BIOL 120 Exam 3
1/89
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
__________ is the uptake of small nutrient molecules by cells lining the digestive tract.
Absorption
What is the proper order of the four stages of food processing?
Ingestion, digestion, absorption, elimination
How does a gastrovascular cavity differ from a digestive tube? The gastrovascular cavity __________.
Has only a singular opening
Cheese proteins become amino acids through __________.
Breakdown
Absorption is how amino acids become __________.
Human proteins
What is true about protein digestion?
Proteins cannot be absorbed without being broken down into amino acids, which get assembled into new proteins inside cells.
Proteins are polymers of __________.
Amino acids
Starches are polymers of __________.
Sugars
__________ are broken down into amino acids when digested.
Proteins
When digested, fats are broken down into __________.
Glycerol and fatty acids
Starch is a type of __________.
Polysaccharide
Your small intestine can absorb __________ without their being further digested.
Fructose
What is the name of the enzyme which begins the breakdown of starch?
Amylase
Starch can be broken down into the disaccharide known as __________.
Maltose
Protein digestion begins in the __________.
Stomach
What is the main component of gastric juice?
Water
_____ is secreted by the _____ and acts to emulsify _____ in the _____.
Bile…liver…fats…small intestine
What acid is responsible for stomach acidity?
Hydrochloric acid
During the process of digestion, large food molecules are broken down into small components that can be absorbed into cells that form the lining of the __________.
Small intestine
Circular folds, villi, and microvilli--tiny projections from the surfaces of cells--increase the __________ for absorption.
Surface area
After moving into cells of the intestinal lining, fatty acids and glycerol are recombined into fats, coated with proteins, and transported into __________, which eventually empty into large veins.
Lymphatic vessels
Sugars and amino acids pass from the intestinal epithelium into __________.
Blood capillaries
The liver removes excess __________ and stores it as glycogen.
Glucose
The liver converts nutrients to other essential substances, such as __________, cholesterol, and fats.
Plasma proteins
What is the order in which food passes through the structures of the digestive system?
Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine
Chemical digestion of food begins where?
The mouth
What is a characteristic of the pharynx?
It is an intersection of the food and air pathways
The opening between the esophagus and the stomach is closed except when a food ball passes through it. If this space were to remain open at all times, there might be a problem with __________.
Regurgitation of food into the esophagus
The liquid in the stomach (gastric juice) that helps with digestion contains __________.
Hydrochloric acid to break down food particles, the enzyme pepsin, and mucus
Villi are __________.
Finger-like projections of the small intestine that aid in absorption of nutrients
Many people who have had colon cancer have part or all of their large intestine removed. Which of the following processes would most likely be affected by this type of surgery?
Elimination
What is true about vitamins and minerals?
Deficiencies in either vitamins or minerals can lead to health problems
What is the name of the eating disorder characterized by self-starvation due to an intense fear of gaining weight?
Anorexia nervosa
What nutrition-related problem is of greatest concern for most Americans?
Obesity
Which major theme of biology is illustrated by the following: Typically, an adult human has 32 teeth. The bladelike incisors are in the middle and help bite off pieces of food. Just to their sides are the pointed canines, used for ripping and tearing--think of the fangs of a dog or a wolf.
Relationship of structure to function
Which major theme of biology is illustrated by the following: Nerve and hormone signals regulate the secretion of gastric juice so that it is discharged only when there is food in the stomach.
Information flow
Which major theme of biology is illustrated by the following: Food primarily consists of large, complex molecules that are not in a form that an animal's cells can use. Thus, the body must break down these nutrients--digest them--to make them useful.
Pathways that transform energy and matter
Which major theme of biology is illustrated by the following: The human digestive system consists of an alimentary canal and several accessory organs (salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder). The accessory organs secrete digestive chemicals into the alimentary canal through ducts.
Interactions within biological systems
What major theme of biology is illustrated by the following: In most mammals, the ability to digest lactose (a sugar found in milk) declines after weaning, because the enzyme lactase, which breaks down lactose, decreases in production. However, in some human populations, a genetic mutation has allowed lactase production to continue into adulthood, known as lactose tolerance.
Evolution
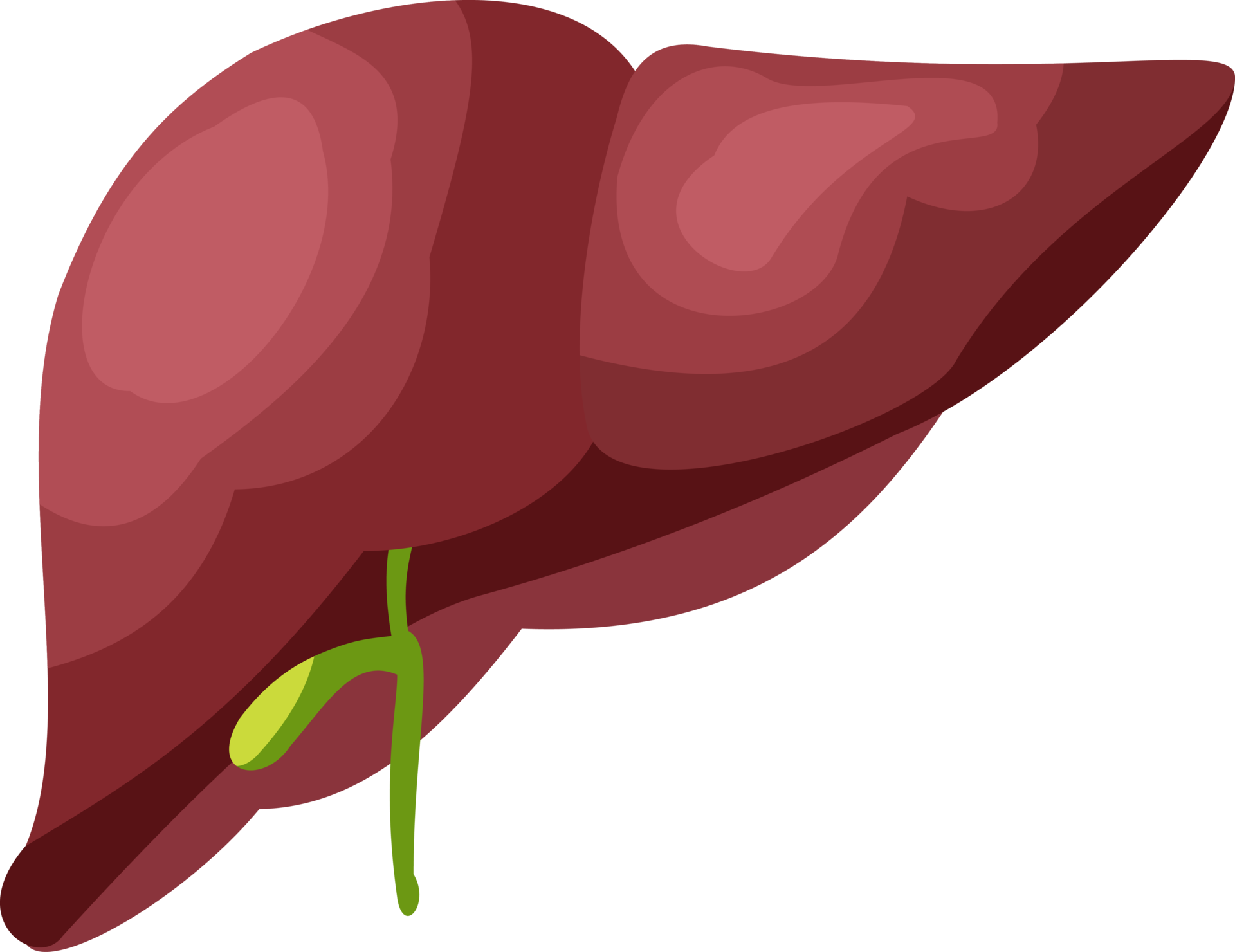
What organ is shown here?
Liver

What organ is shown here?
Gallbladder
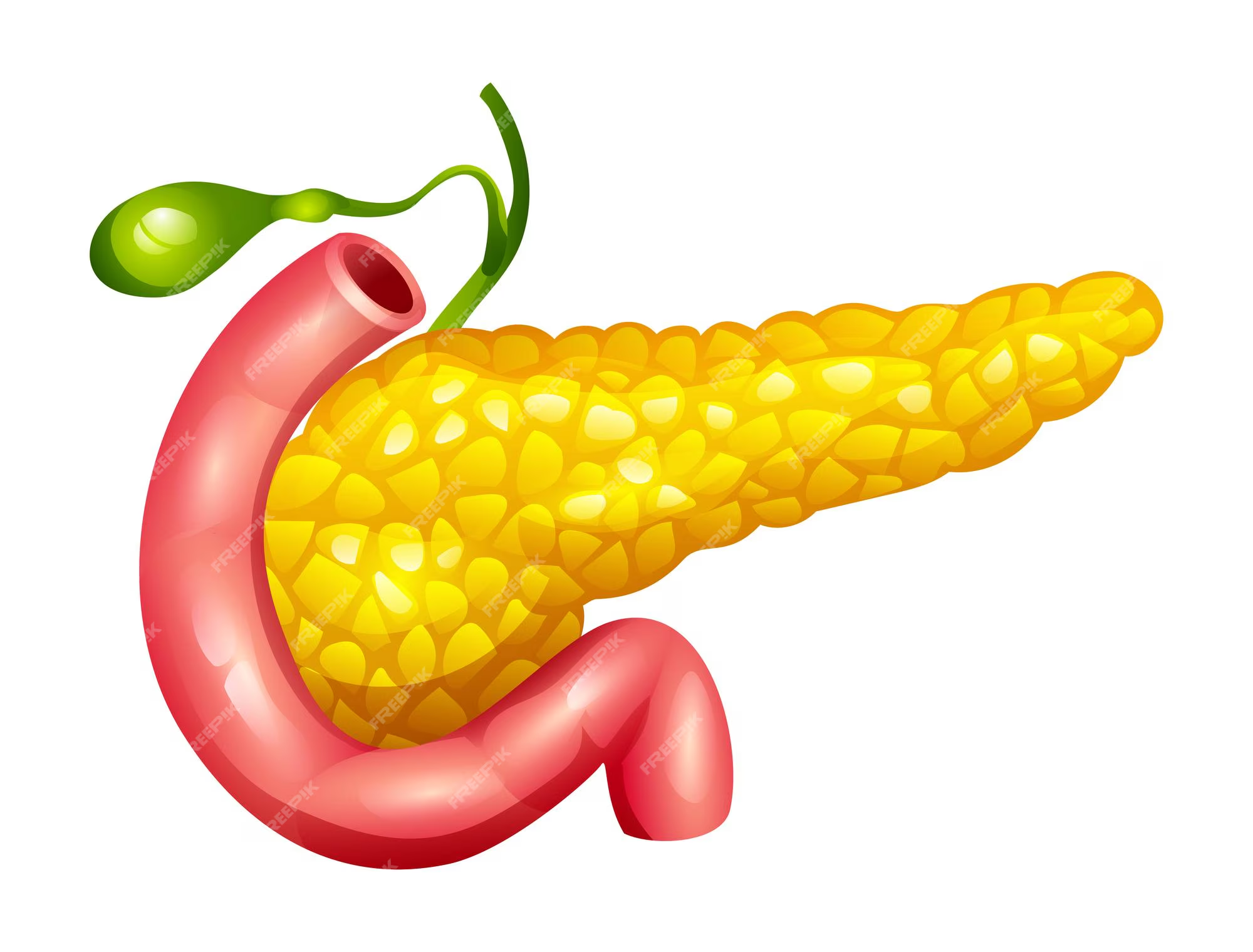
What organ is shown here?
Pancreas
What is the name of the organ that leads into the stomach?
Esophagus
Pepsin is __________.
A powerful enzyme in gastric juice that digests proteins
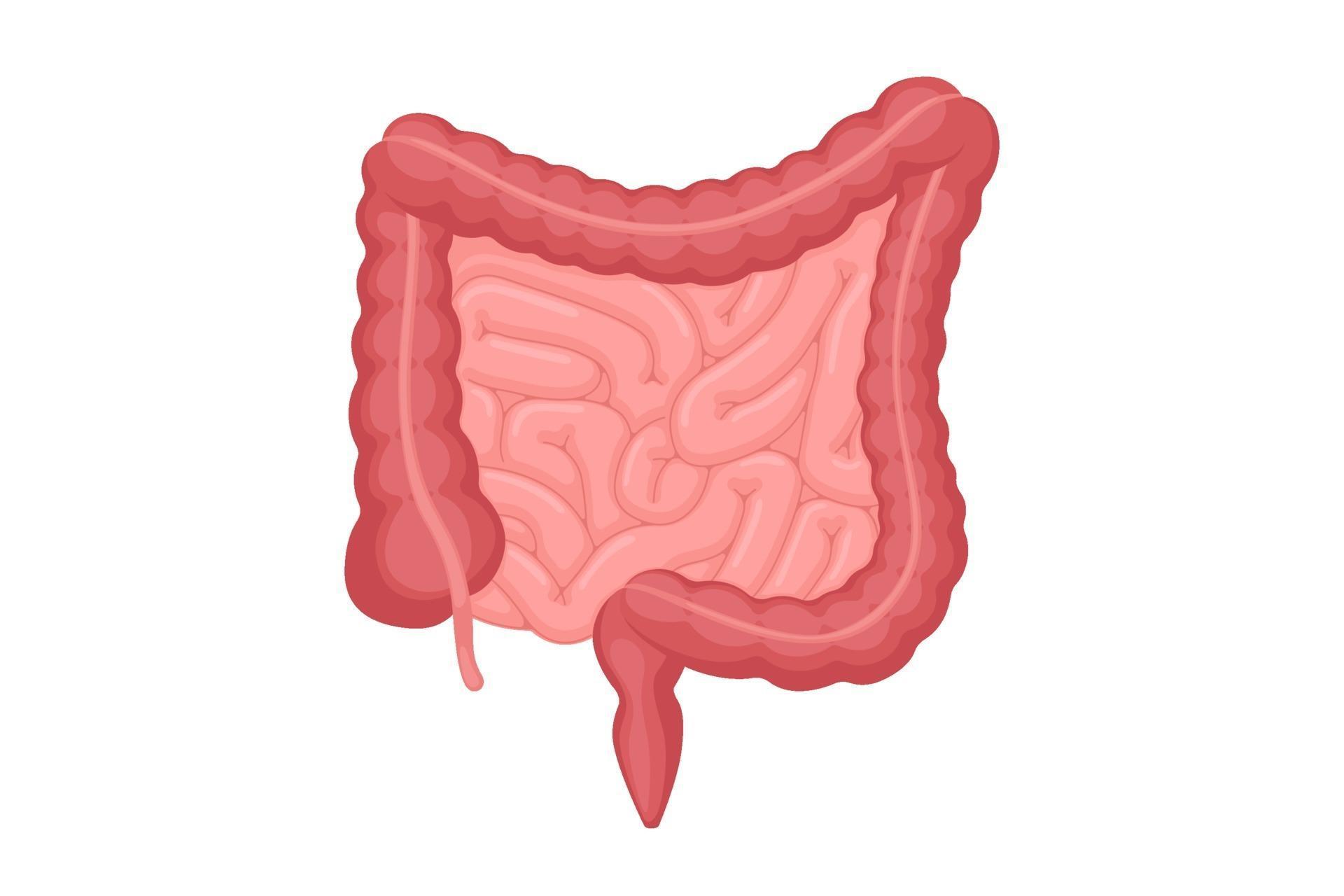
What is the organ depicted here in light pink?
Large intestine
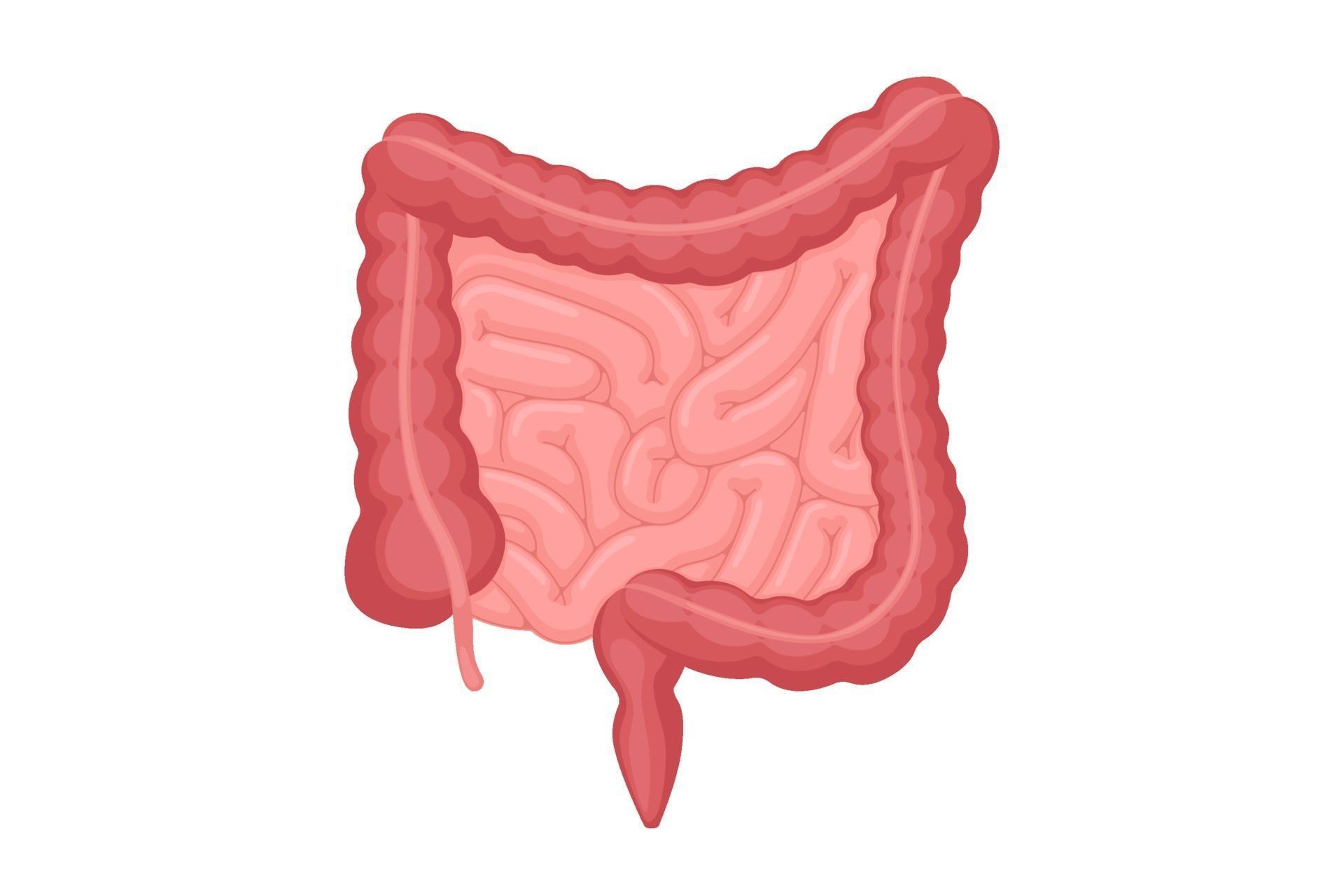
What is the organ depicted here in dark pink?
Small intestine
What is an example of an organism with an open circulatory system?
Spiders
What component is not found in all circulatory systems?
A cavity within the body that allows organs to be directly bathed in blood
Blood returns to the heart via the __________.
Pulmonary veins
From the pulmonary veins, blood flows to the __________.
Left atrium
From the superior vena cava, blood flows to the __________.
Right atrium
From the capillaries of the abdominal organs and hind limbs, blood flows to the __________.
Inferior vena cava
Animals such as hydras and jellies can exchange gasses directly with the environment by __________.
Diffusion
In humans, oxygen is delivered from the environment to the cells of the body by __________.
A closed circulatory system
In animals with a closed circulatory system, gas exchange occurs across the thin walls of __________.
Capillaries
Veins carry __________.
Blood toward the heart
The one-way flow of blood in veins is maintained by __________.
Valves
Because of the changes in blood pressure through the circulatory system, the best way to feel a pulse is by pressing a finger against __________.
An artery
Which vessel has the structure best suited to chemical exchange between the blood and tissues?
A capillary
Trace the path of a red blood cell in a circuit that takes it from the capillary bed of the right kidney to the capillary bed of the left kidney. Assume that you are doing this for an animal with a double circulation system.
Capillary bed of right kidney -> venules -> veins -> right atrium -> right ventricle -> pulmonary arteries -> capillaries of lungs -> pulmonary veins -> left atrium -> left ventricle -> aorta -> arteries -> arterioles -> capillary bed of left kidney
What carries oxygen-poor blood?
Pulmonary arteries
The basic rhythm of the heartbeat is set by the __________.
Sinoatrial node
If your blood pressure were 120/70, this would indicate that __________.
Your blood pressure during systole is 120 and during diastole is 70
Blood pressure that is consistently __________ or higher would indicate that you have hypertension.
140/90
Plasma is where we could find __________ in the blood.
Hormones
Red blood cells lack nuclei and other organelles which allows them to __________.
Have more room to carry hemoglobin
When tissue lining a blood vessel is damaged, the first thing that happens is __________.
Platelets adhere to the damaged tissue
White blood cells play a particularly important role in __________.
Fighting infections
What is the best description for an artery?
It carries blood away from the heart
Lung capillaries are a part of which human circuit?
Pulmonary
A neuron’s nucleus is located in its __________.
Cell body
A nerve impulse moves toward neuron’s cell body along __________.
Dendrites
A nerve impulse moves away from a neuron’s cell body along __________.
Axons
An impulse relayed along a myelinated axon "jumps" from __________ to __________.
Node of Ranvier…Node of Ranvier
Axons insulated by a(n) __________ are able to conduct impulses faster that those not so insulated.
Myelin sheath
What type of cell makes up the myelin sheath of a motor neuron?
Schwann cells
What part of a neuron relays signals from one neuron to another neuron or to an effector?
Synaptic terminal
Using energy from ATP, __________ actively transport ions in both directions across the membrane.
Sodium-potassium pumps
Some __________ are open, allowing certain ions to move out of the cell through them.
Potassium channels
The __________ are closed, preventing certain ions from entering the cell through them.
Sodium channels
The concentration of __________ is higher outside of the cell than inside.
Sodium ions
The concentration of __________ is higher inside of the cell than outside.
Potassium ions
A neuron at resting potential has a __________ charge on the inside relative to the __________ charge on the outside.
Negative…positive
If you touch a hot stove, __________ in your fingertip sense the dangerous heat and convert this stimulus into an electrical signal. This signal leaves your fingertip via nerve cells called __________. These nerves are part of an anatomical division of the nervous system called the __________. The signal travels along these nerves, and then to the spinal cord and brain. These two structures make up an anatomical division called the __________. Within this part of the nervous system, specialized nerves called __________ integrate this information, formulate a response, and then communicate these instructions as nerve impulses to __________. These neurons bring the message to the muscles in your arm to pull your hand away.
Sensory receptors…sensory neurons…peripheral nervous system…central nervous system…interneurons…motor neurons
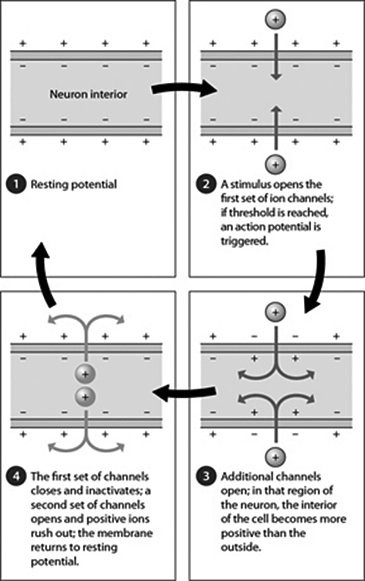
In the figure, in which step is threshold reached if the stimulus is strong enough and a sufficient number of channels open?
Step 2
The __________ is the control center of the nervous system.
Central nervous system