AP CHEM FRQ HOW-TO's
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Kinetic Molecular Theory:
IMFS
Attractions between molecules decrease the force or frequency in which the molecules collide on the sides of the container- decreasing pressure
Reaction rate is determined by?
How does a reaction happen
Reaction’s occur only determined by correct orientation and sufficient energy that is both affected by an increase in Temperature
An increase in surface area(by having more particles) also increases chance of correct orientation
Justification for saturated solution
There is the presence of a precipitate
REMEMBER TO WRITE CHARGES FOR EVERYTHING!!!! They will take all your points off for not including a charge
Examples include CB C5H10NH2+ and if you take apart KHC4H4O6, make sure to have the HC4H4O6+
When explaining exothermic vs. endothermic reactions always include system and surroundings
For example: This reaction is an exothermic reaction with a NEGATIVE enthalpy as temperature is transferred from the system to surroundings, increasing the temperature from 23.5 to 44 degrees celsius
Bond Polarity between Nonpolar elements
The MORE distance between the two elements, in both period and group means more POLARITY as it is determined by the electronegativity difference
Acid + Base net ionic equations KEY thing to remember:
Weak Acids & Bases do NOT completely ionize in water and therefore will not be written as two separate ions in aqueous form, it just stays the same.
Reason why a solution would be acidic, basic or neutral
Neutral: Equimolar amounts of strong acid and base react completely to completely neutralize into a pH of 7
Acidic: Strong Acid and Weak Base produces a CA that will produce more H+ decreasing the pH
Basic: Strong Base and Weak Acid produces a CB that will produce more OH-
increasing the pH
How to justify thermodynamically favorable reactions using entropy and enthalpy?
Use Gibbs Free Energy equation
How does bond energy affect the enthalpy of a reaction?
The greater the bond energy the more energy is required/released
Greater bond energies(stronger bonds) lead to MORE change in enthalpy per mol of reaction because it requires/releases more energy to break/form the bonds
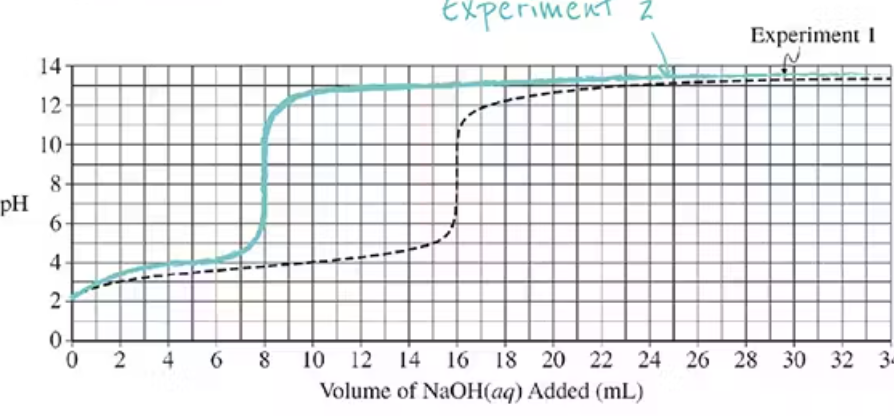
Titration Curve changing molarities of the titrant
Doubling the Molarity of the titrant will amount needed to reach the equivalence point by half
How does a buffer solution work?
A buffer solution maintains a stable pH when small amounts of acid or base are added.
It consists of a weak acid and its conjugate base, or a weak base and its conjugate acid.
They resist change by neutralizing added acids or bases, thereby stabilizing the pH of the solution.
When justifying molecular geometry with VSEPR theory, what should you use?
Electron domains, or if they all have the same # of electron domains, use lone pairs
When explaining which is the best molecular diagram with formal charges, how do you explain which is one is the best?
Just say “The atoms in this molecule have no formal charges, but the other diagrams have nonzero formal charges'“
Changing the components of the buffer the same amount(like the acid or base) does what to the buffer solution in terms of pH and buffer capacity
It will decrease the buffer capacity(the solution’s ability to neutralize a solution)
But it will keep pH constant because the ratio of the components are held constant
Bond length
How to explain differences in bond length in say…
H-Br and H-F
HBr’s bond length is longer as Br has additional electron shells compared to F, increasing its atomic radius which increases the distance between the H and Br atom, causing a longer bond length
How to explain a past-half equivalence comparison of weak acid and its conjugate base