VETM3440 - Clinical Medicine II - Diagnostic Imaging Test 1 (Thoracic Radiology)
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
From Antonina Degroot set via quizlet
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Describe how radiographs are made
- Electrons products at the cathode are sent to the anode in a vacuum at an accelerated speed
- Electrons interact with anode to release x-rays
- X-rays directed to patient and absorb, scatter or transmit
- They hit detector and an image is created (black where x-rays hit, white where they did not)
What two factors can we adjust? Explain them and what increasing them will do to the radiograph.
kVP:
- The potential across the tube (difference in electrical charge)
- Energy of x-rays
mAs:
- Number of x-rays
*increasing either increases exposure*
What are the six Roentgen signs?
Size
Margin
Shape
Opacity
Number
Location
"show me something obvious now lady"
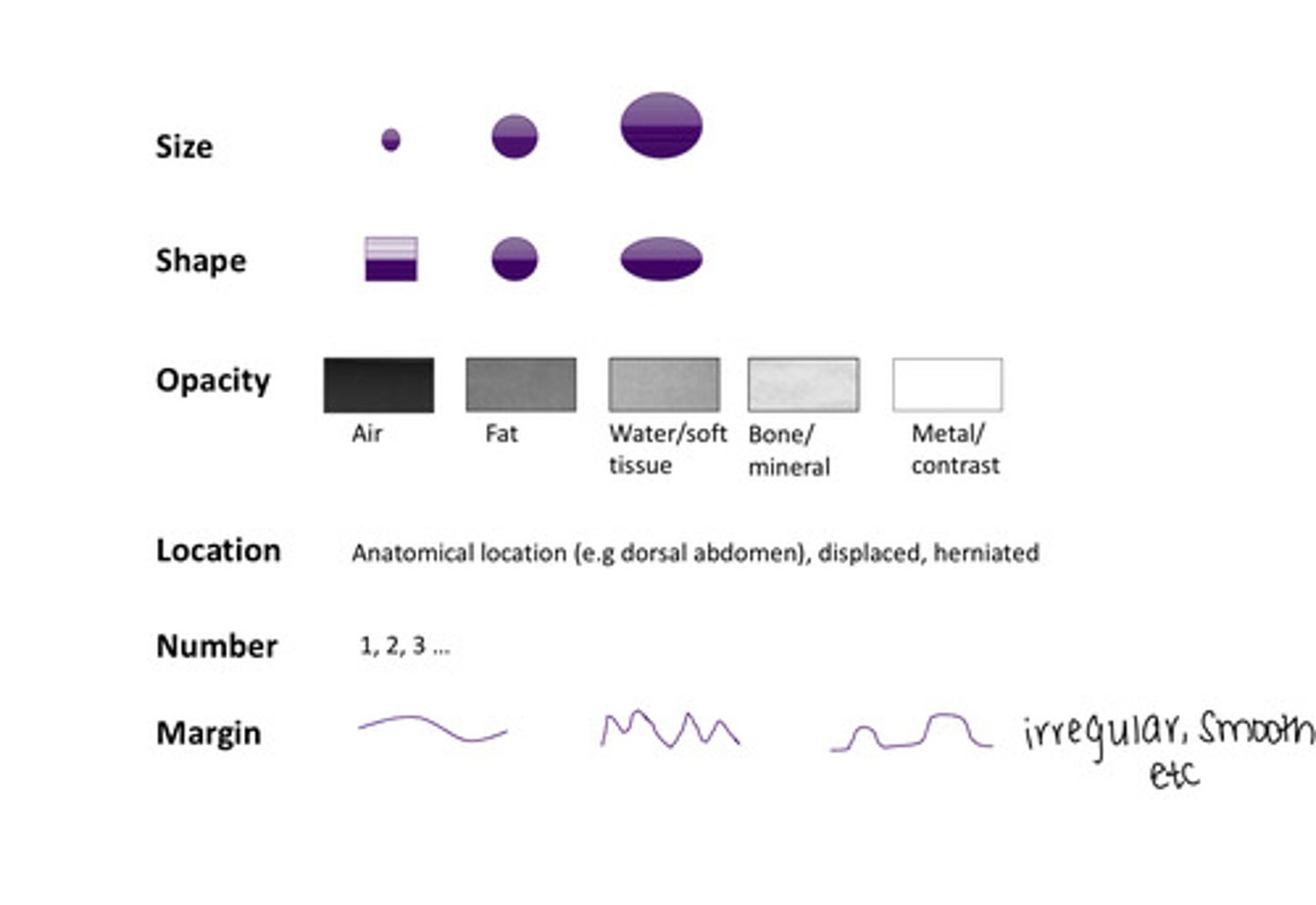
What is opacity a function of?
Tissue type and thickness
Lightest opacity on radiograph?
Metal
Darkest opacity on radiograph?
Air
What is summation?
A special type of superimposition which creates a new opacity which is not actually present in the patient
What does negative summation versus positive summation do?
Negative summation:
- Decreases the opacity artificially (makes things look lighter)
- Ex. Overlapping gas
Positive summation:
- Increases the opacity artificially (makes things look darker)
- Ex. End on vessels overlapping on poles of kidneys
What is silhouetting/border effacement?
Two structures of the same opacity come into contact and you can no longer distinguish them from one another
How does magnification work when taking a radiograph?
Objects farther from the plate are magnified (think of a shadow)
How do we name a radiograph?
From where the beam enters to where the beam exits
Ex.
- Right lateral means that the beam enters from the left and exits on the right
- Ventral dorsal means that the beam enters ventrally and exits dorsally
What features are visible on radiograph in left sided cardiomegaly?
Lateral views:
- Wide and tall heart
- Dorsal tracheal elevation
- Flattened caudodorsal margin
DV/VD Views:
- Left atrium has a rounded opacity/enlargement at 6 o'clock position
- Left auricle 2-3 o'clock is enlarged
- In cats, their heart looks like a "❤️"
What features are visible on radiograph in right sided cardiomegaly?
Lateral views:
- Increased sternal contact
- Rounded cranial margin
- Increased volume of cardiac silhouette cranial to carina
DV/VD Views:
- Heart appears in a reverse "D" shape
- Right atrium at 9-11 o'clock is enlarged
- Mean pulmonary artery at 1-2 o'clock is enlarged
Why is right sided cardiomegaly exceptionally rare?
It means there would be obstruction of blood flow into the lungs
Where are pulmonary veins?
They are located 'central and ventral'
What are the characteristics of pulmonary veins?
- They should be smaller than the 4th rib in lateral and 9th rib in VD as they cross
- They're the same size as their accompanying artery
What is a sign of enlargement (pulmonary hypertension) of a pulmonary artery?
Tortuosity (wiggly) is a sign of enlargement
What are some components of normal lung anatomy?
- Veins are ventral and central
- Arteries and veins are the same size
- We should normally see vessels and airway markings, but not going to see alveoli
List the four pulmonary patterns
1. Unstructured interstitial
2. Structured interstitial
3. Alveolar pattern
4. Bronchial pattern
Describe an unstructured interstitial pattern
- Increased pulmonary opacity
- Partial obscuration of vascular markings
- Can be focal, multifocal or generalized
- Hazy looking
Describe a structural interstitial pattern
Presence of nodules or masses
Describe an alveolar pattern
- Increased pulmonary opacity
- Complete obscuration or vascular markings/ pulmonary vessels
Hallmarks of an alveolar pattern include:
- Air bronchograms
- Lobar sign
*don't need both to be considered alveolar*
What is an air bronchogram?
Air filled (dark) airways completely surrounded by white (kind of looks like a dead Christmas tree)
What is a lobar sign?
An aerated lung against a non-aerated lung
What is the definition of a bronchial pattern? What do you see?
Thickened airways - you should see little "donuts" (little white circles with black in the inside) and lines
How big should vessels be?
No bigger than ribs
How wide should the heart be?
2.5 - 3 intercostal spaces
What is the pleural space?
It is a theoretical space between the lungs and heart, you shouldn't see it normally
List the abnormalities that can occur in the pleural space
- Pleural fissures
- Gas
- Pleural effusion (fluid)
- Pneumothorax (collapsed lungs)
- Extrapleural sign (mass)
What are pleural fissures? Where are pleural fissures located? What do they indicate?
They are thin lines along the margins, between lung lobes - they can indicate scant effusion (get wider as effusion increases in volume)
Where should lungs normally go to?
The body wall
What is a sign of pleural effusion?
Lungs not touching the body wall - the fluid in the pleural space won't let the lungs fully expand
What are some visual indicates of pneumothorax?
- Gas in pleural space
- Lungs retracted
- No lung markings (vessels, bronchi) in air filled regions
- Dorsal deviation of the heart
What is an extrapleural sign?
A specific radiographic feature that helps distinguish pulmonary from extra pulmonary masses or lesions
Pulmonary masses:
- Make an acute angle with the body wall
Extra pulmonary masses:
- Make an obtuse angle with the body wall
What are the contents of the mediastinum?
- Vessels
- Lymphatics and lymph nodes
- Fat
- Esophagus
- Trachea
- Heart/pericardium
- Thymus (in young animals)
How can you tell that there is a cranial mediastinal mass?
The cranial mediastinum will appear widened
Two reasons why the trachea would be narrowed?
- Tracheal collapse
- Tracheal mass
How does a heart based mass look on radiograph in a lateral versus a DV/VD?
- Deviates trachea dorsally immediately cranial to the heart
- Sometimes deviates trachea laterally in a DV/VD
Where do esophageal foreign bodies often get stuck?
At the thoracic inlet, heart base or lower esophageal sphincter
What do esophageal foreign bodies appear as on radiograph?
Mineral or soft tissue structures in the esophagus
What is megaesophagus?
It is the dilation of the esophagus (may be focal or diffuse)
What is pneumomediastinum?
A condition where gas is present in the mediastinum
Three diseases of diaphragm
1. Hiatal hernia
2. Diaphragmatic hernia
3. Peritoneal-pericardial diaphragmatic hernia
What is hiatal hernia? What does it look like on radiograph?
- Herniation of gastric cardia into caudal aspect of the thorax (part of the stomach pushes cranially into thorax)
- Cranially rounded soft tissue or gas structure in plane with esophagus, broad base to diaphragm
What is diaphragmatic hernia?
Herniation of abdominal contents into the thorax (look for liver, spleen, intestines)
What is peritoneal-pericardial diaphragmatic hernia (PPDH) caused by?
- Failure of a midline fusion during development (it is always congenital, never traumatic)
- There are abdominal contents in the pericardial sac
What will PPDH look like?
- If its just the liver, it will appear as a soft tissue opacity
- If there is an intestine, than there will be tubule structures filled with gas
Why would dorsal deviation of the trachea be an artifact and not a true finding?
Due to neck position the trachea can be dorsally deviated (to decide if this is an artifact you can retake views or correlate clinical signs)
How are we able to tell if a mass is pulmonary or not?
Pulmonary masses shouldn't push against the heart