Polyprotic Acids and Salt Solutions in Chemistry
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Polyprotic acids
Acids with multiple protons to donate.
H2SO3
Sulfurous acid, a polyprotic acid example.
Ka1
First acid-dissociation constant, 1.7 x 10^-2.
Ka2
Second acid-dissociation constant, 6.4 x 10^-8.
Acid dissociation
Process of losing H+ ions from acids.
pH dependence
Depends on first dissociation if Ka1 > 1000 x Ka2.
Ascorbic acid
Vitamin C, a polyprotic acid.
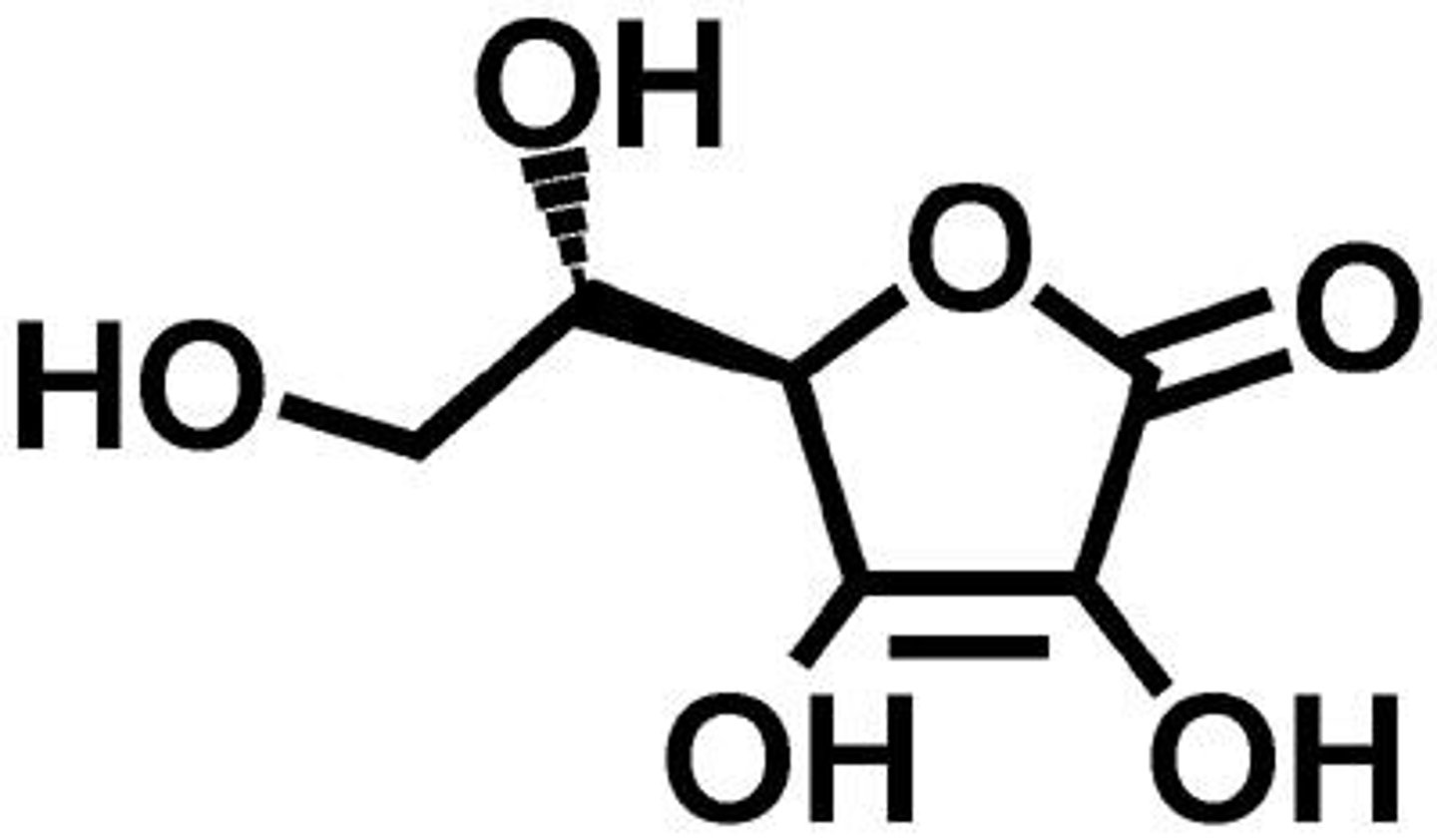
Citric acid
Common polyprotic acid in citrus fruits.
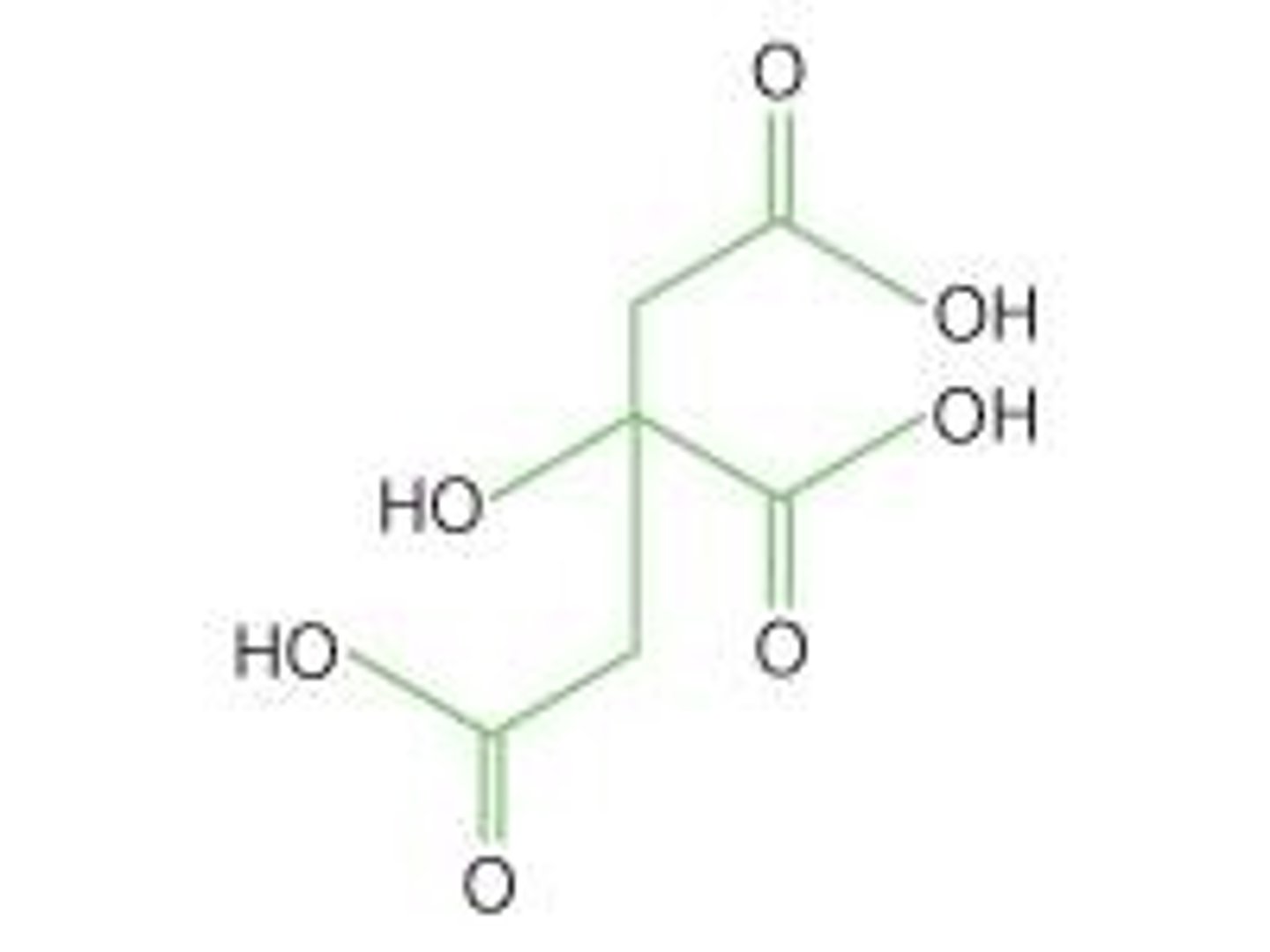
Salt solutions
Solutions formed by dissolving salts in water.
Neutral salts
Salts like NaCl that do not affect pH.
Hydrolysis
Reaction of ions with water producing H+ or OH-.
Conjugate base
Anion formed when an acid donates H+.
Conjugate acid
Cation formed when a base accepts H+.
Ca2+
Conjugate acid of strong base Ca(OH)2.
NO3-
Conjugate base of strong acid HNO3.
Strong electrolyte
Dissociates completely in solution, e.g., Ca(NO3)2.
Na+
Conjugate acid of strong base NaOH.
ClO-
Conjugate base of weak acid HClO.
Weak electrolyte
Partially dissociates in solution, e.g., NaClO.
NH4+
Conjugate acid of weak base NH3.
Cl-
Conjugate base of strong acid HCl.
Common-Ion Effect
Shift in equilibrium due to added common ion.
HF
Weak acid, used in common-ion effect example.
HCl
Strong acid, increases [H3O+] in solution.
pH calculation
pH = -log[H3O+], used for acidity measurement.