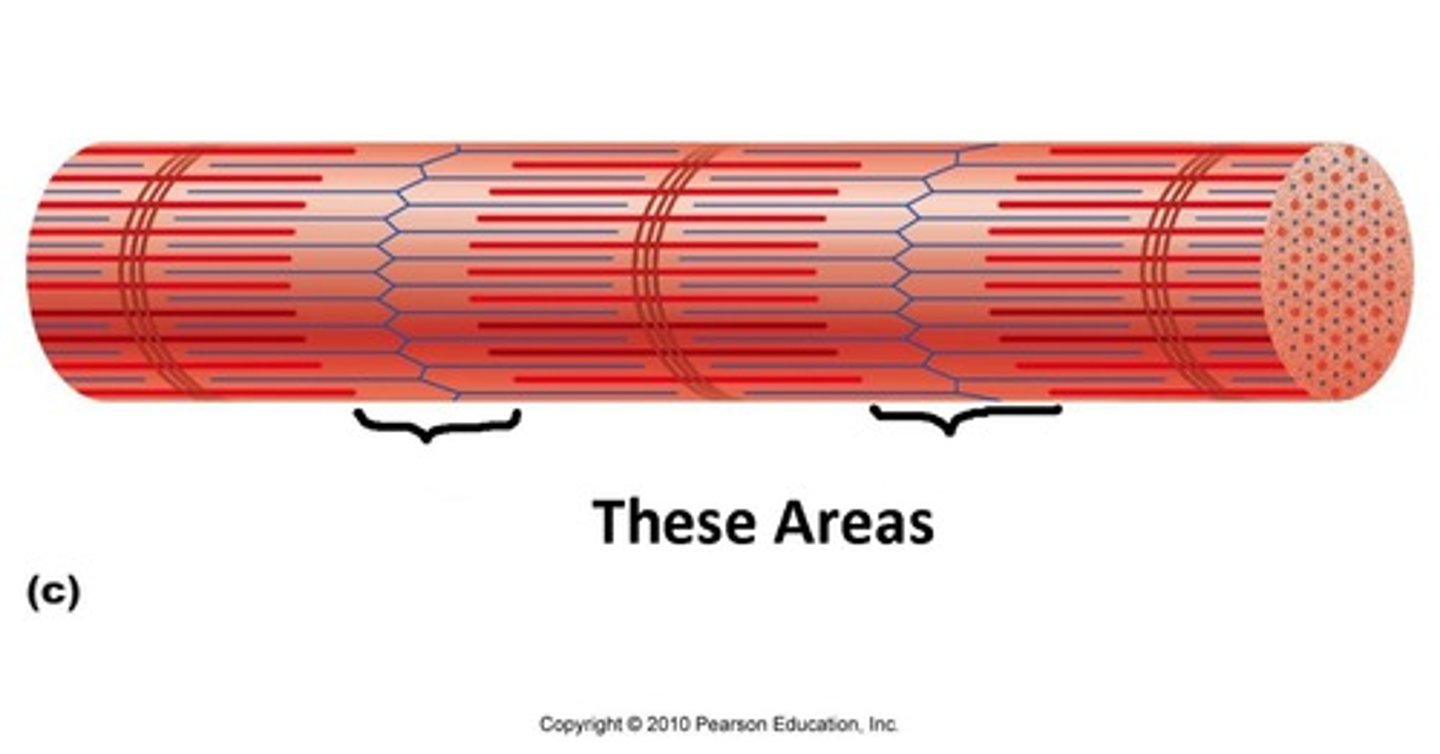
Sarcomere
Contractile unit of a muscle fiber.
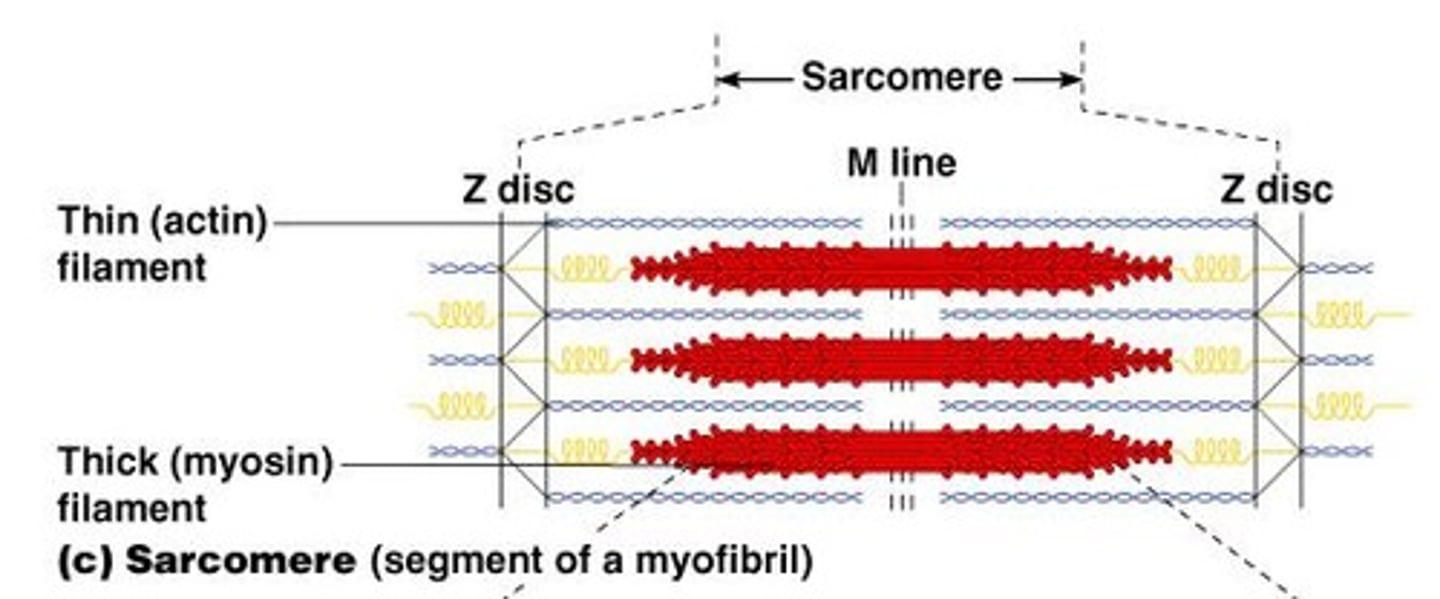
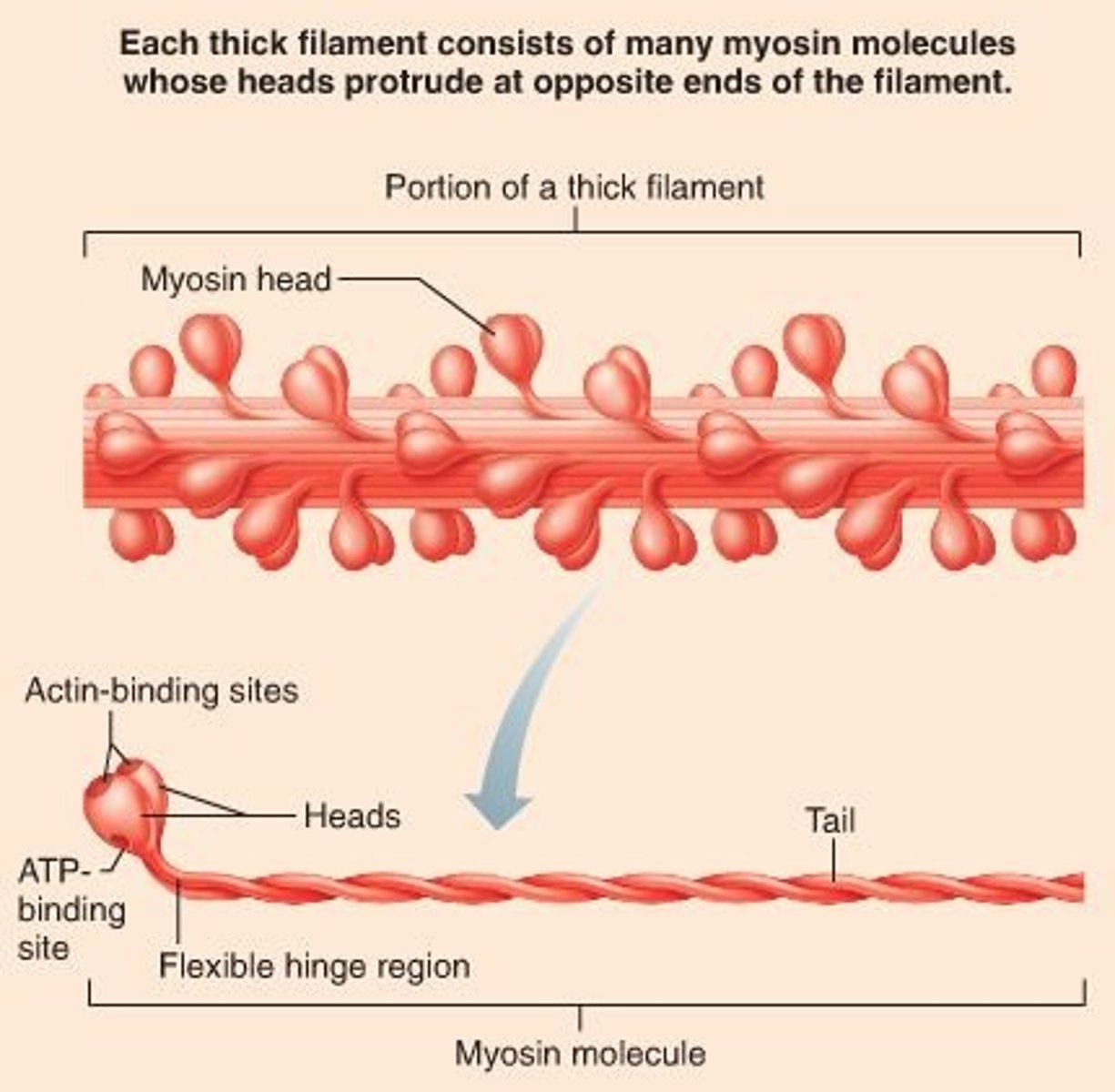
Thick filaments
Myosin filaments composed of the protein myosin.
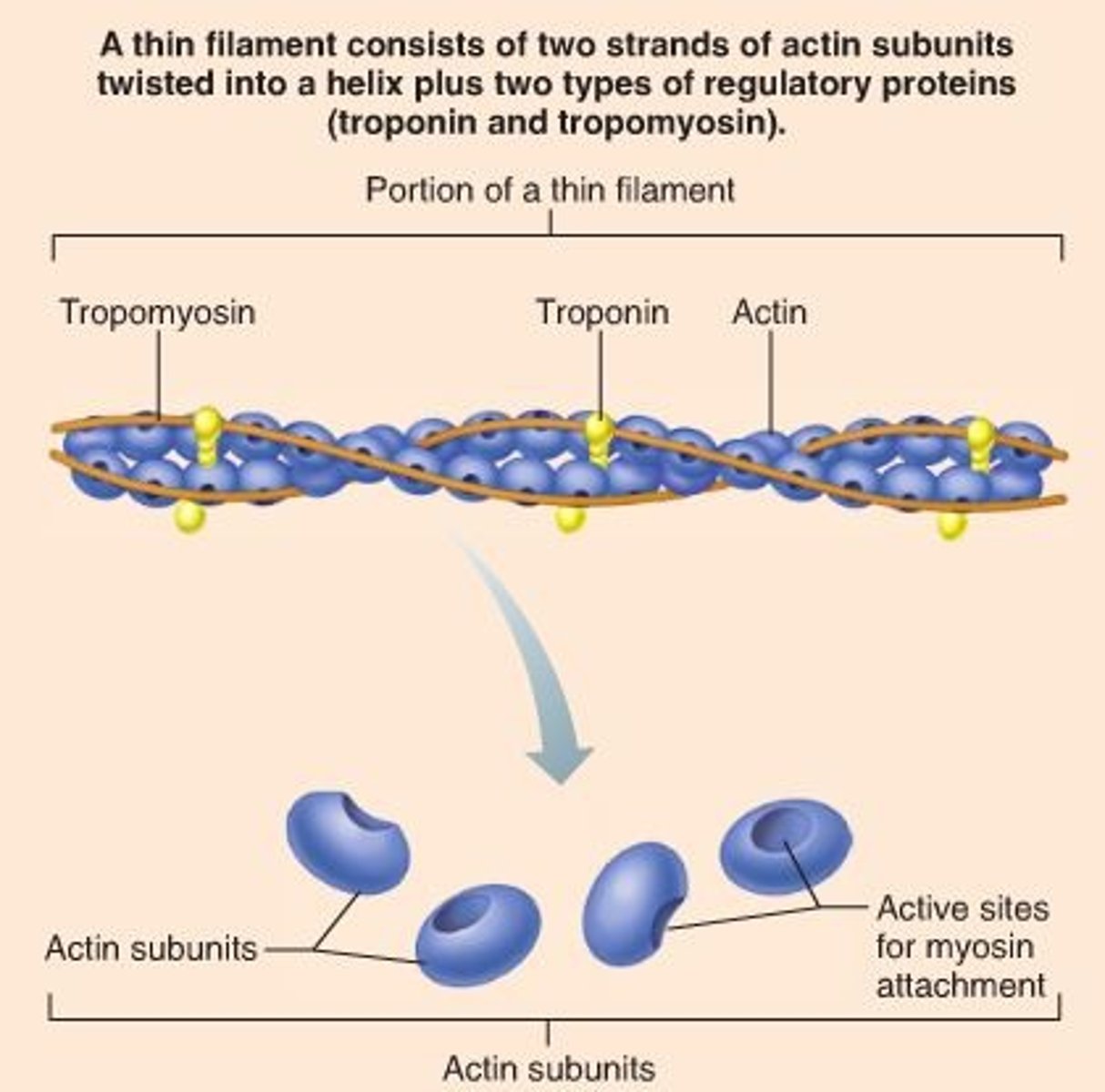
Thin filaments
Actin filaments composed of the protein actin.
Myosin heads
Extensions or cross bridges of myosin filaments.
Irritability of muscle
Ability to receive and respond to a stimulus.

Contractility
Ability to shorten when an adequate stimulus is received.
Motor unit
One neuron and muscle cells stimulated by that neuron.
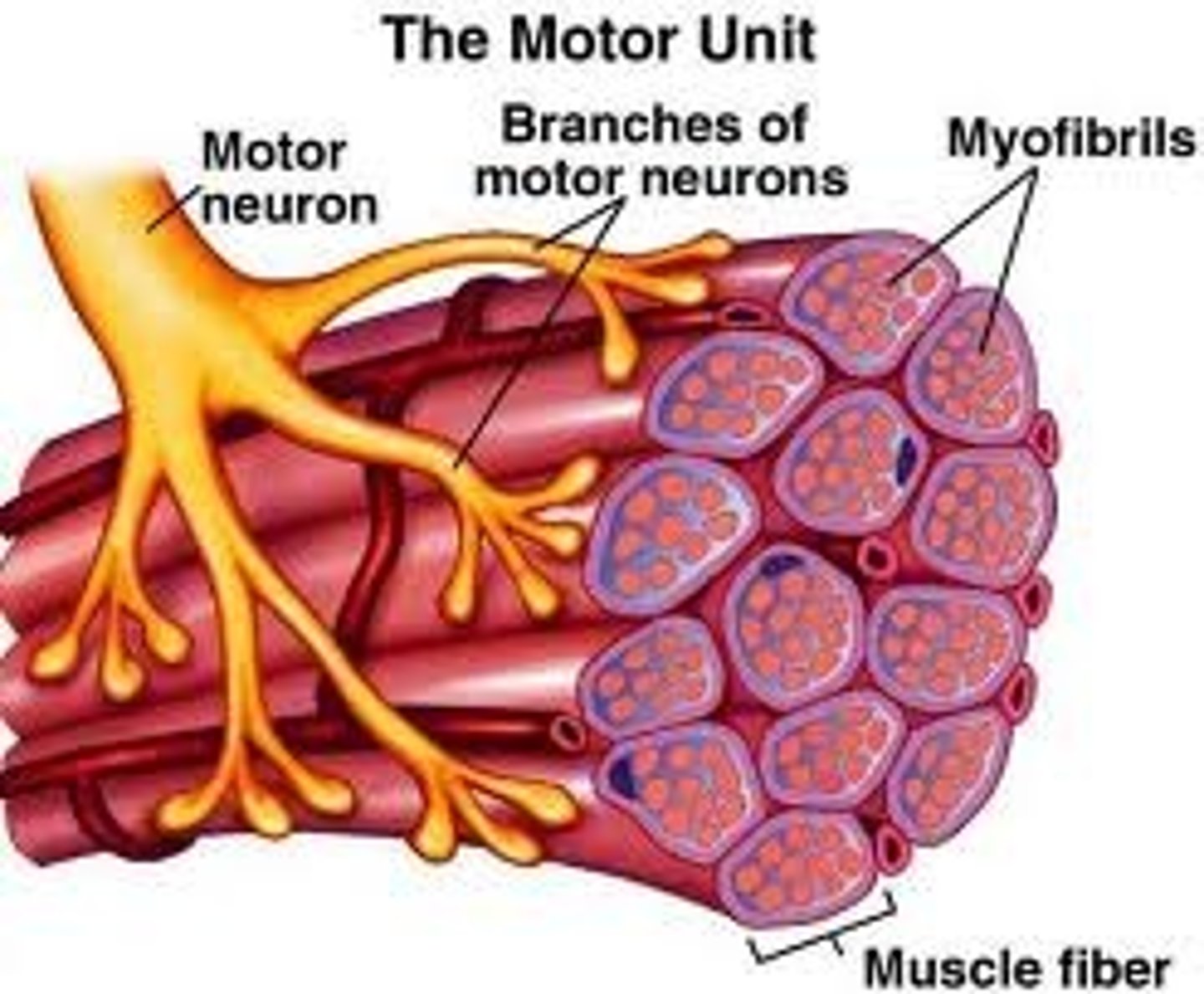
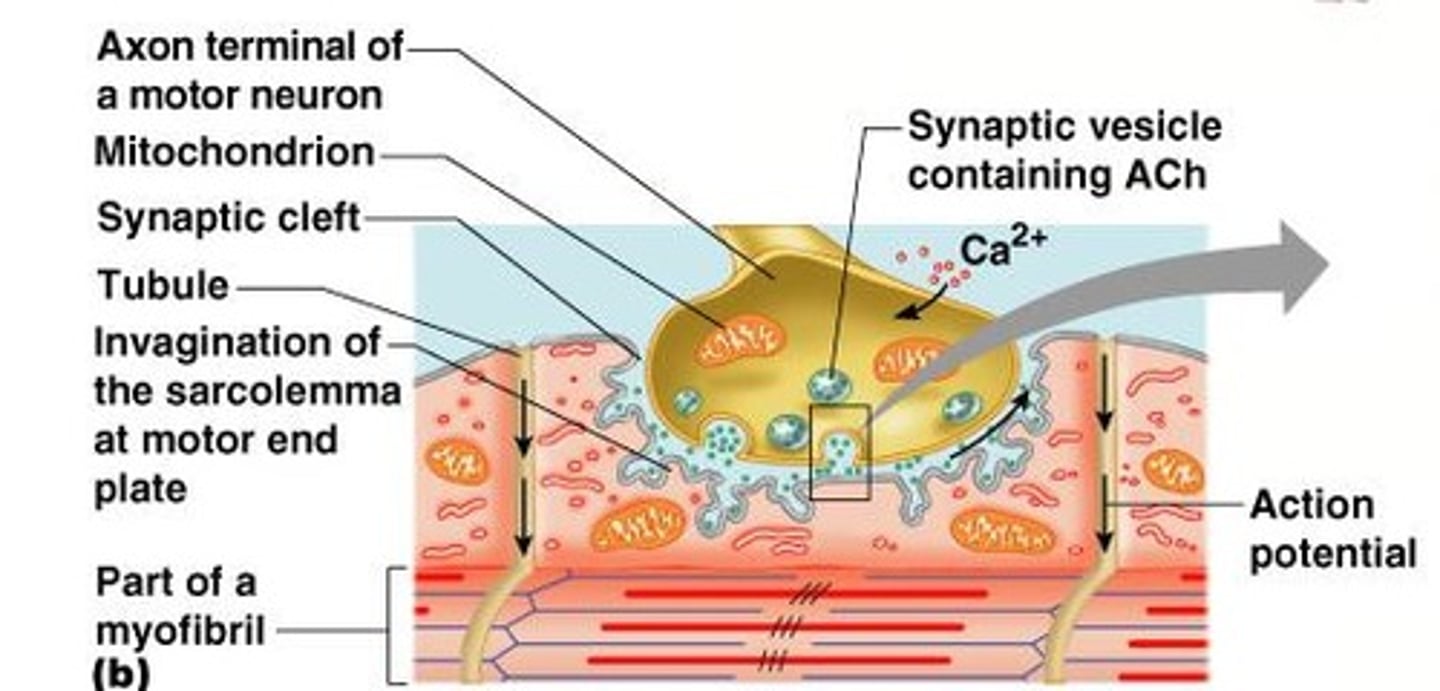
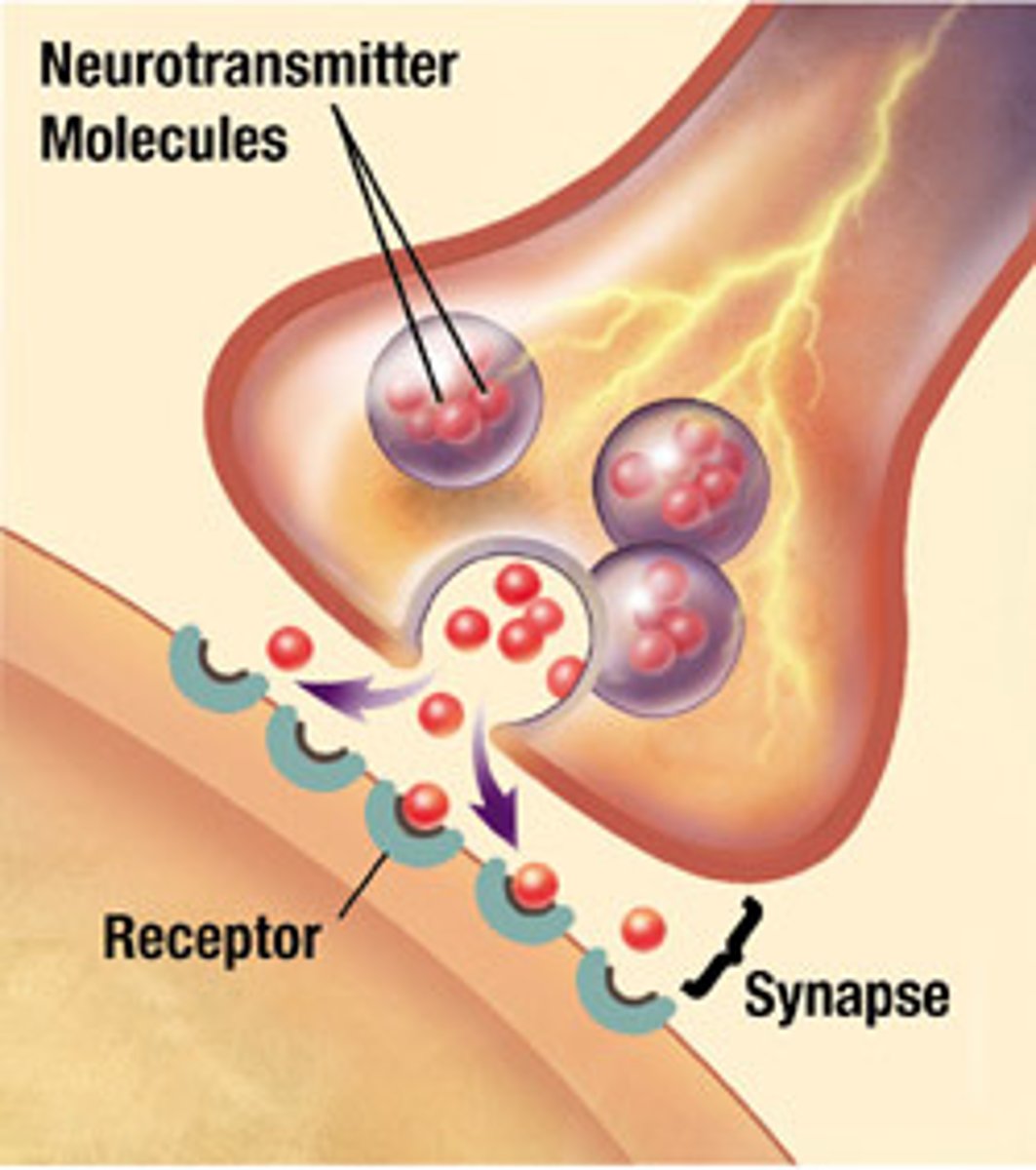
Neuromuscular junctions
Association site of nerve and muscle.
Acetylcholine
Principal neurotransmitter at the vertebrate neuromuscular junction.
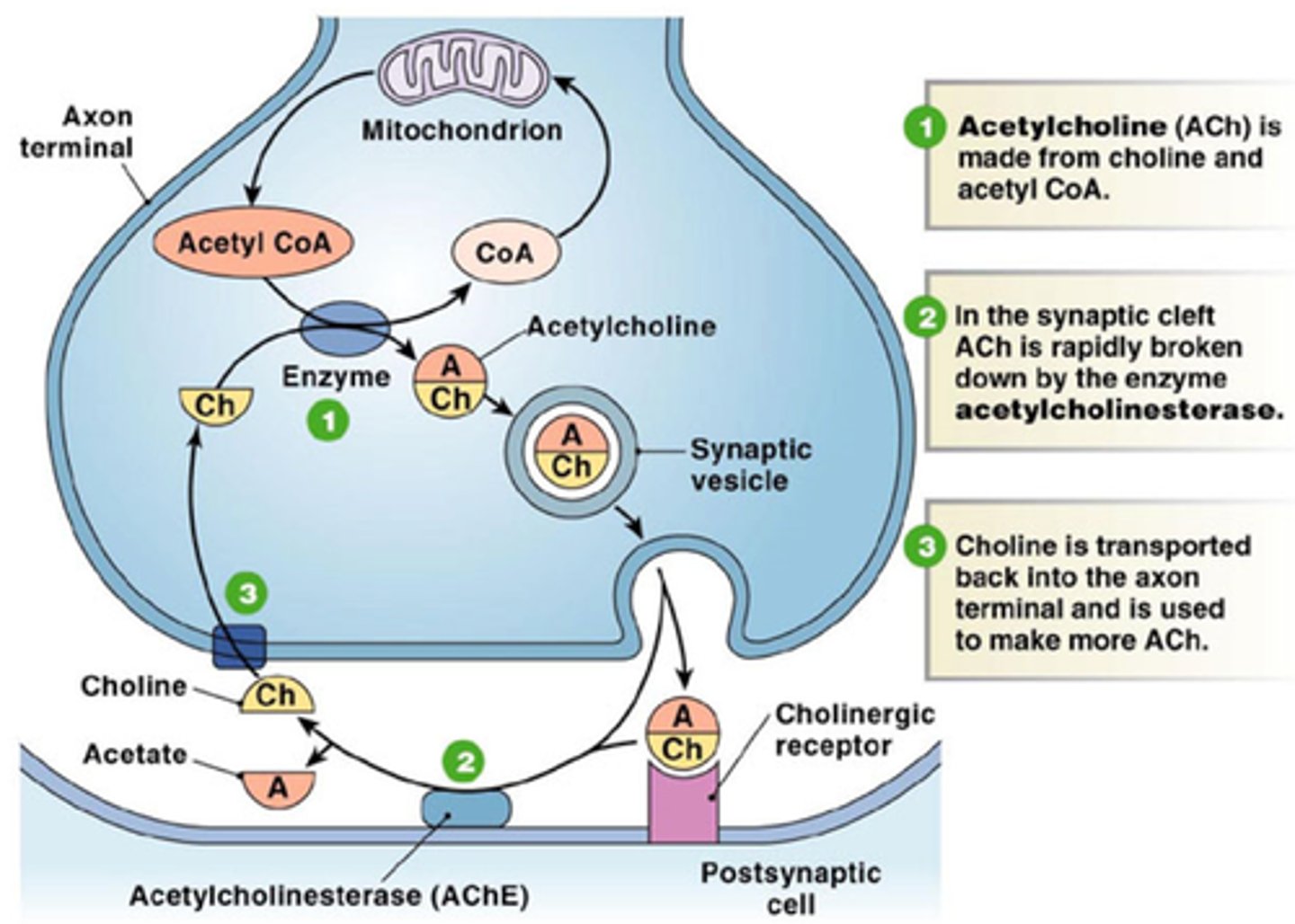
Synaptic cleft
Gap between nerve and muscle filled with interstitial fluid.
Action potential
Generated by sodium rushing into the cell.
Sliding Filament Theory
Activation by nerve causes myosin heads to attach to binding sites on the thin filament.
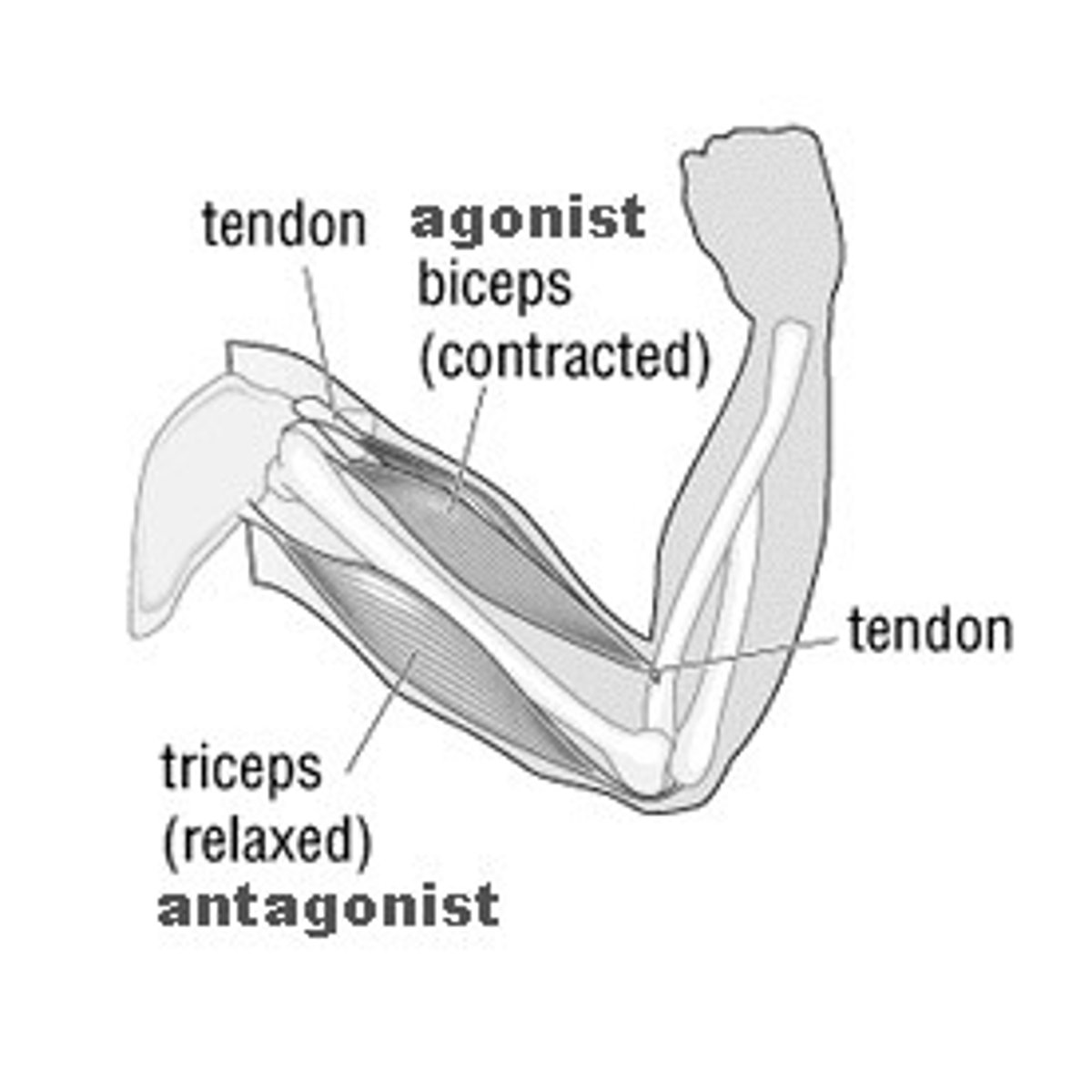
Agonist
Muscle that causes a movement.
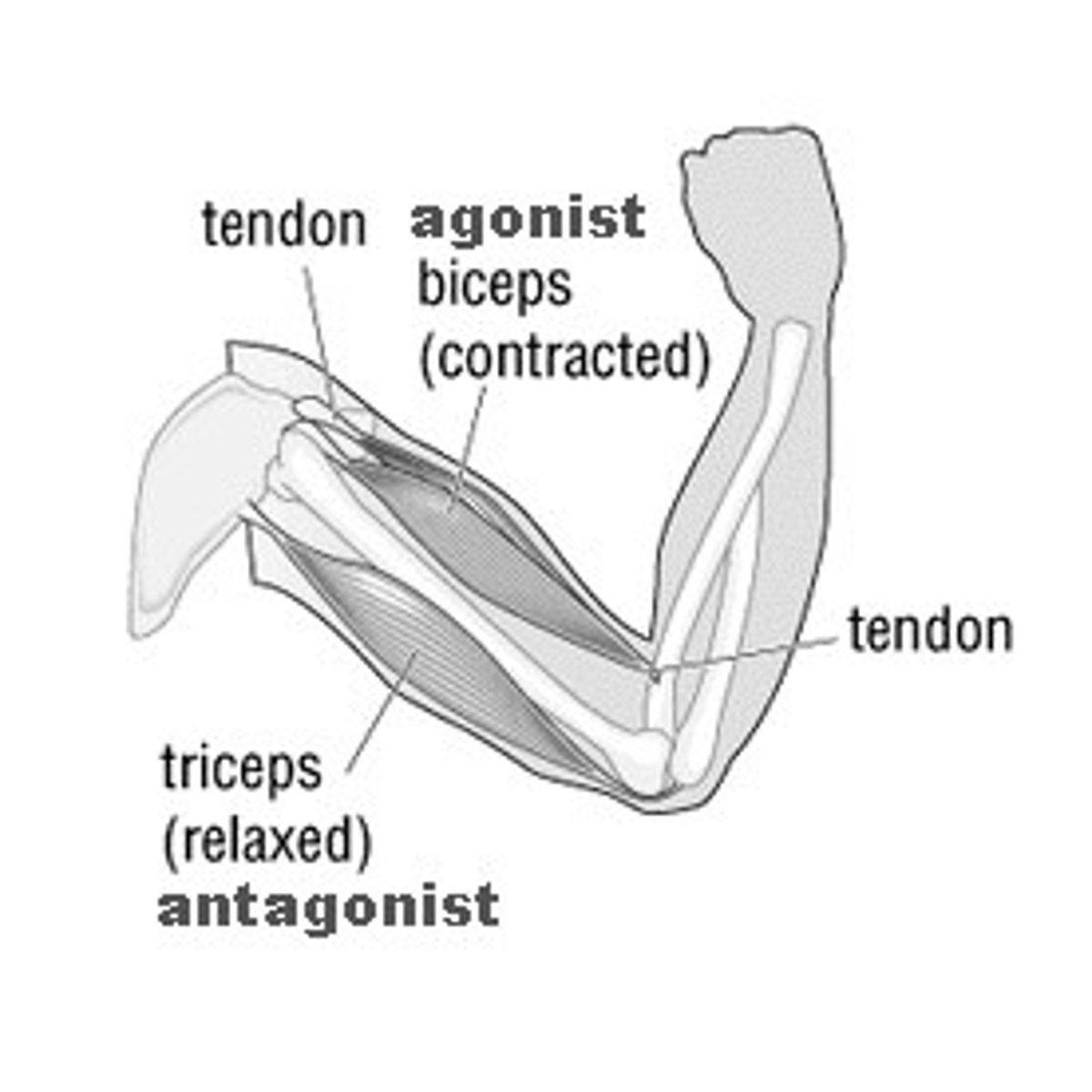
Antagonist
Muscle that opposes the action of another muscle.
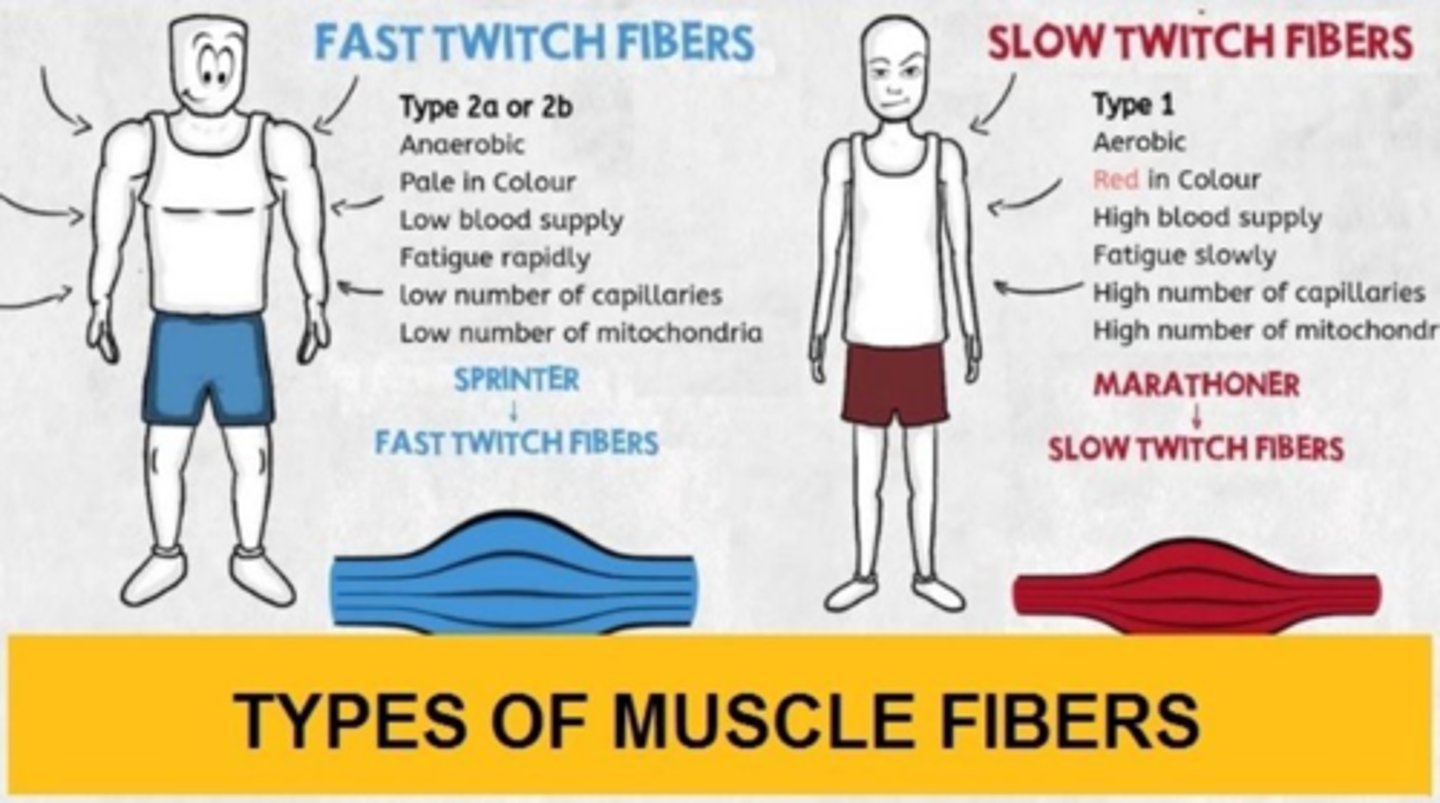
Muscle Fiber Types
Two general categories: fast twitch & slow twitch.
Type I Muscle Fiber
Called slow twitch or slow oxidative fibers, containing large amounts of myoglobin, many mitochondria, and huge blood capillaries.
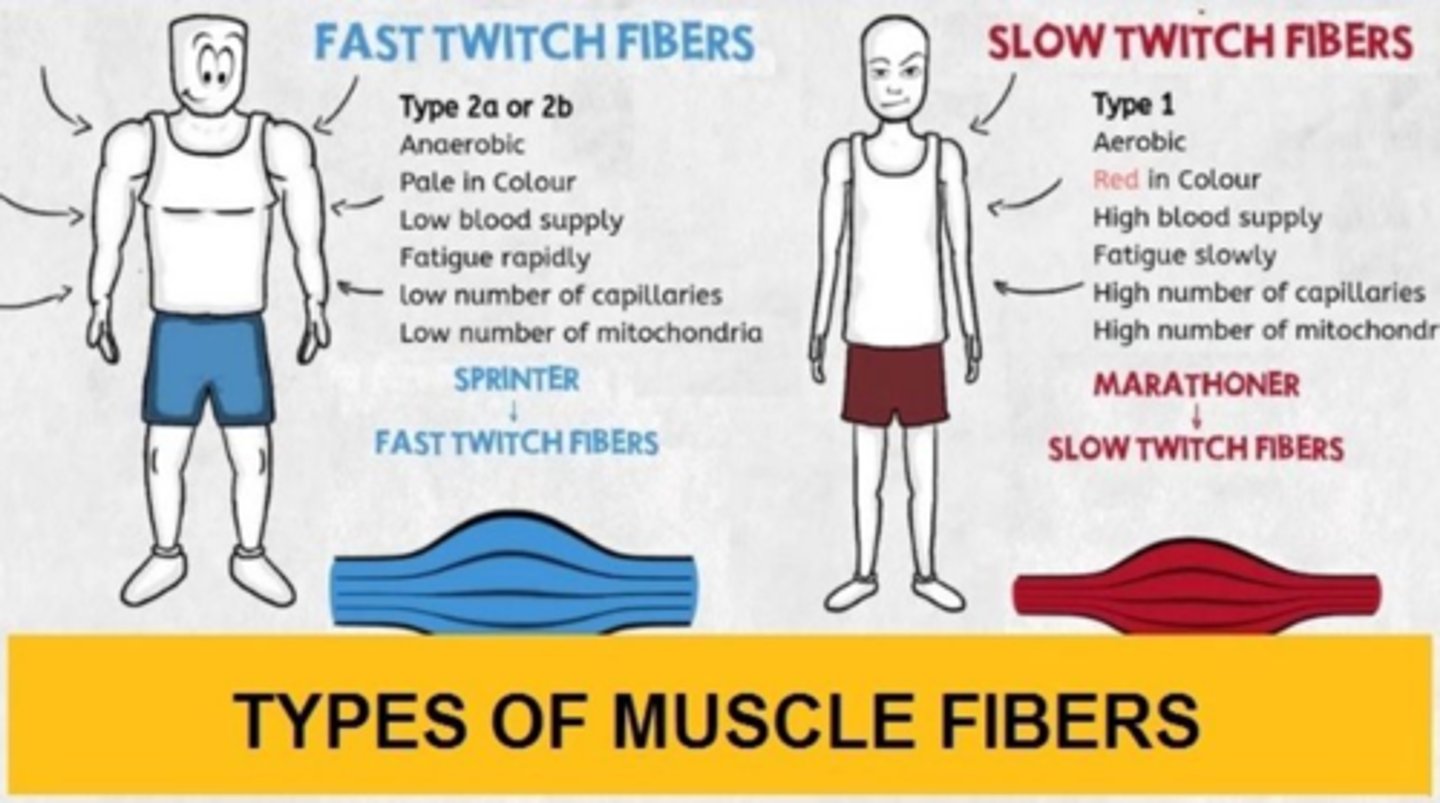
Type II Muscle Fiber: 2 A
Fast twitch or fast oxidative fibers that contain very large amounts of myoglobin and have a fast contraction velocity.
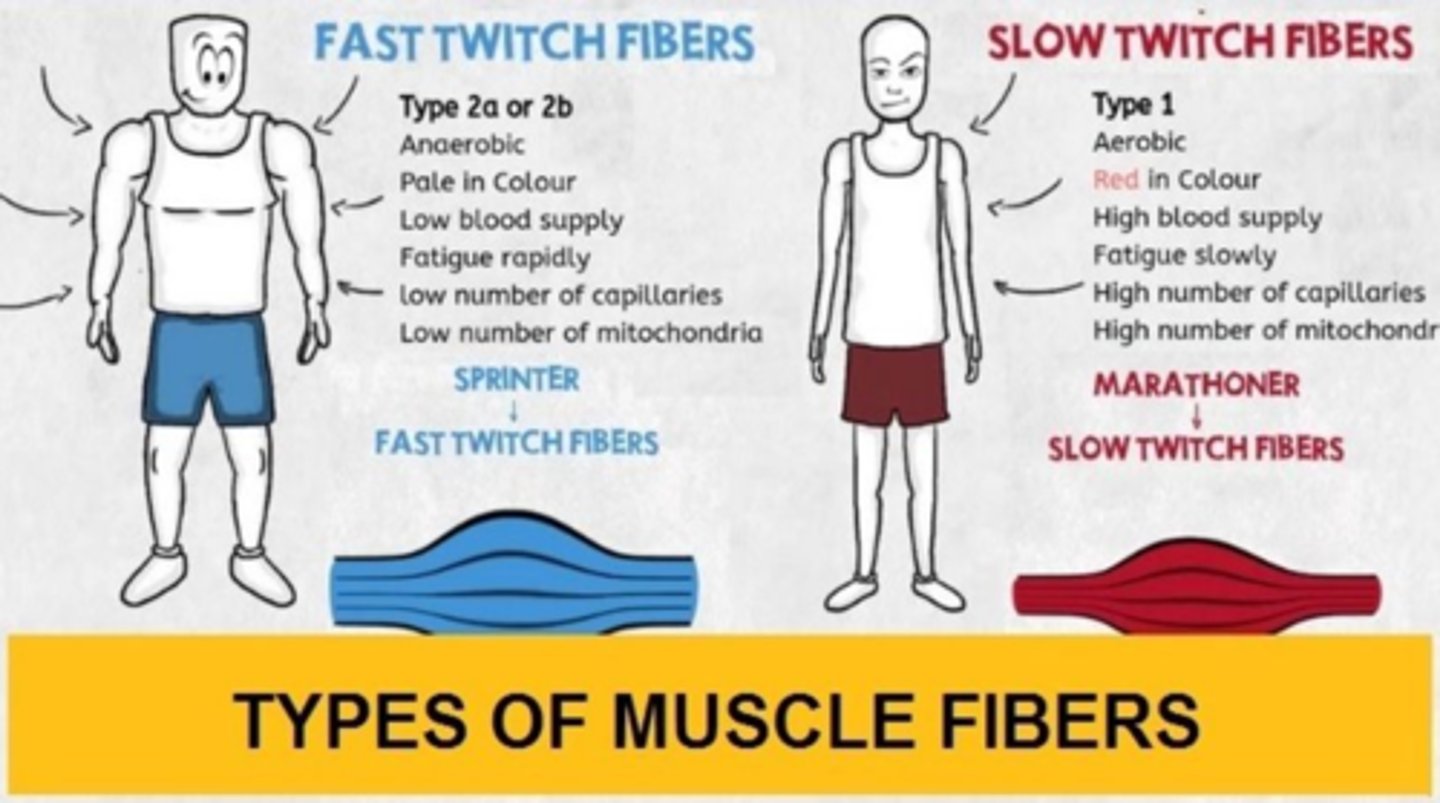
Type II Muscle Fiber: 2 B
Fast twitch or fast glycolytic fibers that contain a low content of myoglobin and generate ATP by anaerobic metabolic processes.
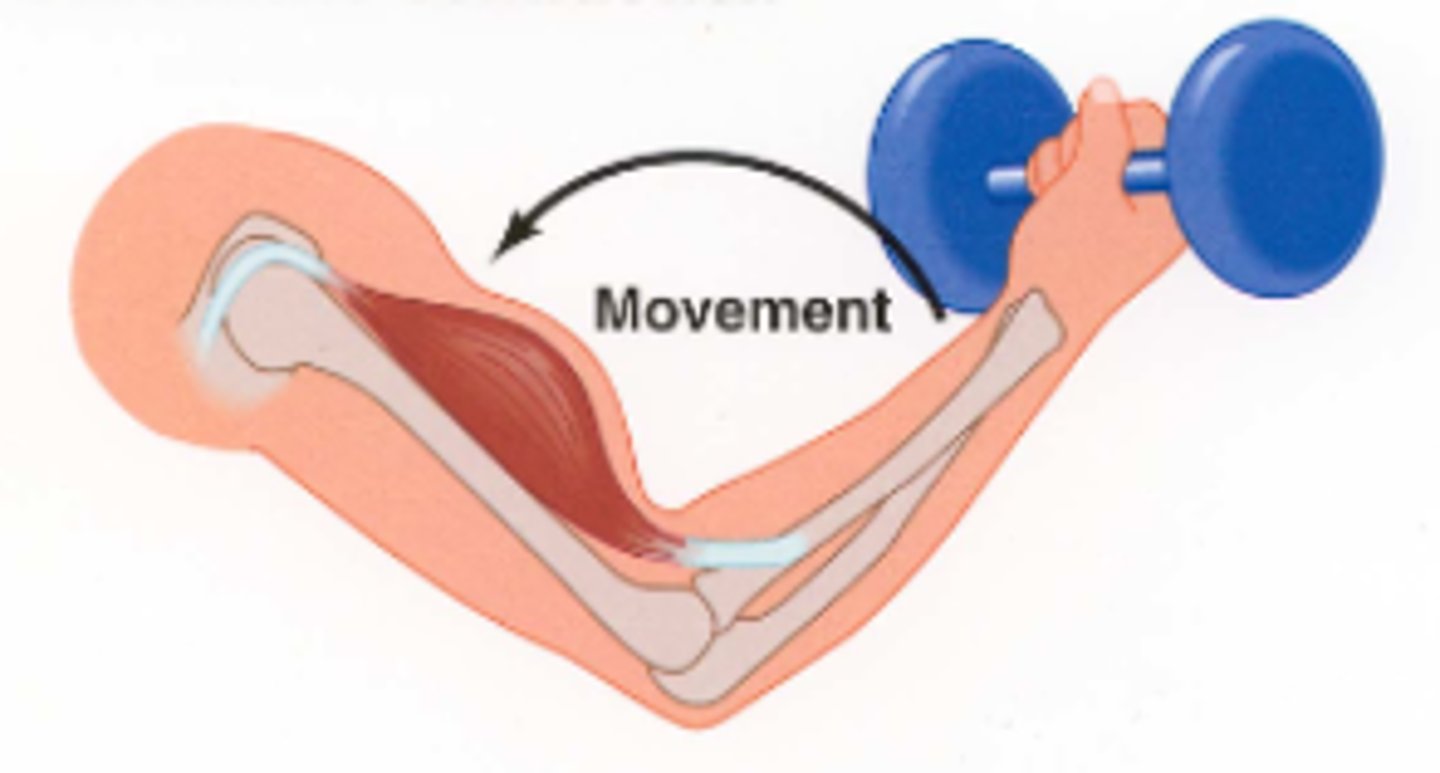
Concentric Contractions
When a muscle is activated and required to lift a load, generating intramuscular tension and shortening the muscle.
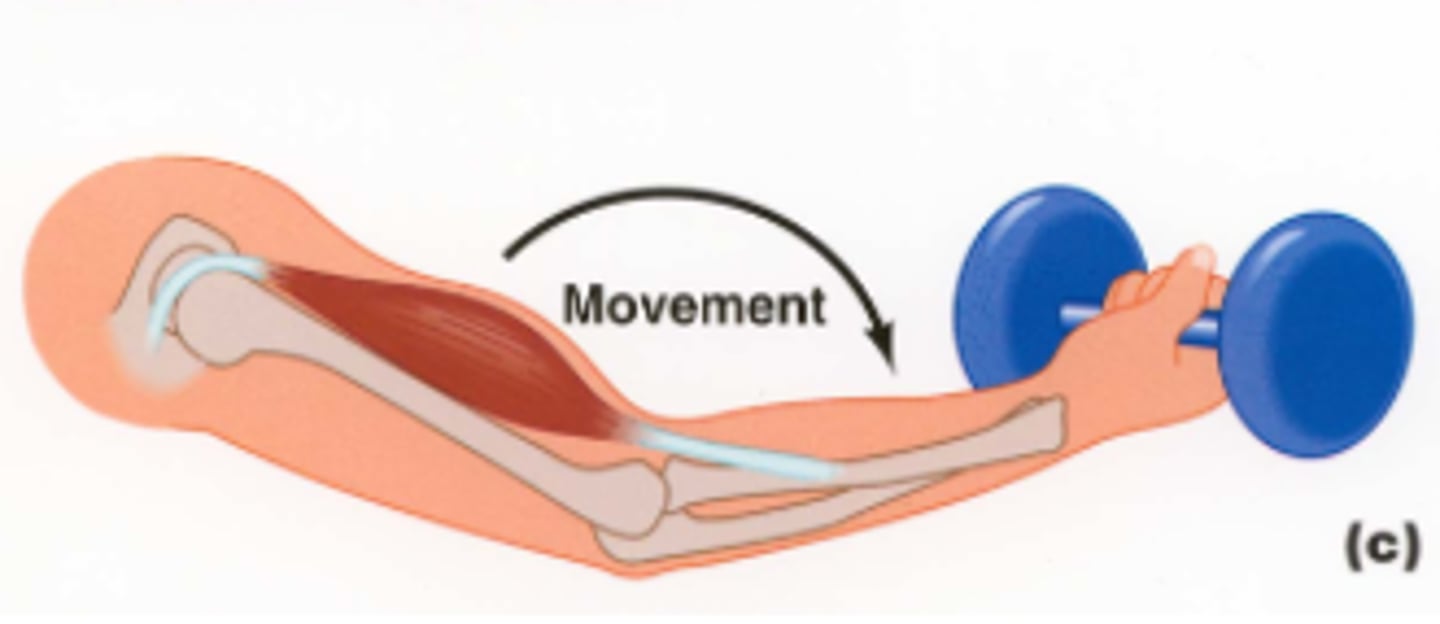
Eccentric Contractions
Occurs when a force applied to the muscle exceeds the momentary force produced by the muscle, resulting in forced lengthening.
Isometric Contraction
A contraction where the muscle is activated but held at a constant length without lengthening or shortening.

Passive Stretch
A type of muscle contraction where the muscle is lengthened while in a passive state, not being stimulated to contract.
Fast Twitch Muscle Fibers
Muscle fibers that generate ATP quickly and are resistant to fatigue.
Slow Twitch Muscle Fibers
Muscle fibers that generate ATP slowly and are very resistant to fatigue.
Contractile Properties of Muscle
Contractile properties refer to how muscles generate force and change length.
Fatigue Resistance in Muscle Fibers
Type I fibers are very resistant to fatigue, while Type II B fibers fatigue easily.
ATP Generation in Muscle Fibers
Type I fibers generate ATP by oxidative metabolic processes, while Type II B fibers generate ATP by anaerobic processes.