R3.3.3 Free radical substitution reactions of the alkanes
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 9:52 PM on 5/5/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
1
New cards
Why alkanes are unreactive
C–H bonds are nonpolar due to small electronegativity difference.
C–C and C–H bonds are strong with high bond enthalpies.
2
New cards
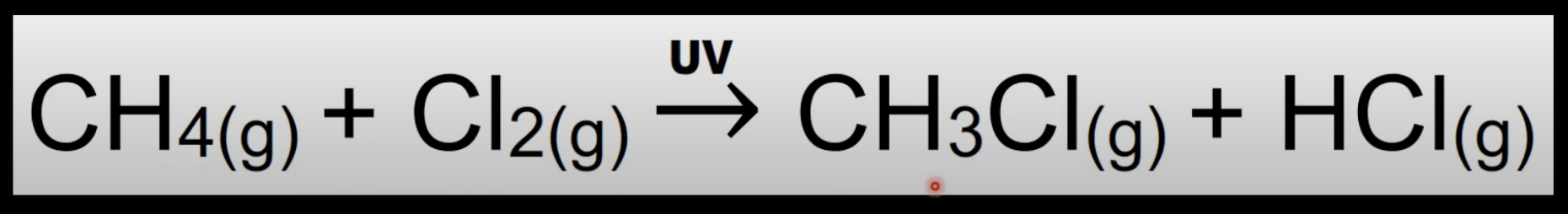
Free-radical substitution
Reaction where a radical replaces an atom in a molecule.
Occurs in presence of halogens and UV light.
3
New cards
Free radical definition
Species with unpaired electron, shown by a dot (•).
Highly reactive and short-lived.

4
New cards
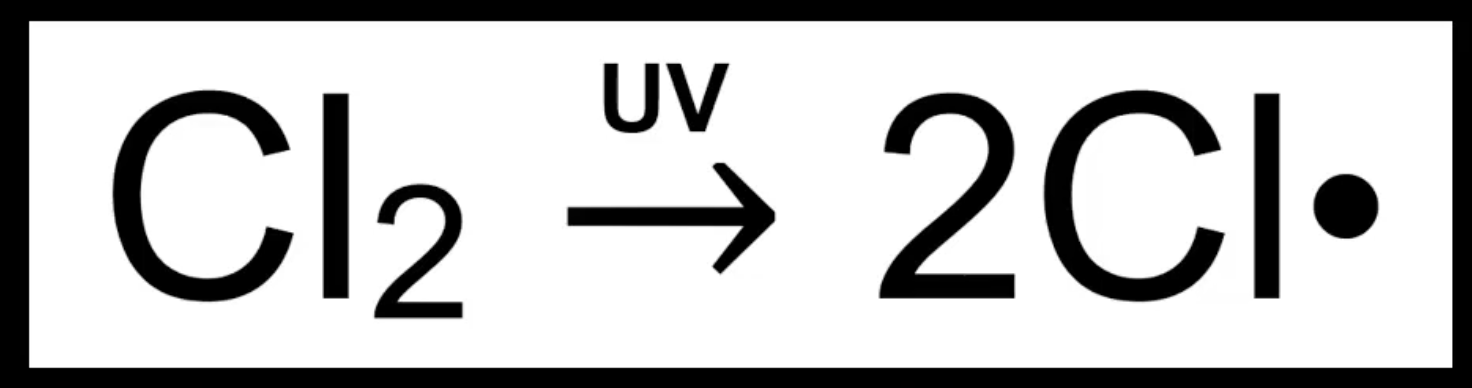
Initiation step
UV light breaks Cl–Cl bond homolytically.
Produces two Cl• radicals.
Starts the reaction chain.
5
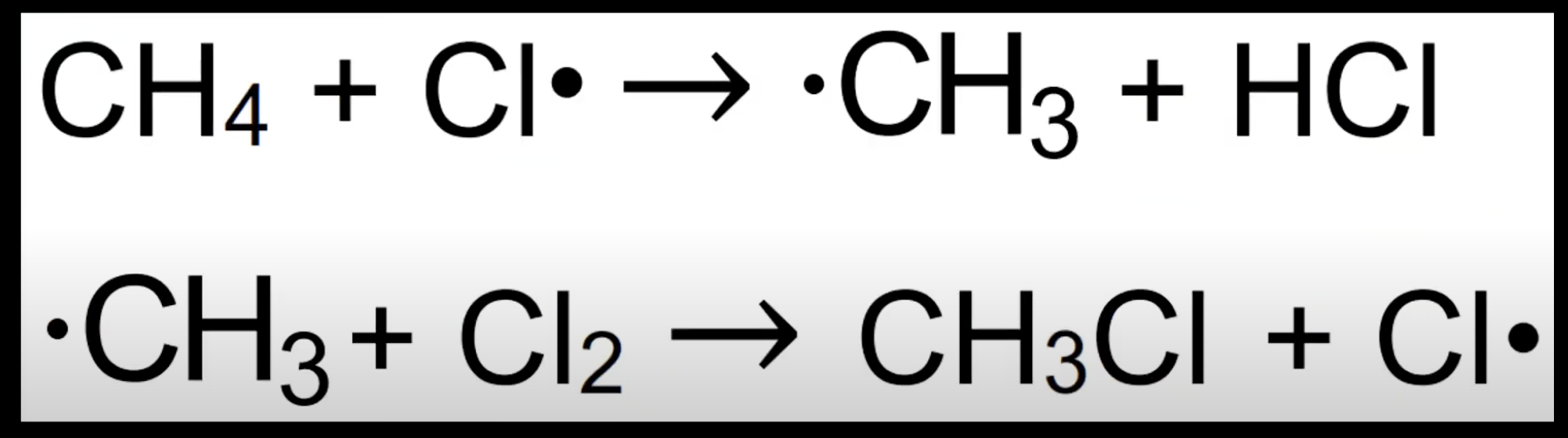
New cards
Propagation step
Radicals react with molecules to form new radicals.
Keeps chain going.
Example: CH₄ + Cl• → CH₃• + HCl.
6
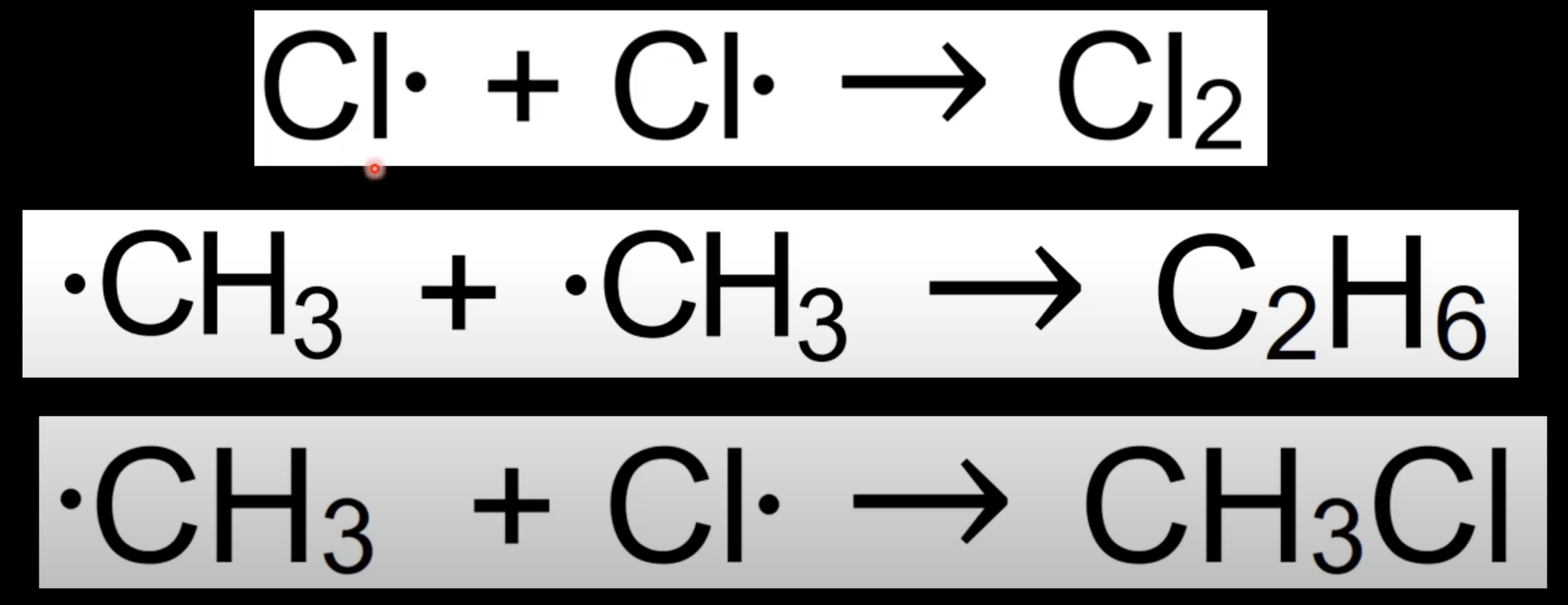
New cards
Termination step
Radicals combine to end chain.
Removes reactive species.
Example: Cl• + CH₃• → CH₃Cl.