2 (copy)
1/79
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
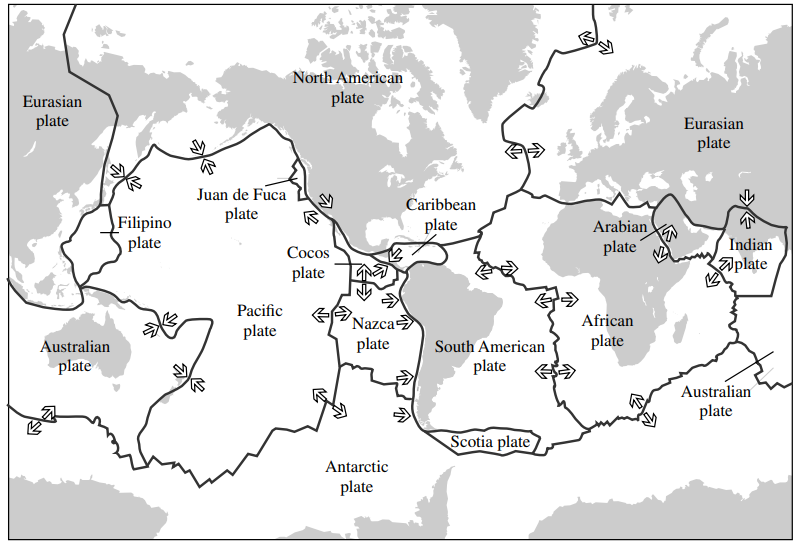
1. Which of the following plate boundaries most likely is characterized by seafloor spreading and rift valleys? (A) Nazca–South American boundary
(B) Australian–Pacific boundary
(C) Antarctic–Pacific boundary
(D) Indian-Eurasian boundary
(C) Antarctic–Pacific boundary
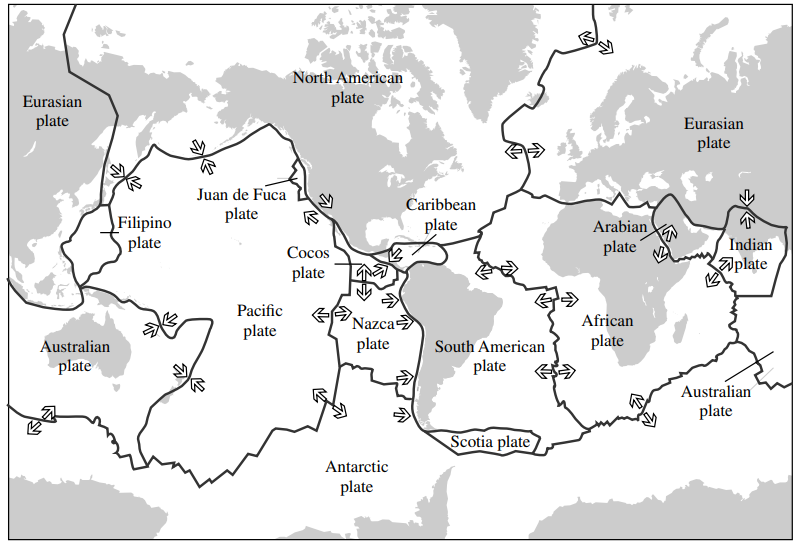
2. Which type of plate boundary typically results in
mountain creation, island arcs, earthquakes, and/or
volcanoes?
(A) Convergent boundary
(B) Divergent boundary
(C) Transform boundary
(D) Triple junction
(A) Convergent boundary
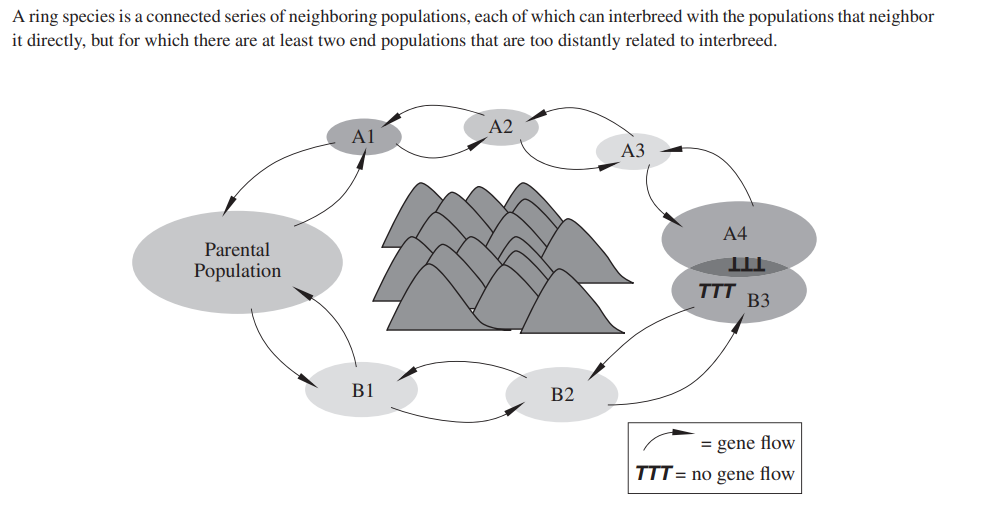
3. For which evolutionary process do ring species provide
evidence most directly?
(A) Speciation
(B) Natural selection
(C) Sexual selection
(D) Extinction
(A) Speciation
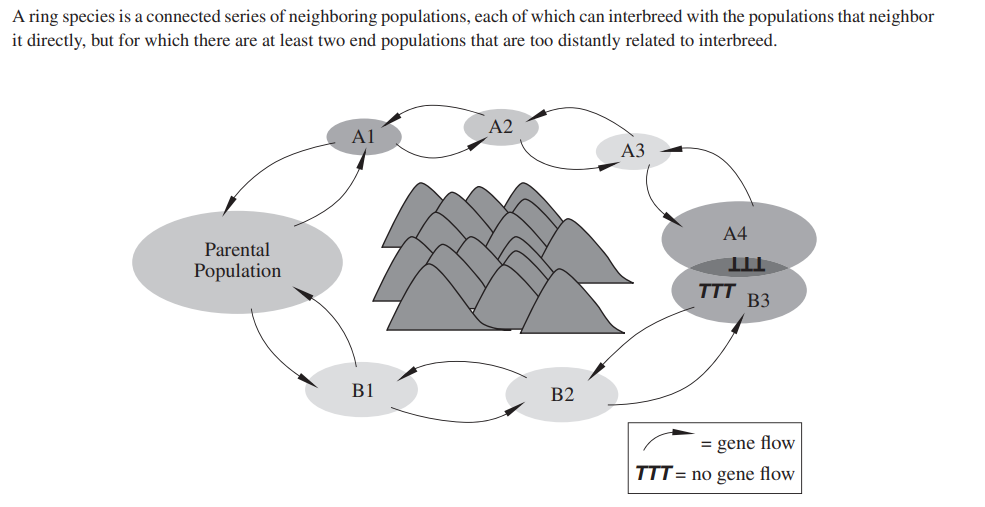
4. Which two populations in the diagram above represent
the end populations?
(A) Parental population and A4
(B) Parental population and B3
(C) A1 and B1
(D) A4 and B3
(D) A4 and B3
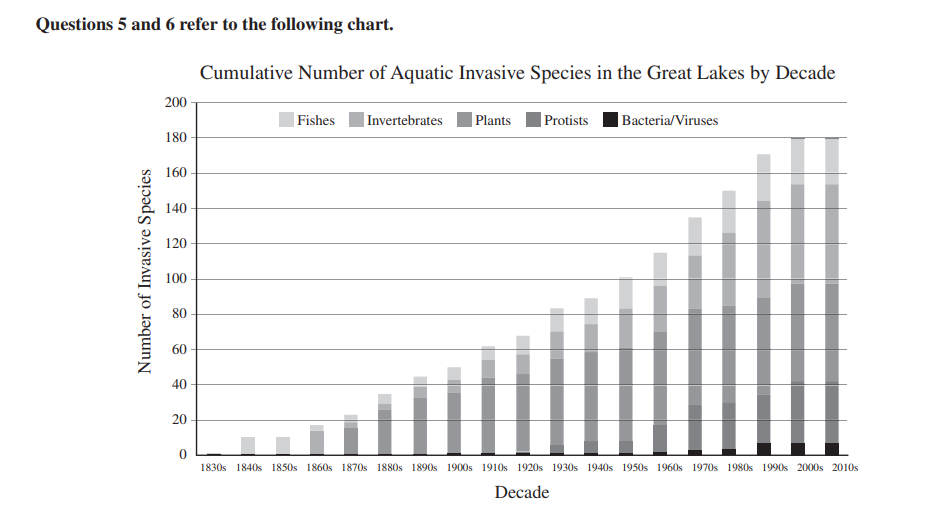
5. Based on the chart, which category of invasive species
in the Great Lakes showed the greatest increase from
the 1950s to the 1960s?
(A) Invertebrates
(B) Plants
(C) Protists
(D) Bacteria/Viruses
(C) Protists
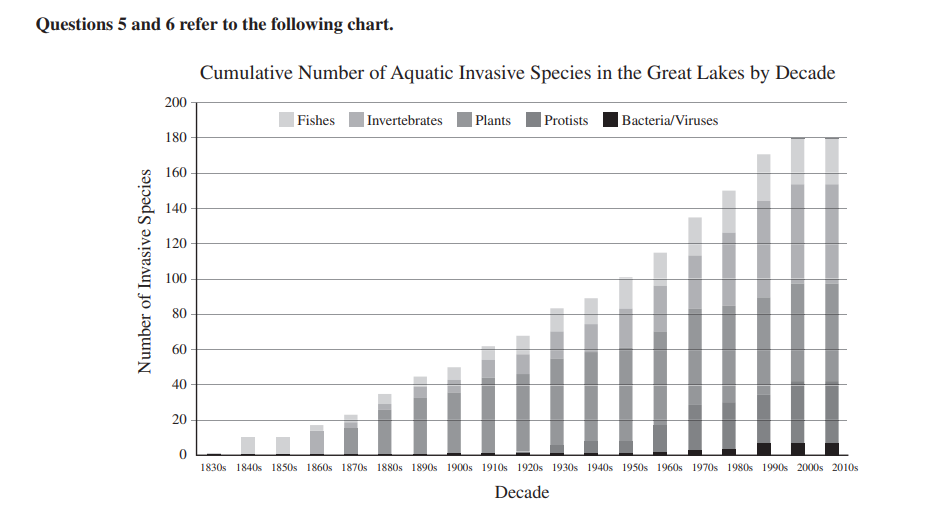
6. Which of the following represents the approximate
percentage increase in the total number of invasive
species in the Great Lakes between the 1980s and the
2000s?
(A) 13%
(B) 20%
(C) 30%
(D) 80%
(B) 20%

7. What type of event might result in a bare area where
this type of ecological succession could occur?
(A) Fire
(B) Tornado
(C) Clear-cutting
(D) Glacial retreat
(D) Glacial retreat

8. Which of the following animal species is likely to exist
in this area during the second stage (Lichen, Algae,
Mosses, Bacteria)?
(A) mites, ants, spiders
(B) nematodes, flying insects
(C) lugs, snails, salamanders, frogs
(D) squirrels, foxes, mice, moles, birds
(A) mites, ants, spiders
Questions 9 and 10 refer to the following information. Soil is a complex, ancient material teeming with living organisms. Soil development is an intricate dance that involves four basic processes and six soil-forming factors. It takes hundreds to thousands to millions of years for a soil to develop its characteristic layers or profile. Any soil you see is a dynamic formation produced by the effects of climate and biological activity (organisms), as modified by topography (relief) and human influences, acting on parent materials over time.
9. All of the following could be components of the
influence of human activity on soil formation EXCEPT
(A) Alteration of soil chemistry
(B) Compaction
(C) Decomposition
(D) Salinization
(C) Decomposition
Questions 9 and 10 refer to the following information. Soil is a complex, ancient material teeming with living organisms. Soil development is an intricate dance that involves four basic processes and six soil-forming factors. It takes hundreds to thousands to millions of years for a soil to develop its characteristic layers or profile. Any soil you see is a dynamic formation produced by the effects of climate and biological activity (organisms), as modified by topography (relief) and human influences, acting on parent materials over time.
10. Which of the following is true about soils used by
humans?
(A) Loamy soils composed of a balanced mixture of
clay, silt, and sand are not ideal for plant growth.
(B) Soil is considered a nonrenewable resource.
(C) Monoculture practices in modern agriculture tend
to enhance soil quality.
(D) The structure of soil (the extent to which it
aggregates or clumps) is unimportant with
respect to its arability.
(B) Soil is considered a nonrenewable resource.
Questions 11–13 refer to the following information. One effect of global climate change is ocean acidification: the ongoing decrease in the pH of the oceans caused by the increase in atmospheric CO2 , which seawater takes up and dissolves. About 30–40% of the carbon dioxide that’s released into the atmosphere due to human activities ends up in seawater and lakes and rivers. CO2 reacts with water to form carbonic acid (H2 CO3 ), and some of the carbonic acid molecules separate into bicarbonate ions (HCO3 – ) and hydrogen ions (H+ ). The increase in hydrogen ions is interpreted as an increase in acidity. This increase can upset the balance of marine ecosystems by interfering with metabolism and immune response in some organisms, making it more difficult for organisms like coral and plankton to form calcium carbonate shells, and (along with ocean warming) contributing to coral bleaching and reef die-offs.
11. Which of the following is NOT a possible effect of
ocean acidification that may impact human life and
industry?
(A) Coral bleaching
(B) Disruption of marine food webs
(C) Release of more CO2
into the atmosphere
(D) Putting endangered species more at risk due to
habitat loss
(C) Release of more CO2
Questions 11–13 refer to the following information. One effect of global climate change is ocean acidification: the ongoing decrease in the pH of the oceans caused by the increase in atmospheric CO2 , which seawater takes up and dissolves. About 30–40% of the carbon dioxide that’s released into the atmosphere due to human activities ends up in seawater and lakes and rivers. CO2 reacts with water to form carbonic acid (H2 CO3 ), and some of the carbonic acid molecules separate into bicarbonate ions (HCO3 – ) and hydrogen ions (H+ ). The increase in hydrogen ions is interpreted as an increase in acidity. This increase can upset the balance of marine ecosystems by interfering with metabolism and immune response in some organisms, making it more difficult for organisms like coral and plankton to form calcium carbonate shells, and (along with ocean warming) contributing to coral bleaching and reef die-offs.
12. Which is likely to be the best long-term solution to the
problem of ocean acidification?
(A) Reducing CO2 emissions
(B) Reducing overfishing and water pollution
(C) Reforestation to add more oxygen to the
atmosphere
(D) Feeding iron to phytoplankton to speed up
photosynthesis
(A) Reducing CO2 emissions
Questions 11–13 refer to the following information. One effect of global climate change is ocean acidification: the ongoing decrease in the pH of the oceans caused by the increase in atmospheric CO2 , which seawater takes up and dissolves. About 30–40% of the carbon dioxide that’s released into the atmosphere due to human activities ends up in seawater and lakes and rivers. CO2 reacts with water to form carbonic acid (H2 CO3 ), and some of the carbonic acid molecules separate into bicarbonate ions (HCO3 – ) and hydrogen ions (H+ ). The increase in hydrogen ions is interpreted as an increase in acidity. This increase can upset the balance of marine ecosystems by interfering with metabolism and immune response in some organisms, making it more difficult for organisms like coral and plankton to form calcium carbonate shells, and (along with ocean warming) contributing to coral bleaching and reef die-offs.
13. The surface pH of the world’s oceans has decreased
since preindustrial times by about 0.11 pH units,
which indicates an increase of almost 30% in the
concentration of H+
ions. If ocean surface pH is
expected to drop by a further 0.3 to 0.5 pH units by
2100, approximately what range of possible increase
does that represent in terms of H+
ion concentration?
(A) 82%–136%
(B) 100%–216%
(C) 173%–355%
(D) 400%–600%
(B) 100%–216%
14. The goal of the second stage of a wastewater treatment
plant is to
(A) remove the large solid material
(B) aerate the water
(C) remove chemicals such as DDT or PCBs
(D) lower the amount of organic material in the water
(D) lower the amount of organic material in the water
15. Which of the following organisms are the first to be
adversely affected by thermal pollution in a stream?
(A) Trees along the bank
(B) Insect larvae in the water
(C) Large fish migrating upstream
(D) Bacteria in the water
(B) Insect larvae in the water
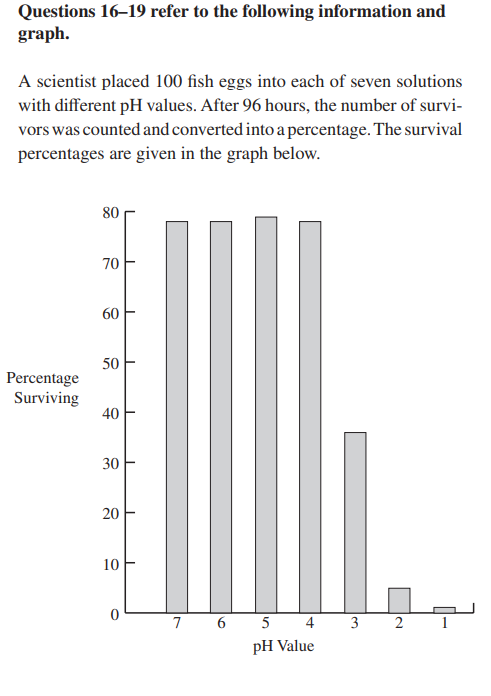
16. Which of the values below best represents the LD50 in
this experiment?
(A) 4.0
(B) 4.5
(C) 3.0
(D) 2.5
(C) 3.0
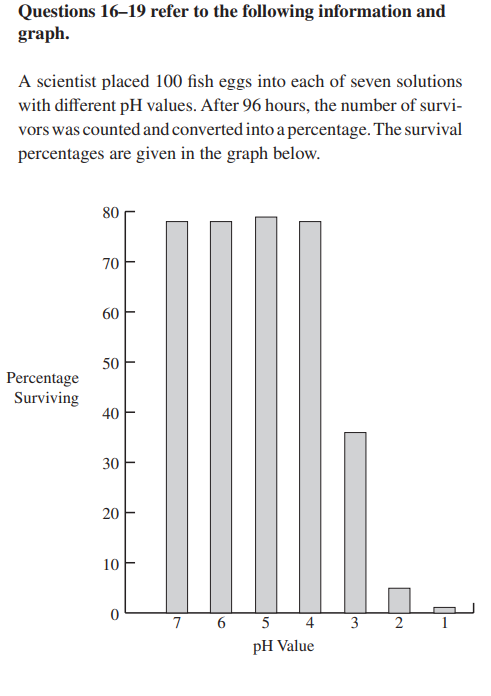
17. Which of the following, if added to the solutions, would
lead to an increase in pH?
(A) Limestone
(B) Carbon dioxide
(C) Nitrogen dioxide
(D) Sulfur dioxide
(A) Limestone
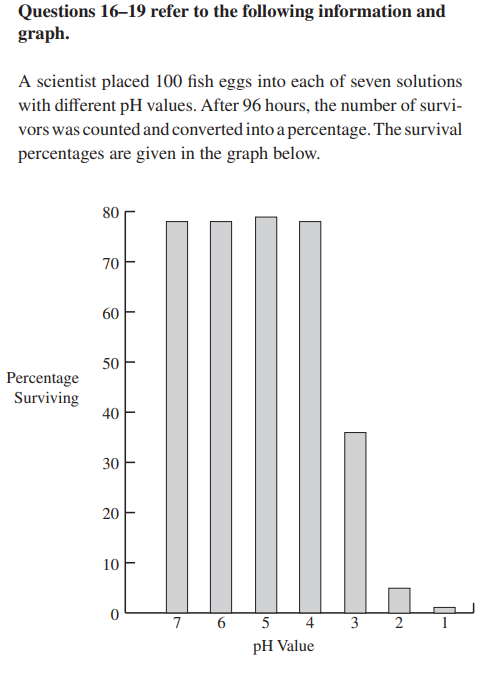
18. Which of the following best describes the goal of the
experiment?
(A) To observe how many fish would hatch at different
pH values
(B) To find out how many fish live in streams with
different pH values
(C) To understand how acid rain affects life in streams
(D) To see what chemical is best at changing the pH of
water
(A) To observe how many fish would hatch at different
pH values
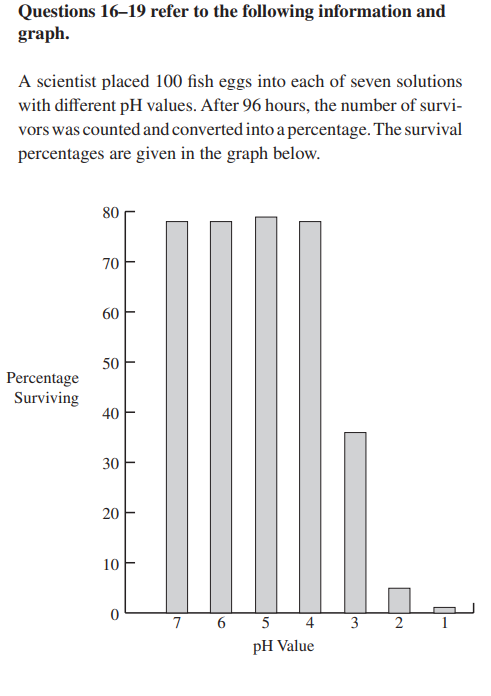
19. The pH value is a measure of the
(A) amount of heavy metals in the water
(B) biochemical oxygen demand (BOD) of the water
(C) concentration of oxygen in the water
(D) concentration of hydrogen ions in the water
(D) concentration of hydrogen ions in the water
20. Which of the following laws created the Superfund
program?
(A) Comprehensive Environmental Response,
Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA)
(B) Resource Conservation and Recovery Act
(C) Clean Air Act
(D) National Environmental Policy Act
(A) Comprehensive Environmental Response,
Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA)
21. Late fall frosts and the northward migration of some tree and plant species may indicate which of the
following global changes?
(A) Increased global temperatures
(B) The effects of more ultraviolet light from the sun
(C) A reduction in the volume of ice at the North and
South Poles
(D) Changes in global precipitation patterns
(A) Increased global temperatures
22. High infant mortality rates are likely to exist in
countries that have
(A) a strong and stable economy
(B) high levels of education for adults
(C) a stable food supply
(D) high levels of infectious diseases
(D) high levels of infectious diseases
23. All of the following statements are true EXCEPT
(A) energy can be converted from one form to
another
(B) energy input always equals energy output
(C) energy and matter can generally be converted into
each other
(D) at each step of an energy transformation, some
energy is lost to heat
(C) energy and matter can generally be converted into
each other
24. Oxygen-depleted zones of the oceans, such as the one
at the mouth of the Mississippi River, are most likely
caused by
(A) a reduction in the plant life in rivers that empty into
the ocean near the dead zone
(B) excessive fertilizers carried into the ocean, which
cause algal blooms that lower the oxygen levels
(C) thermal pollution in the ocean
(D) acid precipitation falling onto the ocean
(B) excessive fertilizers carried into the ocean, which
cause algal blooms that lower the oxygen levels
25. One potential benefit of using genetically modified
foods is
(A) the release of genes to other plants or animals
(B) the resistance of crops against pesticides
(C) their growth in monoculture leads to a reduction in
biodiversity in the area
(D) unknown effects on the ecosystem into which they
are released
(B) the resistance of crops against pesticides
26. Which of the following compounds would probably
supply the greatest amount of useful energy to humans?
(A) The exhaust from a car
(B) Unrefined aluminum ore
(C) A glass bottle
(D) A liter of gasoline
(D) A liter of gasoline
27. Which of the following choices gives the geologic eras
in the correct sequence, from the oldest to the most
recent?
(A) Cenozoic—Mesozoic—Paleozoic—Precambrian
(B) Precambrian—Paleozoic—Mesozoic—Cenozoic
(C) Paleozoic—Precambrian—Cenozoic—Mesozoic
(D) Paleozoic—Cenozoic—Precambrian—Mesozoic
(B) Precambrian—Paleozoic—Mesozoic—Cenozoic
28. Approximately what percentage of the world’s solid
waste does the United States produce?
(A) 50 percent
(B) 33 percent
(C) 10 percent
(D) 5 percent
(B) 33 percent
29. Which of the following correctly describes conservation
easement?
(A) A process that conserves soil from erosion
(B) A binding agreement that preserves land from
further development in exchange for tax write-offs
(C) An agreement that allows a developer to add new
land to a housing project with little input from
neighbors
(D) A practice that prevents the breakdown of stream
banks
(B) A binding agreement that preserves land from
further development in exchange for tax write-offs
30. The highest priority of the Clean Water Act is to
provide
(A) guidance in toxic chemical disposal
(B) funds to reclaim old strip mines
(C) policies to lessen the number of oil spills in the
ocean
(D) policies to attain fishable and swimmable waters
in the United States
(D) policies to attain fishable and swimmable waters
in the United States
31. Which of the following best describes changes in
the genetic composition of a population over many
generations?
(A) Evolution
(B) Mutation
(C) Natural selection
(D) Biomagnification
(A) Evolution
32. Women have fewer and healthier children when all of the following are true EXCEPT
(A) they have little education
(B) they live where their rights are not suppressed
(C) they have access to medicine and health care
(D) the cost of a child’s education is high
(A) they have little education
33. Which of the following is a true statement?
(A) The population size of organisms following a logical population growth is not limited by a carrying
capacity.
(B) The population size of organisms following an exponential growth is limited by a carrying capacity.
(C) Increasing the death rate of a population can lower
the carrying capacity.
(D) Increasing the rate of food production can
increase the carrying capacity.
(D) Increasing the rate of food production can
increase the carrying capacity.
34. An increase in the amount of UV light striking the
Earth as a result of ozone loss will cause which of the
following?
(A) Global climate change
(B) Increased skin cancer rates in humans
(C) Lowering of ocean water levels
(D) An increase in CO2
in the atmosphere
(B) Increased skin cancer rates in humans
35. Ozone in the troposphere can result in all of the
following EXCEPT
(A) eye irritation
(B) lung cancer
(C) bronchitis
(D) headache
(B) lung cancer
36. Which of the following describes the amount of energy that plants pass on to herbivores?
(A) The amount of solar energy in a biome
(B) The First Law of Thermodynamics
(C) The Net Primary Productivity (NPP) of an area
(D) The Second Law of Thermodynamics
(C) The Net Primary Productivity (NPP) of an area
37. The Second Law of Thermodynamics relates to living organisms because it explains why
(A) matter is never destroyed but it can change shape
(B) plants need sunlight in order to survive
(C) all living things must have a constant supply of
energy in the form of food
(D) the amount of energy flowing into an ecosystem is
the same as the amount flowing out of that
system
(C) all living things must have a constant supply of
energy in the form of food
38. Acid deposition most severely affects amphibian
species because amphibians
(A) do not care for their young
(B) are not mammals
(C) need to live in both terrestrial and aquatic
habitats
(D) seldom reproduce
(C) need to live in both terrestrial and aquatic
habitats
39. All of the following are internal costs of an automobile
EXCEPT
(A) car insurance
(B) fuel
(C) pollution and health care costs
(D) raw materials and labor
(C) pollution and health care costs
40. Scrubbers are devices installed in smokestacks to
(A) reduce the amount of materials such as SO2
in the smoke they discharge
(B) clean out the stack so smoke can move rapidly
upward
(C) reduce the amount of sulfur in coal before it is
burned
(D) reduce the amount of toxic ash produced
(A) reduce the amount of materials such as SO2
in the smoke they discharge
41. After ore is mined, the unusable part that remains is
placed in piles called
(A) overburden
(B) seam waste
(C) leachate
(D) tailings
(D) tailings
42. All of the following are examples of externalities
EXCEPT
(A) a construction worker purchasing an automobile
that reduces his commute time to work.
(B) a factory producing air pollution that leads to acid
rain in the neighboring forest area.
(C) the construction of a new football stadium
leading to increased income for local businesses.
(D) driving electric and hybrid vehicles reducing the
amount of greenhouse gas emissions.
(A) a construction worker purchasing an automobile
that reduces his commute time to work.
43. Which fuel contains the greatest amount of sulfur?
(A) Wood
(B) Natural gas
(C) Nuclear reactor fuel rods
(D) Coal
(D) Coal
44. Biological reserves are areas that allow countries to
(A) concentrate agricultural production in one area
(B) set aside critical habitats to ensure the survival of
species
(C) control the flow of rivers and storm waters
(D) provide grazing land in order to ensure economic
growth
(B) set aside critical habitats to ensure the survival of
species
45. Which of the following countries has the shortest
population doubling time?
(A) Denmark
(B) Australia
(C) United States
(D) Kenya
(D) Kenya
46. Which of the following processes leads to an increase
in atmospheric water content?
(A) Precipitation
(B) Transpiration
(C) Infiltration
(D) Condensation
(B) Transpiration
47. Full cost pricing of a refrigerator would include
(A) adding the cost of employee salaries to the total
cost
(B) the refrigerator’s total impact on the environment
(C) the cost of transporting the refrigerator to the retail
store
(D) the value of the refrigerator if it was donated to a
nonprofit group
(B) the refrigerator’s total impact on the environment
48. Since 2000, the atmospheric concentration of which of
the following has decreased as a result of anthropogenic
activity?
(A) Methane
(B) Carbon dioxide
(C) Chlorofluorocarbons
(D) Nitrous oxide
(C) Chlorofluorocarbons
49. During a society’s postindustrial state, the population
will exhibit
(A) rapid growth with a low birth rate and high death
rate
(B) slow growth with a slowing birth rate and a low
death rate
(C) rapid growth with a high birth rate and low death
rate
(D) zero growth with a low birth rate and low death
rate
(D) zero growth with a low birth rate and low death
rate
50. Which of the following is NOT a disadvantage of oldstyle landfills?
(A) They generate gases that can be recovered and used
as fuel.
(B) Bad odors come from these landfills.
(C) Toxic wastes leach into ground water.
(D) Subsidence of the land after the landfill is filled.
(A) They generate gases that can be recovered and used
51. The international treaty concerning endangered species
(CITES) has tried to protect endangered species by
taking which of the following steps?
(A) Making more countries keep these species in zoos
(B) Paying the debts of member countries in order to
relieve the pressure to sell endangered species
(C) Developing a list of endangered species and prohibiting trade in those species
(D) Restoring endangered habitats
(C) Developing a list of endangered species and prohibiting trade in those species
52. In 2000, the population of Country A was 50,000. If
Country A has a constant birth rate of 33 per 1,000 and
a constant death rate of 13 per 1,000, when will the
population of Country A equal 200,000?
(A) 2035
(B) 2050
(C) 2070
(D) 2105
(C) 2070
53. Salt intrusion into freshwater aquifers, beach erosion,
and the disruption of coastal fisheries are all possible
results of which of the following?
(A) Rising ocean levels as a result of global warming
(B) More solar ultraviolet radiation on the Earth
(C) More chlorofluorocarbons in the atmosphere
(D) Reduced rates of photosynthesis
(A) Rising ocean levels as a result of global warming
54. The chemical actions that produce compost would best
be described as
(A) photosynthesis
(B) augmentation
(C) respiration
(D) decomposition
(D) decomposition
55. Which of the sources below would produce non-point
source pollution?
(A) The smokestack of a factory
(B) A volcano
(C) A pipe leading into a river from a sewage
treatment plant
(D) A large area of farmland near a river
(D) A large area of farmland near a river
56. A nation’s gross domestic product represents
(A) the ability to provide health care
(B) the amount of goods it imports
(C) the amount of its economic output
(D) the quality of its environment
(C) the amount of its economic output
57. Which of the following mining operations requires
people and machinery to operate underground?
(A) Mountain top removal
(B) Contour stripping
(C) Dredging
(D) Shaft sinking
(D) Shaft sinking
58. A country’s total fertility rate (TFR) indicates which of
the following?
(A) The life expectancy of women in the country
(B) The average number of babies born to women
between the ages of 14 and 45
(C) The number of babies under one year of age who
die per 1,000
(D) The total use of contraceptives in the country
(B) The average number of babies born to women
between the ages of 14 and 45
59. The wastes stored in Love Canal contaminated the
surrounding area by all of the following methods
EXCEPT
(A) leaching into the ground water
(B) fumes from burning the wastes
(C) runoff into a nearby stream
(D) spilled drums of waste
(B) fumes from burning the wastes
60. All of the following are currently used by humans to
produce energy EXCEPT
(A) nuclear fusion
(B) nuclear fission
(C) harnessing solar energy
(D) harnessing the Earth’s internal heat
(A) nuclear fusion
61. In sea water, carbon is mostly found in the form of
(A) phosphoric acid
(B) carbon disulfide
(C) bicarbonate ions
(D) methane gas
(C) bicarbonate ions
62. Acid rain and snow harm some areas more than others
because certain areas
(A) have more bacteria in the soil than others
(B) have a lesser ability to neutralize the acids
(C) are at a higher elevation than the unaffected areas
(D) are closer to lakes than are the unaffected areas
(B) have a lesser ability to neutralize the acids
63. Which one of the following does NOT store a great deal
of phosphorus?
(A) Rocks
(B) Water
(C) Atmosphere
(D) Living organisms
(C) Atmosphere
64. The addition of oxygen to the early Earth’s atmosphere
most likely occurred through the process of
(A) volcanic outgassing
(B) photosynthesis
(C) meteorite impact
(D) respiration by animals
(B) photosynthesis
65. Scientists use which of the following to estimate
environmental risks to humans?
I. Animal studies
II. Epidemiological studies
III. Statistical probabilities
(A) II only
(B) I and II only
(C) I and III only
(D) I, II, and III
(D) I, II, and III
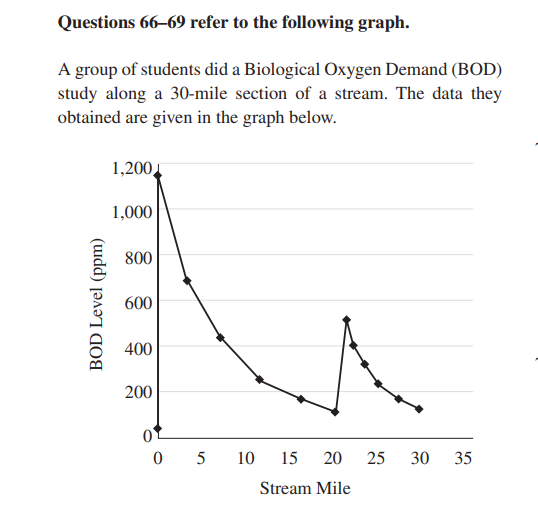
66. Which of the following best describes the type of
pollution at mile 0?
(A) Point source
(B) Acid deposition
(C) Secondary pollutant
(D) Deep well
(A) Point source
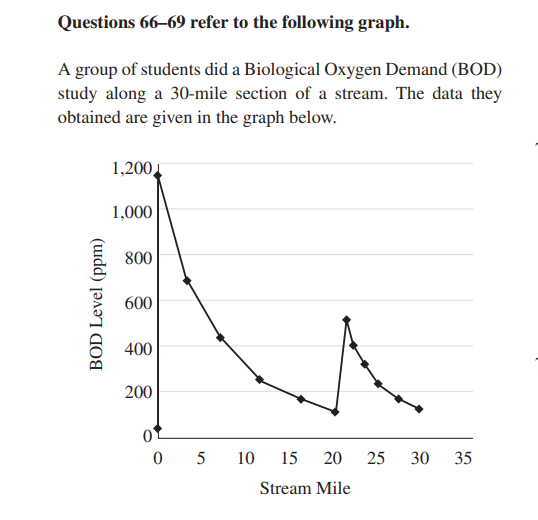
67. The BOD at mile 12 is approximately
(A) 700 ppm
(B) 220 ppm
(C) 200 ppm
(D) 175 ppm
(B) 220 ppm
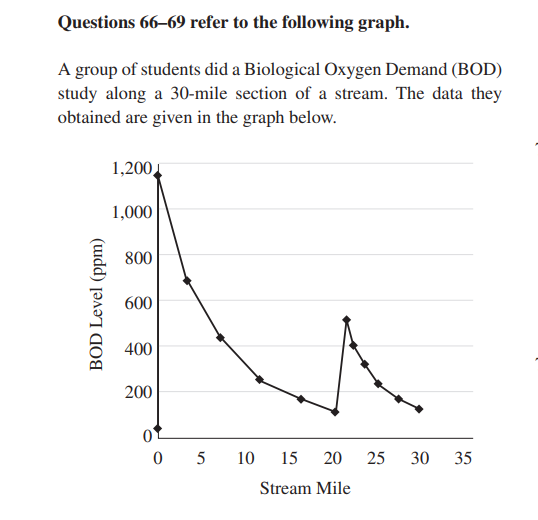
68. The BOD test is designed to directly measure
(A) how much light can pass to the bottom of the
stream
(B) the amount of nitrates in the water
(C) the amounts of coliform bacteria
(D) the rate at which oxygen is being consumed by
microorganisms
(D) the rate at which oxygen is being consumed by
microorganisms
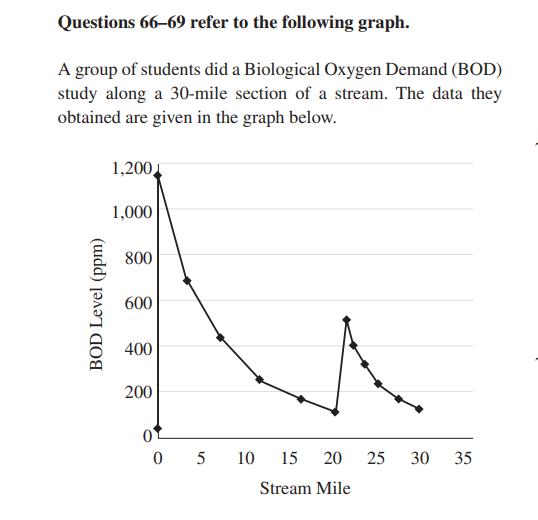
69. Anaerobic bacteria, sludge worms, and fungi are most
likely to be found in which part of this stream?
(A) 0 to 5 miles
(B) 10 to 15 miles
(C) 15 to 20 miles
(D) 25 to 30 miles
(A) 0 to 5 miles
70. Riparian zones are important parts of lands because
they are
(A) the area where most cattle feed when they graze
(B) an area of diverse habitats along the banks of rivers
(C) important buffers against wind
(D) areas where varying amounts of light cause
different layers of plant growth
(B) an area of diverse habitats along the banks of rivers
71. Which of the following is a disadvantage of fish
farming?
(A) It can allow for genetic engineering, which leads to
bigger yields.
(B) It is very profitable.
(C) It can lead to large die-offs due to disease.
(D) It can reduce the pressure to harvest wild species.
(C) It can lead to large die-offs due to disease.
72. The form of nitrogen that plants can use directly is
(A) nitrates
(B) nitrites
(C) N2
gas
(D) methane
(A) nitrates
73. Which of the following best describes the effects of a
thermal inversion?
(A) Cold ocean water moves to the surface and warm
water sinks.
(B) Warm, polluted air rises and mixes with cool upper
air, and pollutants escape.
(C) Warm river water cools when it enters the ocean.
(D) Polluted air at the surface cannot rise because it is
blocked by warm air above it.
(D) Polluted air at the surface cannot rise because it is
blocked by warm air above it.
74. Shifting taxes to tax pollution and waste rather than
taxing the cost of products will allow people to
(A) maximize profit
(B) increase the tax base in a city
(C) use tax money for local schools
(D) shift to a pattern of more sustainable
development
(D) shift to a pattern of more sustainable
development
75. Which of the following molecules is most damaging to
stratospheric ozone?
(A) H2O
(B) CO2
(C) Chlorofluorocarbons
(D) N2O
(C) Chlorofluorocarbons
76. Which of the following ocean zones has the highest
levels of nutrients?
(A) Coastal zone
(B) Euphotic zone
(C) Bathyal zone
(D) Abyssal zone
(D) Abyssal zone
77. Samples of atmospheric gases from past eras can most
easily be obtained from which of the following sources?
(A) Methane gas trapped in oil reserves
(B) Different types of sedimentary rock
(C) Gases trapped in polar ice caps
(D) Mud samples from eutrophic lakes
(C) Gases trapped in polar ice caps
78. Acid deposition on soil kills beneficial decomposers.
Which of the following cycles would be most affected
by the loss of decomposers?
(A) Sulfur cycling
(B) Phosphorus cycling
(C) Hydrologic cycling
(D) Nitrogen cycling
(D) Nitrogen cycling
79. Which of the following is a trace element necessary for
plant growth?
(A) Carbon
(B) Nitrogen
(C) Phosphorous
(D) Magnesium
(D) Magnesium
80. Concerns that people of color and poor people are
disproportionately exposed to environmental pollution
are most likely to be addressed by people who believe
in the
(A) Earth stewardship view
(B) planetary manager view
(C) environmental justice movement
(D) sustainability point of view
(C) environmental justice movement