Unit 3: Chemistry of Life
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
What is the monomer of a carbohydrate?
monosaccharide
Catalyst
a substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction without being changed by the reaction
Activation energy
the minimum amount of energy needed to cause a process (chemical reaction) to occur
Active sites
binds to the enzyme to undergo a chemical reaction
Fatty acid
a hydrocarbon (a carbon chain with hydrogen atoms attached and a carboxyl group at the end)
Solvent
the substance is the dissolving medium
Solute
the substance that is dissolved
Unused carbohydrates are converted into…
lipids
What is the structure of a carbohydrate?
the shape of a carbon ring
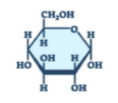
Carbohydrates are made of which elements?
carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
What are the functions of carbohydrates in cells?
used as the main source of energy (sugar), and sometimes for structural purposes (cellulose, which help make cell walls and structures)
What are some examples of carbohydrates?
sugar, starch, glucose
What is the monomer of a lipid?
glycerol and 3 fatty acids
What is the structure of a lipid?
the shape of a letter E (glycerol backbone and 3 fatty acids)

Lipids are made of which elements?
carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
What are the functions of lipids in cells?
used to store energy, for protection, insulation, and buoyancy (also regulates what goes in and out of cells)
Are lipids soluble in water?
no, they don’t like water (they are water repellent)
What are some examples of lipids?
fats, oils, waxes
What are steroids?
(a lipid) they are specific chemicals that regulate our body and homeostasis
Saturated
has the maximum number of hydrogen atoms (solid at room temperature, and its structure has straight lines)
Unsaturated
there is at least one double bond in the fatty acid (liquid at room temperature, its structure has crooked lines, and its better for our body because it is easier to digest)
What is the monomer of a nucleic acid?
nucleotide
What is the structure of a nucleic acid?
3 parts; 5-carbon sugar ring, nitrogenous base (5 different bases), phosphate group
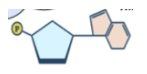
Nucleic acids are made of which elements?
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus
What are the functions of nucleic acids in cells?
used to store and transmit hereditary/genetic information
What are examples of nucleic acids?
DNA, RNA, ATP
What is the function of DNA?
it has the information to make proteins
What is the function of RNA?
it makes the proteins
What is the function of ATP?
it is made from carbohydrates (but is a nucleic acid) and provides energy
What is the monomer of a protein?
an amino acid
What is the structure of a protein?
has an amino group (NH2), carboxyl group, and a side chain (COOH)
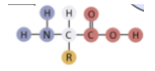
Proteins are made of which elements?
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen
What are the functions of proteins in cells?
hemoglobin carries oxygen in blood, enzymes are biological catalysts (they lower the activation energy, so it takes less energy and time for chemical reactions to occur), builds up muscles and tissues, and structural support
How many amino acids are there?
22 kinds
What are examples of proteins?
hemoglobin, enzymes, keratin, collagen, albumin (from eggs), meat
What happens when proteins are heated up?
they can break down and the structure changes
Equilibrium
when things are in balance
Endothermic reactions
it takes in energy, feels cold
Exothermic reactions
it releases/creates heat, feels hot
Most chemical reactions are…
exothermic
Chemical reactions
they release or absorb energy involving the breaking and forming of bonds
Metabolic reactions
chemical reactions that occur in a cell/in your body
Enzymes
speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction, lowering the activation energy
What affects enzymes?
temperature and pH
Organic
is alive and contains carbon
Why is the carbon atoms a good element?
it has 4 valence electrons, allowing it to bond with many elements (including itself)
What are buffers?
weak acids or bases that can react with strong acids or bases to prevent sudden changes in pH, keeping it stable
Where is water on the pH scale?
7 (middle of the scale, meaning neutral)
What is the range of the pH scale?
0 to 14
More acidic solutions are ____ on the pH scale
lower
More basic solutions are ____ on the pH scale
higher
Acids contain…
higher concentrations of H+ (hydrogen) ions than water
Bases contain…
higher concentrations of OH- (hydroxide) ions than water
How do acids taste?
sour
How do bases taste?
bitter (typically, and is slippery)
What is a weak acid?
vinegar
Density
less dense substances float on denser substances
Cohesion
when water sticks to itself (because of hydrogen bonds)
Adhesion
when water sticks to other stuff
Surface tension
hydrogen bonding creates something like a net, allowing much denser things to float on water
Capillary action
when water adheres to the fiber of a paper/plant and pulls up another water molecule
Universal solvent
water can dissolve many other substances because of its polarity
High specific heat
water can hold heat for a long time (slow to heat, slow to cool)
Solution
all components are evenly distributed throughout (AKA homogeneous mixtures)
Suspension
a mixture of undissolved materials/substances, where each substance can be visibly separated (AKA heterogeneous)
Hydrogen bonds are formed when…
the partial positive and negative charges of the water molecule attract other water molecules (opposites attract), forming weak bonds
Which bond is the weakest?
hydrogen bonds
Which bond is the strongest?
covalent bonds
Covalent bonds are formed when…
electrons are shared by atoms
Ionic bonds are formed when…
one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another (they give/gain electrons to each other), creating an electrical attraction between these two oppositely charged atoms/ions
Compounds
made of two or more different elements
Noble gases
these elements are very stable, because their outer electron shells are completely full
Ion
an atom or molecule that has a charge other than zero (has a positive or negative charge)
Isotope
an atom of the same element with a different number of neutrons in the nucleus, making it unstable
Cation
positively charged ion
Anion
negatively charged ion