Remember for metrics 2
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
what does weak dependence assumption mean for OLS time series
can apply LLN and CLT so OLS estimates converge to true paramteters as sample size grows
white test for heteroskedasticity
page 7
FWLS steps for constant, edu, exper and expersq
p11
robust standard errors: problem, solution, why they work
page 12
how does WLS work
page 9
FWLS steps
page 10
breusch pagan test
page 6
test for serial correlation with strong exogeneity and problems with it
only detects first order serial correlation
if serial correlation exists, the test will be invalid as serial correlation violates strong exogeneity
page 6
what to change between serial correlation test with strong exogeneity vs without
regress ut on lagged residual AND explanatory variables
page 7
quasi differencing procedure (correcting for serial correlation)
page9
feasible generalised least squares procedure
page 10
integrated process definition
transforming unit root processes into weakly dependent ones
why can’t we use standard t test for unit root
OLS regression assumes stationarity and yt is nonstationary
augmented DF test and how does it correct for the “issue”
page 9
low power meaning (consequence of too many lags)
more risk of failing to reject H0 even if it’s false
structural break
change in behaviour of time series, DF may misinterpret as unit root
how do you get spurious regression
regressing two unrelated non-stationary series on OLS → get high R²/significant t stat
when it actually violates OLS assumptions
what is MLE and how to do it
max likelihood estimation
maximising L(B) = finding B that makes the observed data most probable
how to do on page 8
t test for logit/probit and why can we do this
neither have heteroskedastic errors
consistent
asymptotic normality
page 17
likelihood ratio test
page 19
Wald test statistic
page 18
how to estimate the unrestricted model for probit or logit
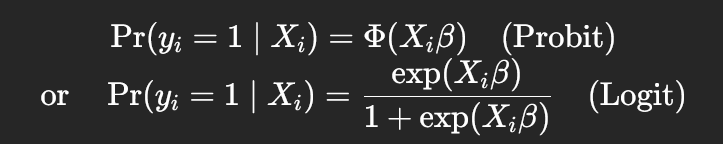
what we use when there’s serial correlation in errors for POLS and write it out, compare to serial correlation correction in time OLS
cluster robust standard errors vs heteroskedasticity-robust standard errors
Fixed effects (how it removes individual effects, dummy model, how they work, B hat estimator)
p10 and 11
when is first differencing consistent
when uit is uncorrelated with xi,t and xi,t-1
issues with FE
page 13
needs strict exogeneity
can’t estimate time invariant variables
explain how E(alphai|Xi) may not = 0 and why POLS can be wrong about the dependent variable effect (cigarette consumption and income)
page 9
efficiency of POLS using cluster robust standard errors
still inefficient as assumes each observation is for a different individual
POLS estimator and consistent when?
page 5
Hausman test, test stat, when to reject, test statistic
page 17
Random effects generalised least squares (RE GLS)
use estimates for the variances of u and alpha to do a quasi-demeaning process
page 8
write the marginal effect at the mean for logit and the average marginal effect for logit
remember to do pdf notation and remember the b hat