Brand Management Final Exam
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
KU Leuven - Spring 2025
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Product Centered
Trademarks may consist of any signs capable of being represented graphically, particularly words, including personal names, designs, letters, numerals, the shape of goods or their packaging.
Word Mark
A type of trademark that consists of words, letters, numbers, or any combination thereof, claimed as a brand identifier.
Figurative mark
A type of trademark that includes visual elements, such as logos or stylized designs, which distinguish goods or services without relying on text.
Figurative mark with letters
A trademark that combines visual elements and text, such as logos integrated with letters or numbers, to identify a brand.
Shape mark
A type of trademark that consists of distinct shapes or packaging designs that identify and distinguish goods or services without reliance on words or logos.
Pattern Mark
Exclusively of a set of elements which are repeated regularly
Color single mark
Single color (without contours)
Genericide
A situation where a trademark becomes generic and loses its distinctiveness, often due to widespread use in common language to refer to a general class of products.
What is an example of Genericide
Q-tip, Band-Aid, Chapstick, Kleenex
Customer-centered definition
Associations that consumers have with something that can be managed professionally (a product, service, person, name)
Overview of brand functions for companies (PHOTO)
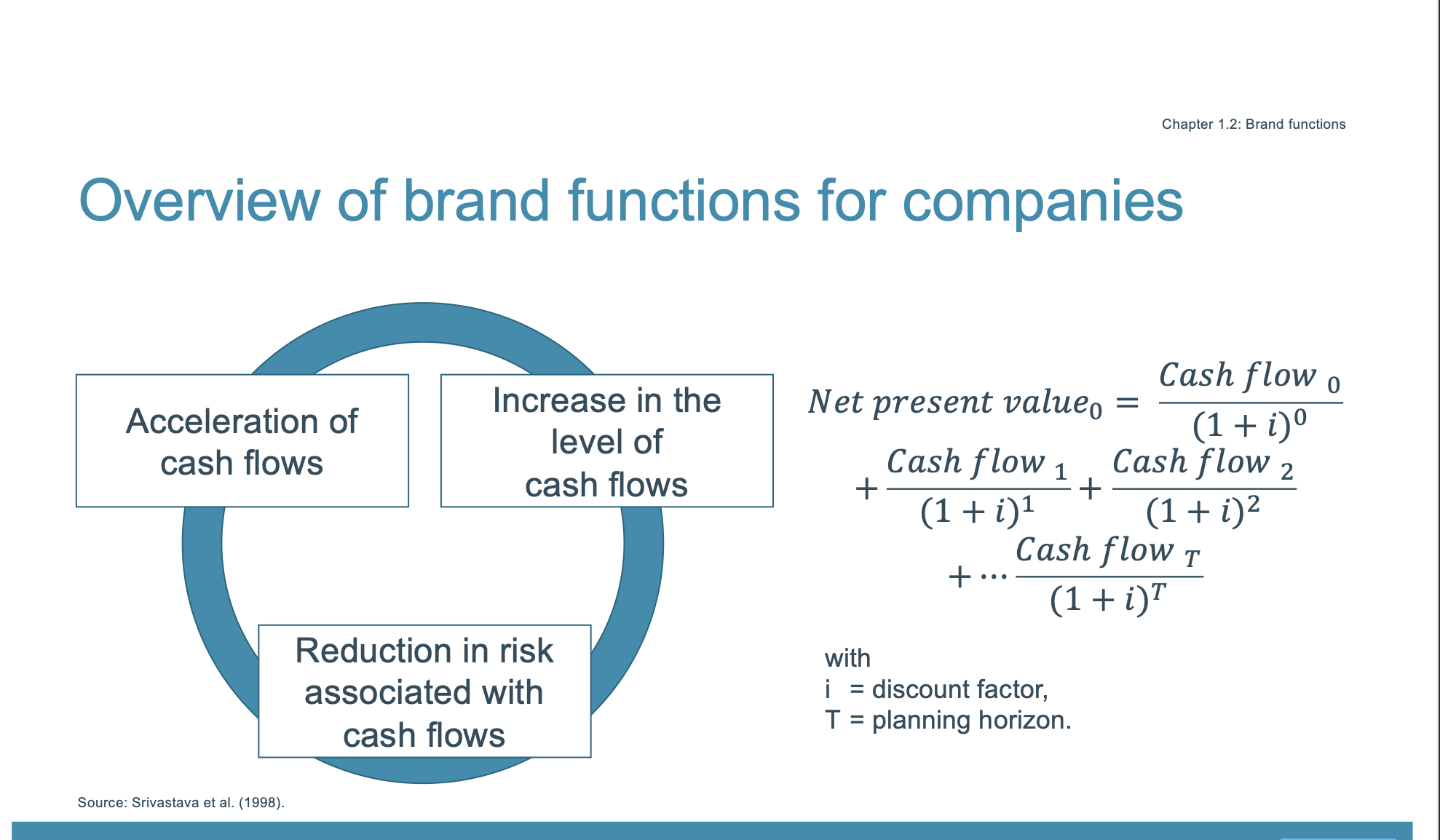
Net present value =
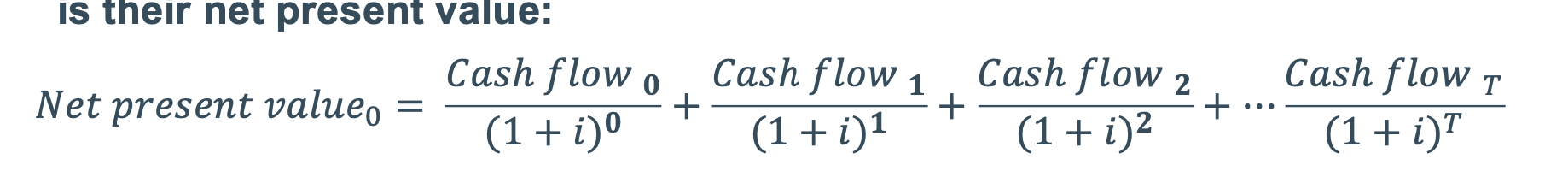
Price premium
Identical product can be sold for higher price to consumers
Sales premium
identical product can be sold more often to consumers
Sales premium dominant
Low prices is part of the brands identity a core function
Price premium dominant
If a high price is part of the brand’s identity and the brand’s high price is linked to strong psychological and/ or social benefits (luxury brands)
Price and sales premium
A brand is positioned as being of higher quality but prices is not a core brand attribute
Brand extensions, co-branding
Uses the company’s accumulated investments in the brand; cash flows of the brand’s other products serve as a “bond” for the extension’s quality
Firm-level risk (type 1)
vulnerability of future cash flow (bankruptcy)
Firm-level risk (type 2)
Variability / volatility of future cash flows
Higher quality perceptions
lower price sensitivity
Corporate reputation effect
As investors have higher awareness levels and stronger and more positive quality associations
BRiC operationalization
Overall role brand plays in customers’ decision making in a specific category
General decision weight
Puts expected brand benefits in relation to other product benefits
Category-level
Measure, not brand-level measure, i.e., it does not vary across brands but only across categories
Associative network memory model
Memory consists of a network of nodes (=stored information or concepts) and connecting links (=strength of association between the nodes)
Brand related information is stored where?
Long-term memory where it is organized as an associative network
Components of brand knowledge (Photo)
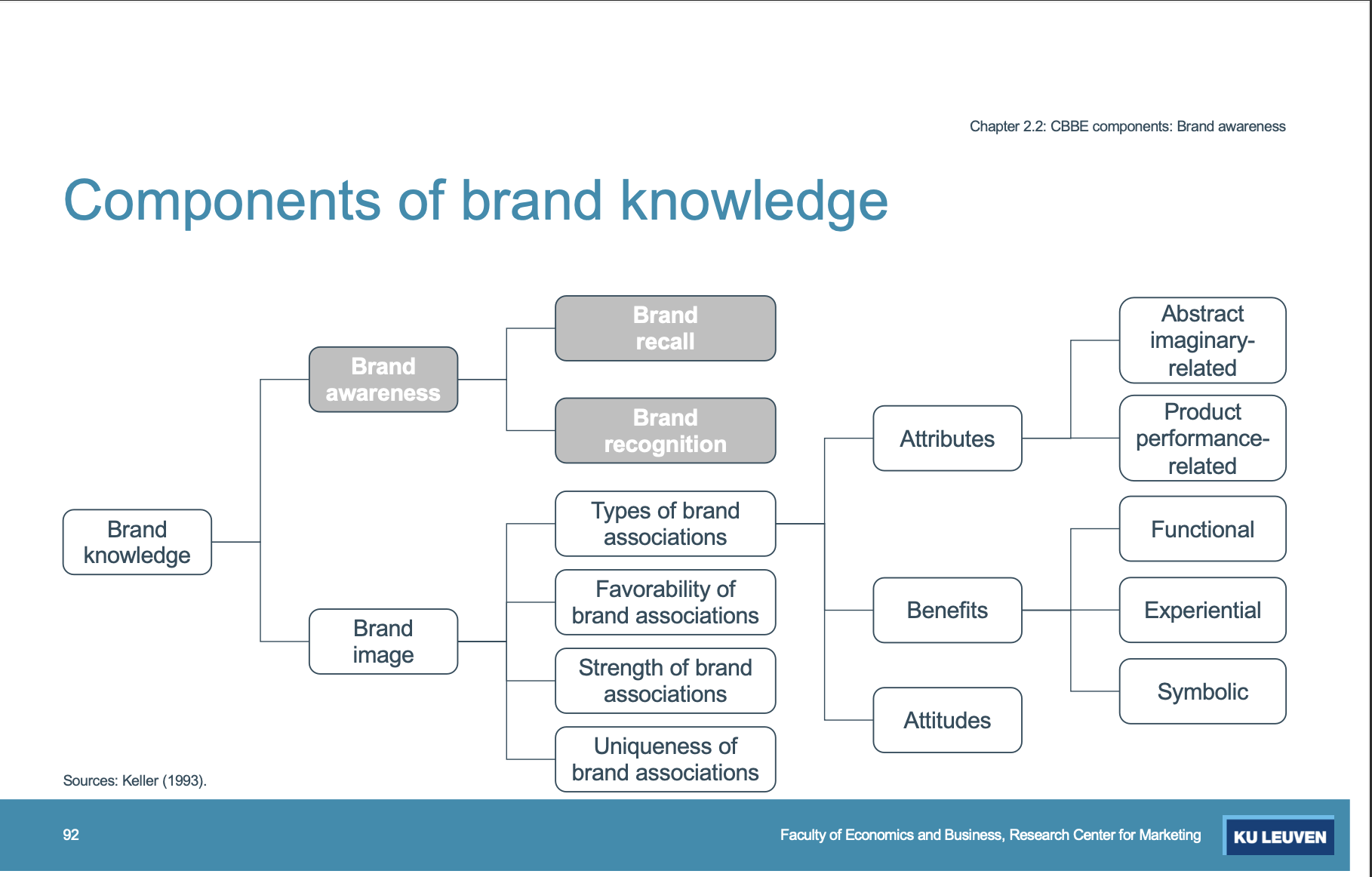
Brand recognition
the degree to which consumers can confirm prior exposure to the brand when provided with a brand element (name, logo, jingle) as a sensory cue
Brand recall
The degree to which consumers can retrieve the brand from memory without a brand cue when given
Set Theory of consumer decision making (Photo)
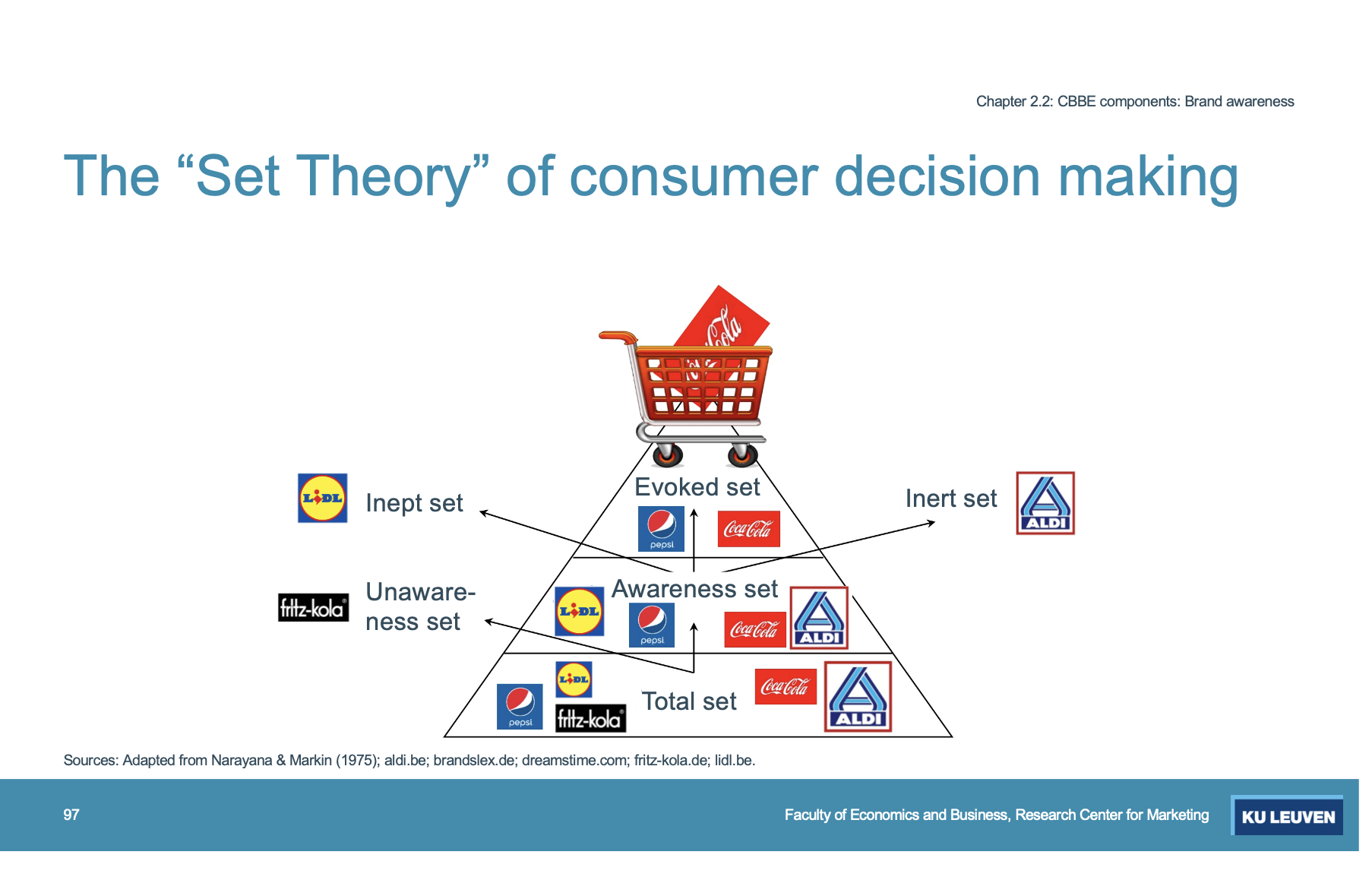
Why does brand awareness matter?
Learning advantages: Create a brand node in consumers’ memory
Consideration advantage: The degree of brand awareness affects the brand’s likelihood of being a member of the consumer’s evoked set
Choice advantages: Can affect decisions about brands even if no other brands associations exist
Brand Image
Set of associations linked to the brand of that consumers hold in memory
What are the components of brand knowledge
Brand image, Types of brand associations, Attributes, Benefits, Attitudes, Abstract-related, Product performance-related, Functional, experiential, Symbolic
Brand attributes
Features that characterize the brand and are related to the brand’s performance
Brand Benefits
Personal value that a consumer associates with a brand and its usage
What are some characteristics/ dimensions of brand associations
Strength, Favorability, and Uniqueness
Non monetary brand equity
Analyzing brand awareness and brand image
Monetart brand equity
Measuring future earnings that are attributable to the brand
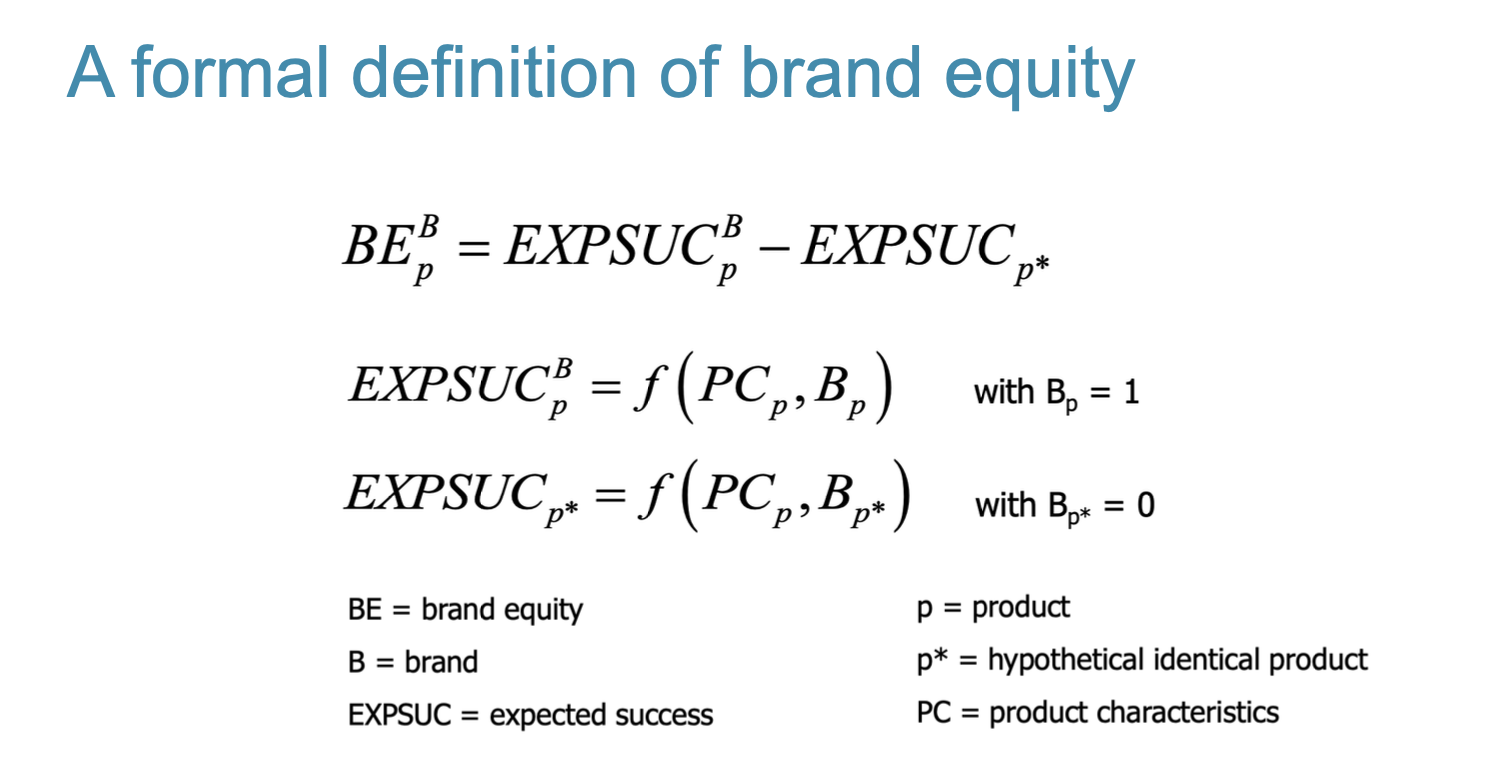
Formal definition of brand equity (PHOTO)
Brand earnings
Revenue x Royalty Rate
Brand Value
Determine the future revenue stream, apply the royalty rate, and discount the estimated future royalty stream (net present value)
Four possible cases for a revenue premium
The difference in revenue (net price x volume) between a branded product and the corresponding unbranded product (a weak private label)