PAS407 - Class Skull, Scalp and Face
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
What is the neurocranium?
protective case for the brain
what are the parts of the skull?
1. neurocranium
2. calvaria
3. basicranium
what are the 8 bones of the neurocranium?
§ Four singular bones centered on the midline
· Frontal, ethmoidal, sphenoidal, and occipital
§ two sets occurring as bilateral pairs
· temporal and parietal
calvaria is?
skull cap
basicranium is?
cranial floor
the viscerocranium is?
the facial bones
- 15 irregular bones
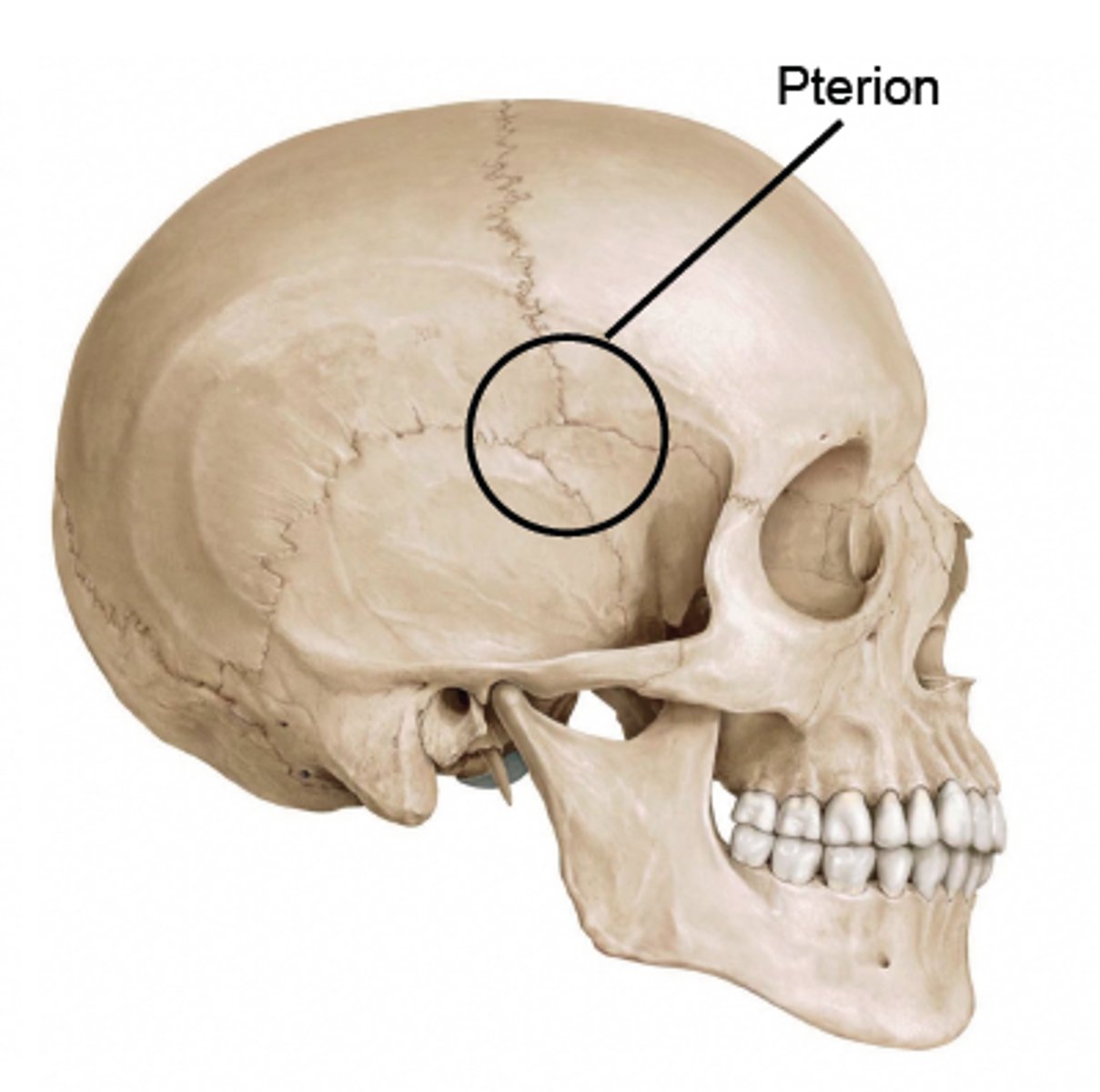
what is the pterion? what is it's clinical significance?
o distinguishes H-shaped formation of sutures that unite the frontal, parietal, sphenoid (greater wing), and temporal bones.
§ Represents weak point in cranium, susceptible to fracture
§ Pterion fractures complicated by presence of middle meningeal artery deep to this space
what 3 processes come off the temporal bone?
1. zygomatic process
2. styloid process
3. mastoid process
What are the pterygoid processes?
o consists of lateral and medial pterygoid plates
o extend inferiorly on each side of the sphenoid
What is the sella turcica?
o a.k.a Turkish saddle
o central depression for pituitary gland
What are the 5 layers of the scalp?
Skin
Connective tissue
Aponeurosis
Loose connective tissue
Pericranium
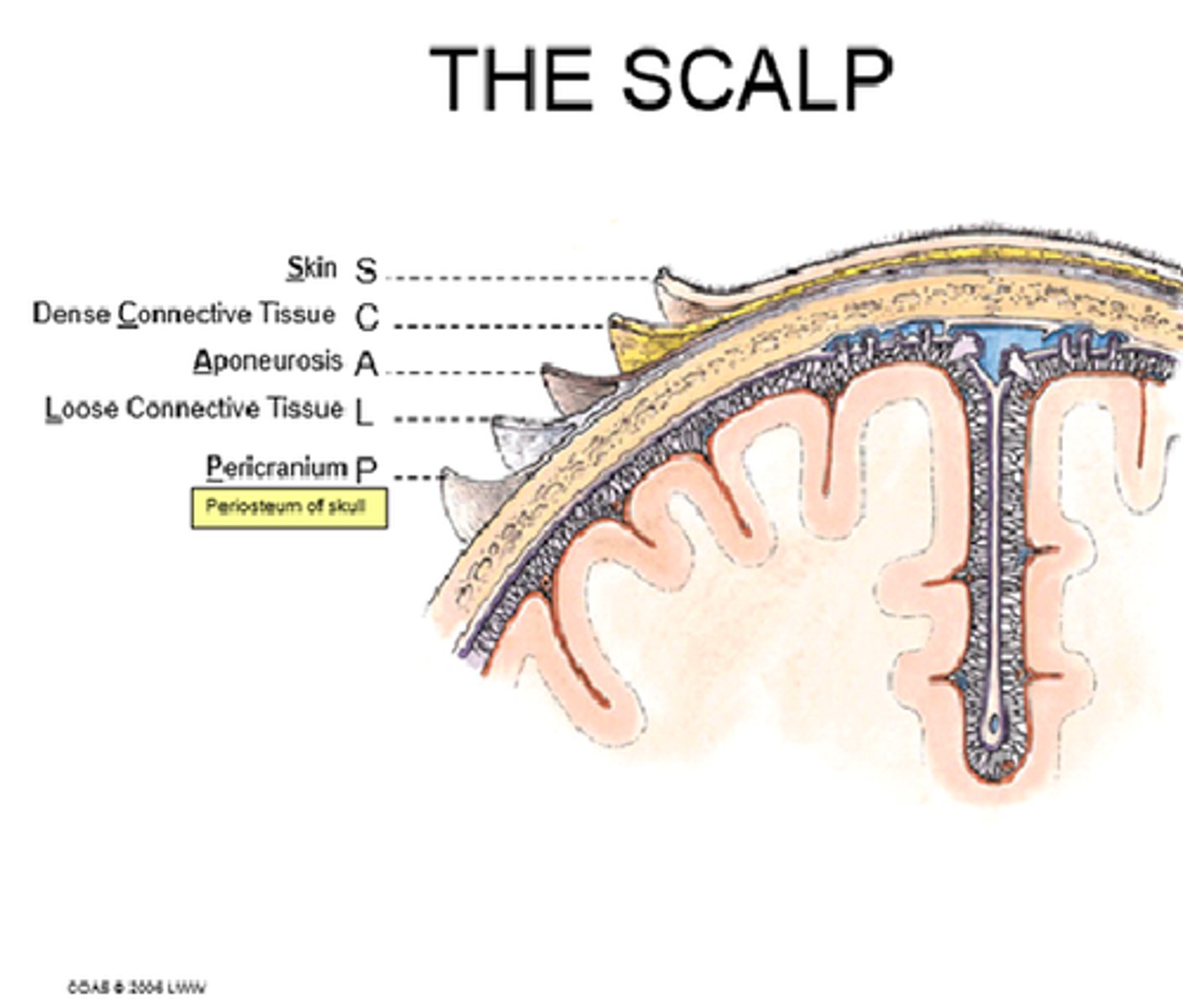
what's the mnemonic for the 5 layers of the scalp?
SCALP
what do the muscles of the face and scalp generally do?
· Embedded in the subcutaneous tissue of the anterior and posterior scalp, face, and neck.
· Move the skin and change facial expressions to convey mood.
· Function by pulling the skin.
what are the 5 main muscles of the face and scalp?
- occipitofrontalis
- orbicularis Oris
- orbicularis oculi
- buccinator
- platysma
action of occipitofrontalis
raises eyebrows, wrinkles forehead
action of orbicularis oris
compresses and purses lips
action of orbicularis oculi
closes eye
action of buccinator
· Keeps the cheek taut during chewing
· Compresses the cheeks and lips against the teeth and gums
action of platysma
contracts to tense skin along neck
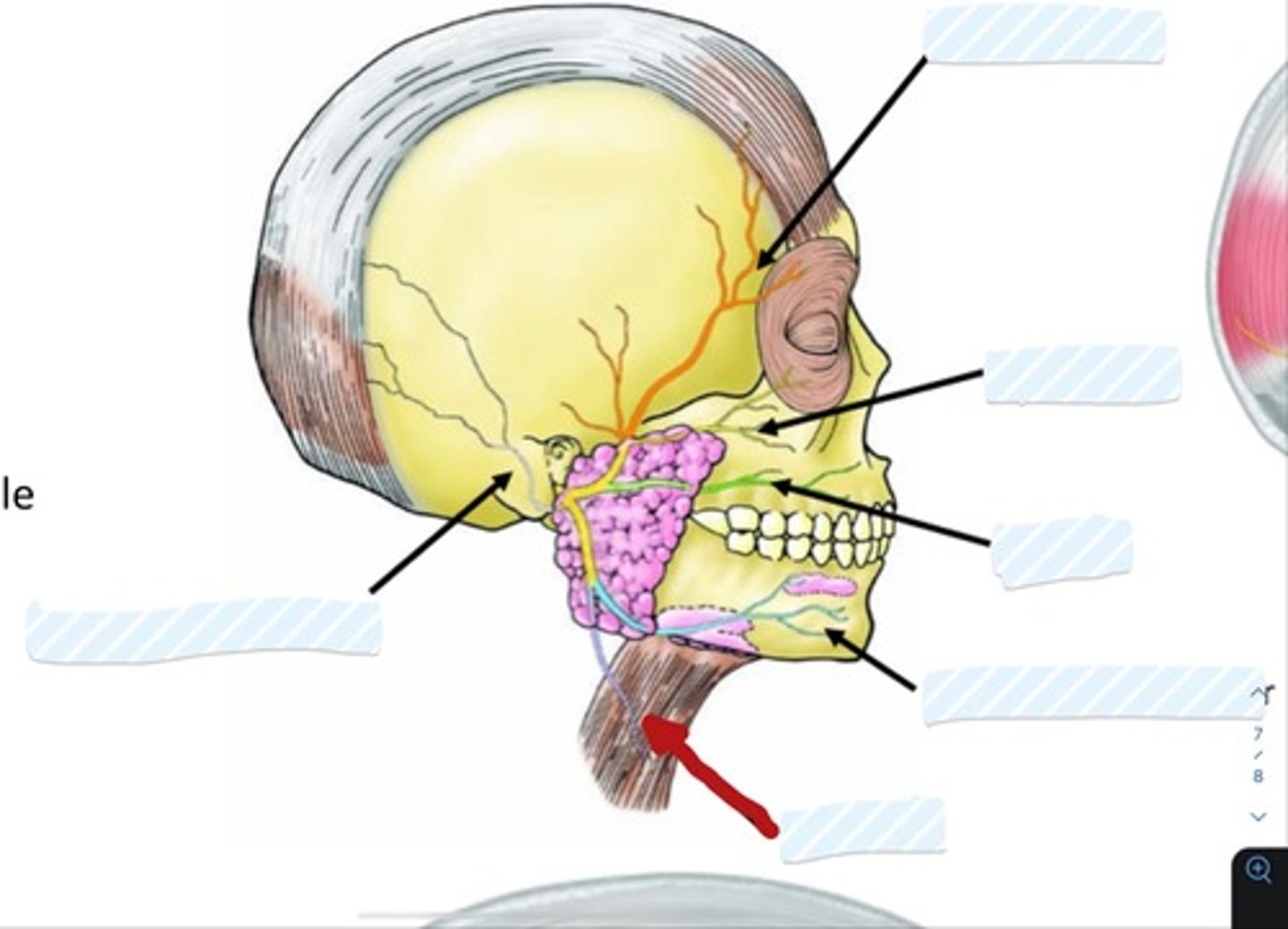
what are the 3 divisions of the trigeminal nerve that go to the face/scalp?
1. Opthalmic n.
2. maxillary n.
3. mandibular n.
the Opthalmic nerve does what?
Supplies the skin overlying the anterior scalp
the maxillary nerve does what?
§Supplies the maxillary region of the face
the mandibular nerve does what?
three sensory branches that supply the jaw region
the mandibular nerve gives off what branch?
auriculotemporal n.
(runs anterior to the ear)
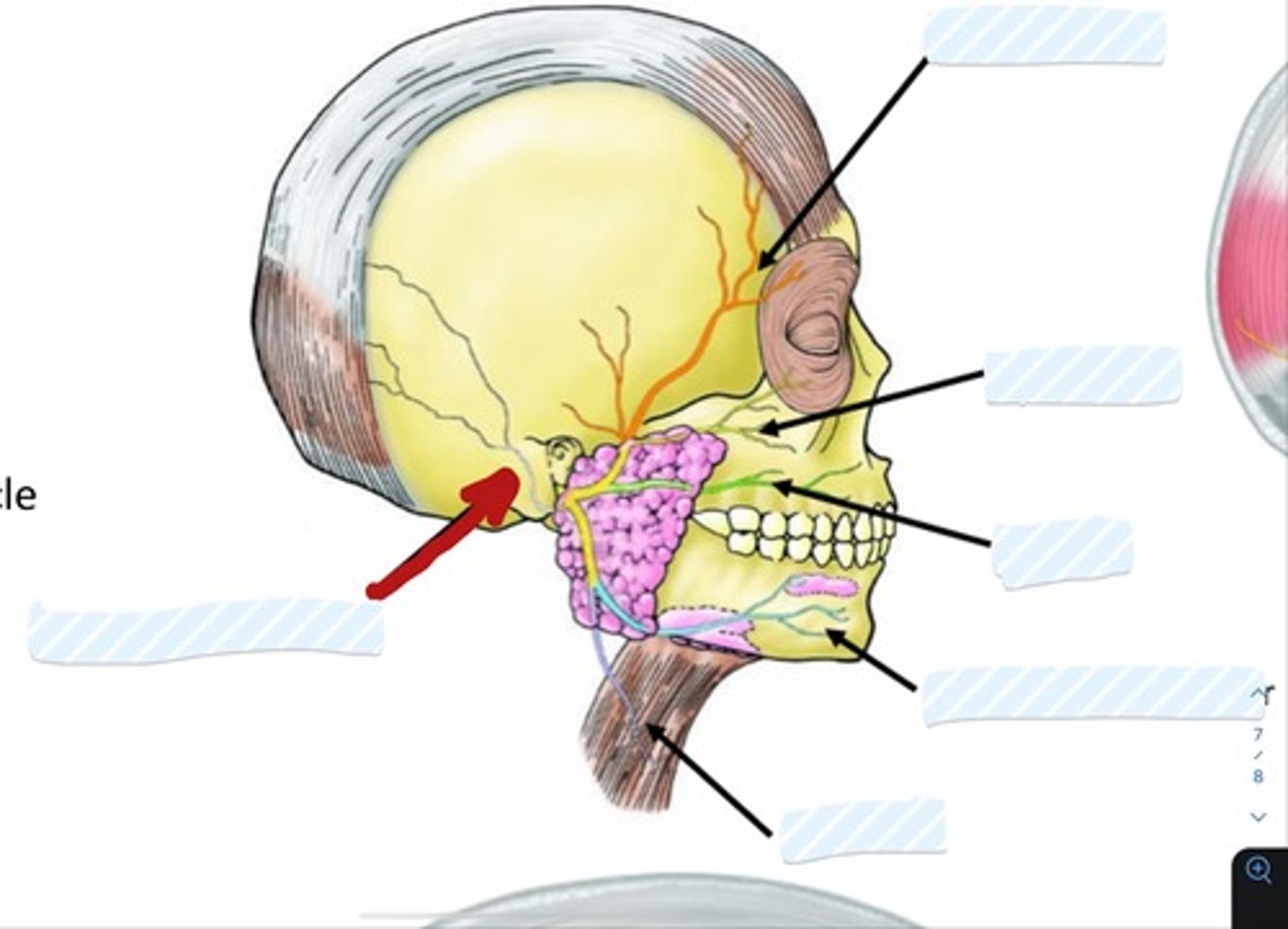
what is a mnemonic for remembering the 5 branches of the facial nerve?
Two
Zebras
Bit
My
Coccyx.
What are the 5 branches of the facial nerve?
1. temporal
2. zygomatic
3. buccal
4. marginal mandibular
5. cervical
what does the temporal branch supply?
auricularis superior and auricularis anterior, the frontal belly of the occipitofrontalis, superior part of the orbicularis oculi.
what does the zygomatic branch supply?
orbicularis oculi and other facial muscles
what does the buccal branch supply?
supplies buccinators
upper parts of orbicularis oris
inferior fibers of levator labii superioris
what does the marginal mandibular branch supply?
risorius and muscles of the lower lip and chin
what does the cervical branch supply?
platysma
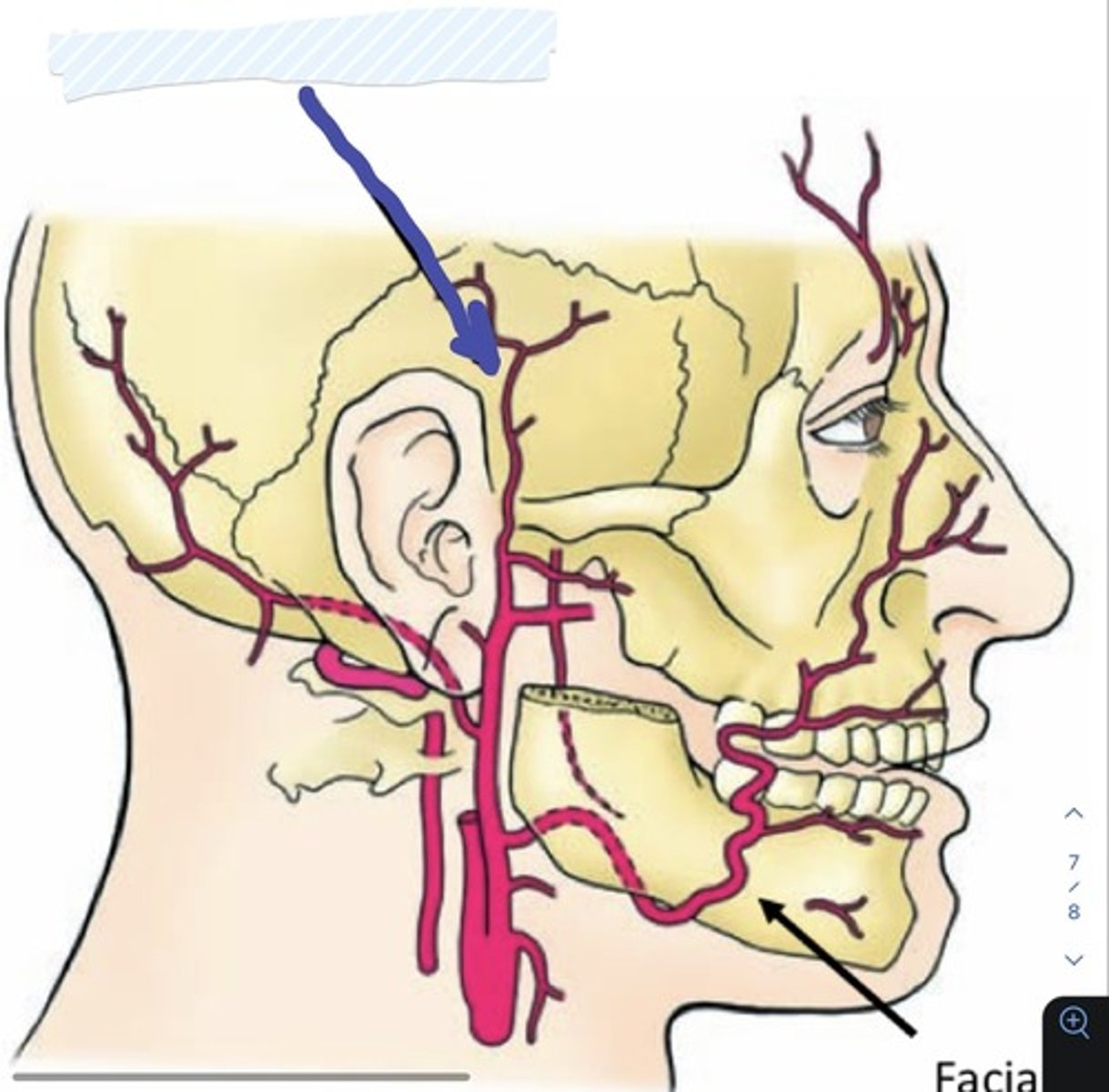
what are the vasculature of the face?
1. facial artery
2. superficial temporal artery
what is the major arterial supply to the face?
facial artery
what does the facial artery arise from?
external carotid a.
what 2 branches does the facial artery give off (and to where)?
1. superior and
2. inferior labial branches
to the upper and lower lips
what does the superficial temporal artery divide into? (2)
1. frontal branches
2. parietal branches
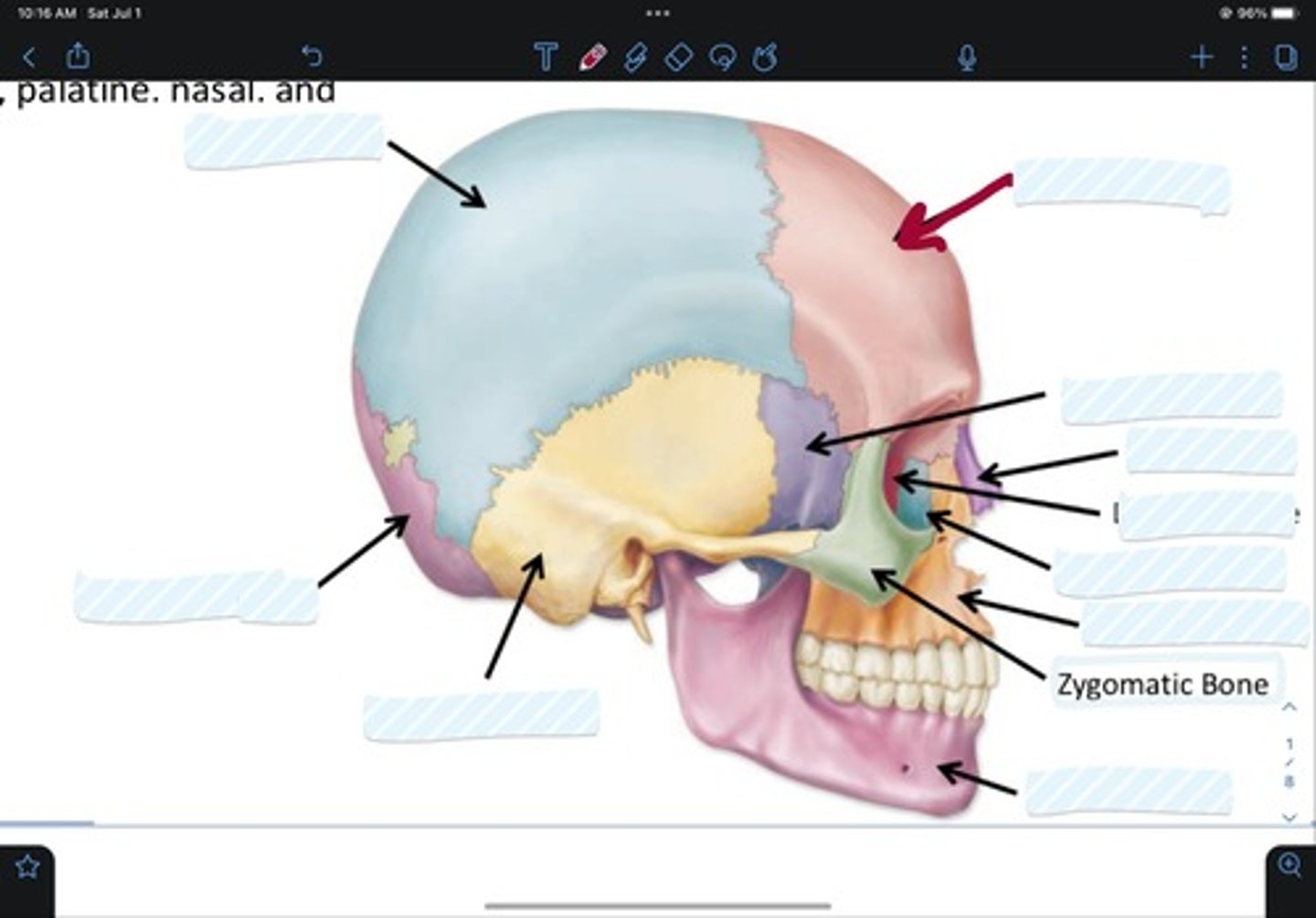
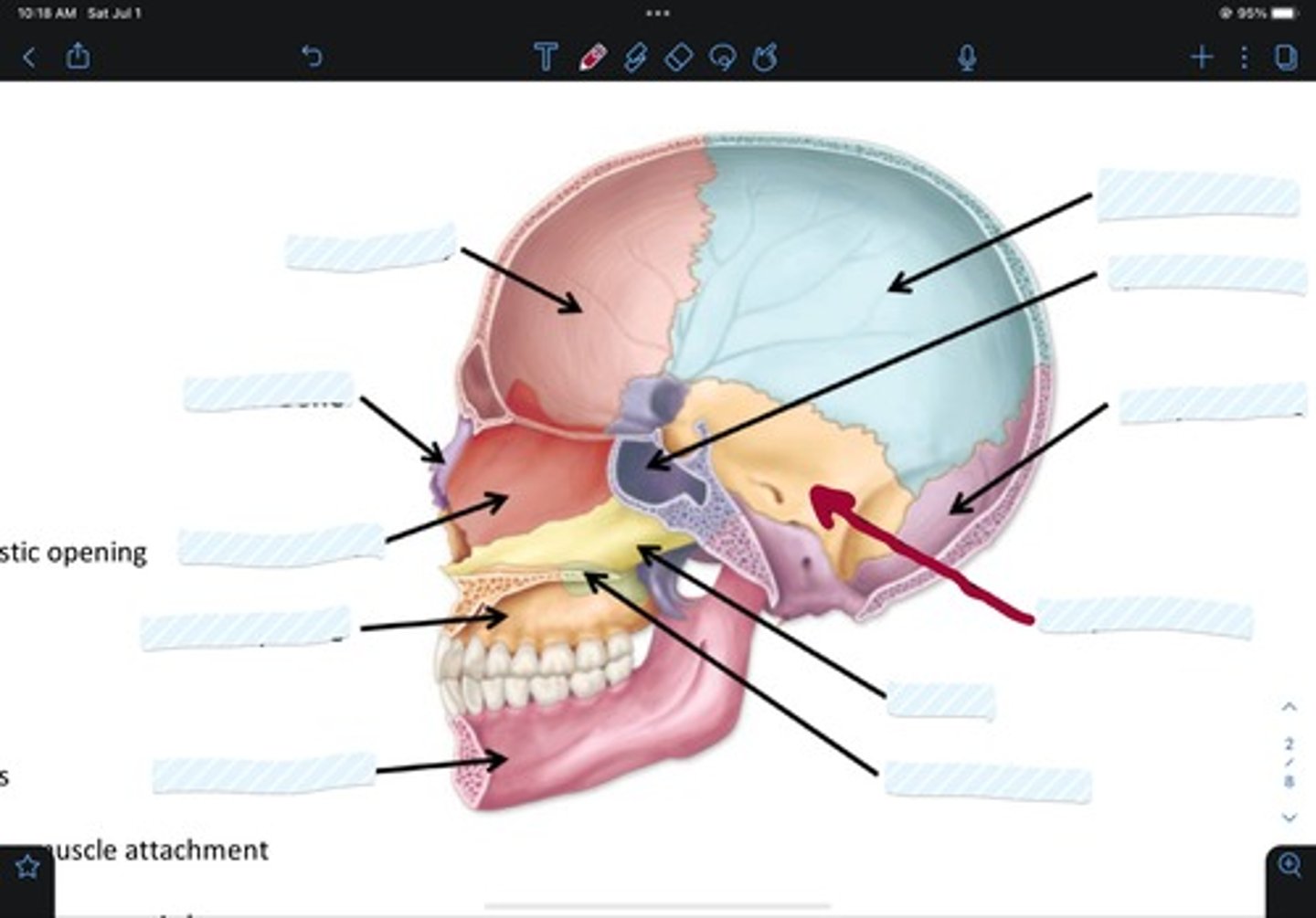
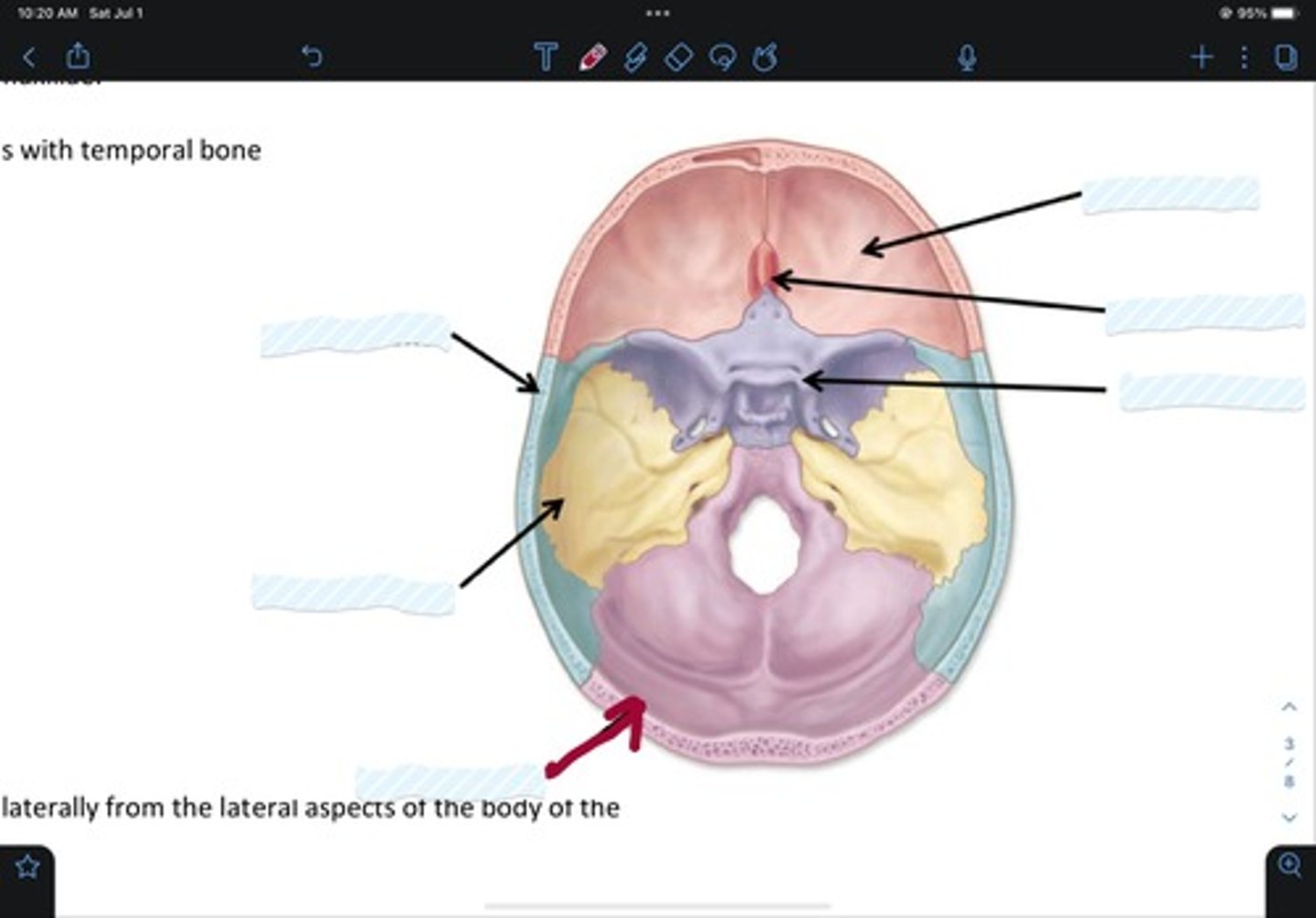
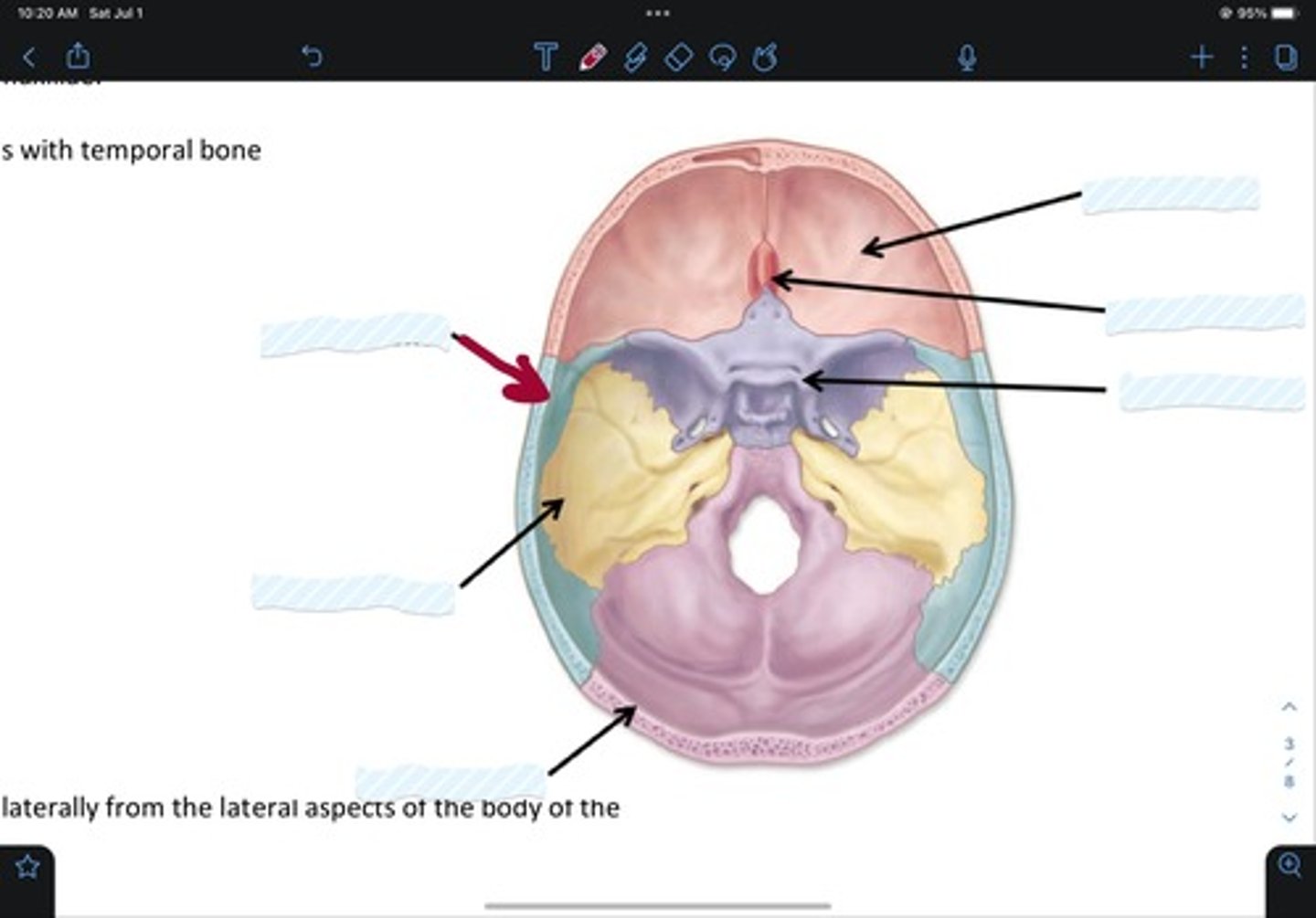
Frontal bone
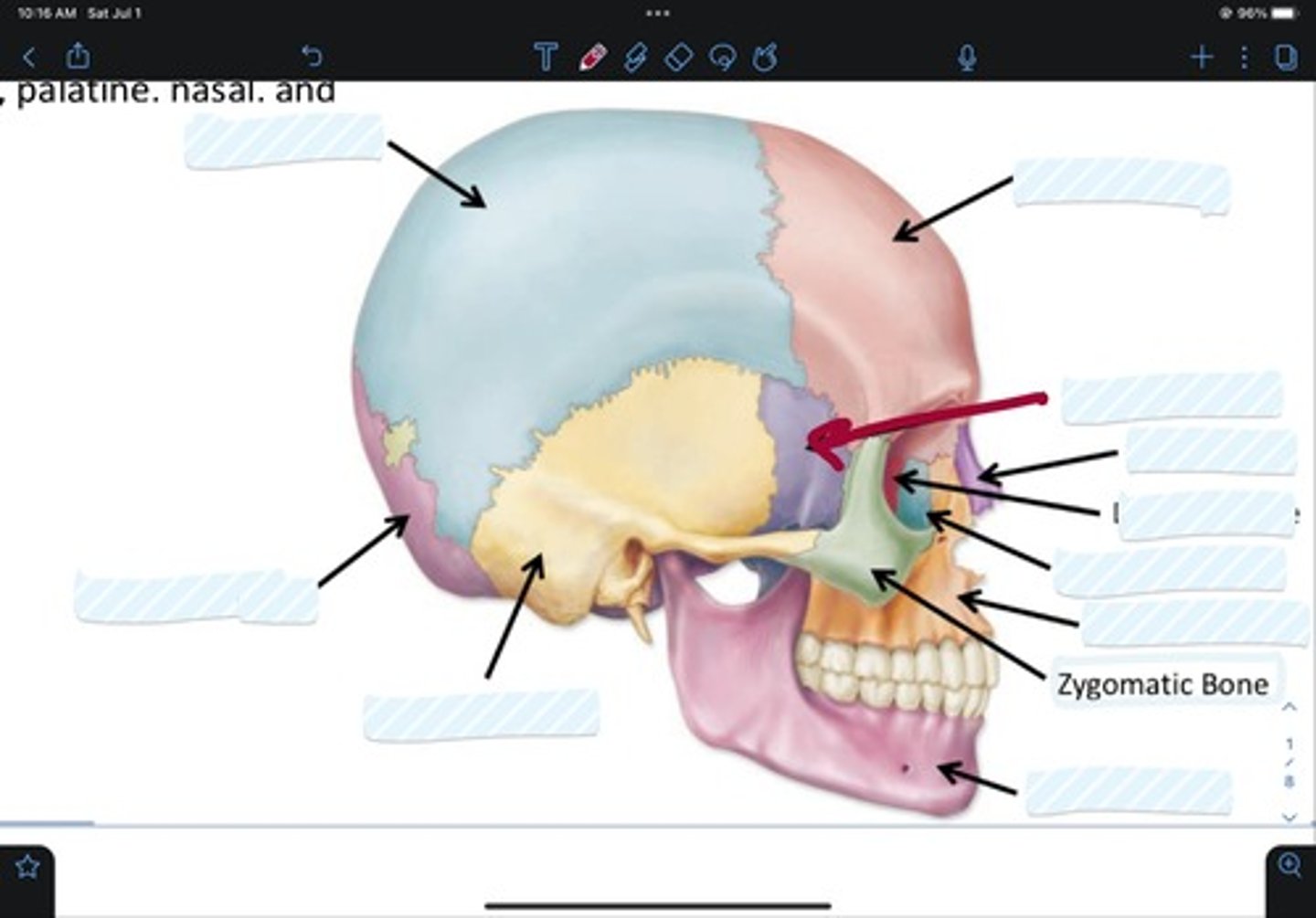
Sphenoid bone
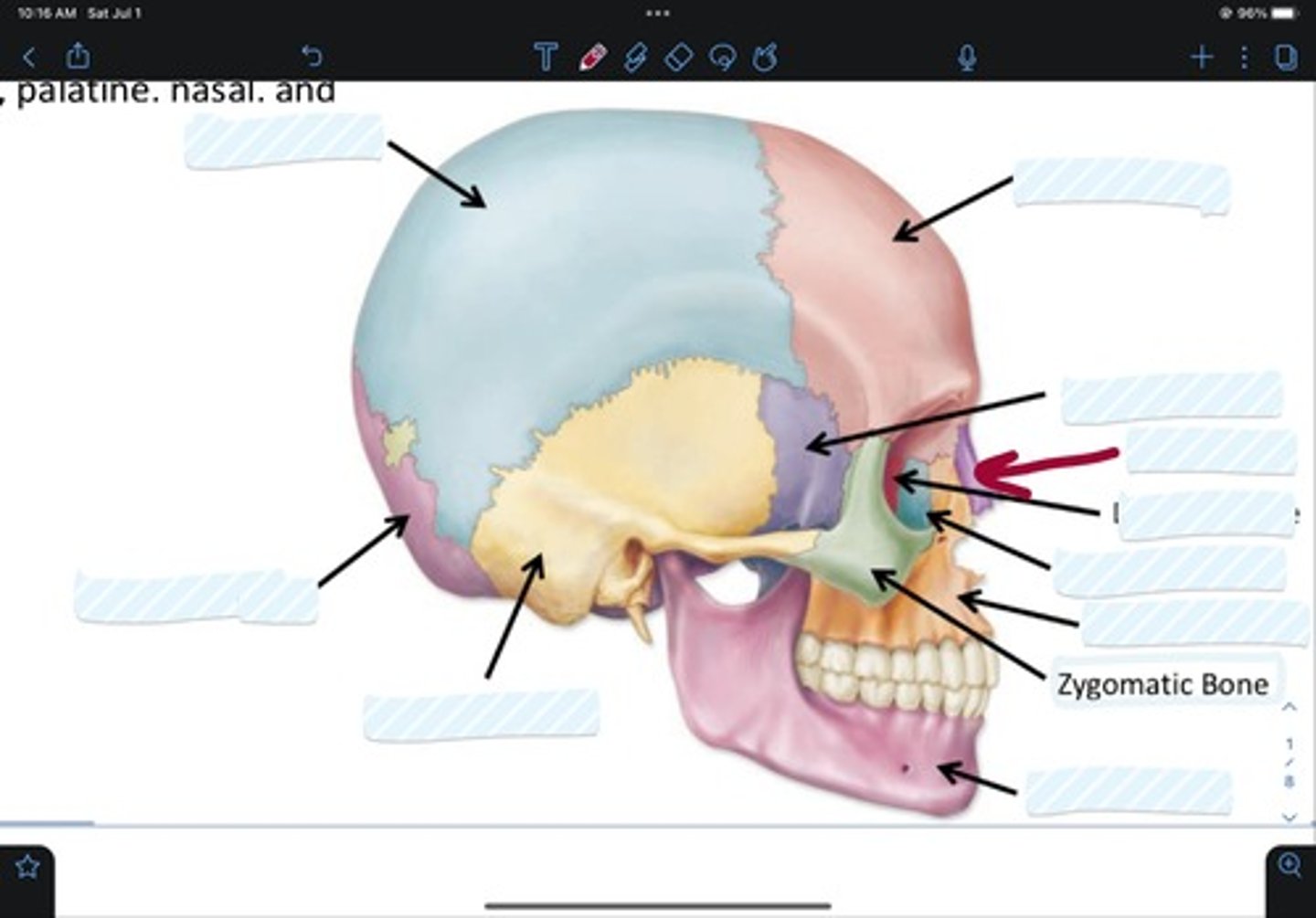
Nasal bone
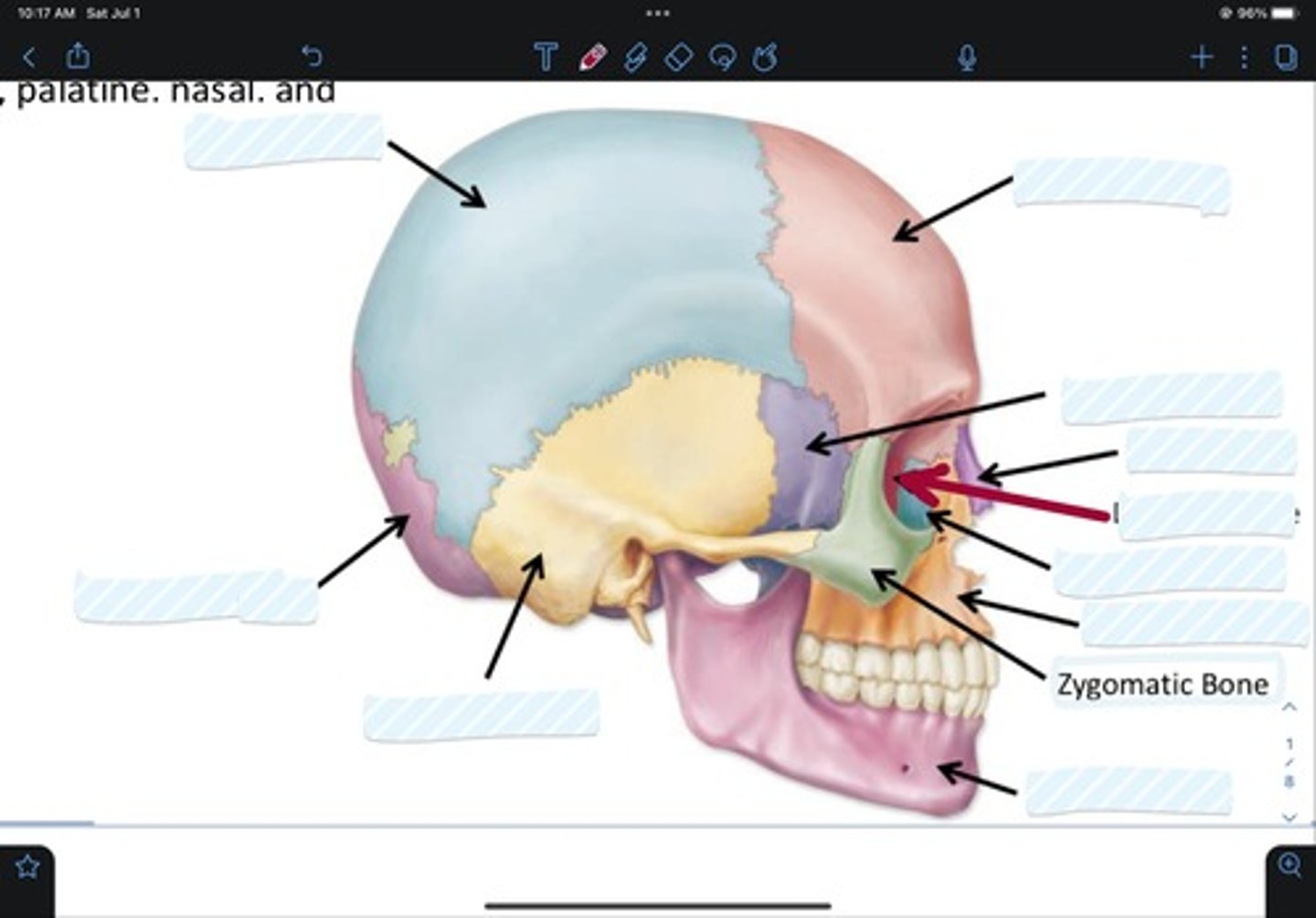
Ethmoid bone
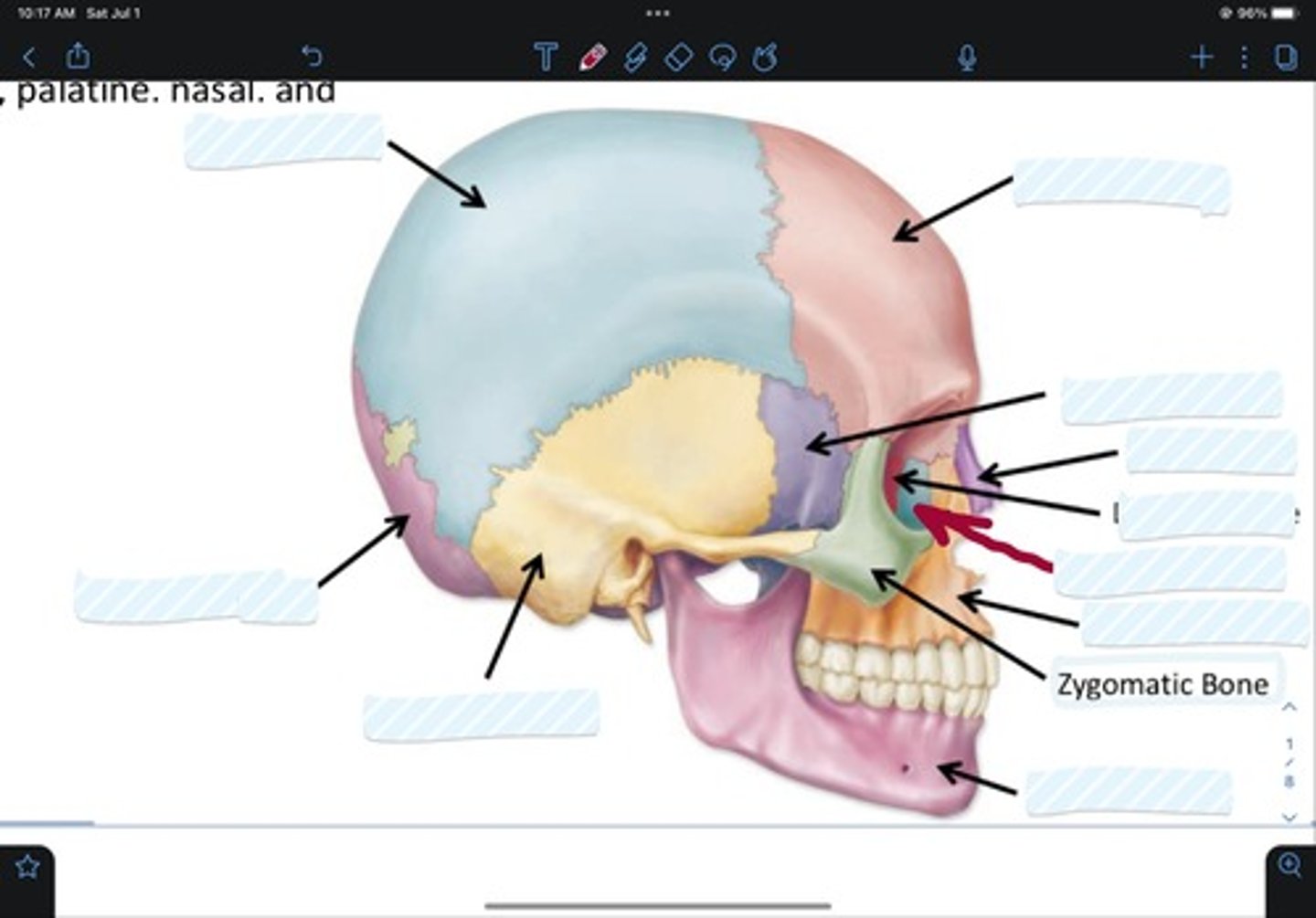
Lacrimal bone
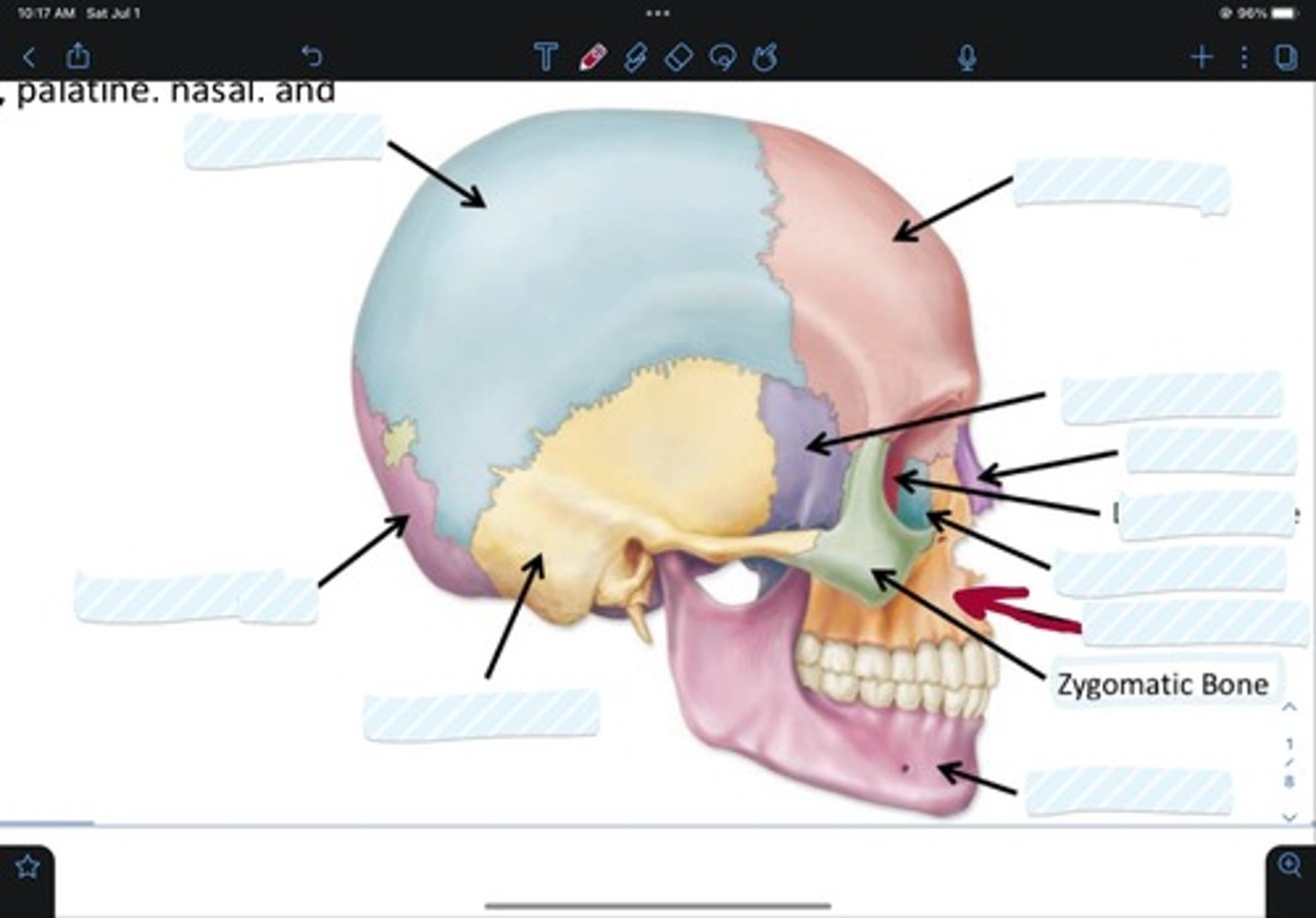
Maxillary bone
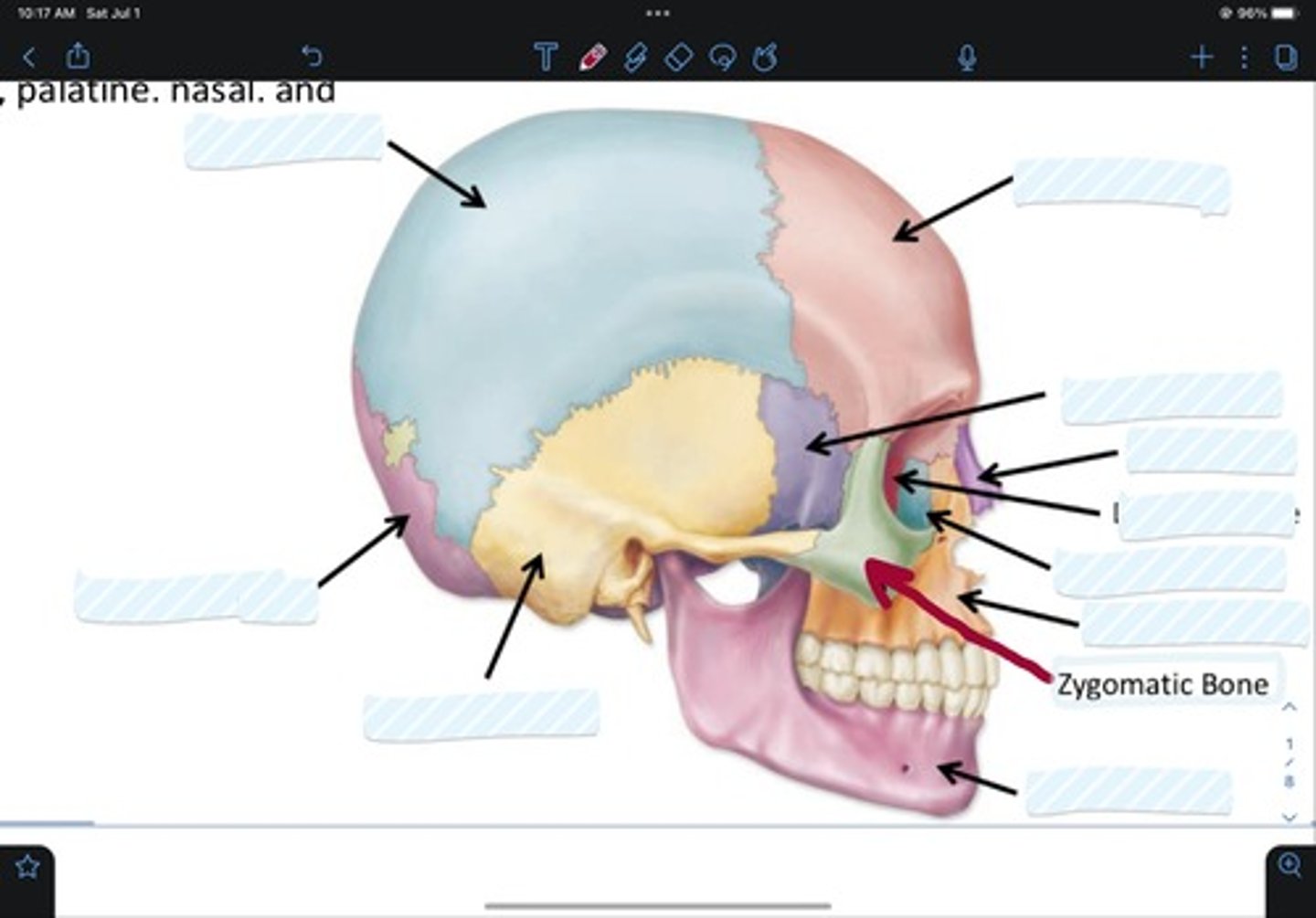
Zygomatic bone
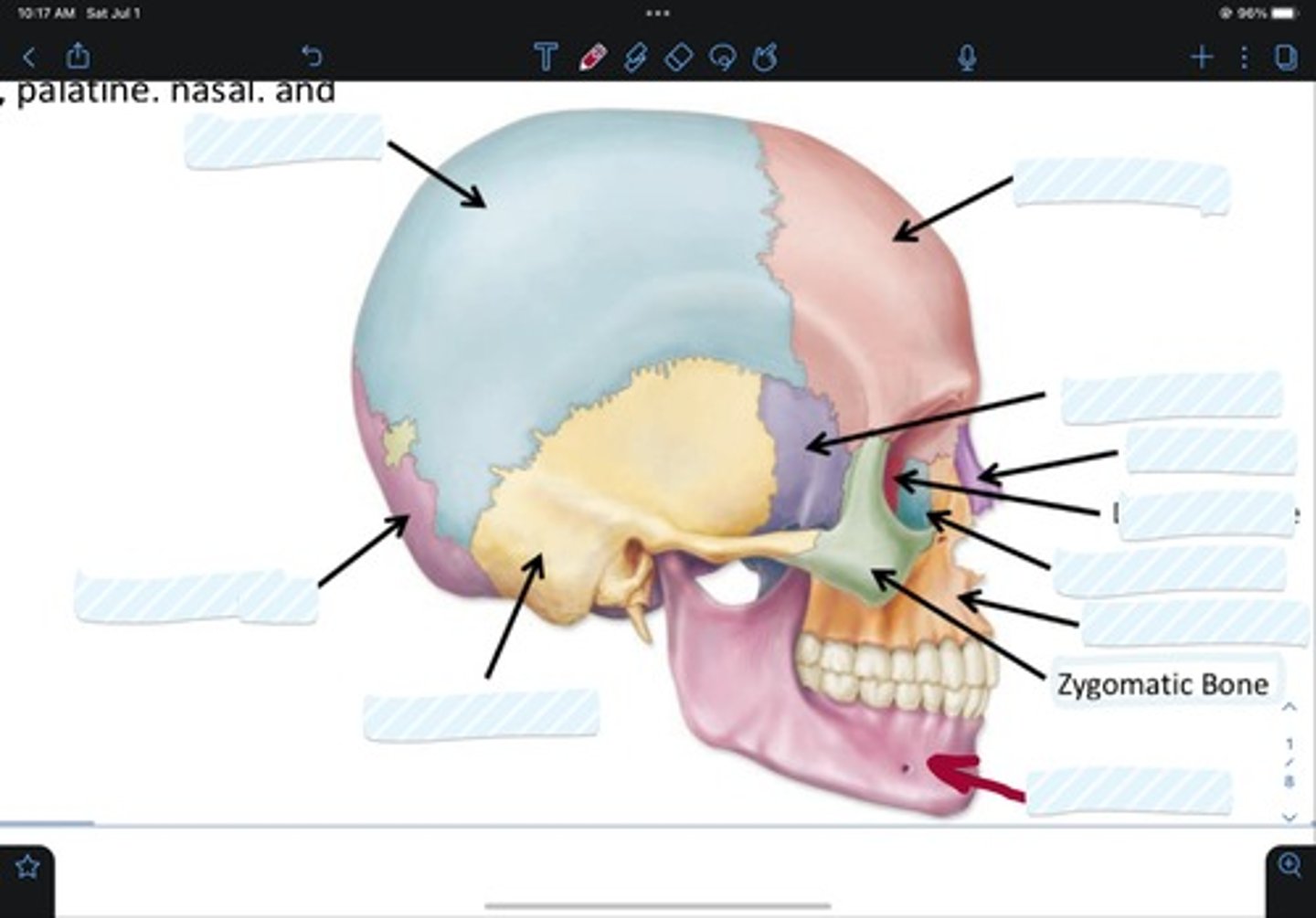
Mandible bone
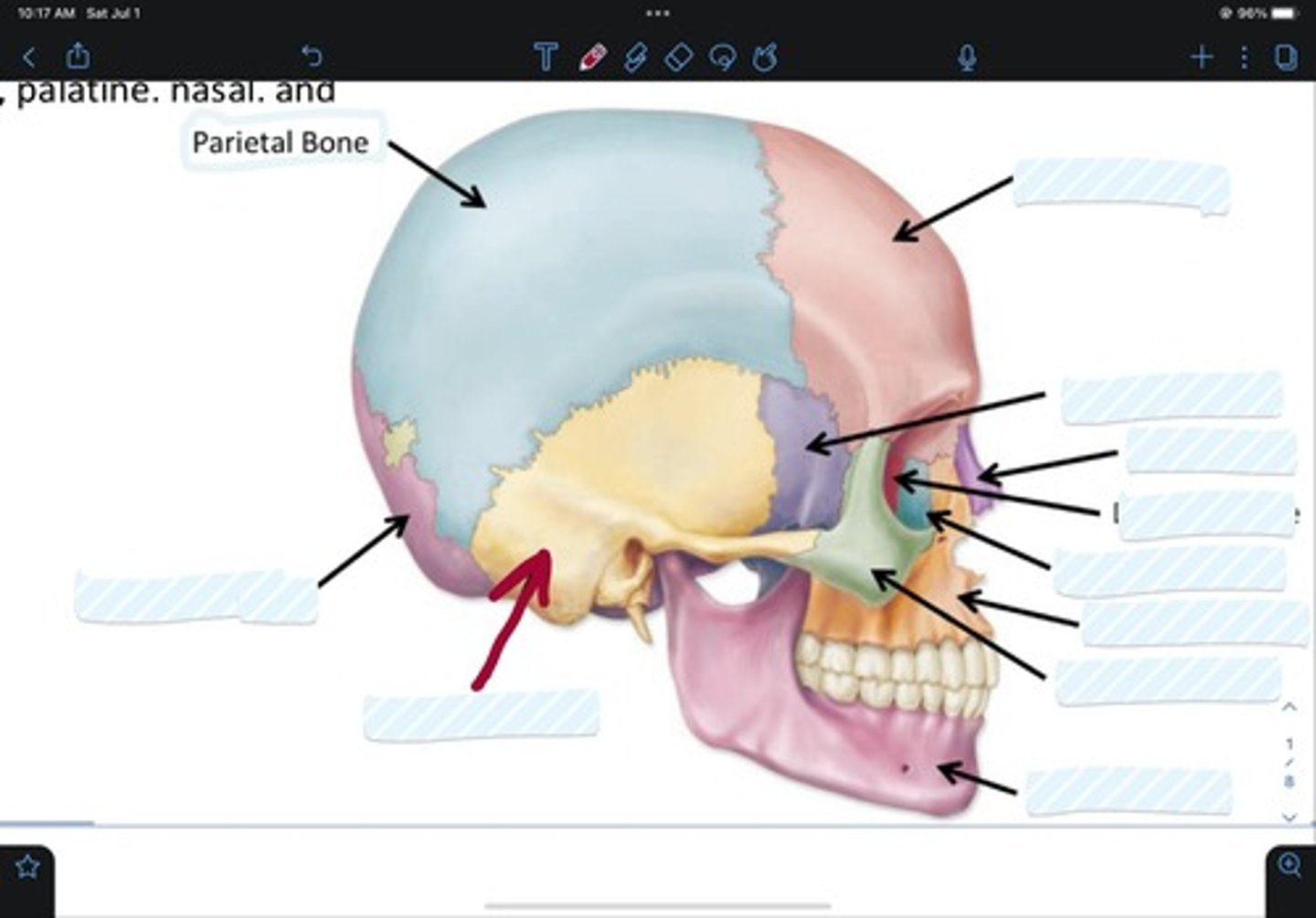
Temporal bone
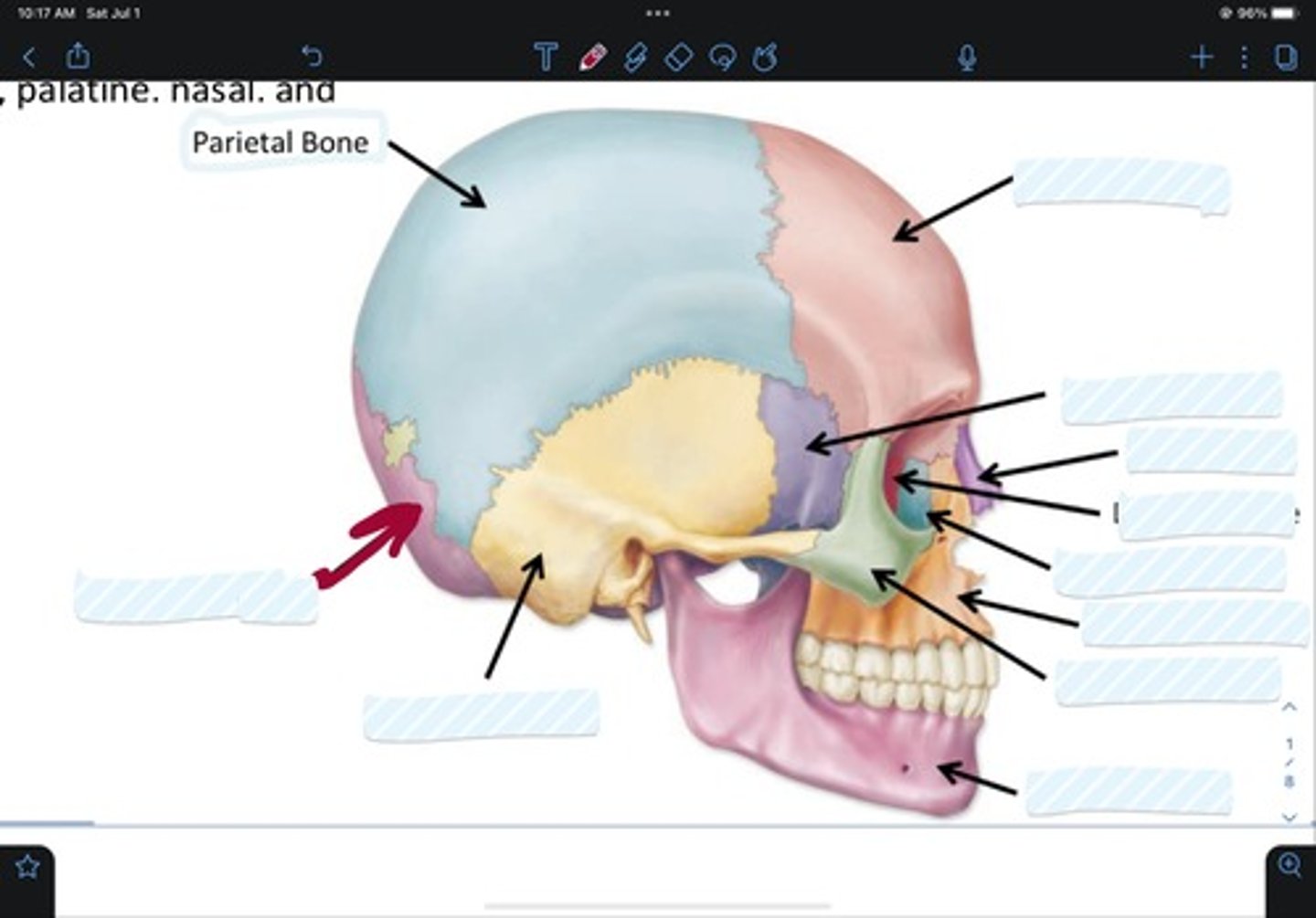
Occipital bone
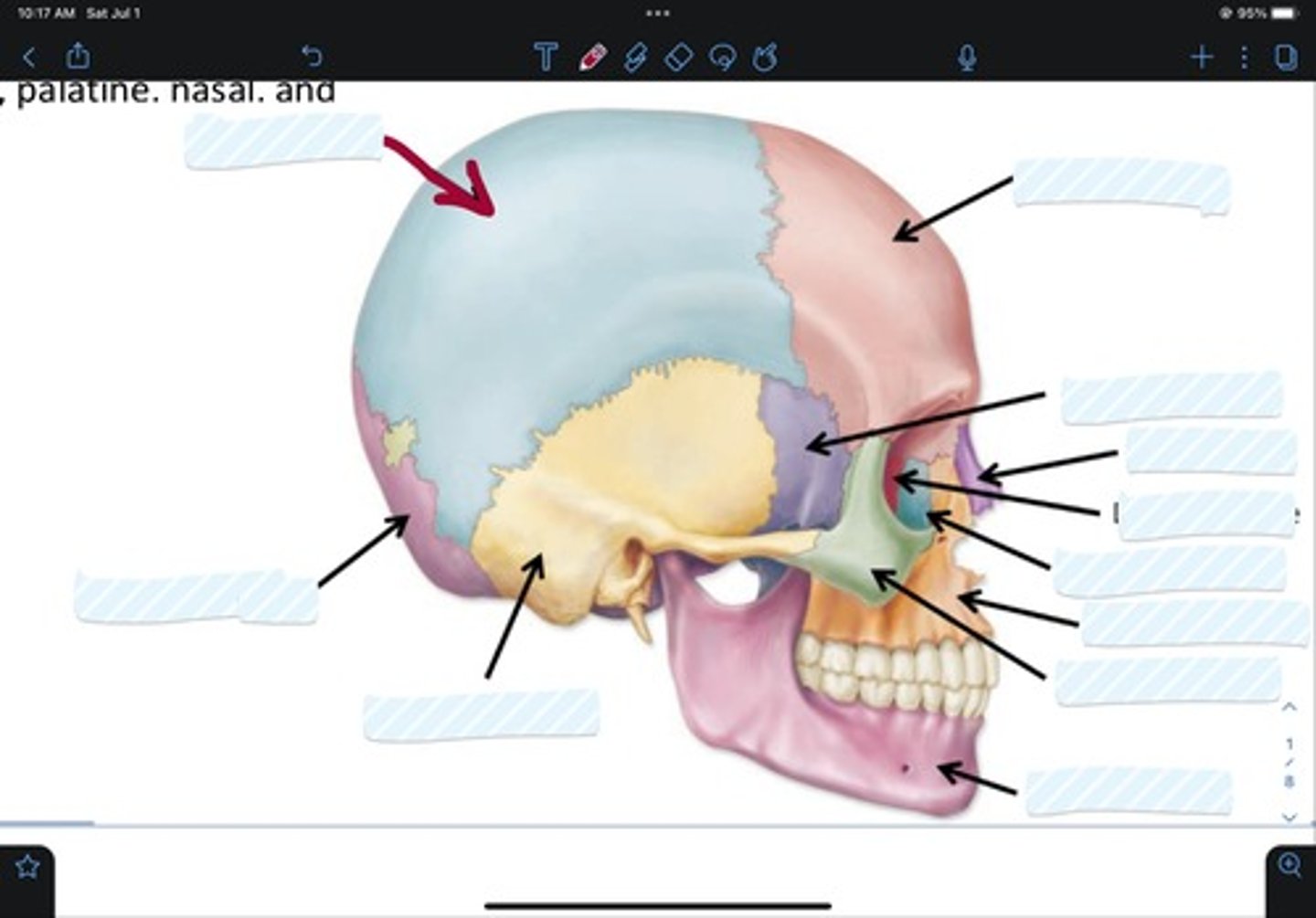
Parietal bone
Parietal bone
Sphenoid bone
Occipital bone
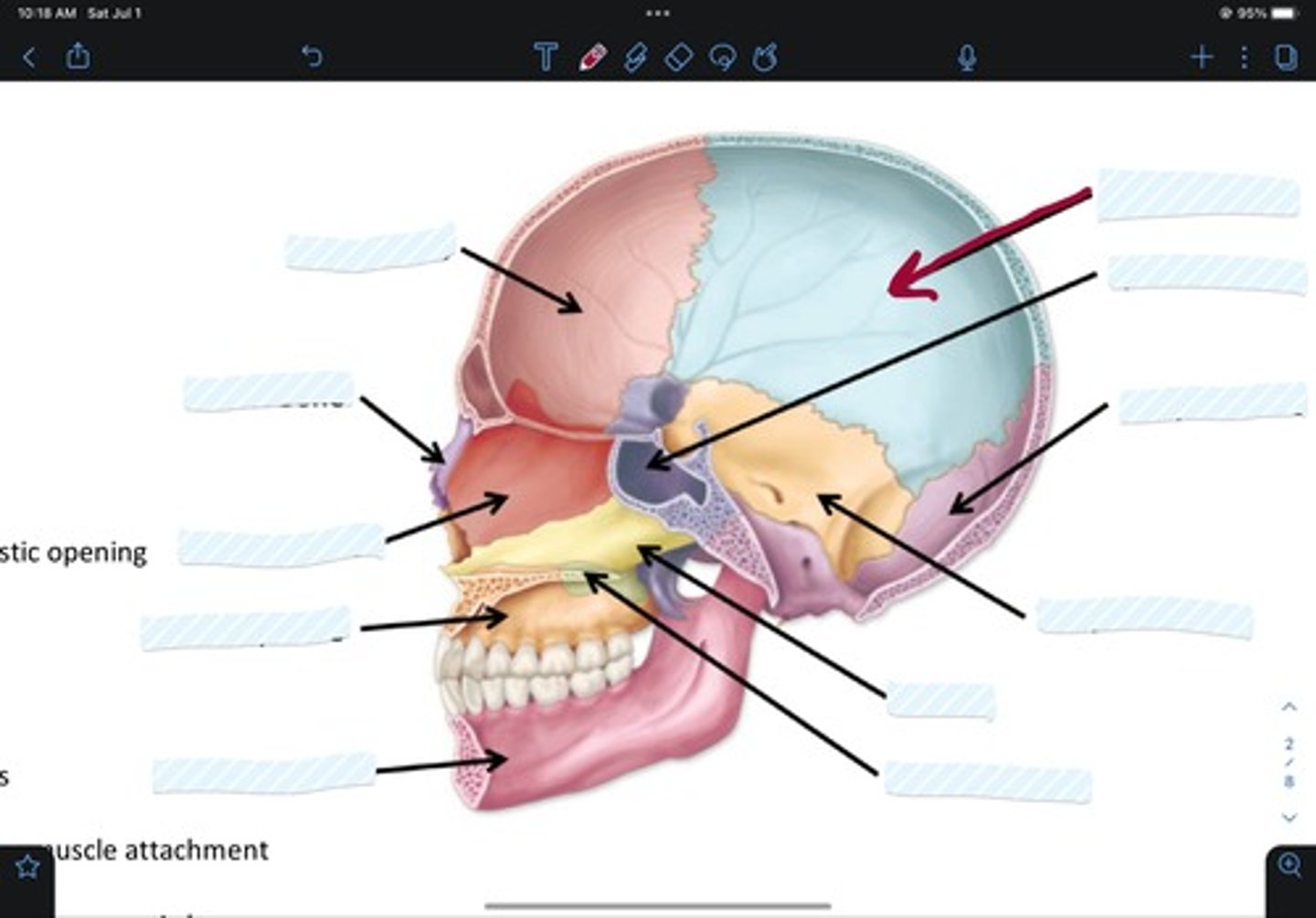
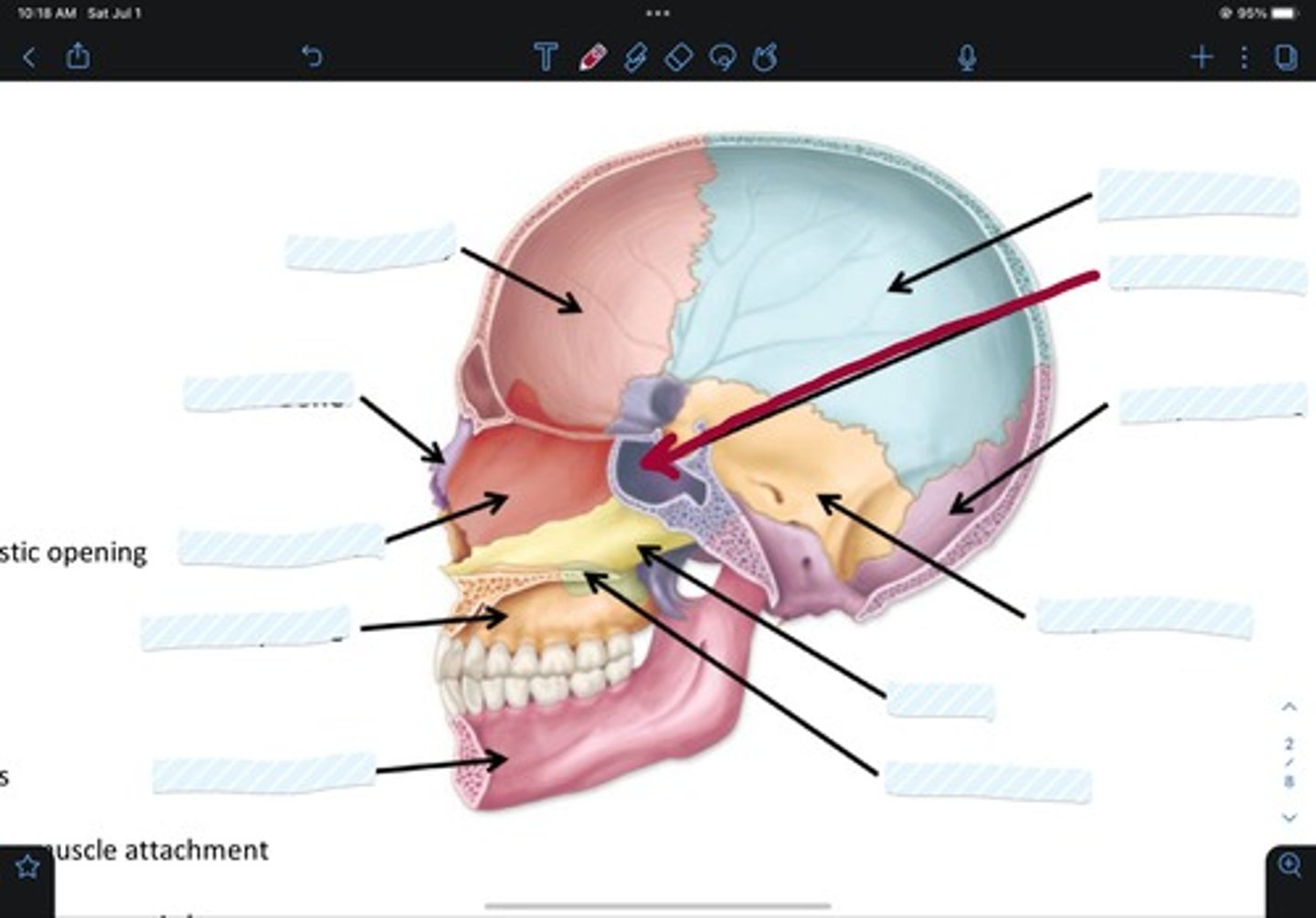
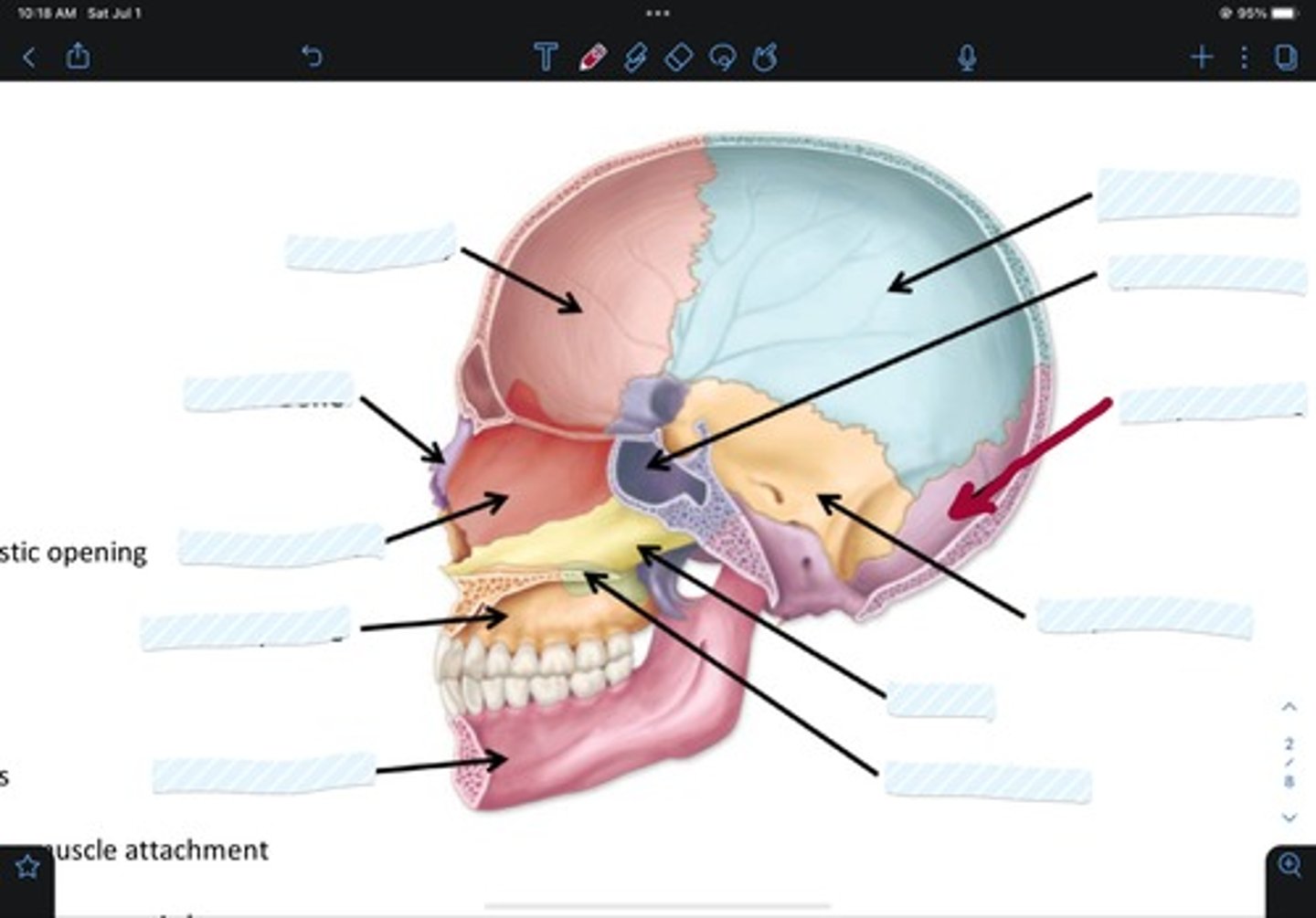
Temporal bone
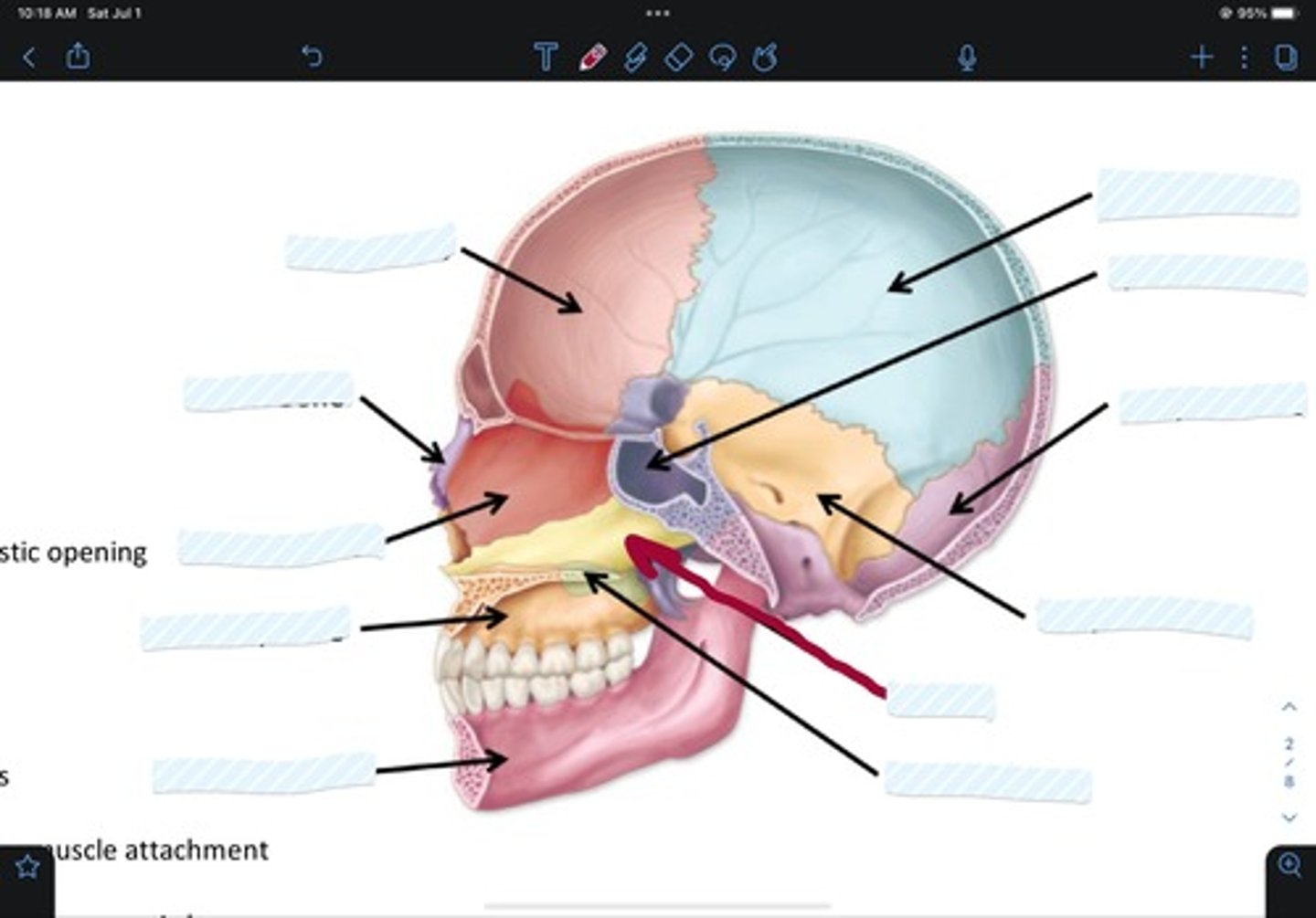
Vomer
Palatine bone
Mandible bone
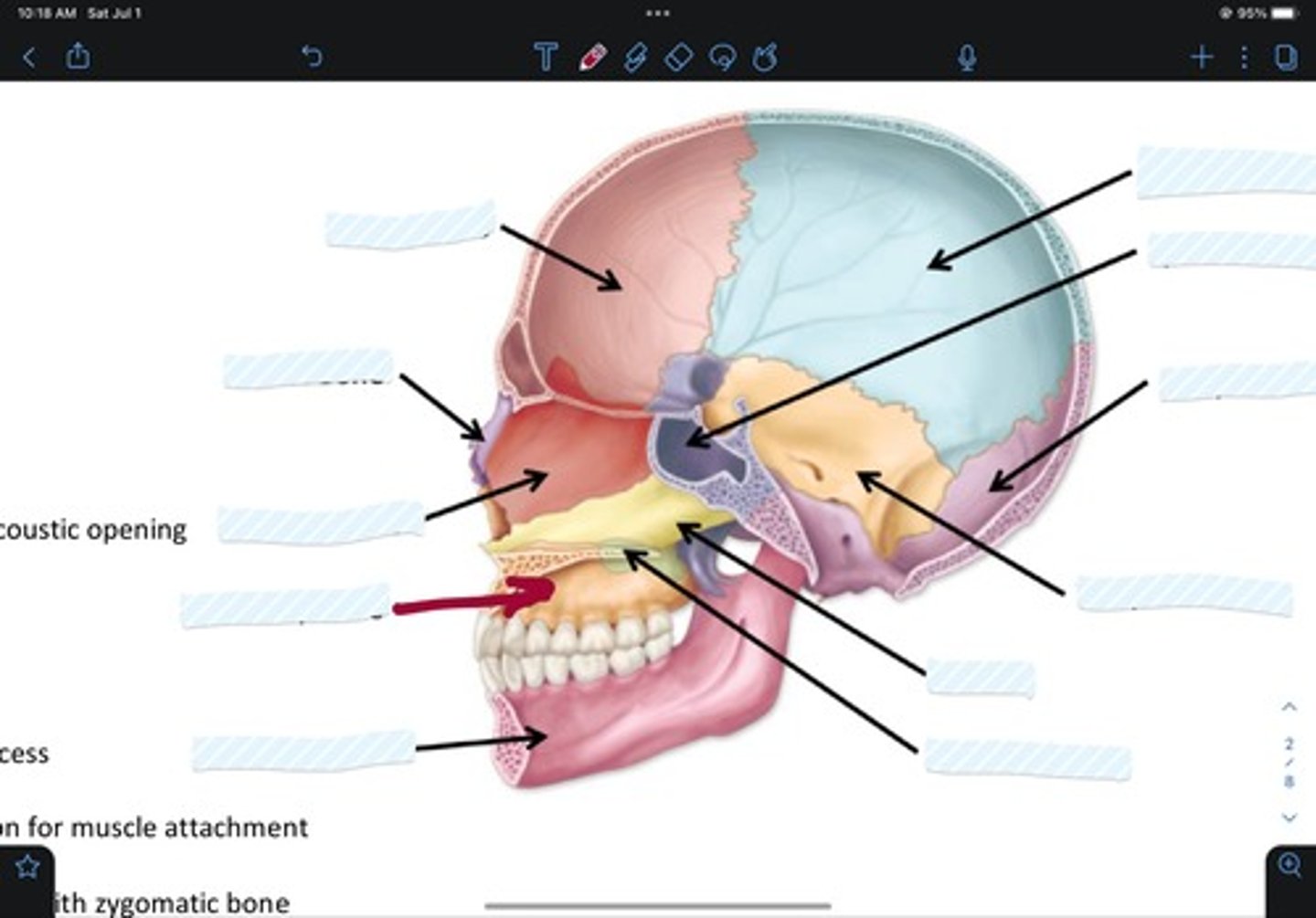
Maxillary bone
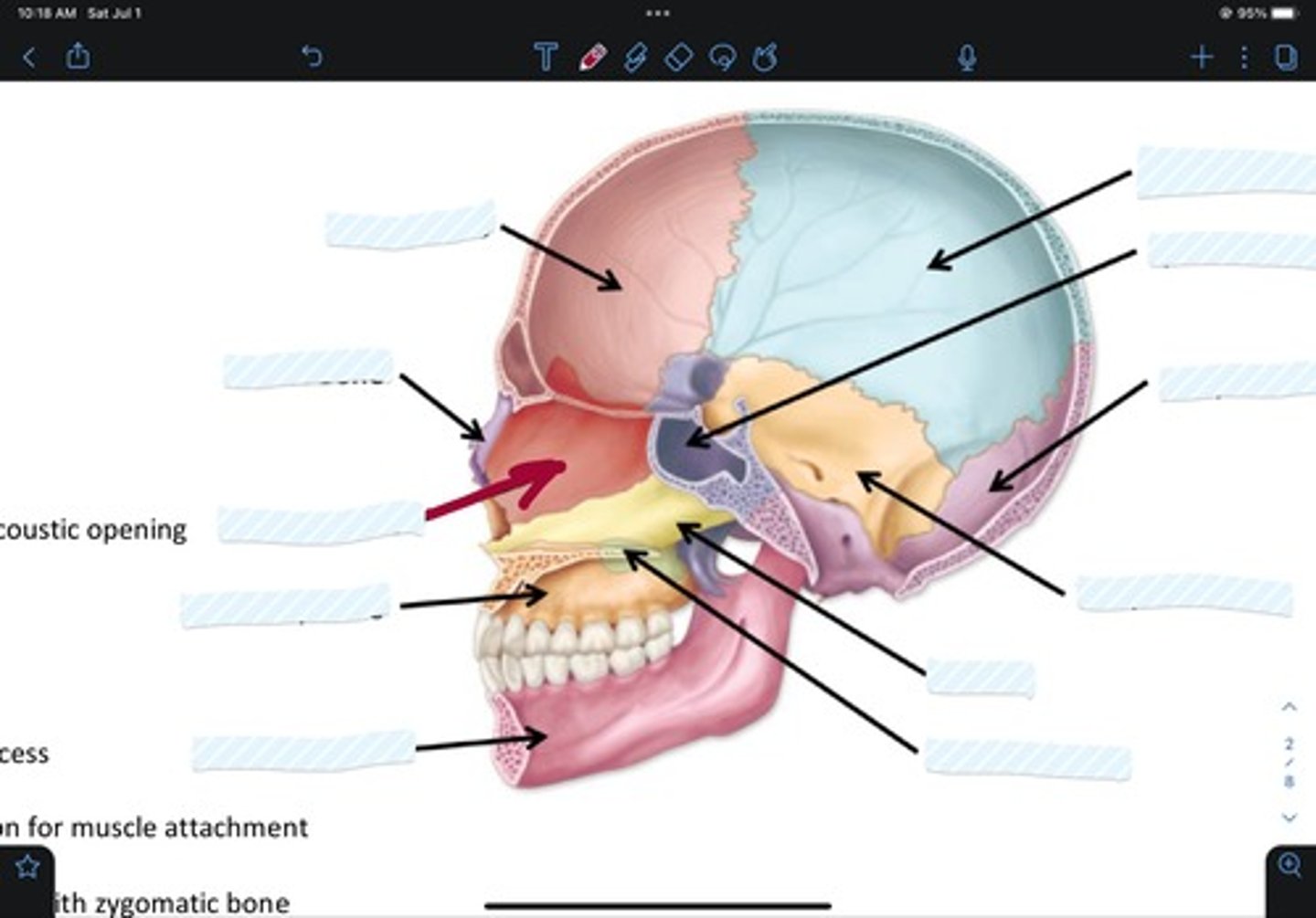
Ethmoid bone
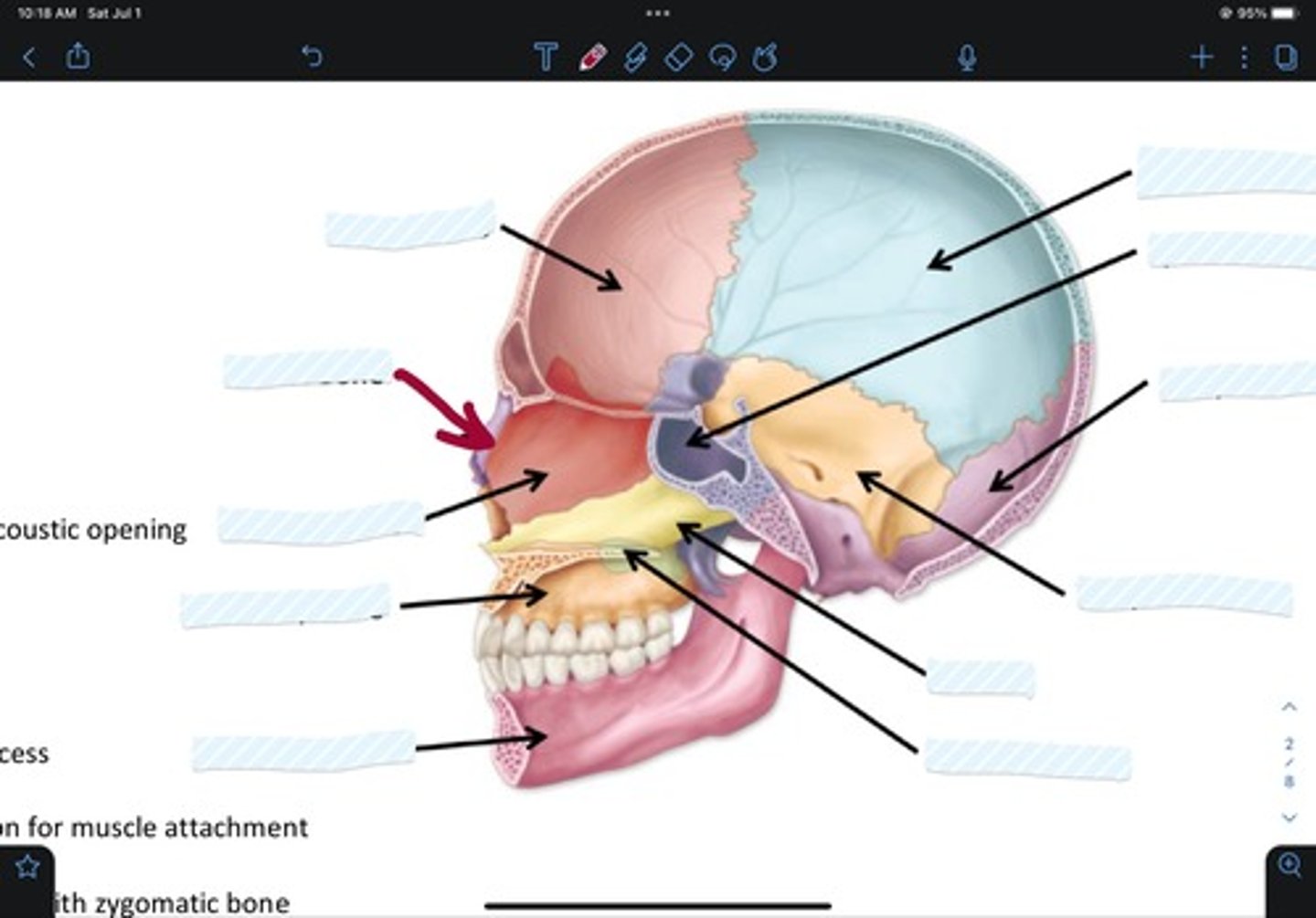
Nasal bone
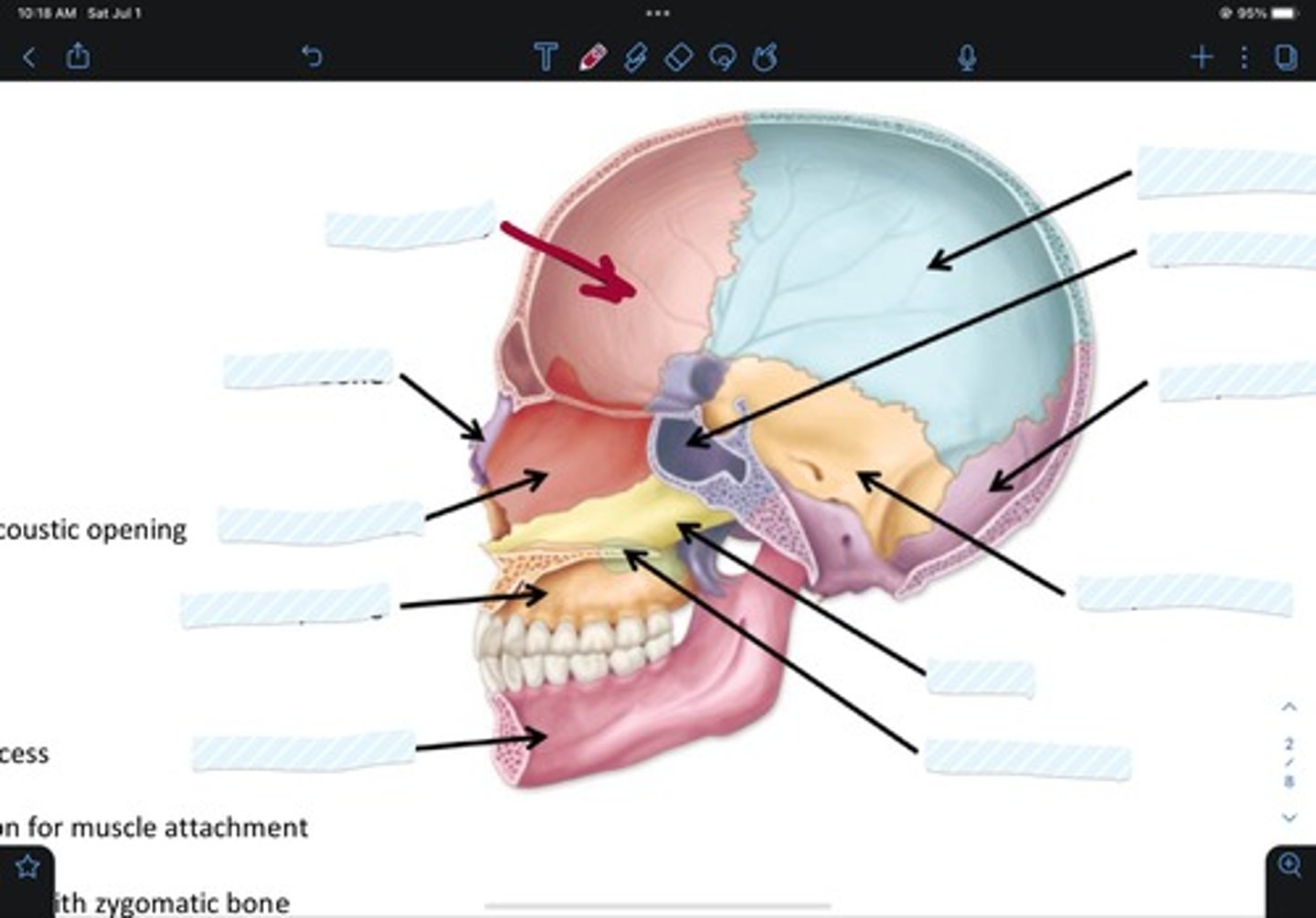
Frontal bone
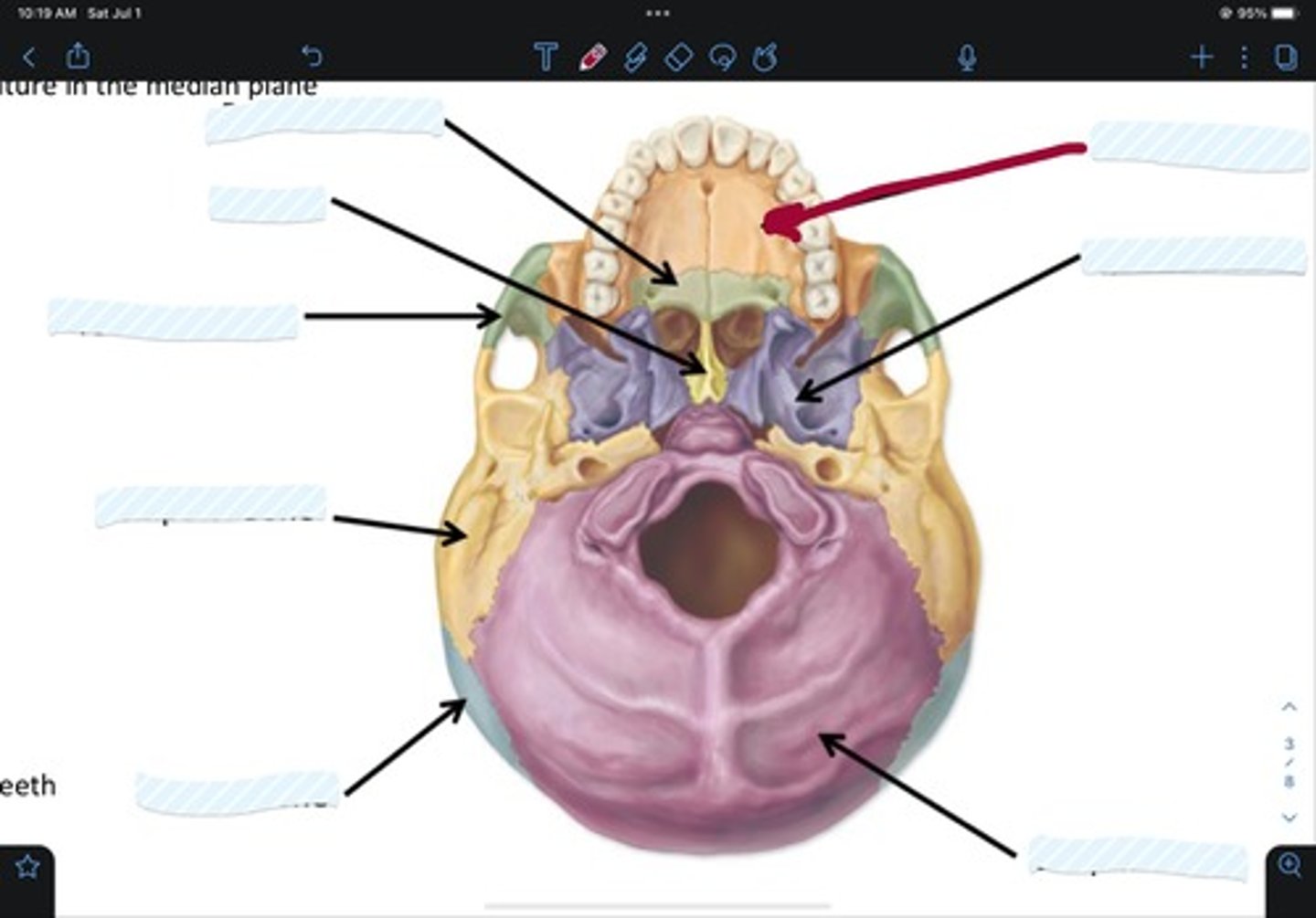
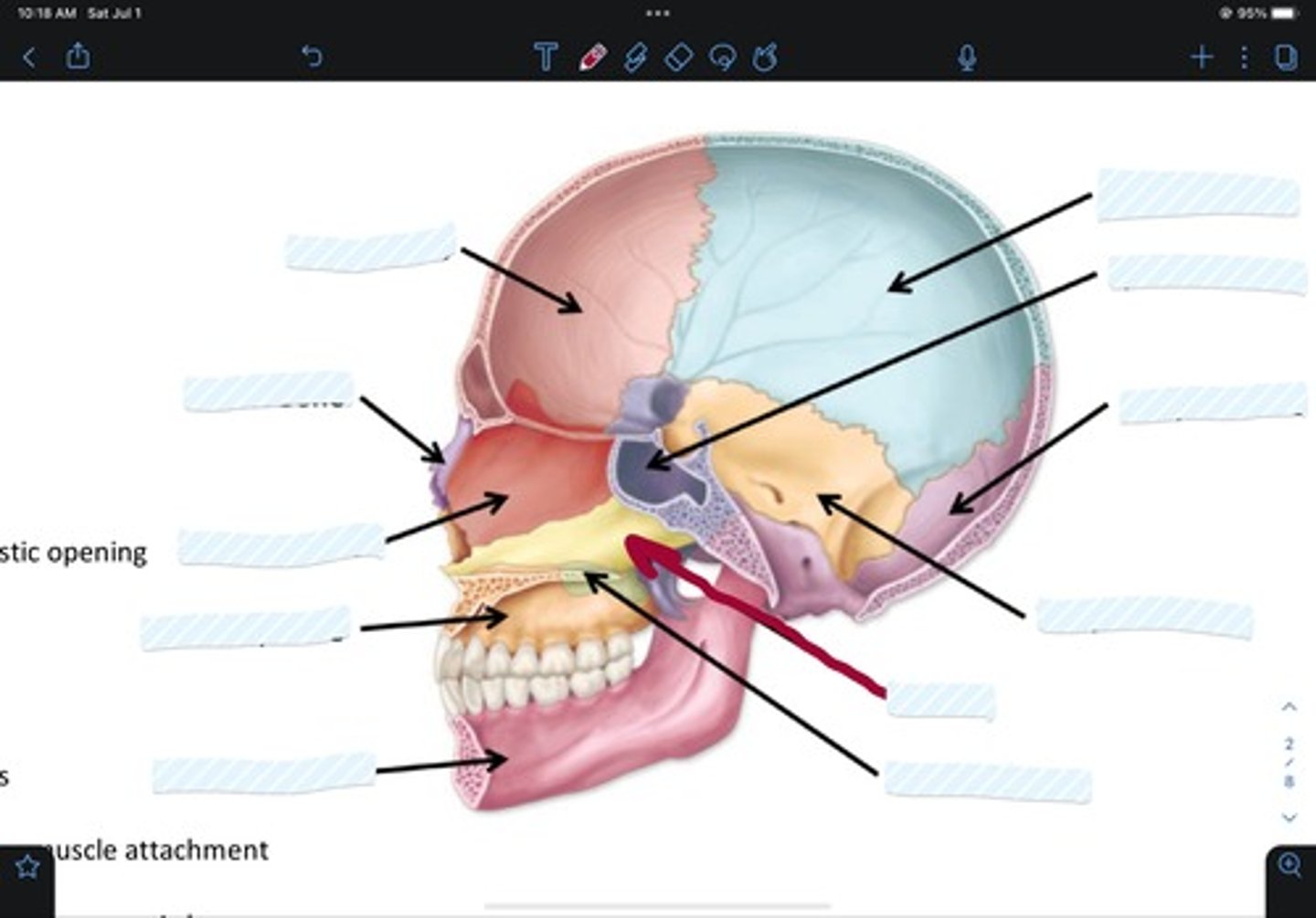
Maxillary bone
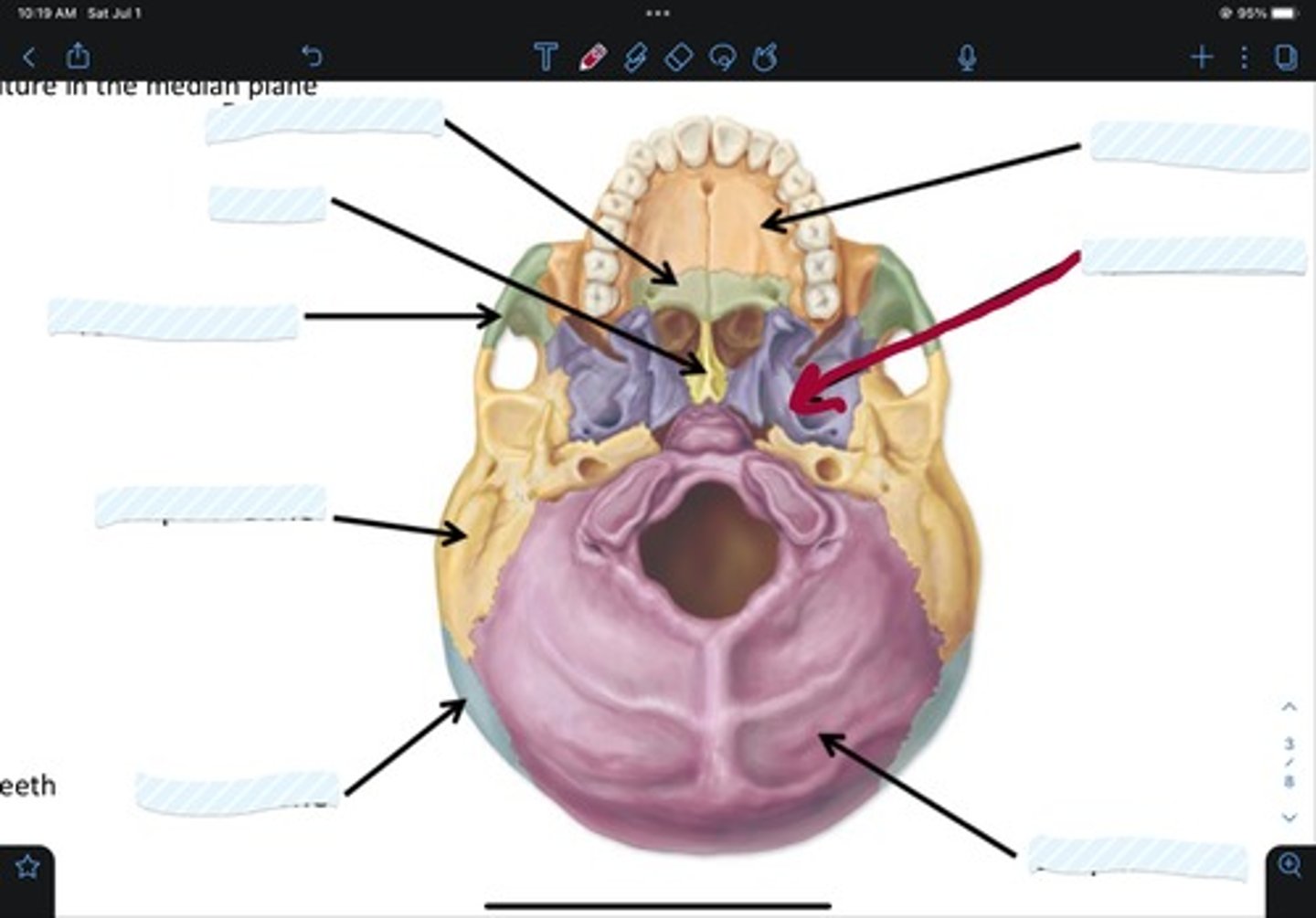
Sphenoid bone
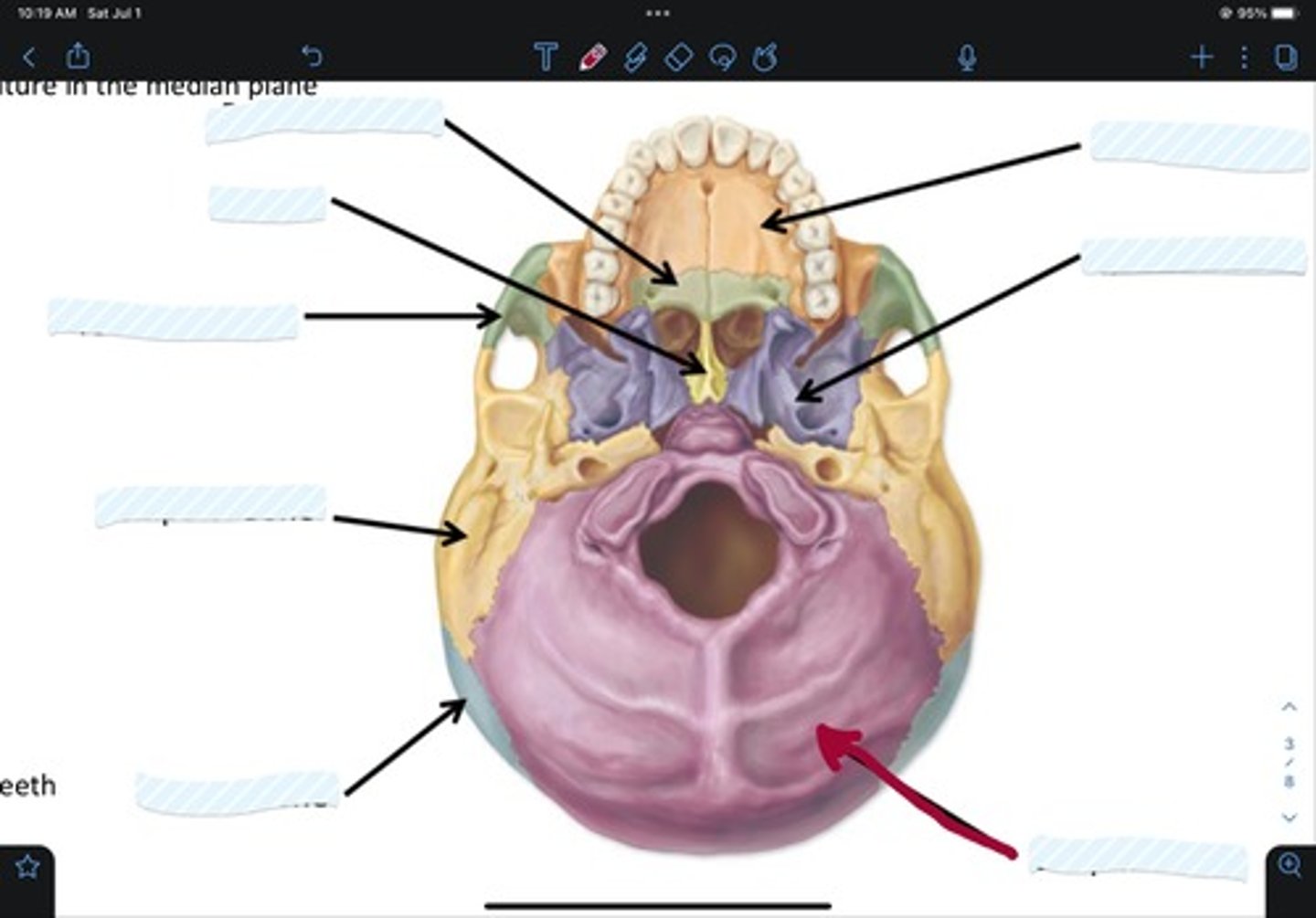
Occipital bone
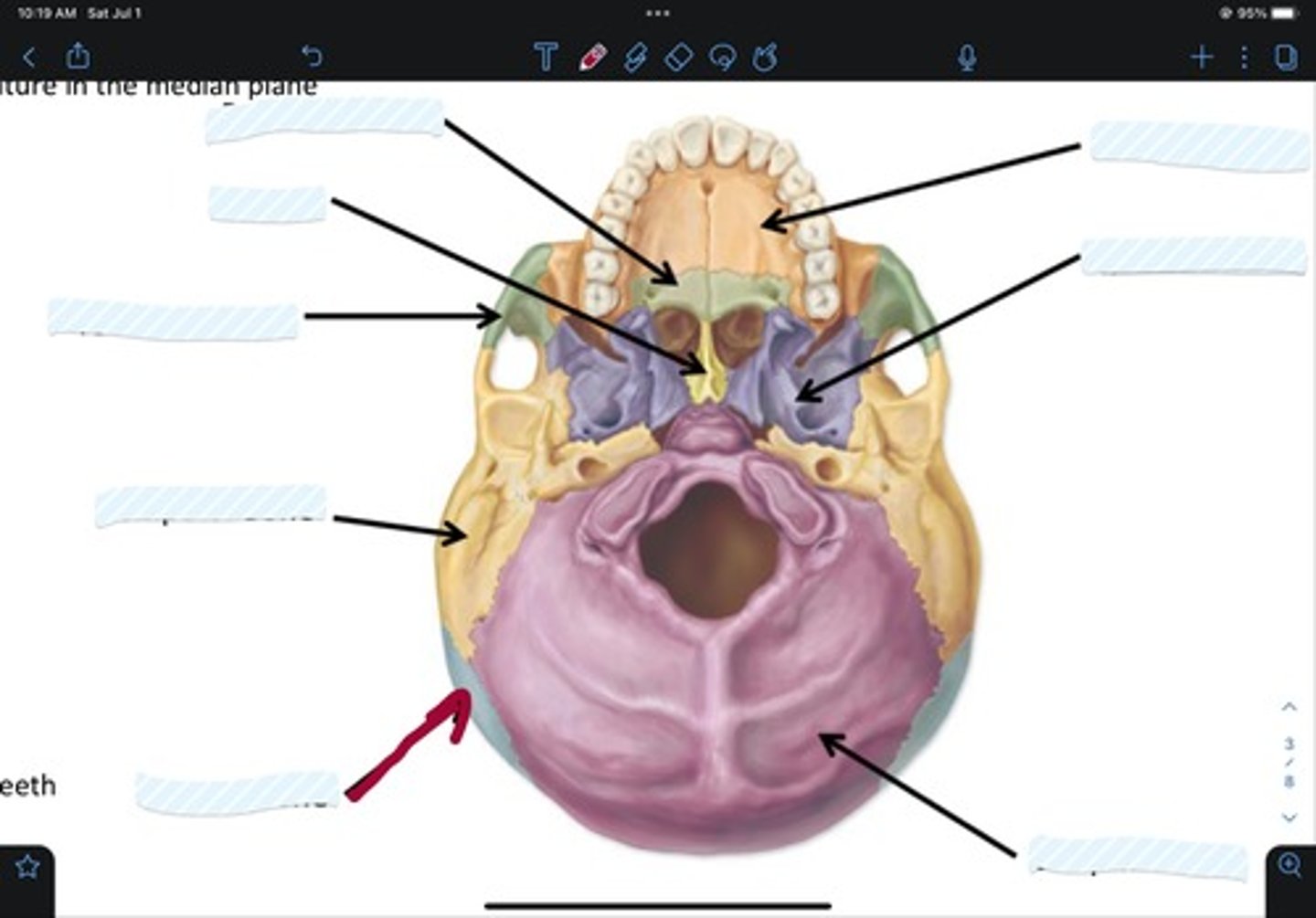
Parietal bone
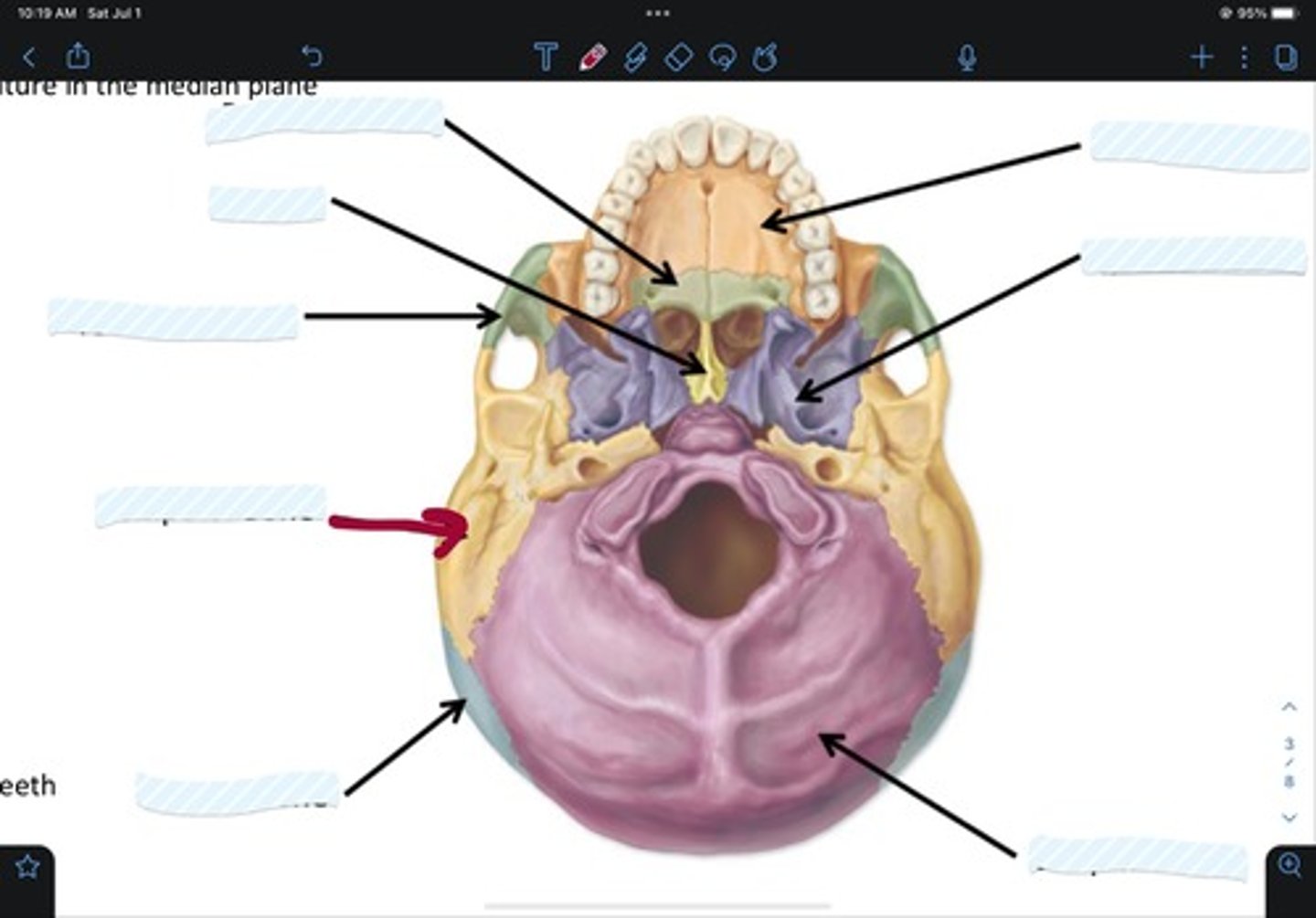
Temporal bone
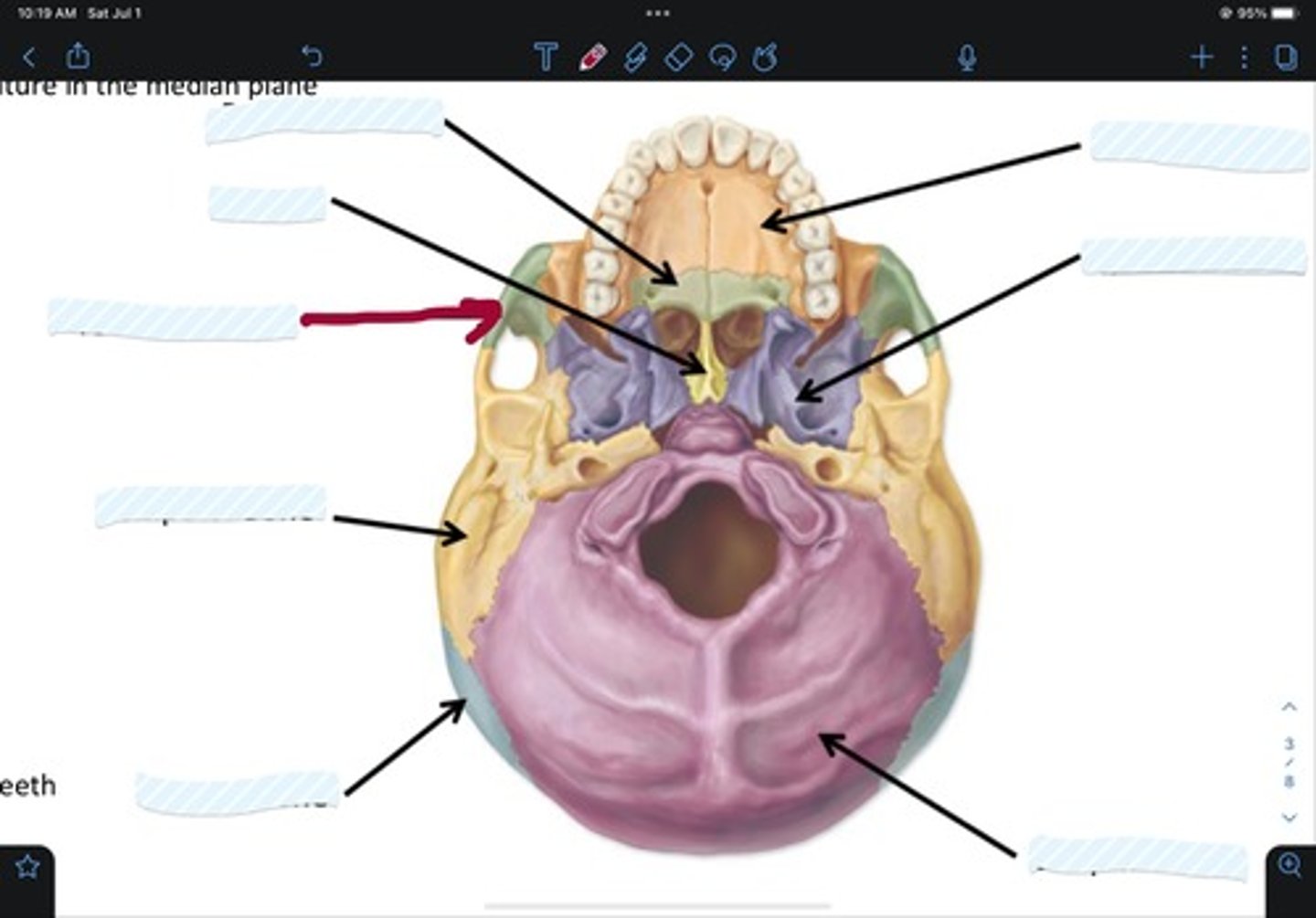
Zygomatic bone
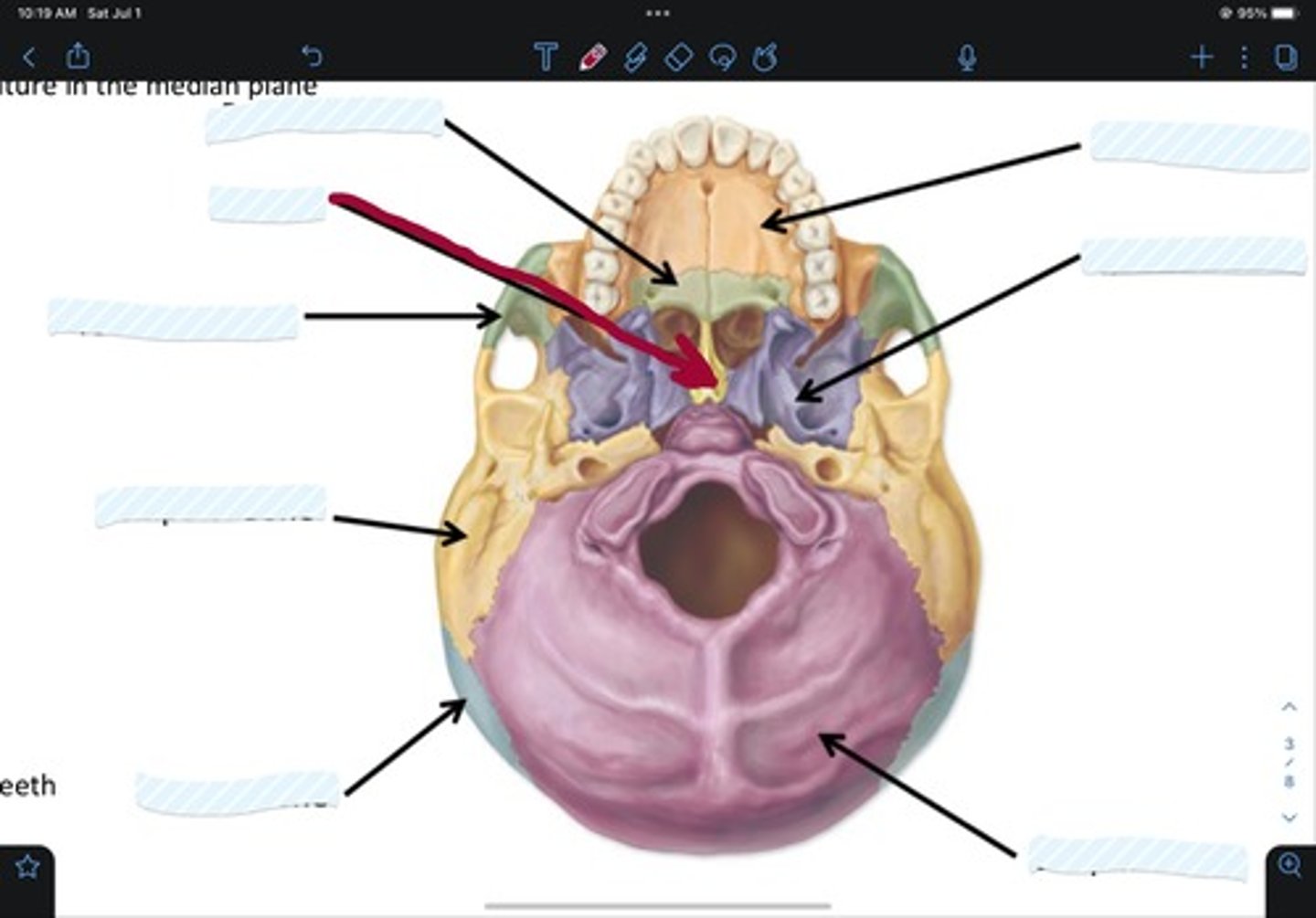
Vomer
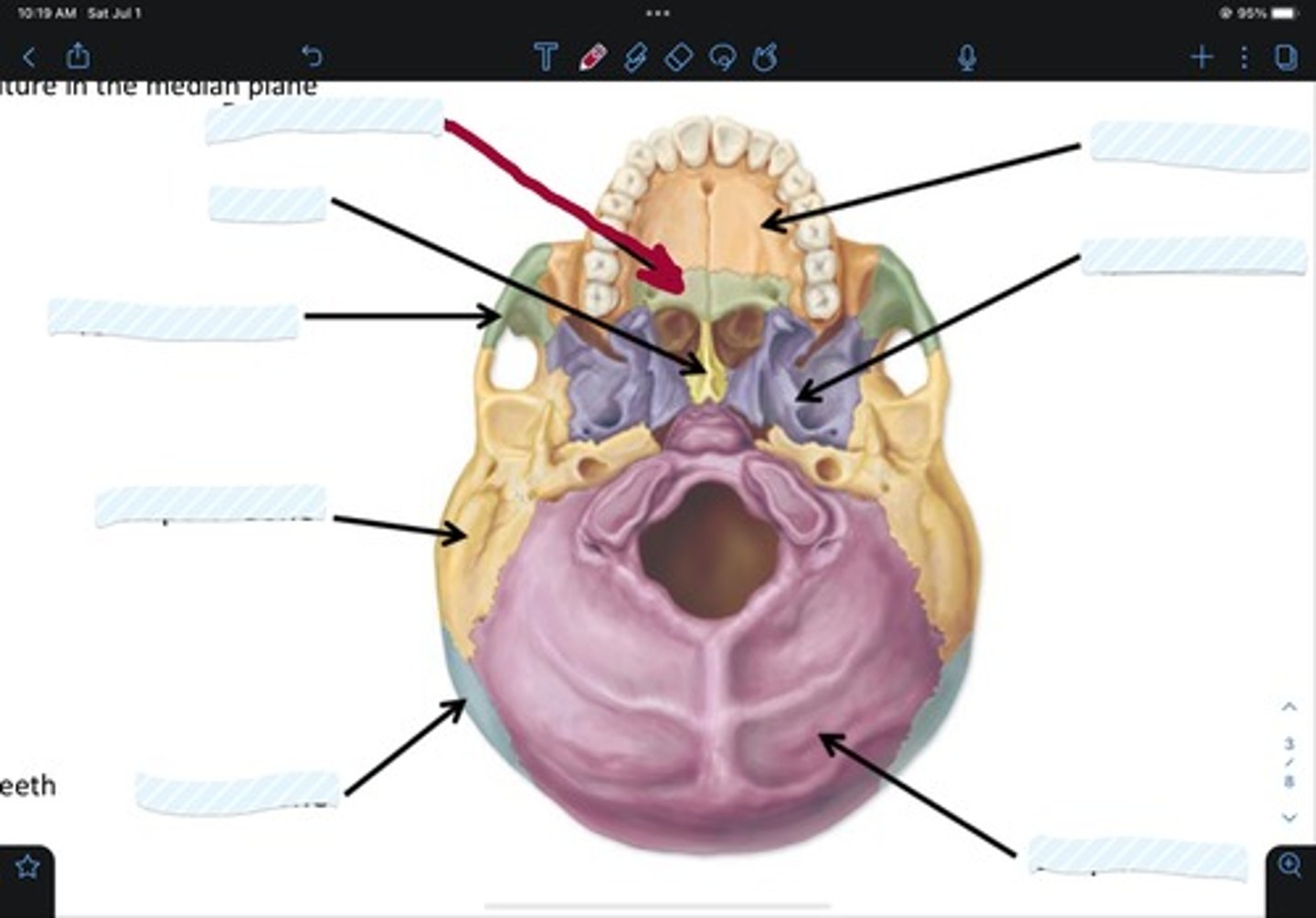
Palatine bone
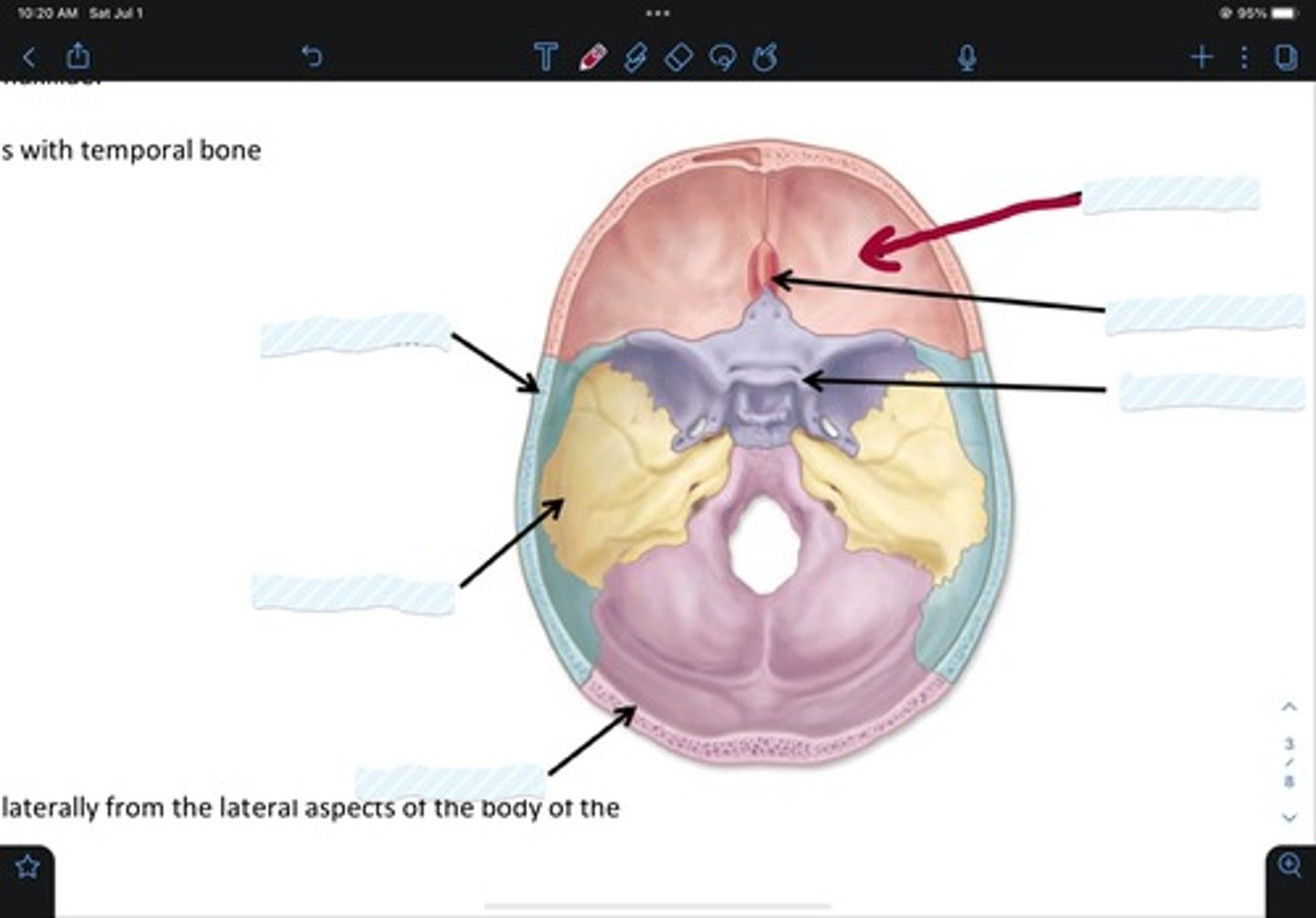
Frontal bone
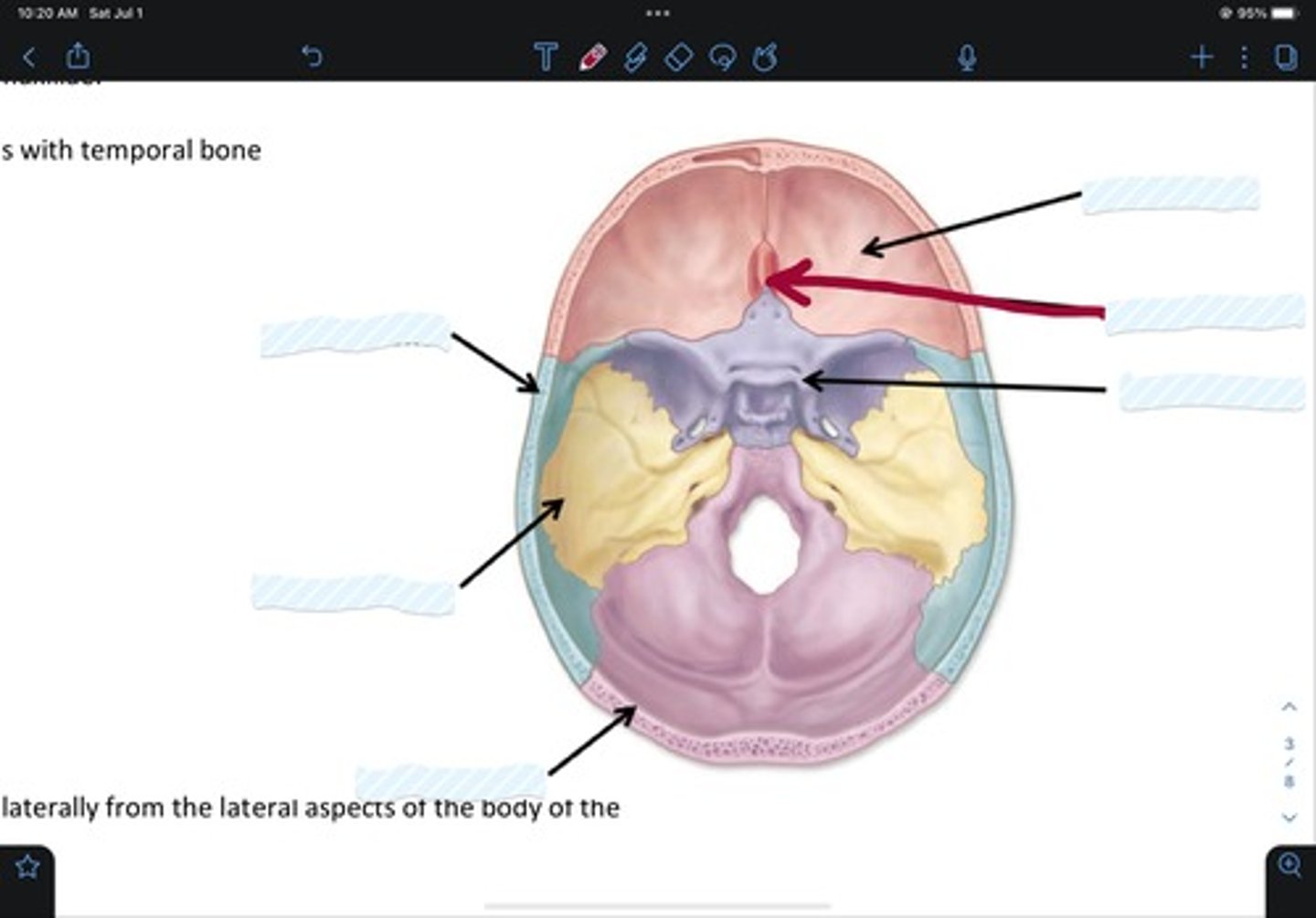
Ethmoid bone
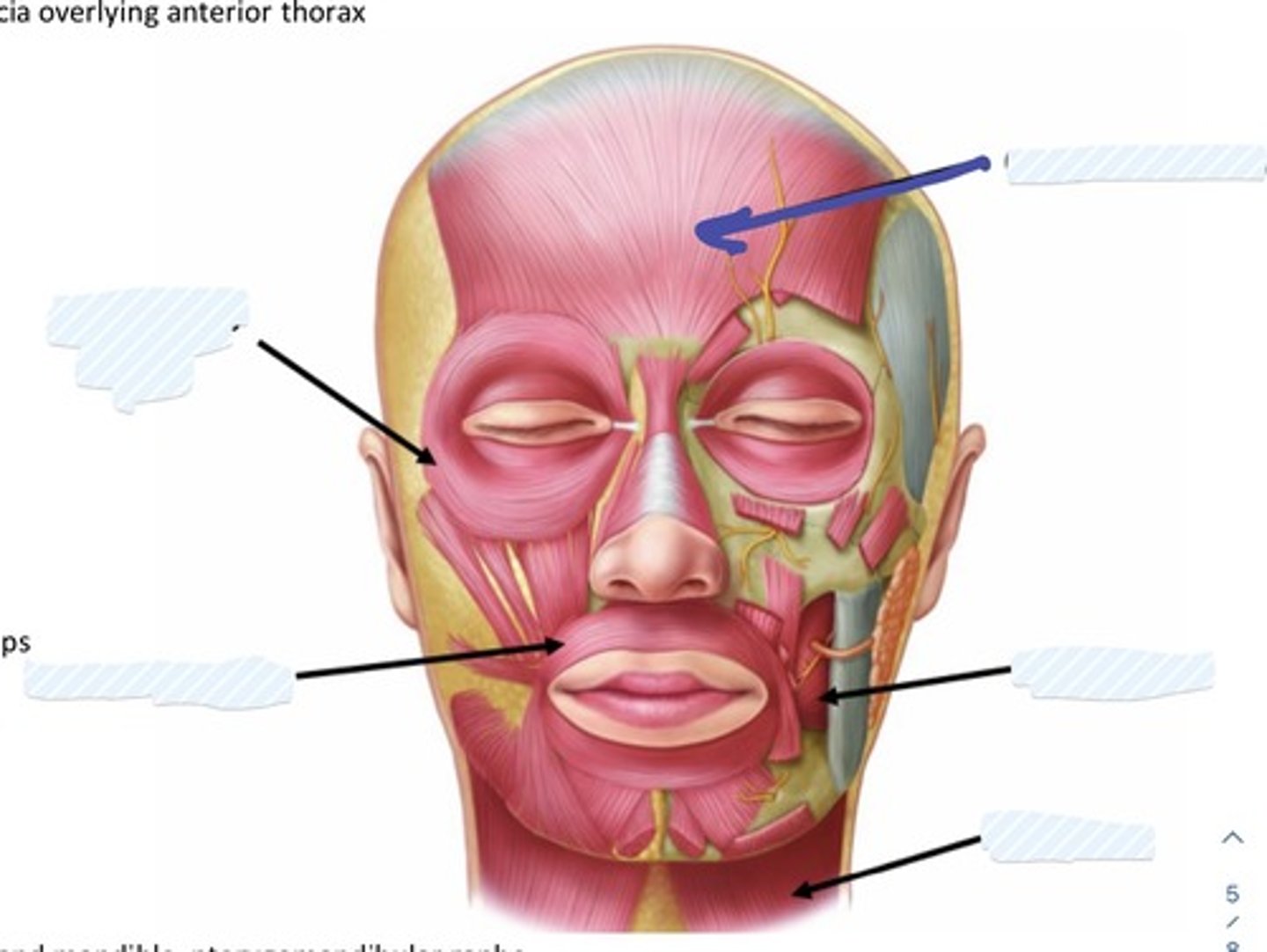
Occipitofrontalis m.
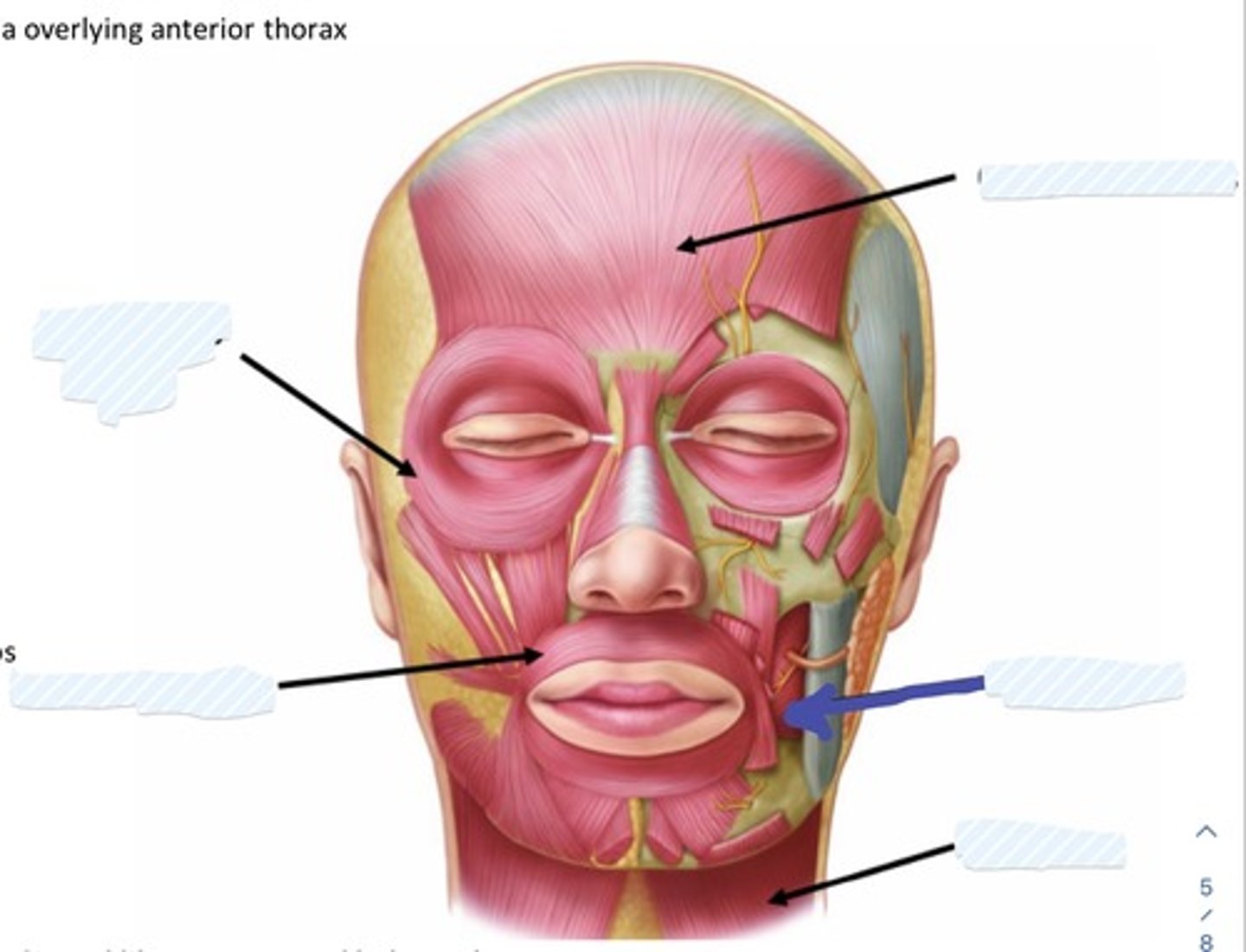
Buccinator m.
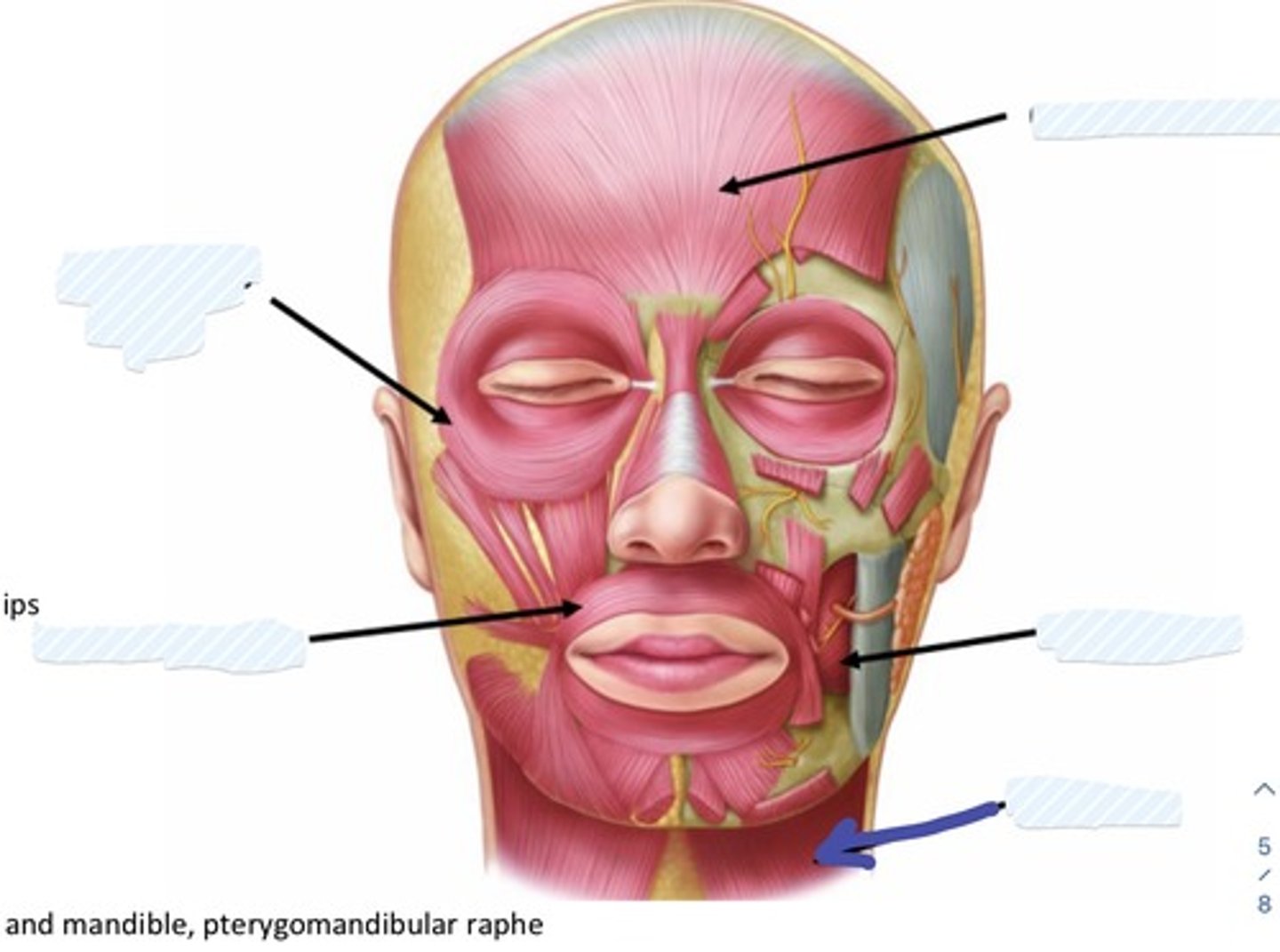
Platysma m.
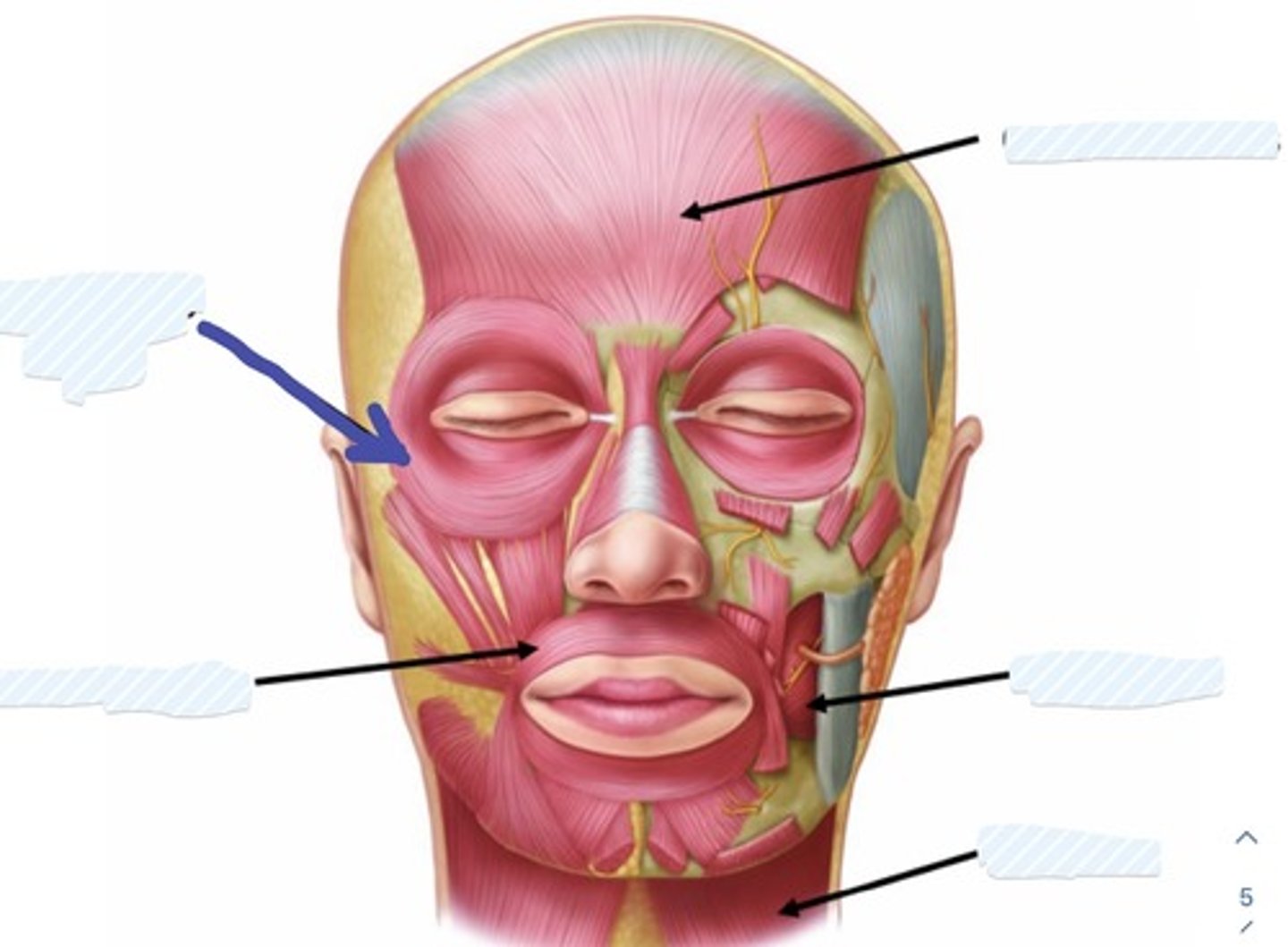
Orbicularis Oculi
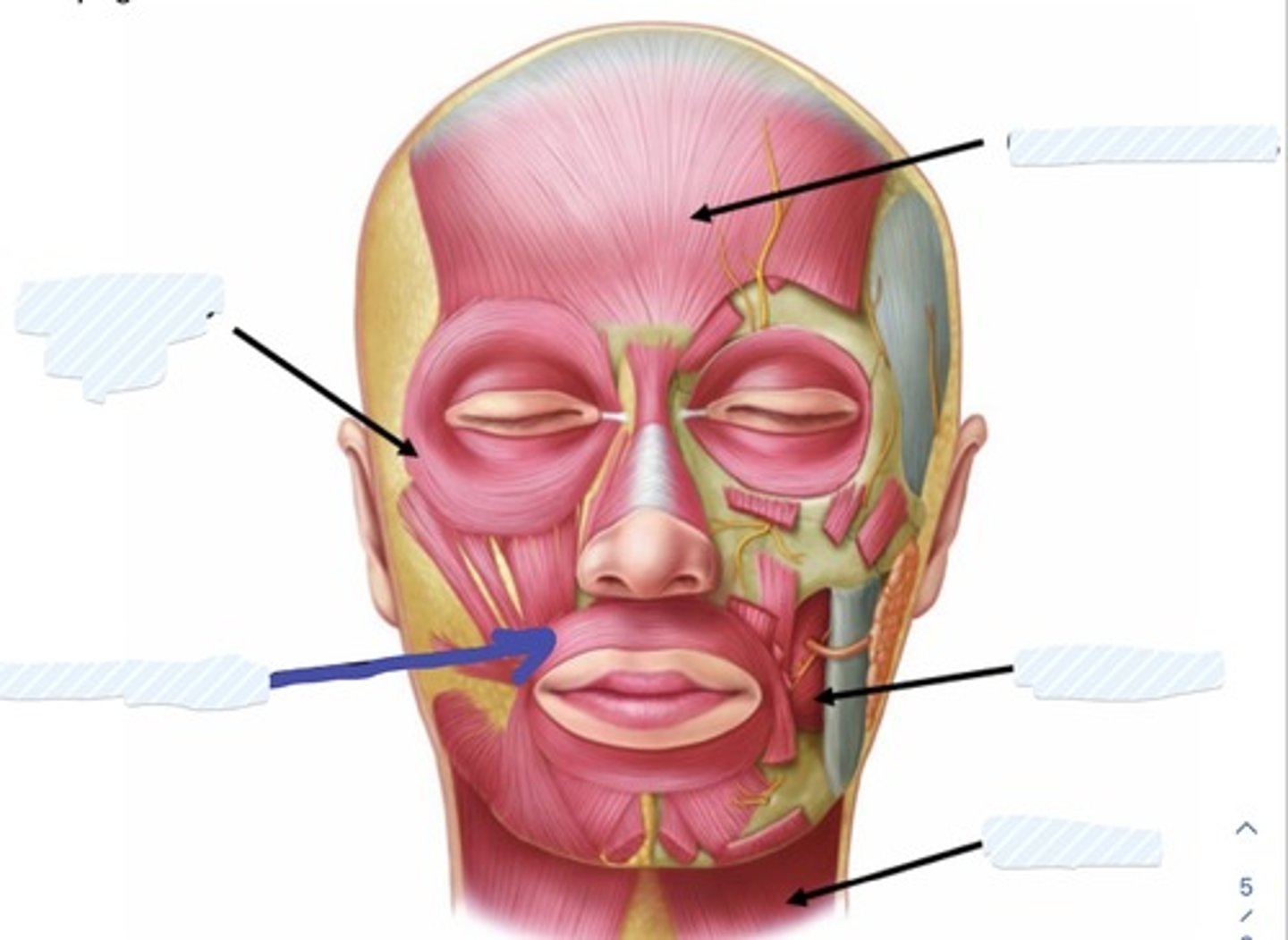
Orbicularis Oris
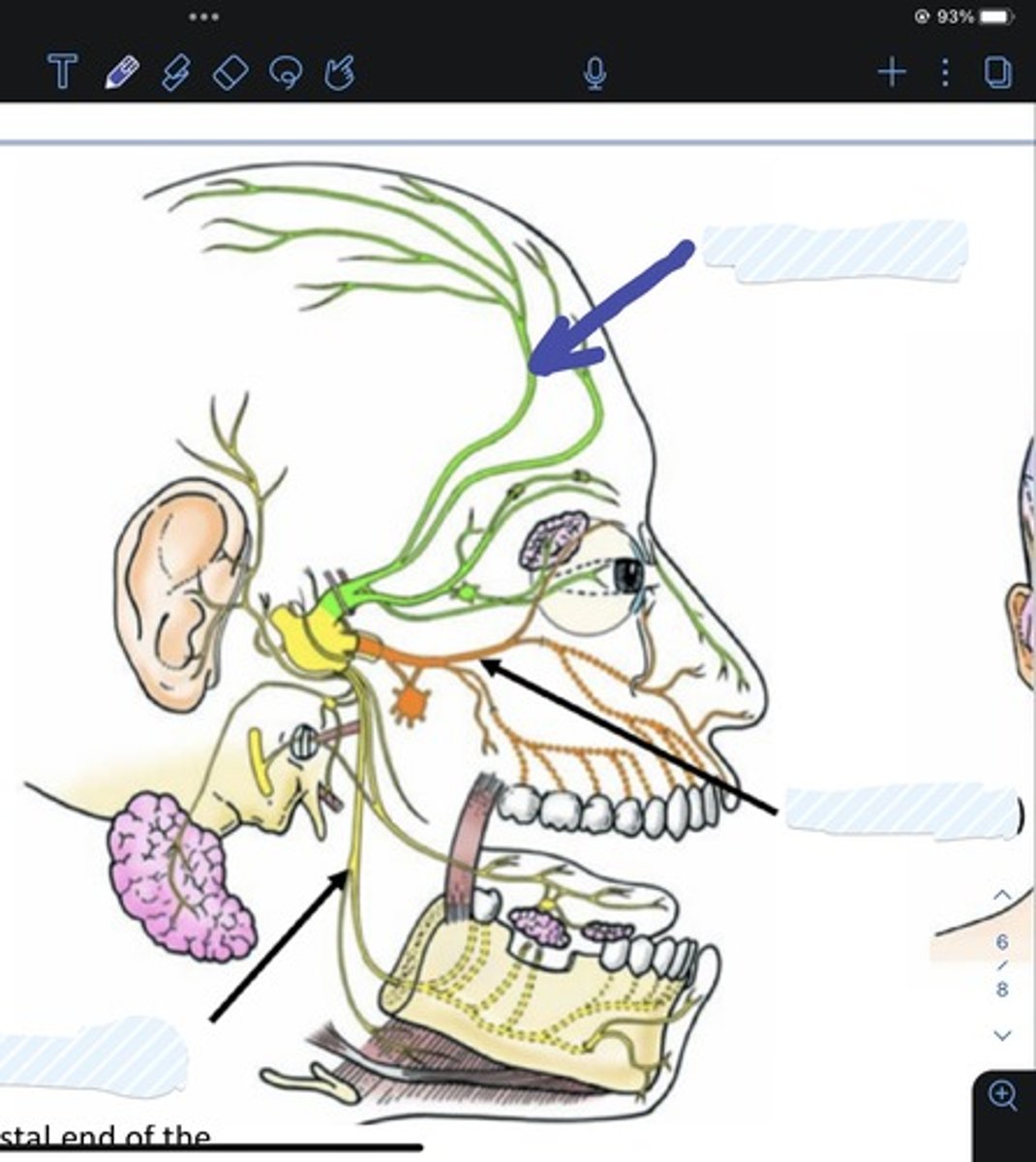
Ophthalmic (V1) (division of trigeminal nerve V)
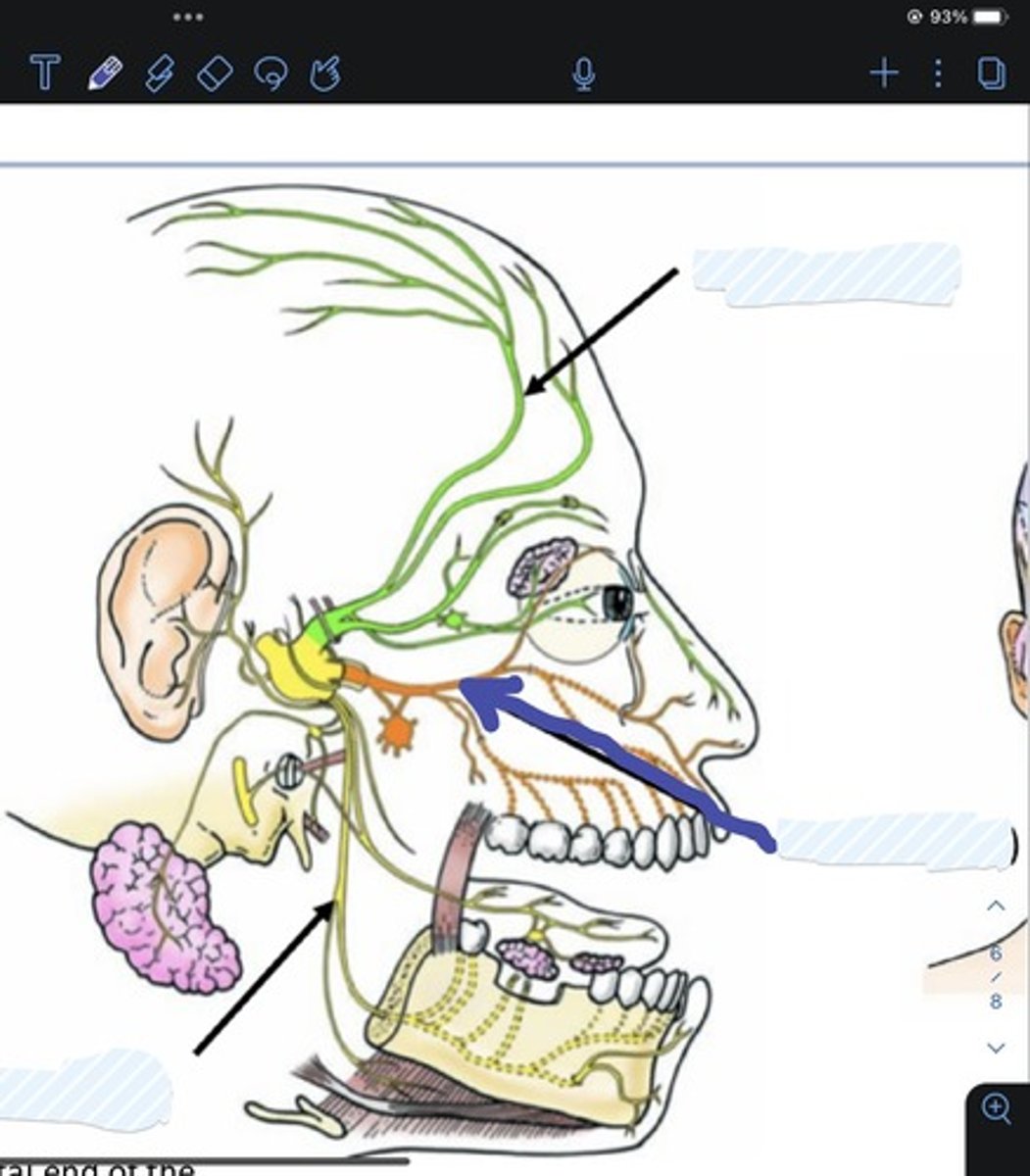
Maxillary (V2) (division of trigeminal nerve V)
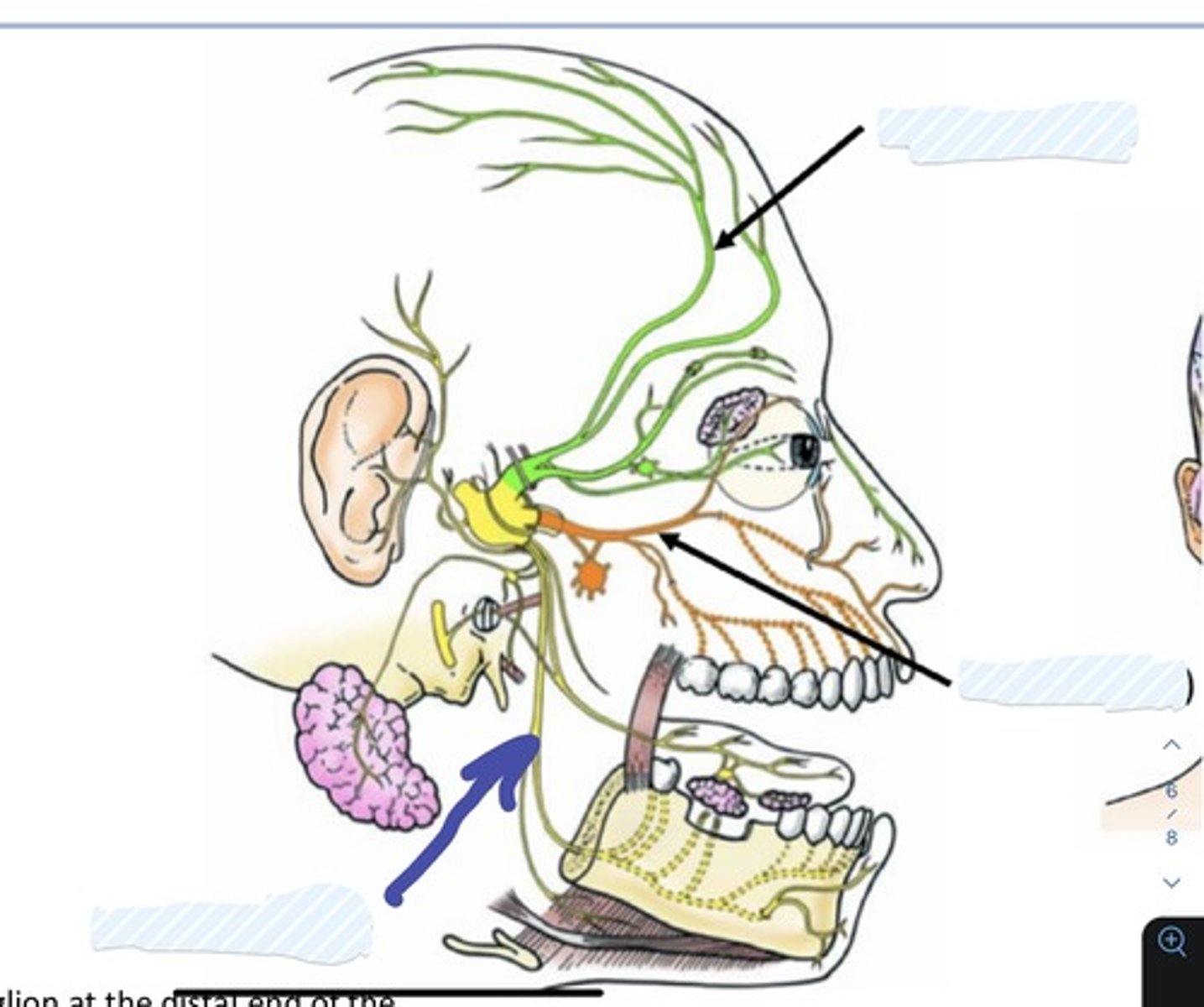
Mandibular (V3) division of trigeminal nerve
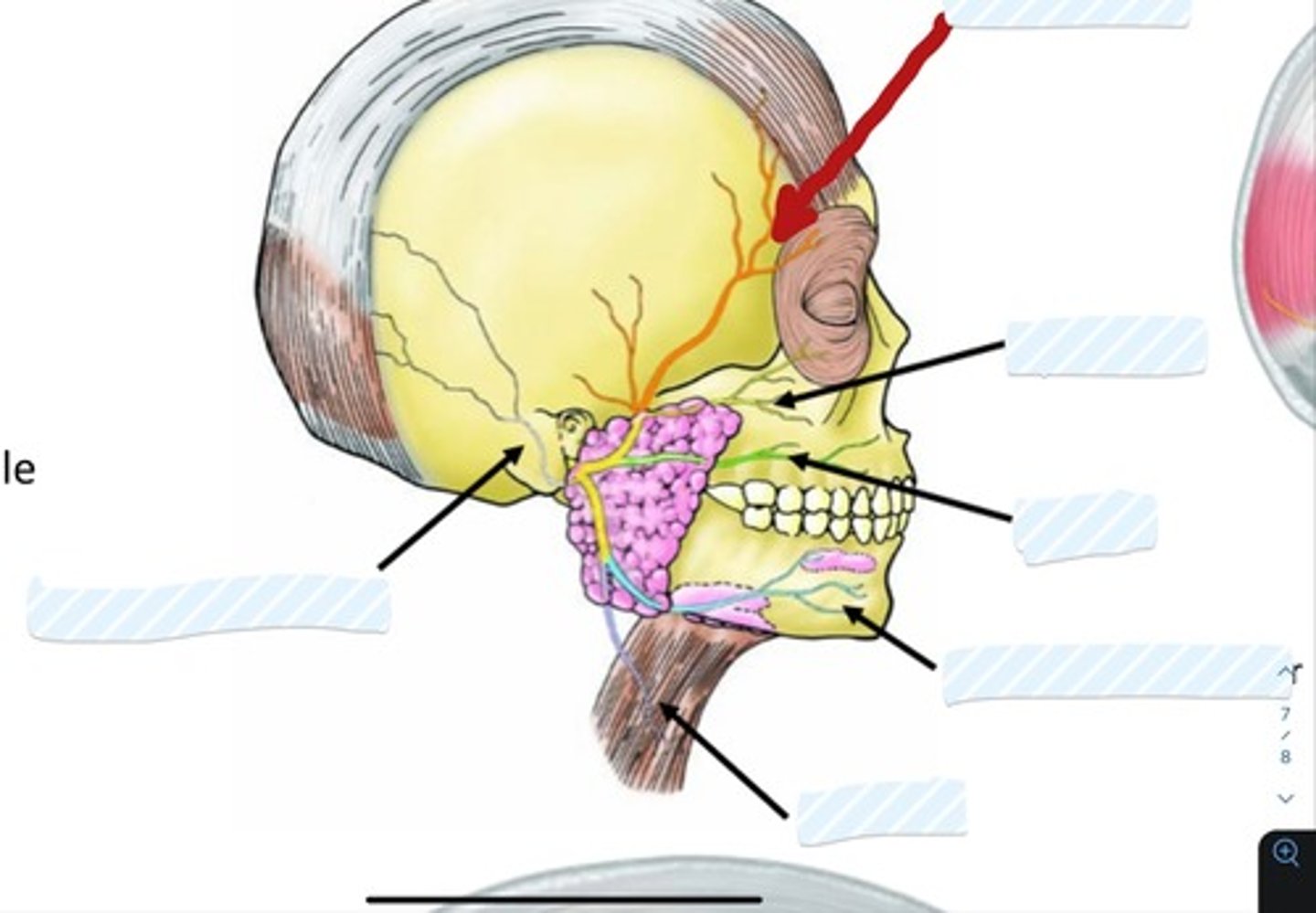
Temporal branch of facial nerve
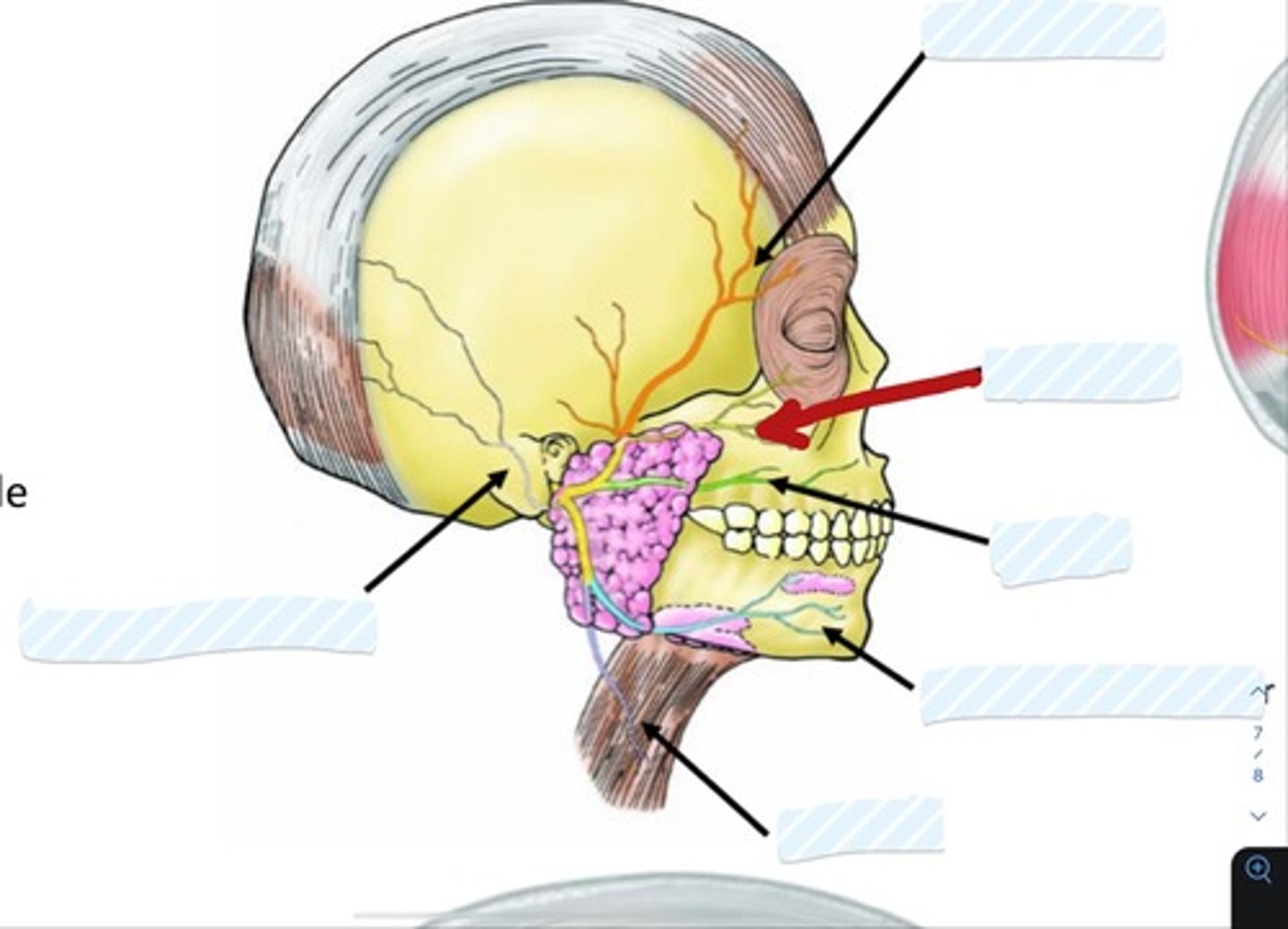
Zygomatic branch of facial nerve
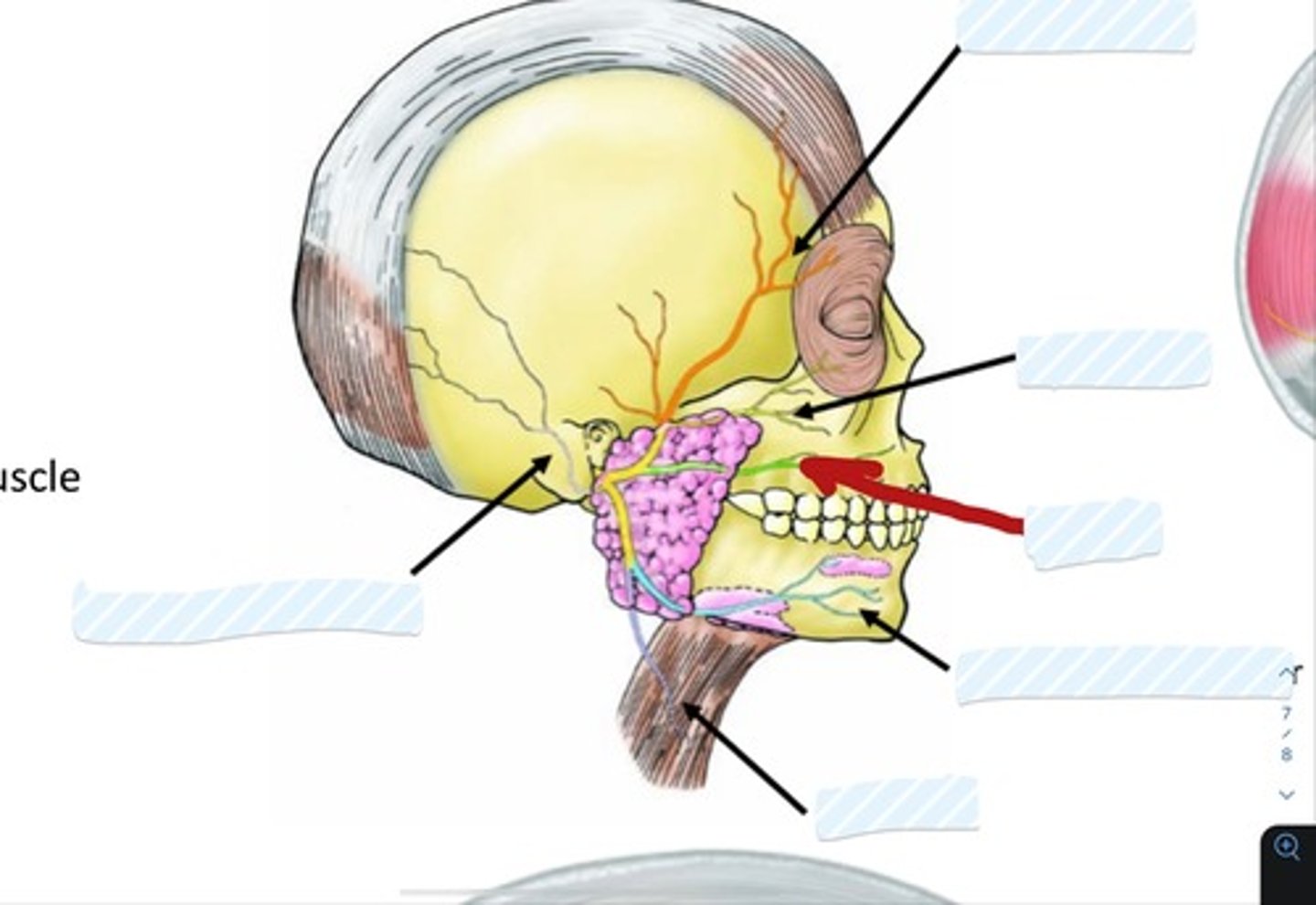
Buccal branch of facial nerve
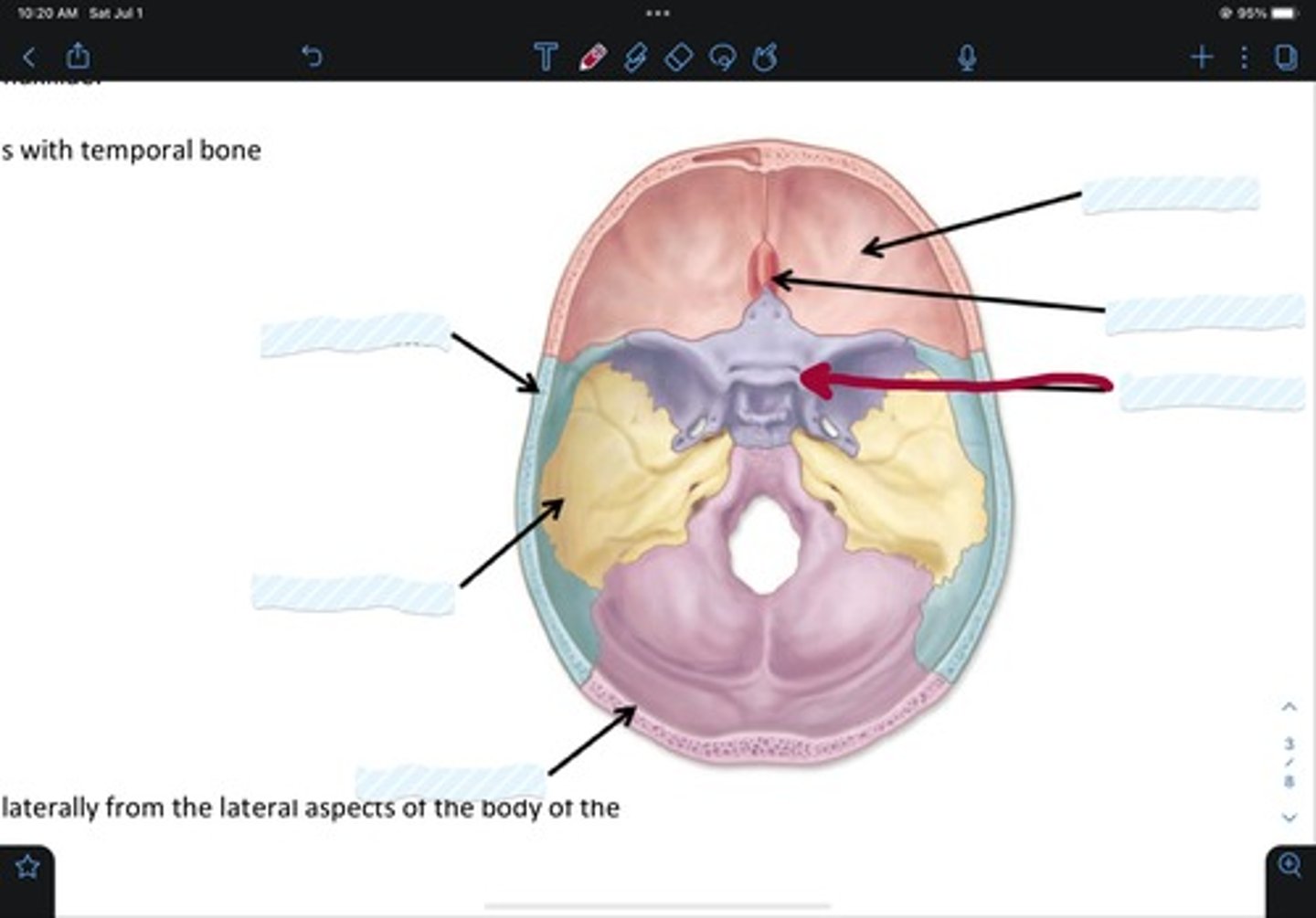
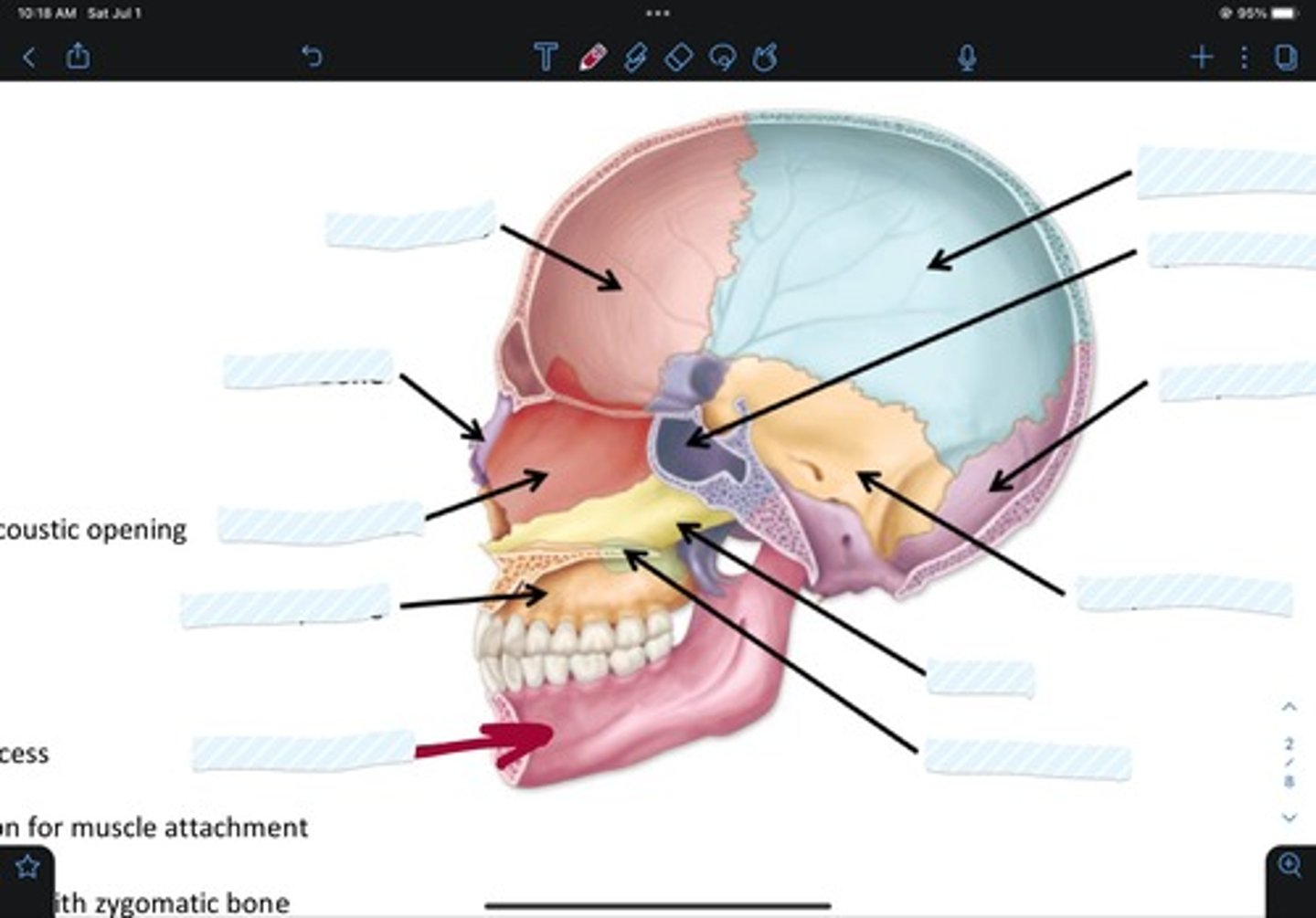
Sphenoid bone
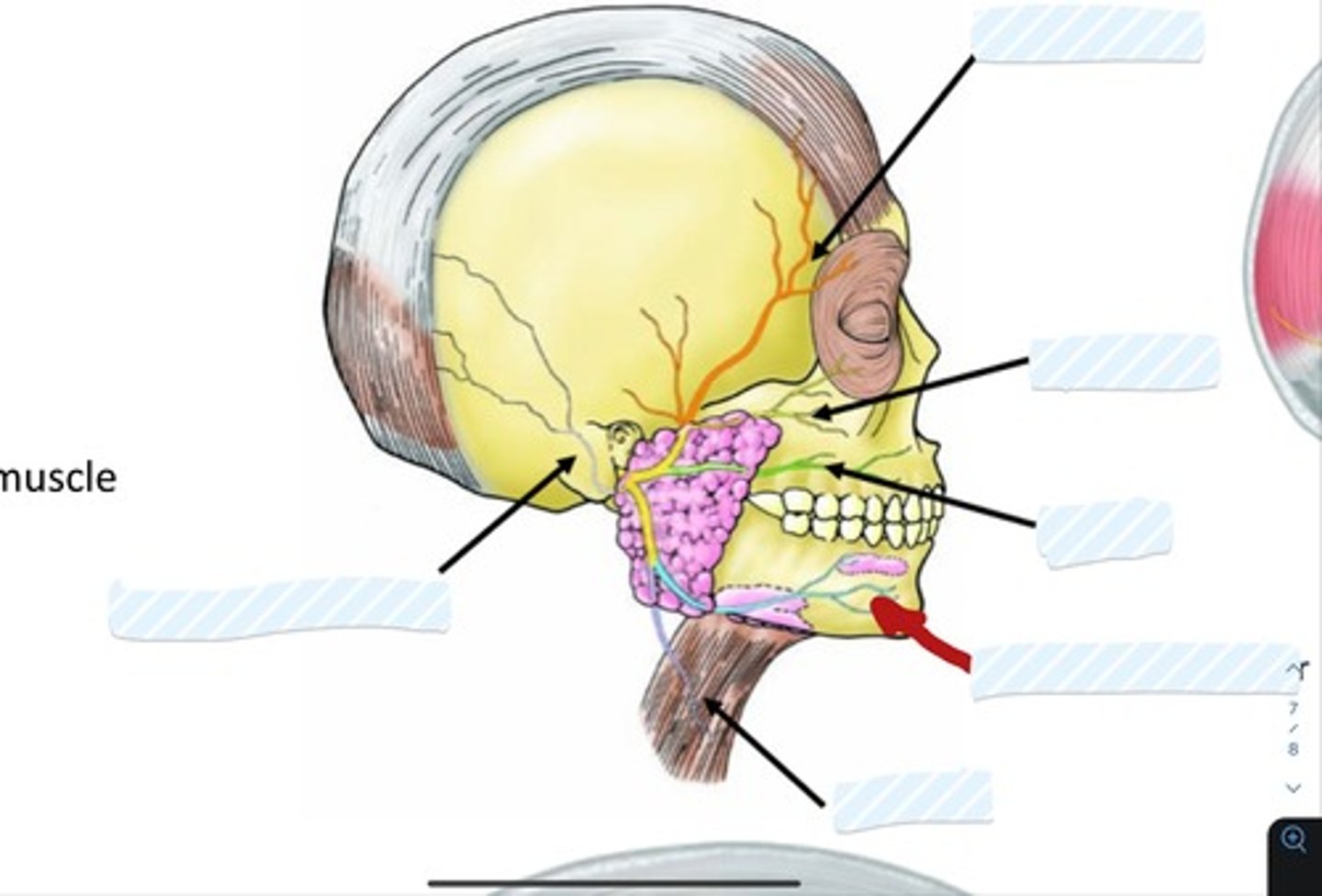
Marginal mandibular branch of facial nerve
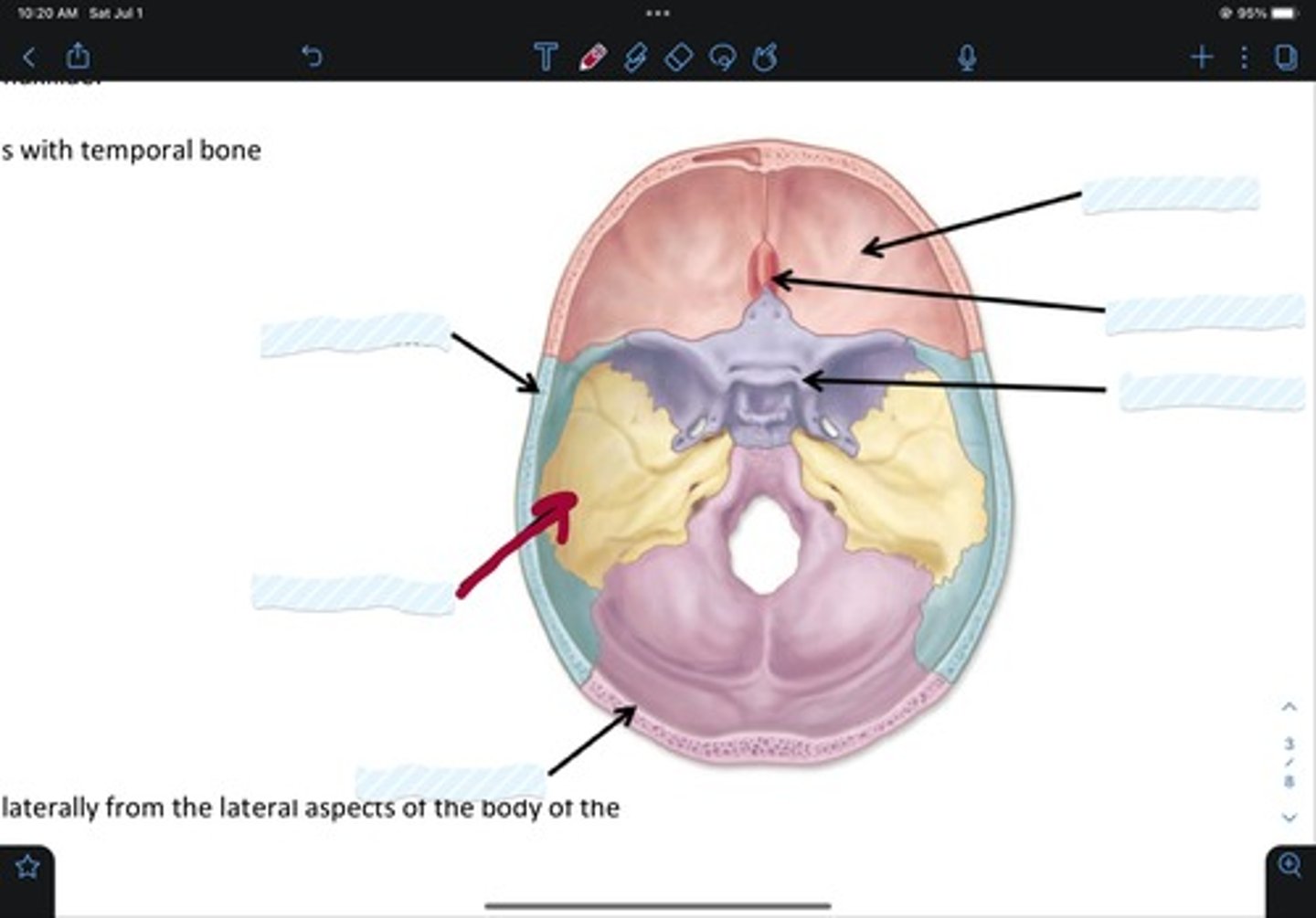
Temporal bone
Cervical branch of facial nerve
Occipital bone
Posterior auricular n.
Superficial temporal a.
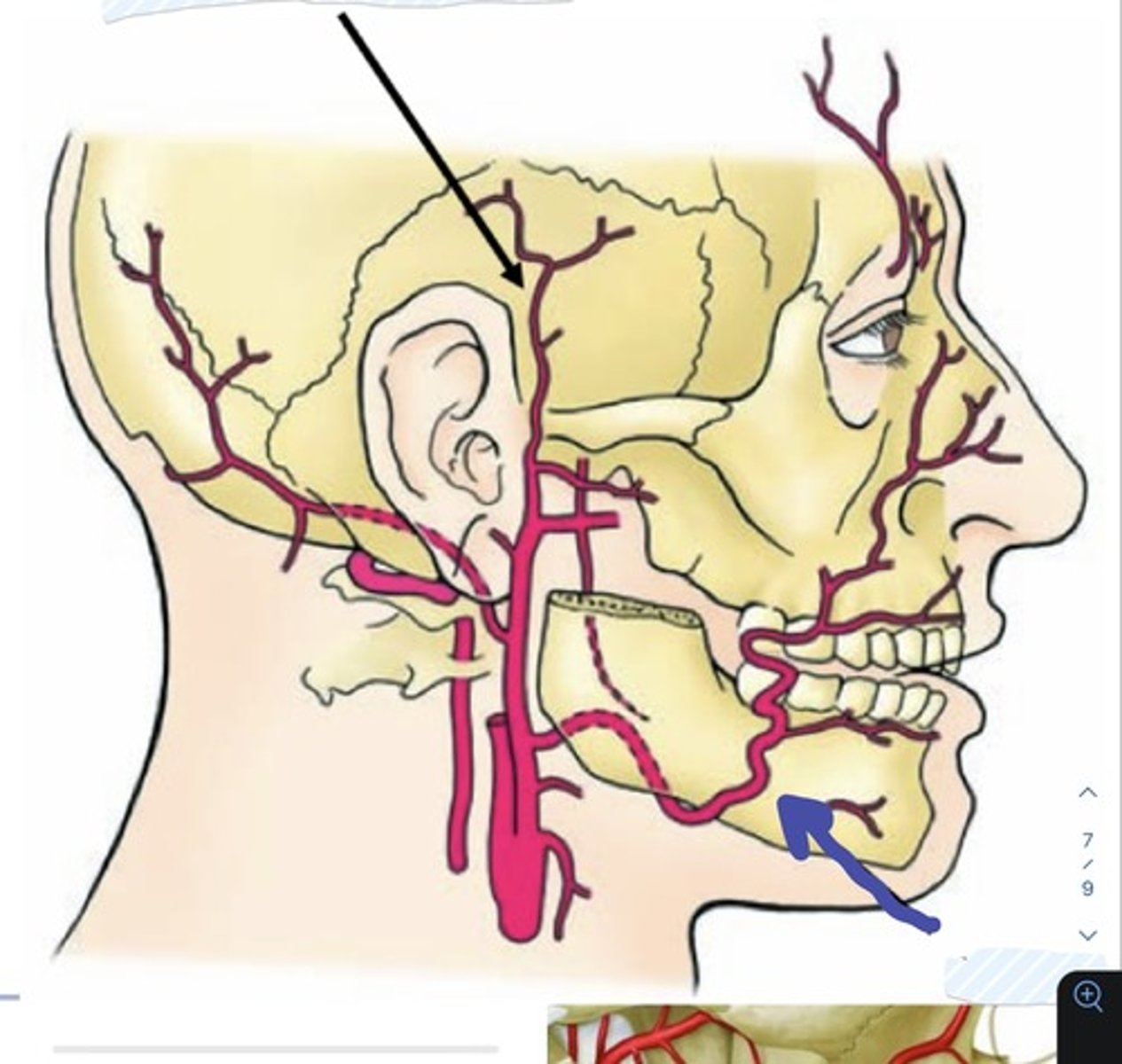
Facial a.
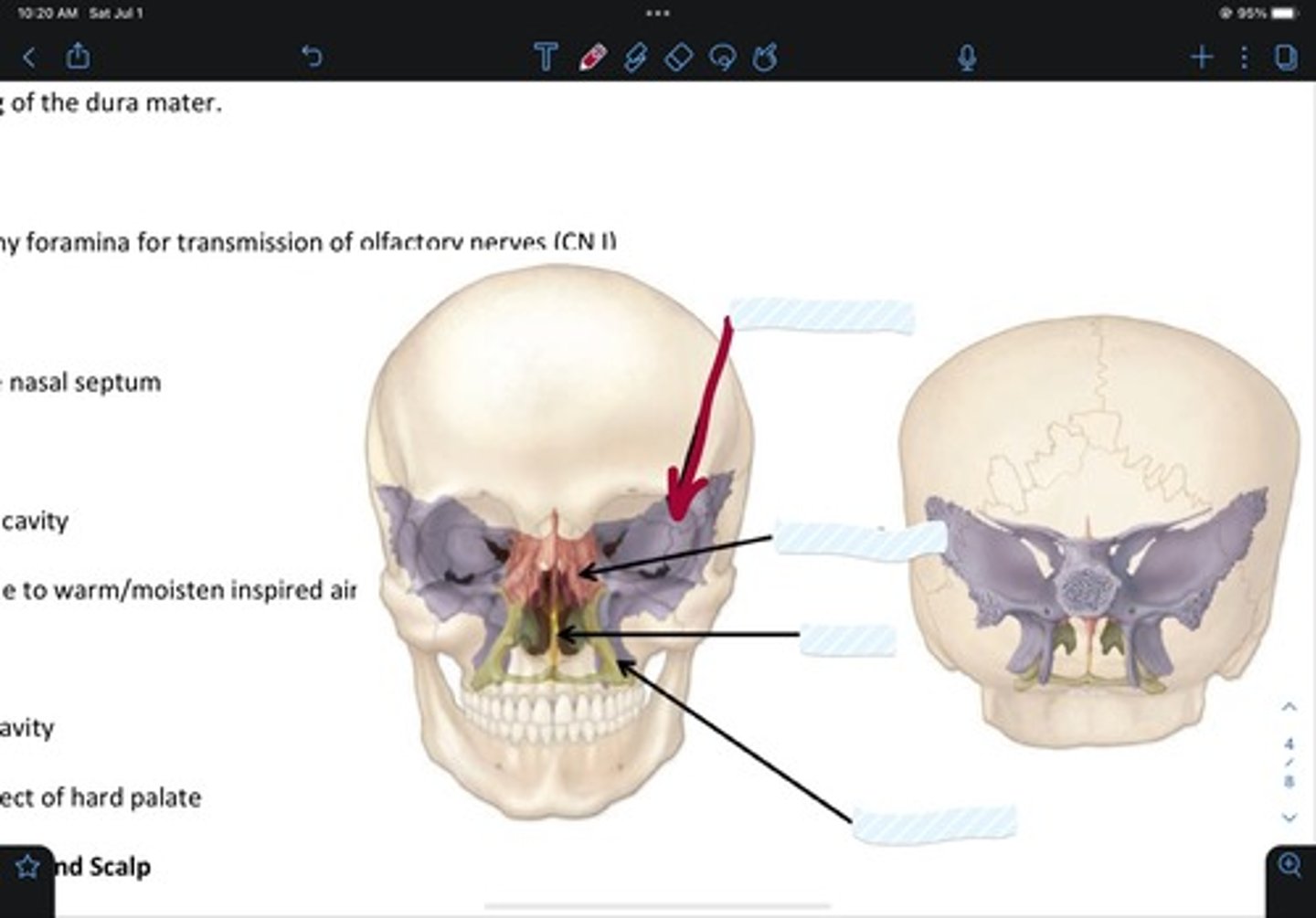
Sphenoid bone
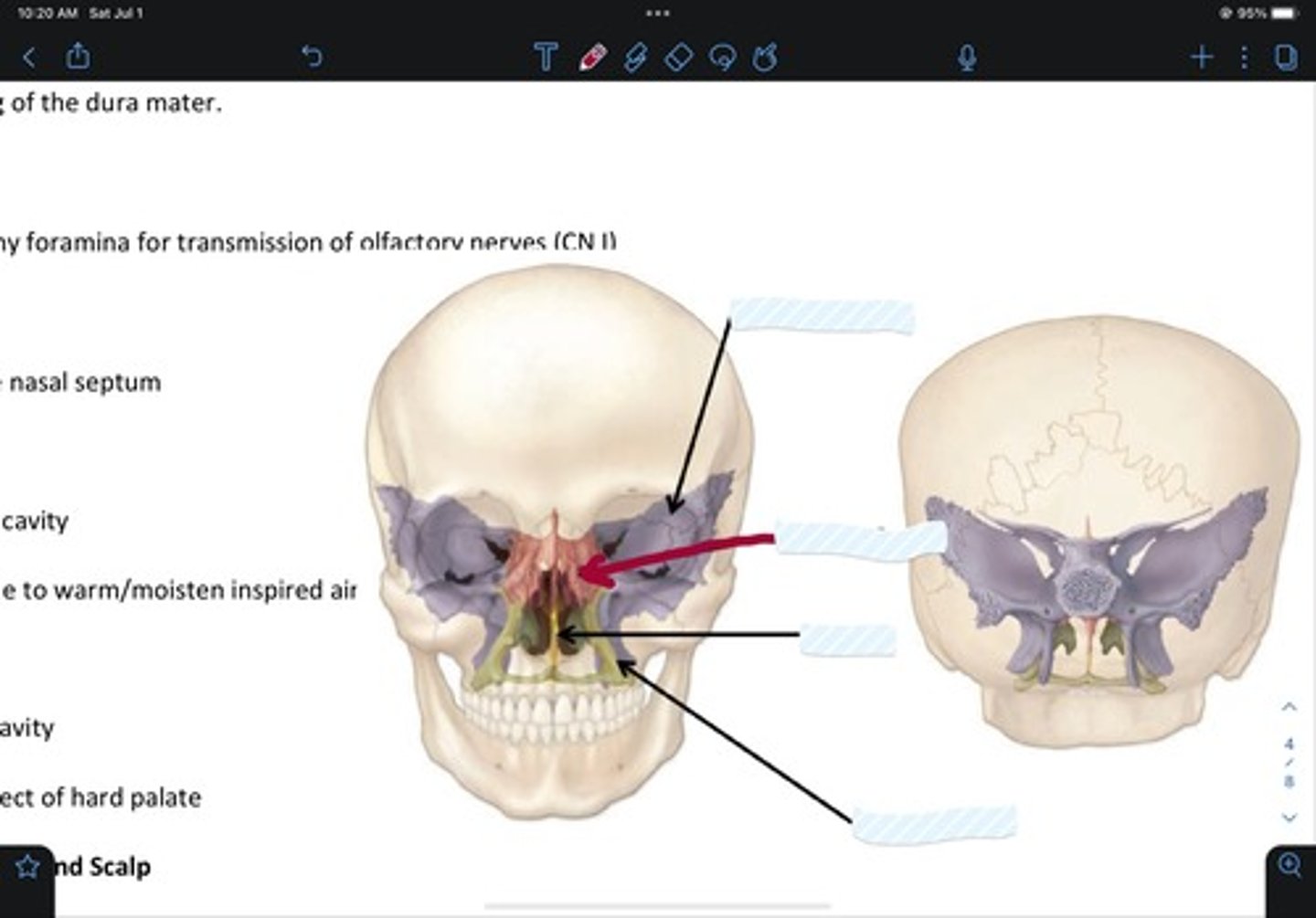
Ethmoid bone
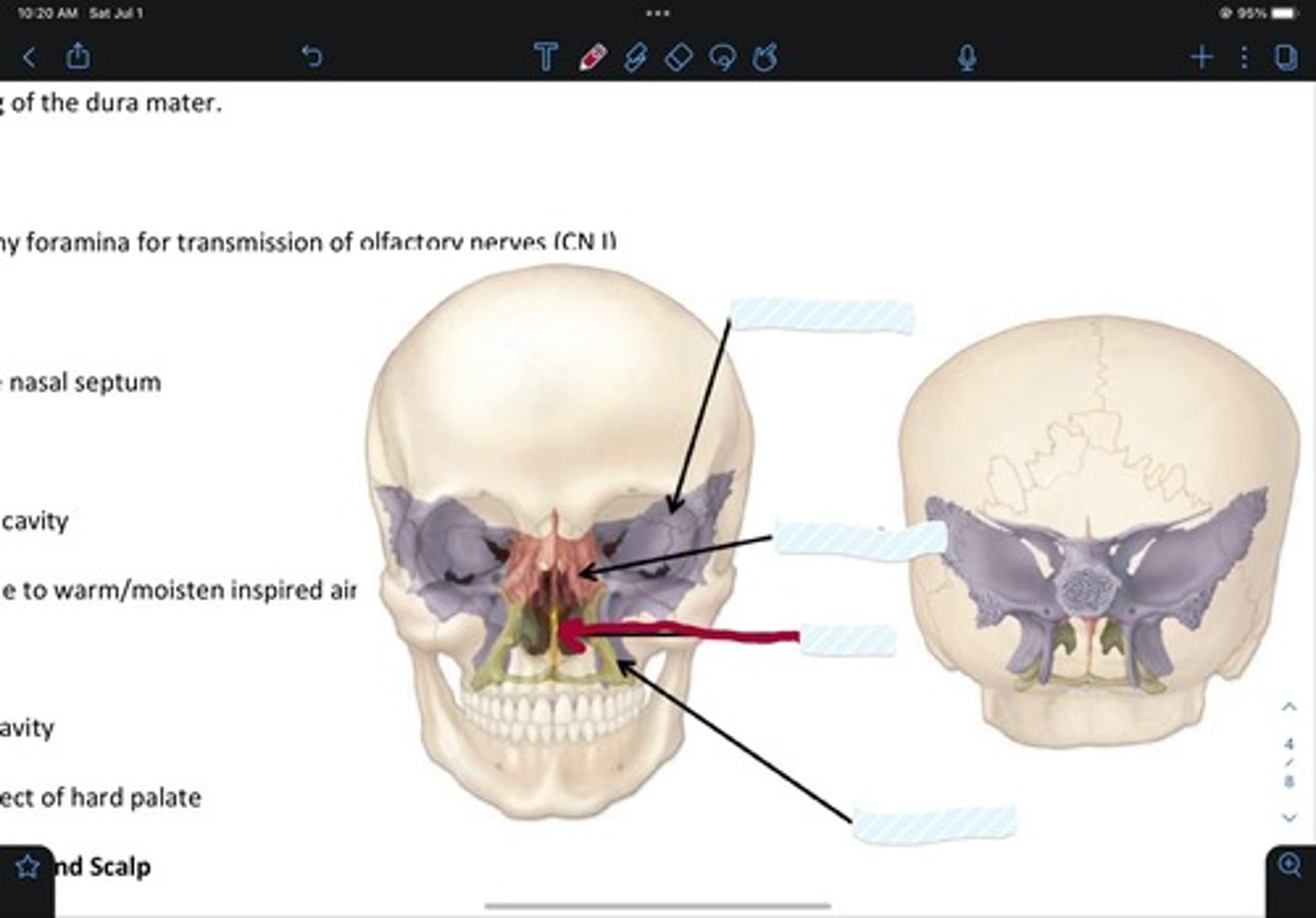
Vomer
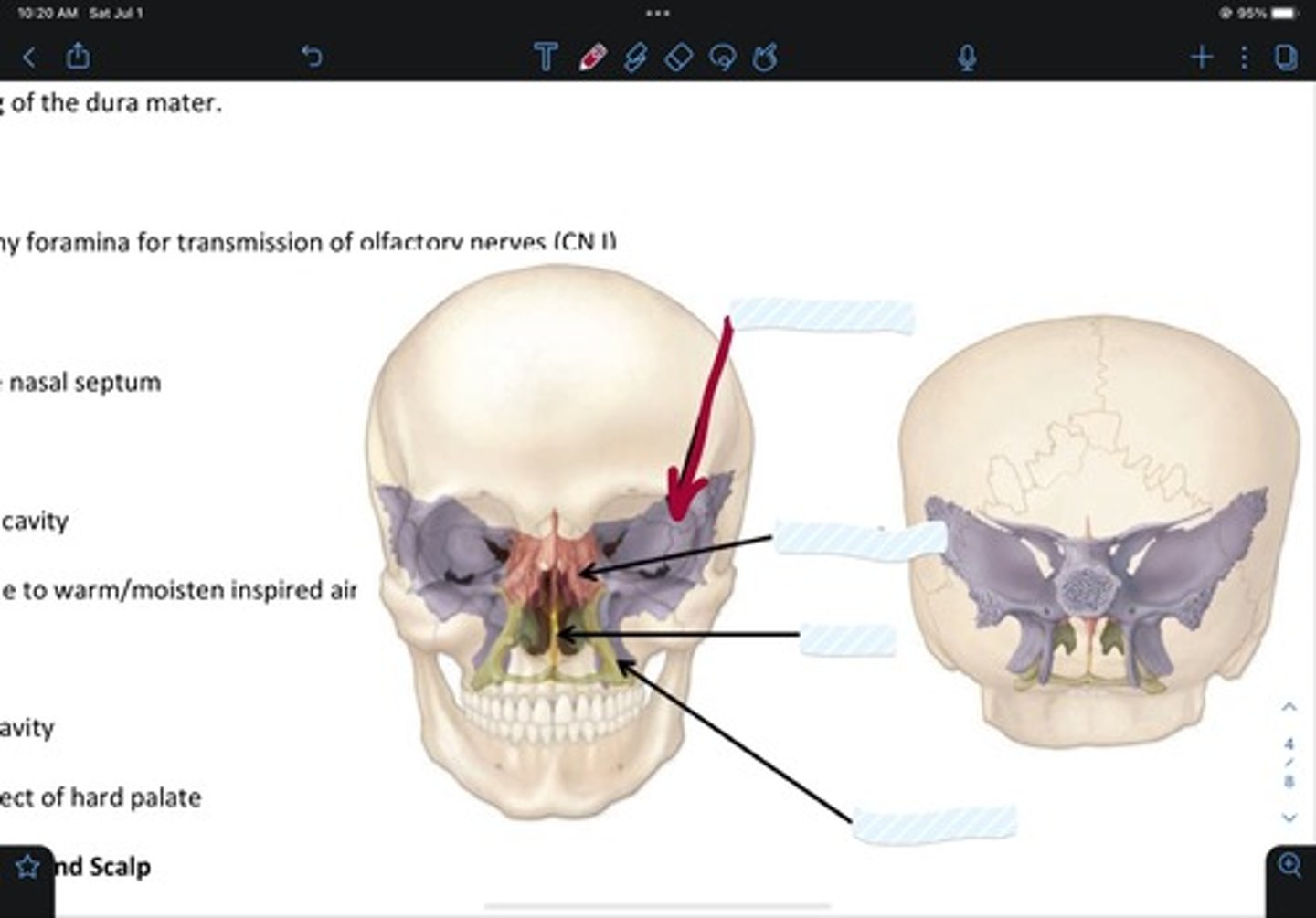
Sphenoid bone
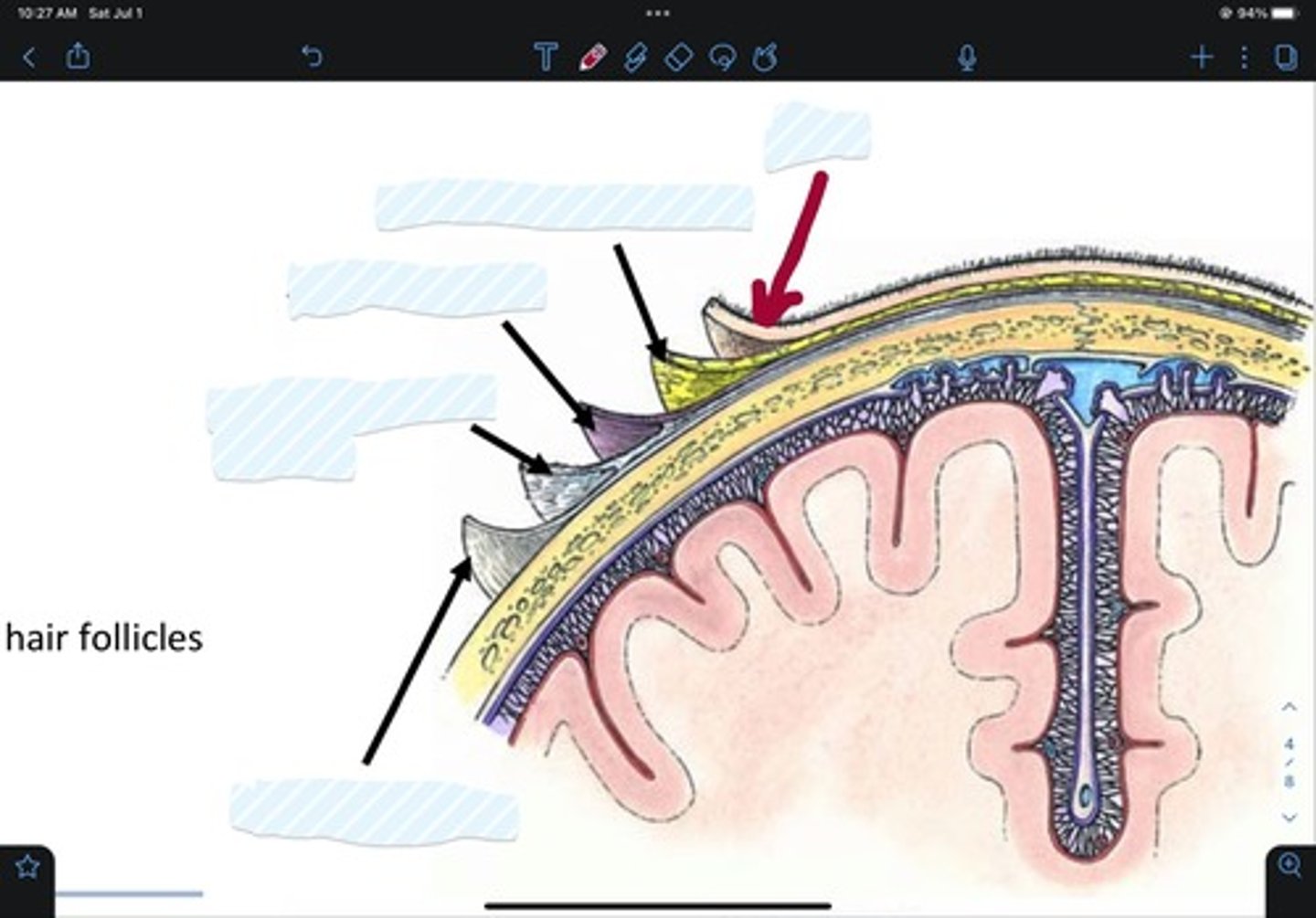
Skin of scalp
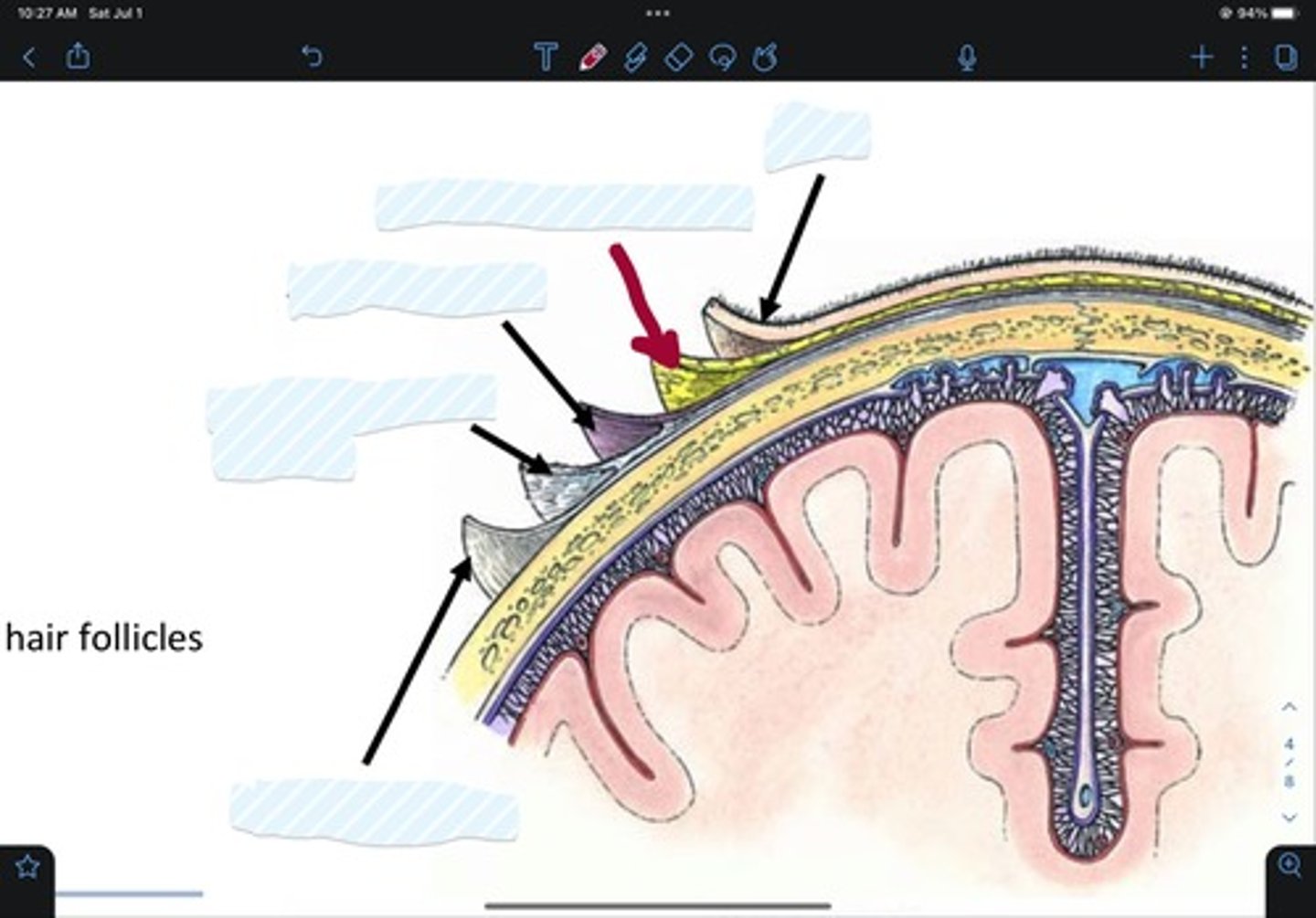
Connective tissue of scalp
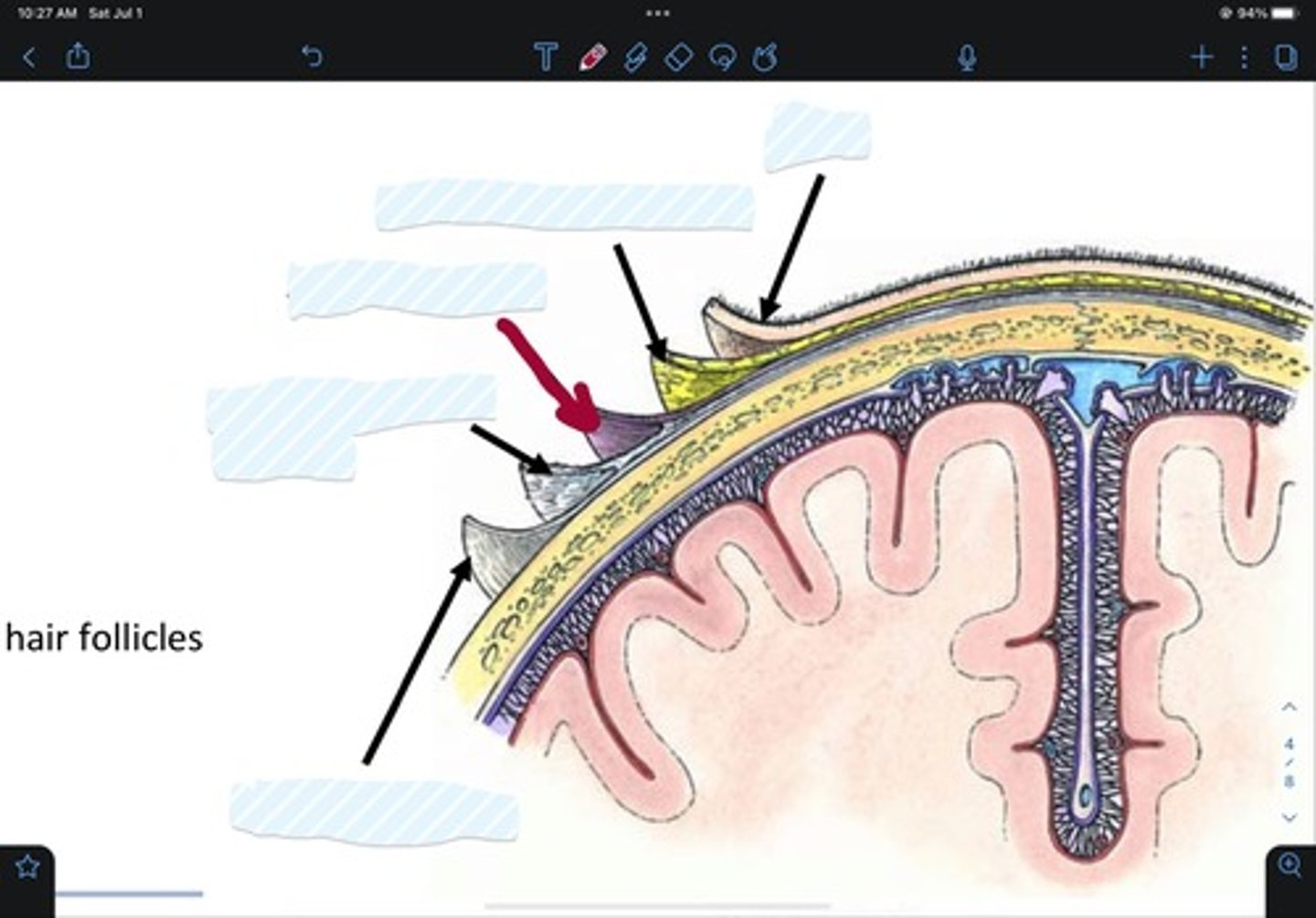
Aponeurosis of scalp
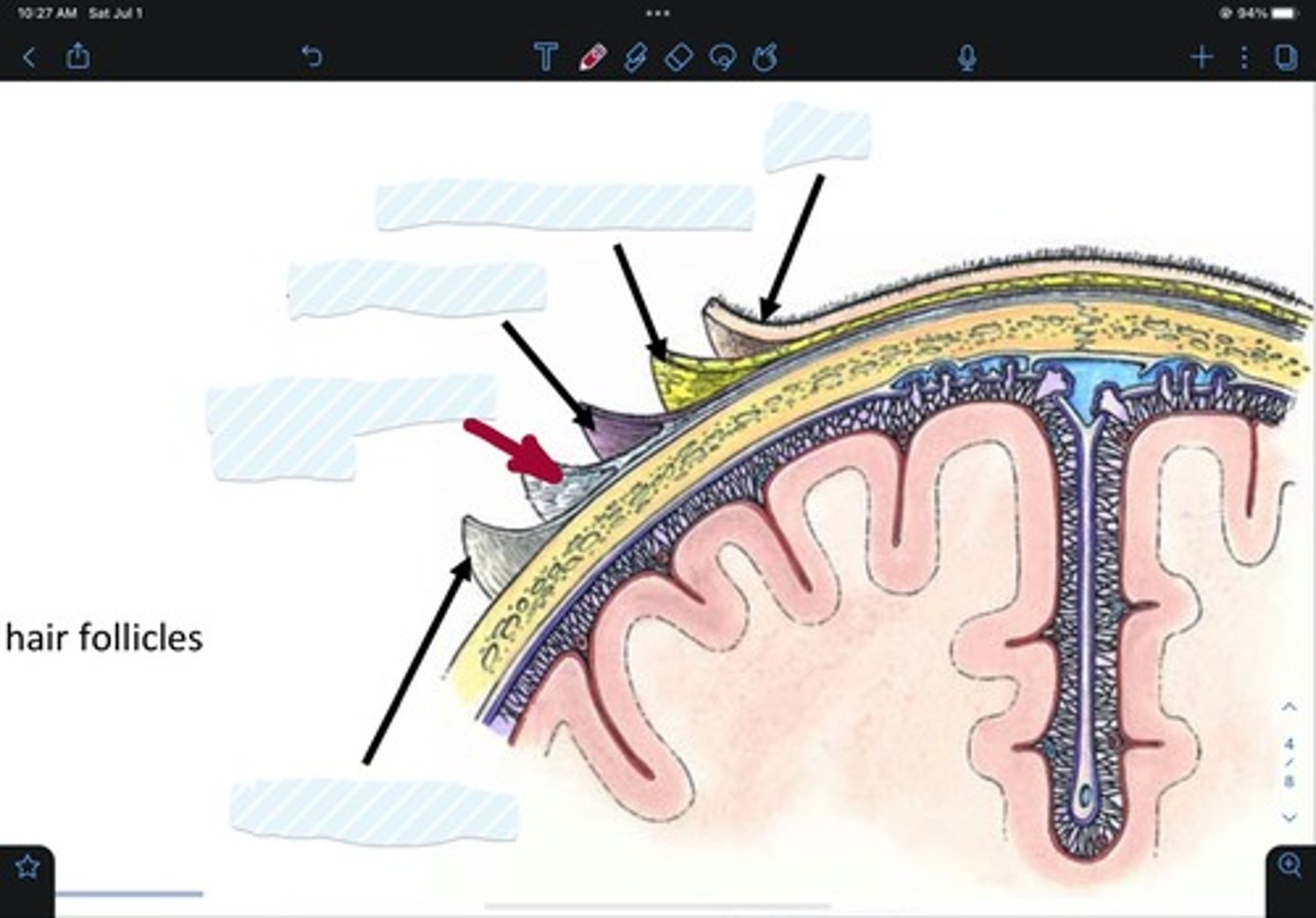
Loose areolar tissue of scalp
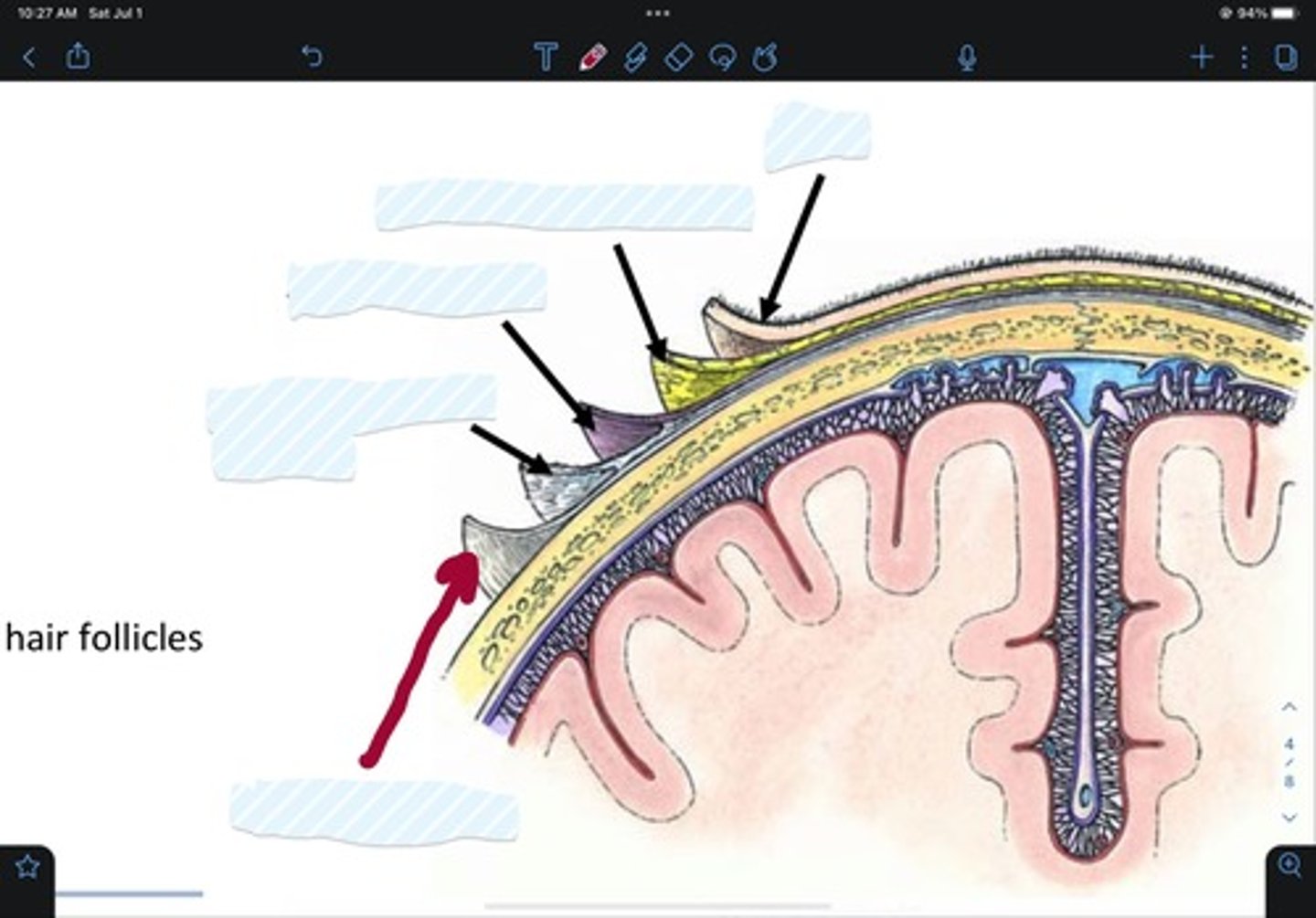
Pericranium of scalp
Parietal bone