Economics Exam 3 Review
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Guide
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
1
New cards
Interest Rate Effect
* Decline in price level means lower interest rates that can increase certain levels of spending
* As IR goes up, investments go down
* AD shifts left
* As IR goes up, investments go down
* AD shifts left
2
New cards
Real Balance Effect
* Price level falls, the purchasing power of existing financial balances rises
* As purchasing power goes up, AD will shift right
* As purchasing power goes up, AD will shift right
3
New cards
Foreign Purchase Effect
* Domestic prices go down, our good is cheaper compared to foreign goods
* As exports increase we will sell more to the world and AD will shift right
* As exports increase we will sell more to the world and AD will shift right
4
New cards
What way does the AD curve shift with expansionary (contractionary) Fiscal Policy?
* AD curve shifts to the right with expansionary fiscal policy
* AD curve shifts to the left with contractionary policy
* AD curve shifts to the left with contractionary policy
5
New cards
According to the foreign purchase effect, if price levels rise (lower) in the US relative to other countries what happens to NX?
It increases
6
New cards
Know the determinants of Aggregate Demand and how if they change they would cause AD to shift
* Determinants: C, I, G, Xn
* Consumer spending, changes in interest rates or expected returns, gov spending, and changes in national income changes abroad
* Consumer spending, changes in interest rates or expected returns, gov spending, and changes in national income changes abroad
7
New cards
What is the money multiplier, how do you calculate it? If given numbers can you find the total amount of economic activity created given an injection of a certain amount.
\
Example - MPC = 0.75 and we inject 5 billion…AD would shift right by…
\
Example - MPC = 0.75 and we inject 5 billion…AD would shift right by…
* Definition: A change in spending changes real GDP more than the initial change in spending - when money is re-spent in the economy, how many times it is re-spent
* MM = 1/(1-MPC)
* Ex: = 4, so the MM would be 4. If 5 billion injected then GDP would go up to 20 billion
* MM = 1/(1-MPC)
* Ex: = 4, so the MM would be 4. If 5 billion injected then GDP would go up to 20 billion
8
New cards
What are the 3 periods of time for Aggregate Supply and what is fixed or flexible in each one
* Immediate Short run - both input and output prices are fixed - straight horizontal line
* Short Run - input prices fixed, output flexible - bowing sloping supply, next 3-6 months
* Long Run - Both are flexible and can vary - straight up and down one, 1-3 years
* Short Run - input prices fixed, output flexible - bowing sloping supply, next 3-6 months
* Long Run - Both are flexible and can vary - straight up and down one, 1-3 years
9
New cards
What are some ways that AS in the short run will shift left or right?
* Anything that will cause firms to not have the ability to produce more or cause them to produce more.
* Taxes, input costs changing, wars, government regulations
* As input prices go up, supply less
* Input prices go down, so supply is more
* Increase corporation taxes - less money has for inputs so less outputs
* Taxes, input costs changing, wars, government regulations
* As input prices go up, supply less
* Input prices go down, so supply is more
* Increase corporation taxes - less money has for inputs so less outputs
10
New cards
What does productivity measure and how is it important to the AS curve?
* Productivity measures how much can you make, and how fast and how good = measures real output per unit of input
* Increases in productivity reduce costs and decreases in productivity increase costs therefore they are important to the AS curve
* Productivity affects supply
* Increases in productivity reduce costs and decreases in productivity increase costs therefore they are important to the AS curve
* Productivity affects supply
11
New cards
How do personal and business taxes effect AD and AS?
* Inversely, as taxes go up we spend less and firms have less cash flow to buy inputs
* Also works the other way around
* As corporations taxes go up, they have less money to use - businesses, buying less so producing less so AD would shift to the left
* Also works the other way around
* As corporations taxes go up, they have less money to use - businesses, buying less so producing less so AD would shift to the left
12
New cards
How is AD and AS possible effected with changes in the exchange rate (value of the dollar compared to other countries)
* As the dollar gets weaker, our goods are cheaper relative than before and we will export more and AD will shift to the right, AKA increase
* Dollar Depreciation -> AD increases
* Dollar Appreciation -> AD decreases
* Dollar Depreciation -> AD increases
* Dollar Appreciation -> AD decreases
13
New cards
Graphically how do we show demand-pull inflation or cost-push inflation?
o Demand-Pull- A shift in the AD graph to the right
o Cost-Push- A shift in AS to the left
14
New cards
Graphically how do we know/show a recession?
* When you are to the LEFT of your long run aggregate supply and long run output
* A leftward shift in Aggregate Supply when the price level is downwardly inflexible
* A leftward shift in Aggregate Supply when the price level is downwardly inflexible
15
New cards
Can you graphically give a situation to show how the AS/AD model would adjust?
\
i.e. graphically how would the graph change if the government issued everyone over the age of 18 a $1,400 stimulus check
\
i.e. graphically how would the graph change if the government issued everyone over the age of 18 a $1,400 stimulus check
Shift demand to the right, so this increases consumption, and causing the GDP to go up, causing AD to go right.
16
New cards
Discretionary fiscal policy vs. Nondiscretionary fiscal policy
* Discretionary - Sledgehammer, when Congress has to vote on changes in taxation or changes in government spending (ex. stimulus package/check or tax cuts)
* Nondiscretionary - Laws already in place that nudge GDP get back to long run output (ex. unemployment insurance, SNAP, WIC)
* Nondiscretionary - Laws already in place that nudge GDP get back to long run output (ex. unemployment insurance, SNAP, WIC)
17
New cards
Why are prices downward inflexible?
* Menu Costs - costs to reprint the menus (not going to lower or raise the prices because of recession)
* Wage Contract - Norwood is on contract with OU, so even if something happens with the economy, the wage he gets is constant
* Consumer Behavior - We freak out or we buy a lot depending on what is happening with the economy (If prices are low we will buy more)
* Wage Contract - Norwood is on contract with OU, so even if something happens with the economy, the wage he gets is constant
* Consumer Behavior - We freak out or we buy a lot depending on what is happening with the economy (If prices are low we will buy more)
18
New cards
What are some automatic stabilizers? What do they do?
* Taxes, Welfare, Unemployment insurance…
* Taxes very directly with GDP and transfers vary inversely with GDP
* There are laws that are already in place to help nudge the economy back to long run output.
* Taxes very directly with GDP and transfers vary inversely with GDP
* There are laws that are already in place to help nudge the economy back to long run output.
19
New cards
What business cycle phases go with each fiscal policy?
o During an expansion business cycle there should be contraction fiscal policy
o During a recessionary business cycle there should be a expansionary fiscal policy.
20
New cards
What is one major drawback with fiscal policy?
It is run by people that need to get elected to keep their jobs
21
New cards
What are the main tools of fiscal policy?
* Taxes
* Government Spending
* Government Spending
22
New cards
What is a budget deficit, how does it happen, and how is it different than the national debt?
* Budget Deficit: the year to year debt that the US government incurs
* Budget Deficit is caused by more Expansionary Fiscal Policy NOT being offset by Contractionary Fiscal Policy
* National Debt: Summation of all the yearly debts that we have incurred
* Budget Deficit is caused by more Expansionary Fiscal Policy NOT being offset by Contractionary Fiscal Policy
* National Debt: Summation of all the yearly debts that we have incurred
23
New cards
What is the crowding effect?
It is when Expansionary Fiscal Policy is used and it raises interest rates that then crowds out private investments from happening
24
New cards
What is the biggest variable that affects your personal spending?
income/disposable income
25
New cards
Holding all else equal when income goes up what happens to savings and consumption?
They also go up
26
New cards
When you save money you give up _______ money. In regards to the consumption schedule and saving schedule if you start to spend more how does your saving schedule shift? (remember it works vis versa)
* Spending
* Takes longer to save for later
* Takes longer to save for later
27
New cards
If personal taxes increase (decrease) what happens to your level of consumption and savings?
It goes down if there’s an increase because you lose more of you income to taxes.. so less to spend and less to save
28
New cards
How is the marginal propensity to consume calculated?
* MPC = It is the Change in Consumption divided by the Change in Income
* MPS = Change in Savings divided by the Change in Income
* Income 200, Consumption 220
* New Income 220 and Consumption is 230
* MPC = (230-220)/(200-220) = 10/20 = .5 = MPC
* MPS = Change in Savings divided by the Change in Income
* Income 200, Consumption 220
* New Income 220 and Consumption is 230
* MPC = (230-220)/(200-220) = 10/20 = .5 = MPC
29
New cards
What is dissavings?
* When you spend more than you make
* If you DI is $500 and consumption is $450 do you have Dissavings?
* No you do not
* If you DI is $500 and consumption is $550 do you have dissavings?
* Yes you do
* If you DI is $500 and consumption is $450 do you have Dissavings?
* No you do not
* If you DI is $500 and consumption is $550 do you have dissavings?
* Yes you do
30
New cards
What cause the investment demand curve to shift from the left or the right?
\
Hint changes in interest rates will NOT cause a shift but it will cause a slide along it.
\
Hint changes in interest rates will NOT cause a shift but it will cause a slide along it.
* Anything that will cause firms to not have the ability to produce more or cause them to produce more
* Taxes, input costs changing, wars, government regulations
* Taxes, input costs changing, wars, government regulations
31
New cards
What helped John Maynard Keynes come up with the aggregate expenditures model?
After the great depression he proposed this model
32
New cards
Referring to the Aggregate Expenditures Model as we added more parts of GDP to the model it would shift ____ or ____ depending on if the new component was positive or negative.
Left or right
33
New cards
What makes GDP goes up and down…
allows AD to shift right or left
34
New cards
Good Test Question: Marginal Propensity is 0.9%, inject 100, Multiplier is 10
1000 is the answer
35
New cards
What does MPC + MPS equal?
1
36
New cards
Government Spending increases, what happens?
* Aggregate Demand increases (as long as interest rates and tax rates do not change)
* More transportation projects
* More transportation projects
37
New cards
Government spending decreases, what happens?
* Aggregate Demand decreases
* Less military spending
* Less military spending
38
New cards
Input Prices
* Domestic Resource Prices
* Labor - increase or decrease in labor force
* Capital - machinery
* Land - the land you sit on or the strip mall
* Prices of imported resources:
* Imported oil - needed for almost all firms
* Exchange rates - input parts from overseas
* Labor - increase or decrease in labor force
* Capital - machinery
* Land - the land you sit on or the strip mall
* Prices of imported resources:
* Imported oil - needed for almost all firms
* Exchange rates - input parts from overseas
39
New cards
Productivity
* Real output per unit of input
* Increases in productivity reduce costs
* Decreases in productivity increase costs
* Productivity = total output/total inputs
* Per-unit production cost = total input cost/total output
* Increases in productivity reduce costs
* Decreases in productivity increase costs
* Productivity = total output/total inputs
* Per-unit production cost = total input cost/total output
40
New cards
Fiscal Policy is designed to:
* Achieve full-employment
* Control Inflation
* Encourage economic growth
* Control Inflation
* Encourage economic growth
41
New cards
Expansionary Fiscal Policy
* Use during a recession
* Increase gov spending
* Decrease taxes
* Combination of both
* Create a deficit
* Increase gov spending
* Decrease taxes
* Combination of both
* Create a deficit
42
New cards
Contractionary Fiscal Policy
* Use during demand-pull inflation
* Decrease government spending
* Increase taxes
* Combination of both
* Create a budget surplus
* Decrease government spending
* Increase taxes
* Combination of both
* Create a budget surplus
43
New cards
Tax Progressivity
* Progressive tax system
* Proportional tax system
* Regressive tax system
* Proportional tax system
* Regressive tax system
44
New cards
Problems of Timing - Fiscal Policy
* Recognition Lag - recognize when to react
* Administrative Lag - congress is voting and passing
* Operational Lag - we voted, stimulus check, go
* Administrative Lag - congress is voting and passing
* Operational Lag - we voted, stimulus check, go
45
New cards
Other problems with Fiscal Policy
* Political Considerations
* Future policy reversals
* Offsetting state and local finance
* Crowding-out effect
* Future policy reversals
* Offsetting state and local finance
* Crowding-out effect
46
New cards
What is owed to the holders of U.S. securities?
* Treasury Bills
* Treasury notes
* Treasury bonds
* U.S. Savings bonds
* Treasury notes
* Treasury bonds
* U.S. Savings bonds
47
New cards
What components are involved in Aggregate demand?
* Change in one of the determinants
* Multiplier
* Multiplier
48
New cards
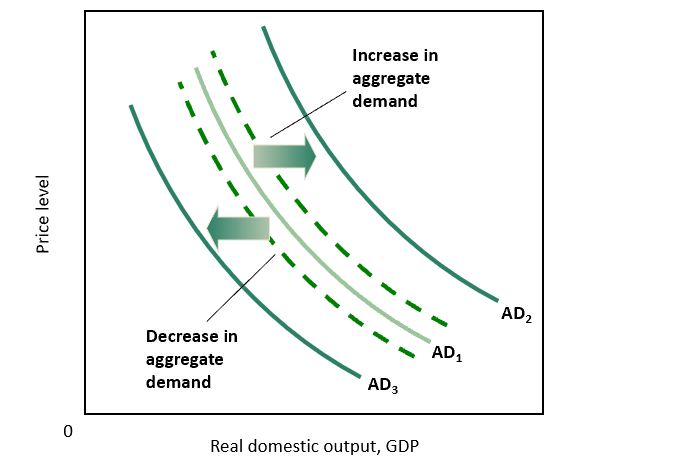
Changes in Aggregate Demand
* Dashed lines - initial effect
* Solid lines - after the multiplier takes effect
* Solid lines - after the multiplier takes effect
49
New cards
Main driver of consumption
Disposable Income
50
New cards
Consumer Wealth
Difference between household assets (homes and stocks and bonds) and liabilities (loans and credit cards) - literally disposable income
51
New cards
Household borrowing
Borrow money now, spend now
52
New cards
Expected returns
The expected profit you will get from your investment
53
New cards
National Income Abroad
* Higher foreign income → AD increases
* Lower foreign income → AD decreases
* Lower foreign income → AD decreases
54
New cards
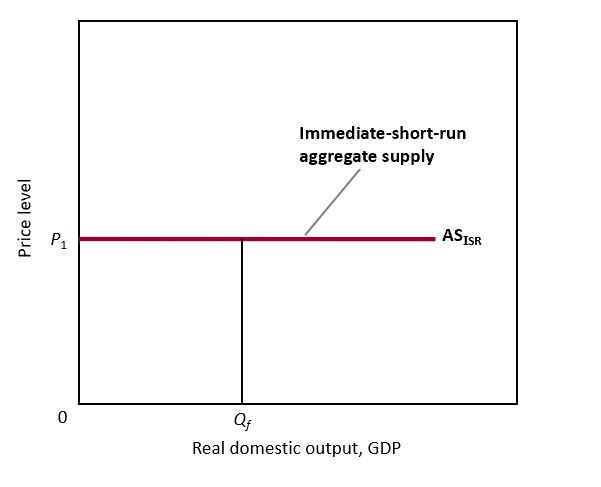
Aggregate Supply in the Immediate Short Run Graph
* Straight horizontal lone
* Flat, input is fixed, output is fixed
* Flat, input is fixed, output is fixed
55
New cards
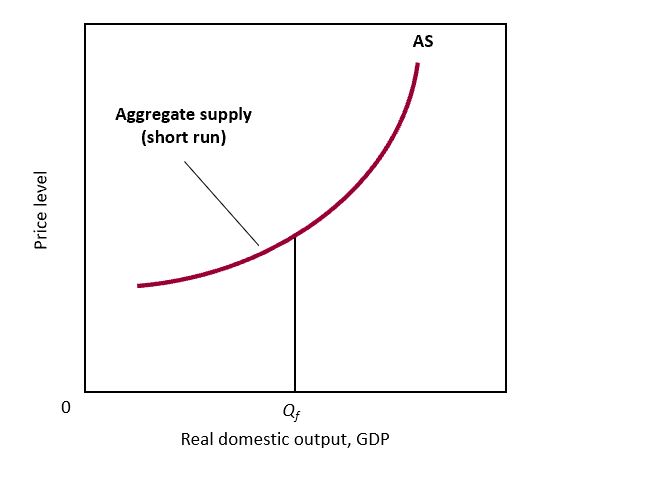
**Aggregate Supply Curve Short Run Graph**
* Bowed a little
* Next 3-6 months of the production of goods and services in our economy
* Never leave out services
* Output is fixed
* Blip if something changed like if there is a shortage of wheat
* Next 3-6 months of the production of goods and services in our economy
* Never leave out services
* Output is fixed
* Blip if something changed like if there is a shortage of wheat
56
New cards
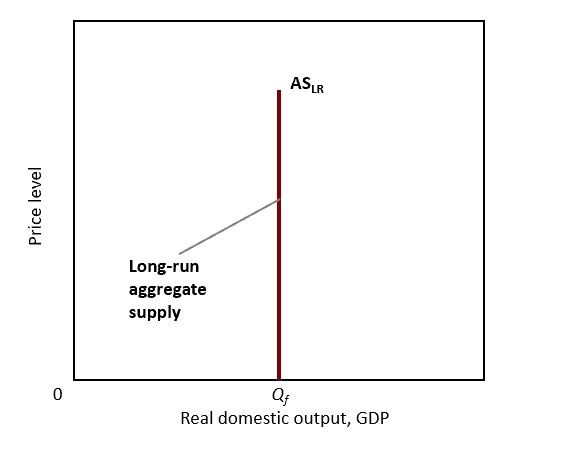
Aggregate Supply in the Long Run
* Straight vertical line
* For this to ever shift there has to be a permanent change to the economy like if we allowed more immigrants in, more workers mean more output, etc.
* For this to ever shift there has to be a permanent change to the economy like if we allowed more immigrants in, more workers mean more output, etc.
57
New cards
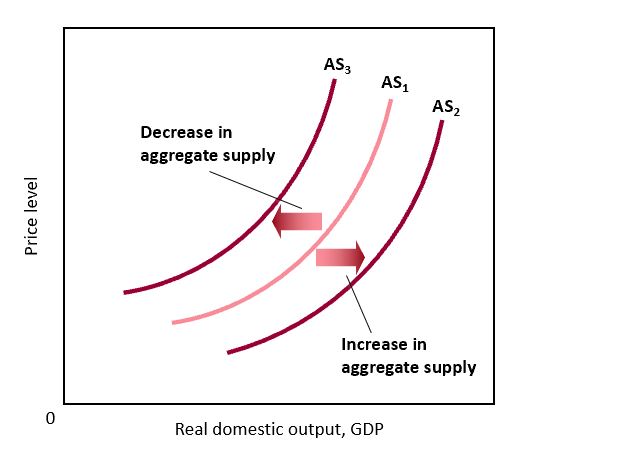
Changes in Aggregate Supply
* An increase is a shift to the right and a decrease is a shift to the left
* Pandemic - we saw a decrease
* One we marry agg supply and demand we can see all these changes
* Pandemic - we saw a decrease
* One we marry agg supply and demand we can see all these changes