Psychopharmacology: Drugs, Addiction, and Mental Health
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
122 Terms
Psychoactive Drugs
Chemicals altering cognition, mood, or behavior.
Psychopharmacology
Study of drugs affecting the nervous system.
Pharmacokinetics
How the body affects drugs' absorption and elimination.
Metabolism
Chemical process of breaking down drugs.
Distribution
How drugs spread through the bloodstream.
Elimination
Process of removing drugs from the body.
Pharmacodynamics
How drugs affect the body after binding.
Affinity
Drug's ability to bind to receptors.
Efficacy
Effectiveness of a drug after binding.
Oral Administration
Swallowed pills or liquids; low bioavailability.
Injection
Direct drug delivery via needle; high bioavailability.
Inhalation
Rapid drug absorption through lungs.
Insufflation
Snorting drugs for quick effects.
Agonist
Enhances neurotransmitter action at receptors.
Direct Agonist
Mimics neurotransmitter by binding to receptors.
Indirect Agonist
Increases neurotransmitter action without receptor binding.
Antagonist
Blocks or hinders neurotransmitter action.
Substance Use Disorder
Addiction harming health and relationships.
Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD)
Uncontrollable alcohol use affecting health.
Korsakoff Syndrome
Neurodegenerative disease from thiamine deficiency.
Alcohol Withdrawal Syndrome
Severe symptoms after stopping alcohol use.
Delirium Tremens (DTs)
Severe alcohol withdrawal with hallucinations.
GABA
Inhibitory neurotransmitter, reduces neuronal excitability.
GABAA receptors
Binding sites for GABA and alcohol.
Alcohol
GABA agonist, increases dopamine levels.

Nicotine
Acetylcholine agonist, highly addictive.
Dopamine
Neurotransmitter linked to reward and pleasure.
Carcinogenic
Substances that can cause cancer.
Teratogens
Drugs causing birth defects.
Cocaine
Psychostimulant causing euphoria and increased arousal.

Crack cocaine
Crystallized cocaine, more addictive form.
Amphetamine
Psychostimulant, highly addictive, increases dopamine.
Methamphetamine
Crystallized form of amphetamine, smoked.

Dopamine reuptake inhibitors
Block transporters, increasing dopamine levels.
Opioids
Analgesics, reduce pain, increase dopamine.
Endogenous Opioid System
Body's natural pain relief system.
Opioid receptors
Mu, delta, kappa; involved in analgesia.
Hallucinogens
Affect consciousness, produce hallucinations.
Psychedelics
Hallucinogens like LSD and psilocybin.
Dissociative hallucinogens
PCP and ketamine, alter perception.
5-HT2A receptors
Serotonin receptors affected by hallucinogens.
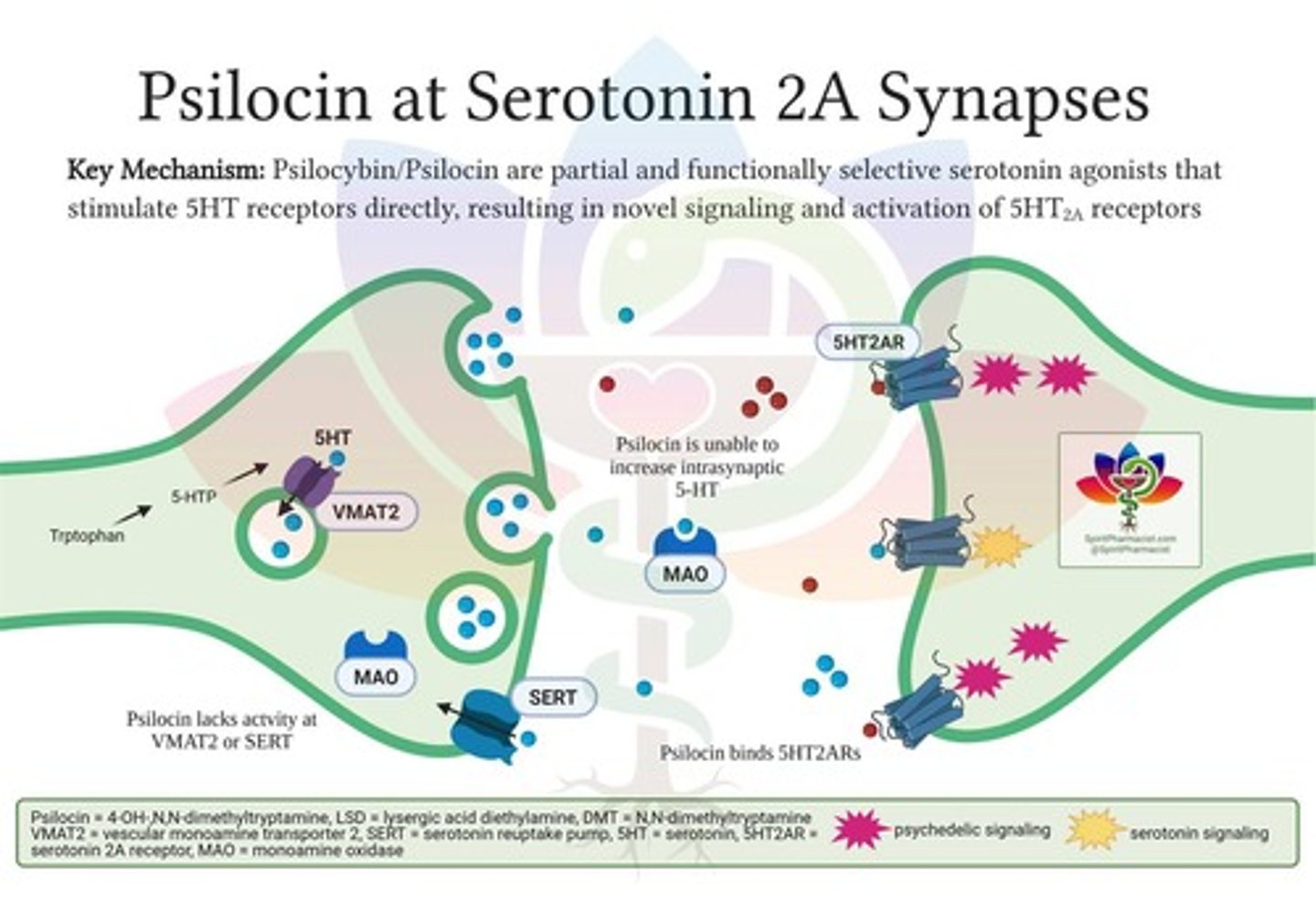
Drug tolerance
Reduced response to a drug over time.
Metabolic tolerance
Body increases enzymes to counteract drugs.
Psychological tolerance
Conditioned response to drug-related stimuli.
Overdose
Occurs more often in unfamiliar environments.
Drug Sensitization
Increased response to drug intake over time.
Behavioral Sensitization
Greater response after initial drug exposure.
Addiction
Compulsive behaviors causing harm to self and others.
Social Stigma
Negative societal perception of addiction.
Risk Factors
Adolescents, trauma, and mental health disorders.
Negative Reinforcement Theory
Drugs taken to alleviate withdrawal symptoms.
Positive Reinforcement Theory
Drugs taken for euphoric pleasure.
Mesotelencephalic Dopamine System (MTDS)
Dopamine pathway activated by drugs and rewards.
Ventral Tegmentum
Sends signals to the nucleus accumbens.
Nucleus Accumbens
Brain region involved in reward and addiction.
CREB
Gene activator that increases with drug use.
Dynorphin
Reduces pleasurable feelings from drugs.
ΔFosB
Protein linked to craving behavior and sensitization.
BDNF
Promotes dendritic branching and learning.
Incentive-Sensitization Theory
MTDS sensitized to drugs and associated stimuli.
Classical Conditioning
Learning through association with drug stimuli.
Instrumental Conditioning
Increased craving due to drug-related stimuli.
Dorsal Striatum
Brain region crucial for learning and cravings.
Long-lasting Sensitization
Sensitization persists beyond withdrawal symptoms.
Relapse
Return to drug use after abstinence.
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
Condition affecting social interaction and communication.
Hypersensitivity to stimuli
Overreaction to sensory input in individuals.
Repetitive behavior
Engaging in the same actions repeatedly.
Need for routines
Preference for predictable and consistent schedules.
Diagnosis rate
1 in 59 children diagnosed with ASD.
Genetic factors
Inherited traits contributing to developmental disorders.
Environmental exposure
Contact with heavy metals and pesticides linked to ASD.
Associated disorders
Conditions like Down syndrome and fragile X syndrome.
Vaccine myth
No evidence linking vaccines to autism.
Nucleus accumbens
Brain region reacting differently to rewards in autism.
Amygdala overactivation
Increased activity leading to overwhelming stimuli.
Prefrontal cortex overactivation
Excessive activation affecting decision-making and behavior.
Applied behavioral analysis
Therapy using learning methods to improve behavior.
Vasopressin research
Investigating hormone's role in autism treatment.
Oxytocin research
Studying hormone's potential effects on social behavior.
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
Disorder characterized by inattention and hyperactivity.
Executive functioning issues
Difficulties in planning and executing tasks.
Gender diagnosis disparity
ADHD diagnosed more in boys than girls.
Comorbid conditions
ADHD often occurs with anxiety and epilepsy.
Dopamine neurons
Neurons involved in attention and reward pathways.
Psychostimulants
Medications like Ritalin that stimulate dopamine activity.
Major Depressive Disorder
Condition marked by persistent sadness and anhedonia.
Anhedonia
Inability to feel pleasure in activities.
Gender prevalence in depression
Twice as likely in women compared to men.
Monoamine hypothesis
Theory linking depression to low monoamine levels.
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)
Medications that increase monoamine activity in synapses.
Cheese reaction
High blood pressure from certain food interactions.
Tricyclic antidepressants
Older class of antidepressants with potential side effects.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
Common antidepressants that affect serotonin levels.
Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs)
Medications that enhance norepinephrine in the brain.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Therapy focusing on changing negative thought patterns.
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)
Anesthesia and muscle relaxants used during procedure.
ECT Electricity Level
Electricity runs through brain at 800 milliamps.
ECT Memory Effect
Patients typically do not remember the procedure.
ECT Effectiveness
Provides fast relief from depression symptoms.