Functional Cognition Midterm
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
What is functional cognition?
-combination of cognition and function
-observable performance of everyday activities resulting from a dynamic interaction between cognitive abilities, activity demands, and the task environment
What is a reductionist model?
-isolates aspects like memory, problem solving, EF
-focuses on deficits and not strengths
Benefits of a reductionist model
-helps explain behaviors
-provide a basis for comparison (good to track recovery from injury)
-strong psychometric properties
Drawbacks of a reductionist model
-does not always translate to performance!
-may not reflect functional abilities
Task considerations for fun cog
-salience
-motivation
-familiarity
Environment considerations for fun cog
-dynamic or static
-familiar or novel
-support or hindrance
Condition considerations for fun cog
-strengths and limitations
-compensations
-awareness
LAUNDRY EX - task considerations
-how often they do it
-location of machine
-separation of colors?
LAUNDRY EX - environment considerations
-location of machine
-social support
-are dirty clothes spread out or in something like a laundry bin
LAUNDRY EX - cognition considerations
-sequencing of task
-number of steps
-timing for when its done
-recognizing mistakes
Attention
- a hierarchical system
- the higher on the hierarchy, the more systems involved, so more likely something is impaired
Attention hierarchy
1) arousal/alertness
2) vigilance
3) selective attention
4) capacity
1) Arousal/alertness
focused attention
-automatic brain systems to extract information from the environment and select a behavior response
-EX: do they turn when you say their name?
2) Vigilance
sustained attention
-ability to maintain alertness over a period of time
-EX: conversation, listening to a lecture
3) Selective attention
-ability to select information necessary for a task (filter)
-EX: listening to professor and not the sound of the keyboard
4) Capacity
alternating and divided attention
-ability to change focus/allocate attentional resources
-EX: cooking a lot of things at once
Reticular activating system (RAS)
-brainstem; automatic
-regulates sleep and wake cycles
-attending to tasks throughout the day
**supports sustained attention + tonic alertness
Thalamus
-sensory information processing
-"filter" for sensory information (what information do we actually need to focus on?)
**supports selective attention
Colliculi
-superior colliculus: visual attention
-inferior colliculus: auditory attention
**supports selective attention and alternating attention
Parietal lobe
-fine tuned filter like the thalamus
-visual + spatial aspects of attention
**supports selective attention and allocation of resources (alternating and divided attention - how much attention we need to give up to each task)
Anterior cingulate
-link between subcortical and cortex
-inhibit over learned responses
-complex behavior selection (what is the appropriate response to this experience)
Frontal lobes
-selection of response (initiate and inhibit)
-selection of info to be held online (in the moment)
-considered EF (higher levels of attention)
Posner and Peterson Model: three systems of attention
-Alerting
-Orienting
-Executive
Alerting system
base level
-vigilance/sustained attention
Orienting system
-prioritizes sensory input
Executive system
-exercises top-down control
-resolves conflicts
-detects sensory info that requires conscious attention
Memory stages
1) attention
2) encoding
3) storage
4) retrieval
1) Attention
process incoming information
2) Encoding
initial stages of memory where information is analyzed
3) Storage
memory is retained, transient memories are moved to a. location of the brain for more permanent recall
*when you know info will be needed in the future
4) Retrieval
Where memories are recalled, locating of existing memories
Retrograde amnesia
-problem with recall
-stage 4
Anterograde amnesia
-problem with encoding/storage
-stage 2 + 3
Atkinson-Shiffrin Model of Memory
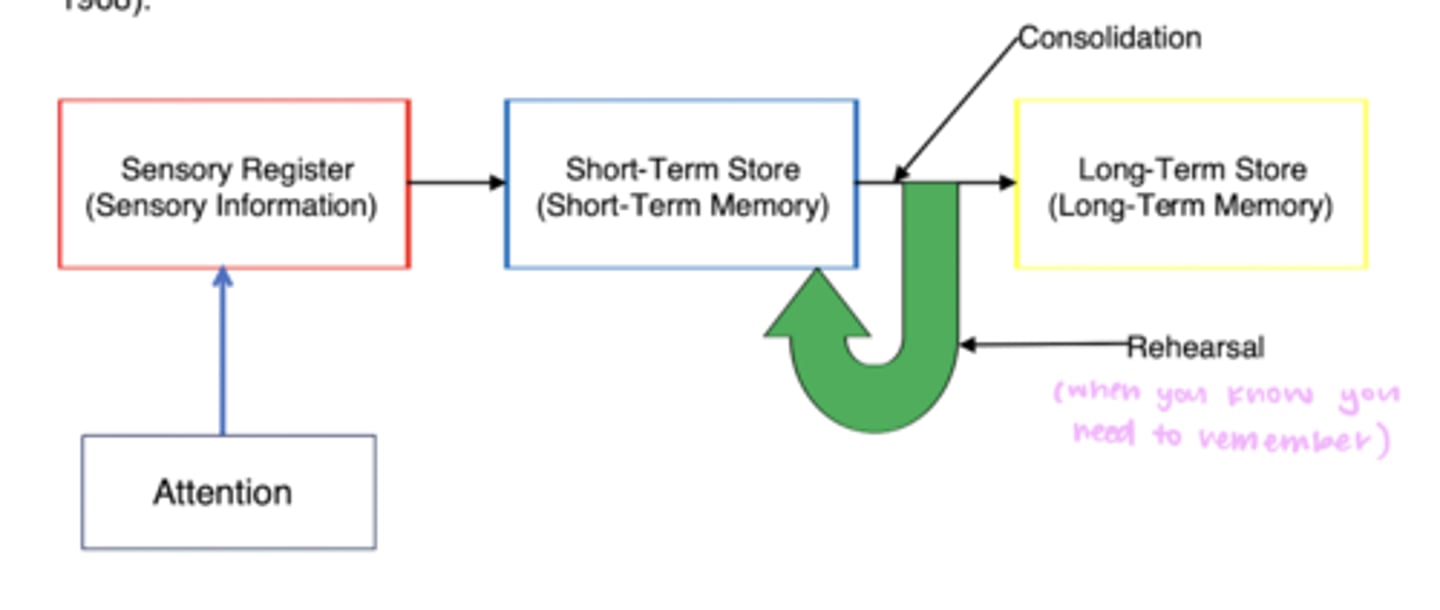
Atkinson-Shiffrin Example: ordering pizza
- attention: recognize you are hungry, attending to body
-sensory register: what kind of pizza sounds good; SEEING how many people to buy pizza for
-short term store/working memory: remembering what type of pizza everyone wants
-long term store: memorize pizza number; telling them your address, giving your phone number
Long term memory: declarative (explicit) memory
-semantic memory
-episodic memory
-prospective memory
Semantic memory
general knowledge
-"grass is green"
Episodic memory
past personal experiences
-remembering childhood vacation
Prospective memory
remembering to do things in the future
-taking meds at a specific time
Nondeclaritive (implicit) memory
-procedural memory (skills)
-priming and perceptual learning
-classical conditioning/behavioral learning
Procedural memory (skills)
memory for skills
-typing on a computer
-riding a bike
Priming and perceptual learning
if you see fast food ads all day, you will want a burger not a salad
-color coding notes or planner
Classical conditioning/behavioral learning
response is learned as a result of pairing of two stimuli
-do a behavior because you know what outcome would be
-anxiety when alarm goes off in morning
Baddeley's working memory model
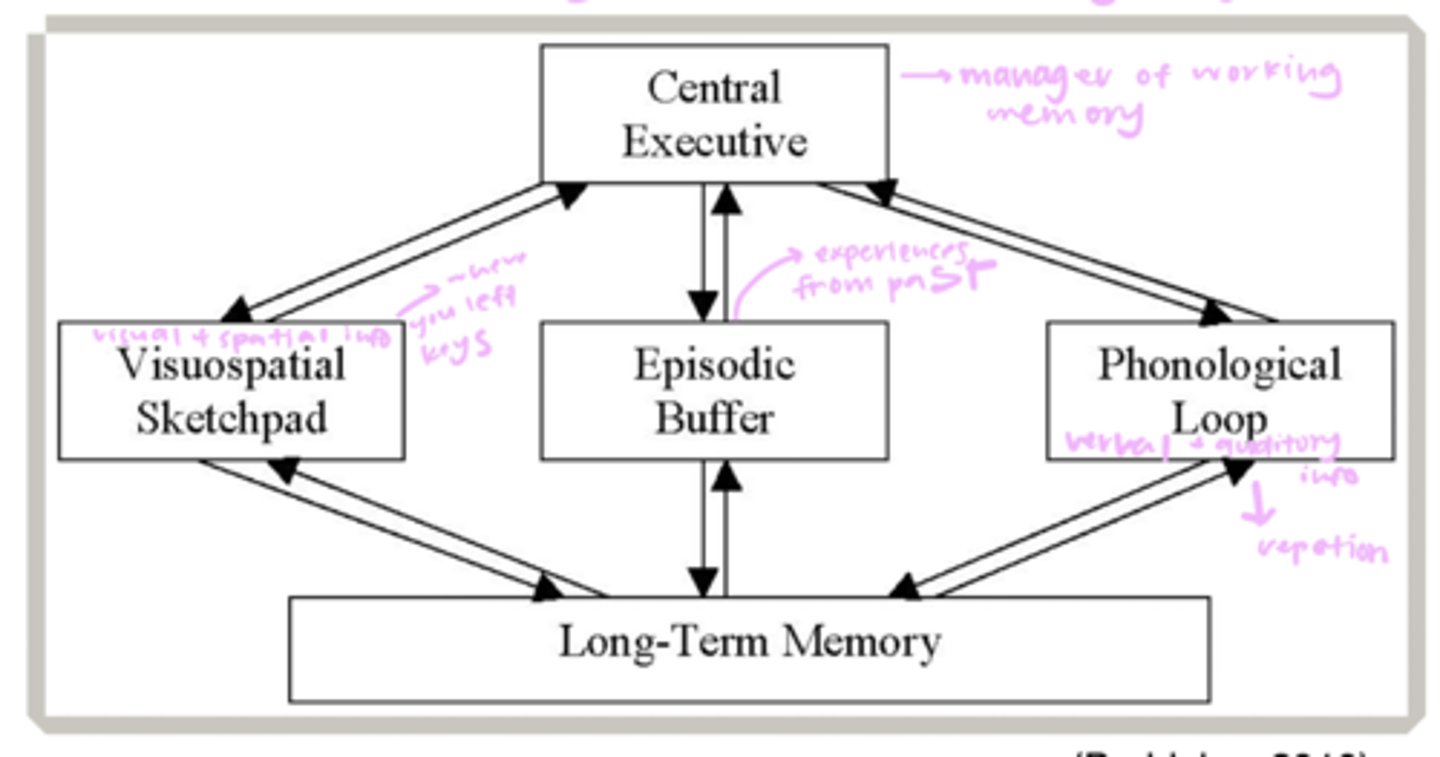
Baddeley's - central executive
-plans future actions
-retrieval of LTM
-integrates new information
Baddeley's - visuospatial sketch pad
-holds visual and spatial information
Baddeley's -phonological loop
-holds verbal and auditory information
Baddeley's - episodic buffer
integrates information with LTM and chunks info based on prior knowledge in order to improve storage and later retrieval
Prefrontal cortex
-most well-established cognitive portion of the brain
-EF, workin memory, abstract thinking, social cognition
-**connected with every functional portion of the brain
Executive functions
umbrella term
-no single behavior can be tied to EF
-abilities that allow a person to adapt to new situations and develop and follow their life goals
-EF is gateway to skill acquisition
Executive function examples!
-initiation (starting behavior)
-response inhibition (stopping behavior)
-planning/organization (sequencing + timing behavior)
-multitasking (more than one task)
-goal-directedness (intentionality)
-task persistance (maintaining behavior)
-awareness (monitor+modify own behavior)
-problem solving (solutions + choices)
Common symptoms of executive DYSfunction
-impulsivity
-confabulation (unintentionally recalls false mems and thinks they are accurate)
-difficulty planning
-euphoria
-poor sequencing
-lack of insight
-apathy
-disinhibition
-aggression
-perseveration (invol repetition of thought or behavior)
-poor decision making
Shallice's Supervisory Attention System
four hierarchical levels of behavior
-action units
-schemata
-contention scheduling
-supervisory attentional system
Shallice - action units
basic abilities
-reaching for an object
Shallice - schemata
part of a task
nest of action units closely associated with each other through repetition and practice
-reaching for water AND taking a drink
Shallice - contention scheduling
routine + whole task
basic interface between incoming stimuli (or thoughts_ and schemata
quick selection of routine behaviors in well-known behaviors
-what we are used to (route home)
Shallice - supervisory attentional system
conscious cognitive controlled processing
-taking a different route home because of flooding)
Levels of awareness
-intellectual (most basic)
-emergent
-anticipatory
Intellectual
"self awareness"
-knowledge that they have limitations
Emergent
"on-line monitoring"
-ability to recognize that they are having a problem while it is occurring
Anticipatory
"on-line monitoring"
-ability to anticipate problems before they occur
Reliability
-consistency of test takers scores, under similar testing conditions
Validity
tests measures what it is supposed to measure - performance on test relates to what is being assessed
**many different types
Construct validity
tests what concept it says it is testing
Convergent validity
how well it correlates with other measures
Divergent validity
a measure that is uncorrelated with different measures
Content validity
how comprehensive it is in that construct
Face validity
if it looks believable
Concurrent validity
extent it correlates with another well assessed measure of the same construct at the same time
Predictive validity
how well it predicts an outcome
Sensitivity
test identifies the true positive, actual positives are correctly found
*** ability of test to determine individuals WITH condition
Specificity
test identifies true negative, individuals without cognitive impairment are correctly identified
*** ability of test to determine individuals WITHOUT condition
Cognitive Functional Evaluation (C-FE)
Revised
1. Occupational history/narrative
2. Cognitive factors
(3, 4, 5 can go in any order after 1 + 2)
3. Occupational performance
4. Self-awareness and beliefs
5. Environmental factors
Evaluation methods for C-FE
-Interviews
-Self reports and informant reports
-Performance based assessments
Occupational history
-saliency (what is important to the client?)
-novel vs procedural/habitual (how familiar are they with certain tasks)
-motivation (what motivates them?)
tools: semi structured interview, GAS
Cognitive factors - cognitive screening
Cog screening
-baseline of where to start
-should not be the sole basis for treatment plan (only preliminary data)
tools: MMSE, short blessed, MOCA, SLUMS, TMT
Cognitive factors - neurocognitive testing
designed to measure isolated constructs to localize brain lesions and serve as diagnostic tool for supporting diagnosis
tools: BIT, TEA, TBMT
Occupational performance
performance based testing + functional observation
tools: weekly calendar, multiple errands, EFPT, EFPTe, PASS, actual reality, AMPs
Self-Awareness and Beliefs
-clients own understanding of their cognitive profile
-self awareness and beliefs can be observed at any point in the C-FE
Environmental factors
-safety
-accessiblity
-social support
-resources
tools: home occupational environmental assessment, safety assessment of function and the environment for rehabilitation
True negative
someone WITHOUT the condition NOT being identified with the condition
True positive
someone WITH the condition being identified WITH the condition
False negative
someone WITH the condition NOT being identified with the condition
False positive
Someone WITHOUT the condition being identified WITH the condition
Positive predictive value (PPV)
-percentage of individuals with a positive test that are accurately identified (they have condition)
**closer to 100%, the better
Negative predictive value (NPV)
-percentage of individuals with a negative test that do not have the condition
**closer to 100% the better
EFPTe
Executive functioning in IADLs and home activities (cooking, phone, bills, meds)
-initiation, organization, sequencing, judgment and safety, completion
-used for higher PLOF (EFPT for lower)
EFPTe scoring criteria
cues-based
have to do two cues in each section to move onto next
cue levels: verbal guidance, gestural guidance, verbal direct, physical assistance, do for participant
EFPTe population
mild cognitive impairment
higher PLOF
**NOT APPROPRIATE for severe cognitive deficits
EFPTe settings
home
outpatient
CTPA
** working in library
inventory and phone messages
-work based tasks
CTPA scoring criteria
inefficiencies, rule breaks, interpretation failure, task failure, inventory control accuracy
CTPA population
people who want to return to work
higher cognitive functioning
NOT APPROPRIATE FOR: retired, not working
WCPA
weekly calendar planning activity
3 versions varying by difficulty (2 most common)
WCPA scoring criteria
accuracy, total time to complete, number of rules followed, strategy use (number and frequency), planning time
WCPA settings/population
lots of settings, even adolescent versions, seen more in OP, HH, IPR
-not appropriate for: super severe cognitive deficits, motor impairments w dominant hand impacted, visual impairments
PASS
26-task related assessment focuses on ADL, IADL, and functional mobility skills that a client may have
PASS scoring criteria
safety, independence, adequacy (process + quality)
PASS settings/populations
a lot of them; some subtests better for diff populations
not appropriate for children
PASS cueing structure
9 cues
1. verbal encouragement
2. verbal indirect
3. verbal direct
4. gestural
5. task/environmental rearrangement
6. demonstration
7. physical guidance
8. physical support
9. full assist/do it for them)