anatomy term 2 year 1 complex mcc
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
what is the organisation of the body
cell - tissue - organ - organ system- organism
define superior/ inferior
towards/ away from the head
define anterior/ posterior
nearer to the from/ back of the body
define medial/lateral/ intermediate
nearer/ further from the midline/ between two structures
define ipsilateral/contralateral
on the same/ opposite side as another structure
define proximal/ distal
nearer/ further to the attachment of a limb to the trunk
define superficial/ deep
towards/ away from the surface of the body
define flexion/ extension
decreasing/ increasing angle of a joint
define abduction/ adduction
moving limb away/ towards midline of the body
define dorsiflexion/ plantar flexion
pointing foot up/ down
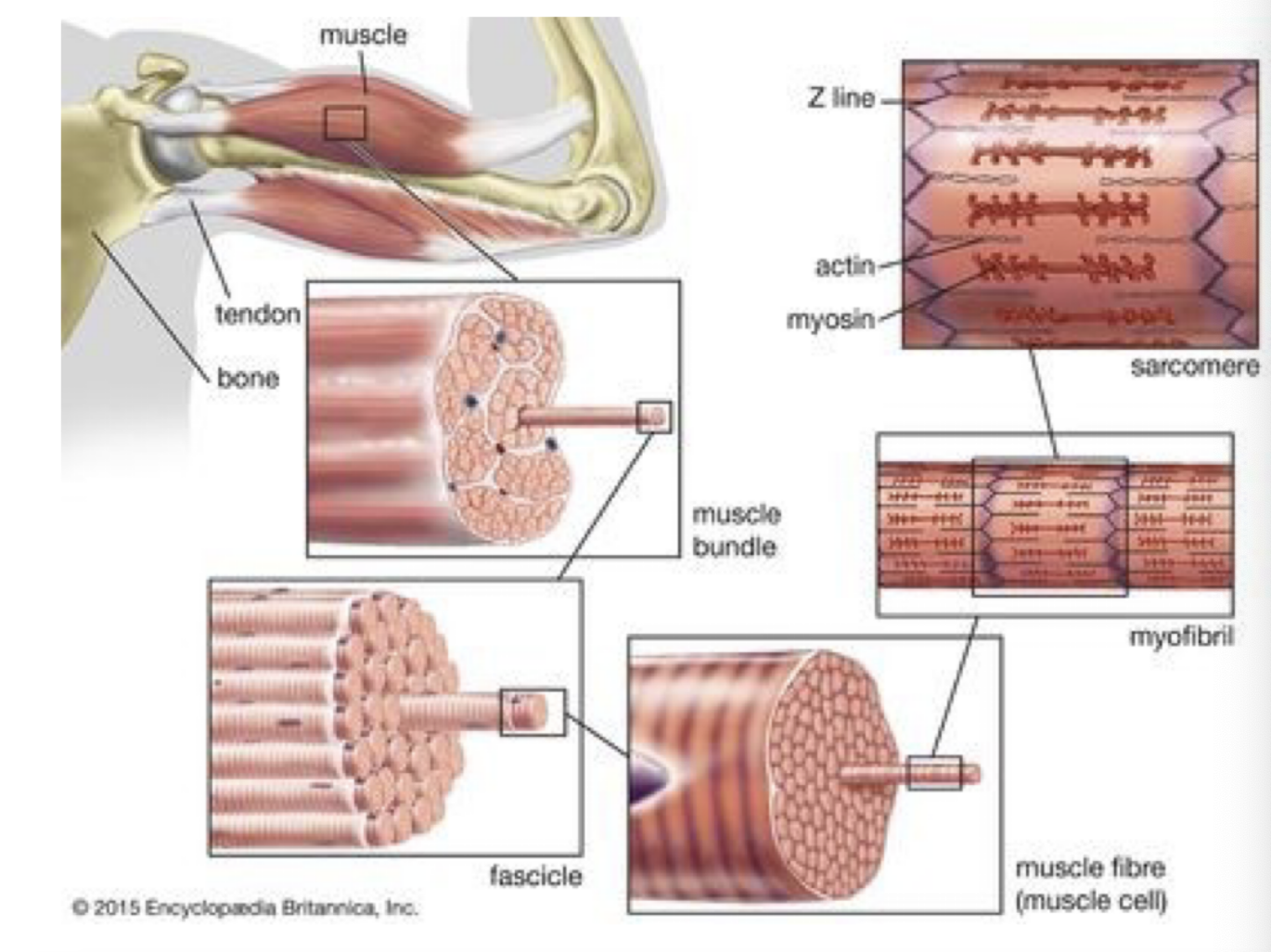
define myofibril
long thread like structures inside muscle fibres made up of repeating units (sarcomeres) responsible for muscle contractions
define sarcomere
basic unit of a myofibril extending from one Z line to the next
what are sarcomeres made up of
thick filaments (myosin) and thin filaments (actin), along with regulatory proteins like troponin and tropomyosin.
What are the major bands and lines seen in a sarcomere?
Z-line: boundary of each sarcomere
A-band: dark band, contains thick filaments
I-band: light band, contains thin filaments
H-zone: center of A-band, only thick filaments
M-line: center of the H-zone, holds thick filaments together
How do sarcomeres change during muscle contractions
During contraction, the sarcomere shortens as actin filaments slide over myosin filaments. The I-band and H-zone decrease in width, but the A-band remains the same.
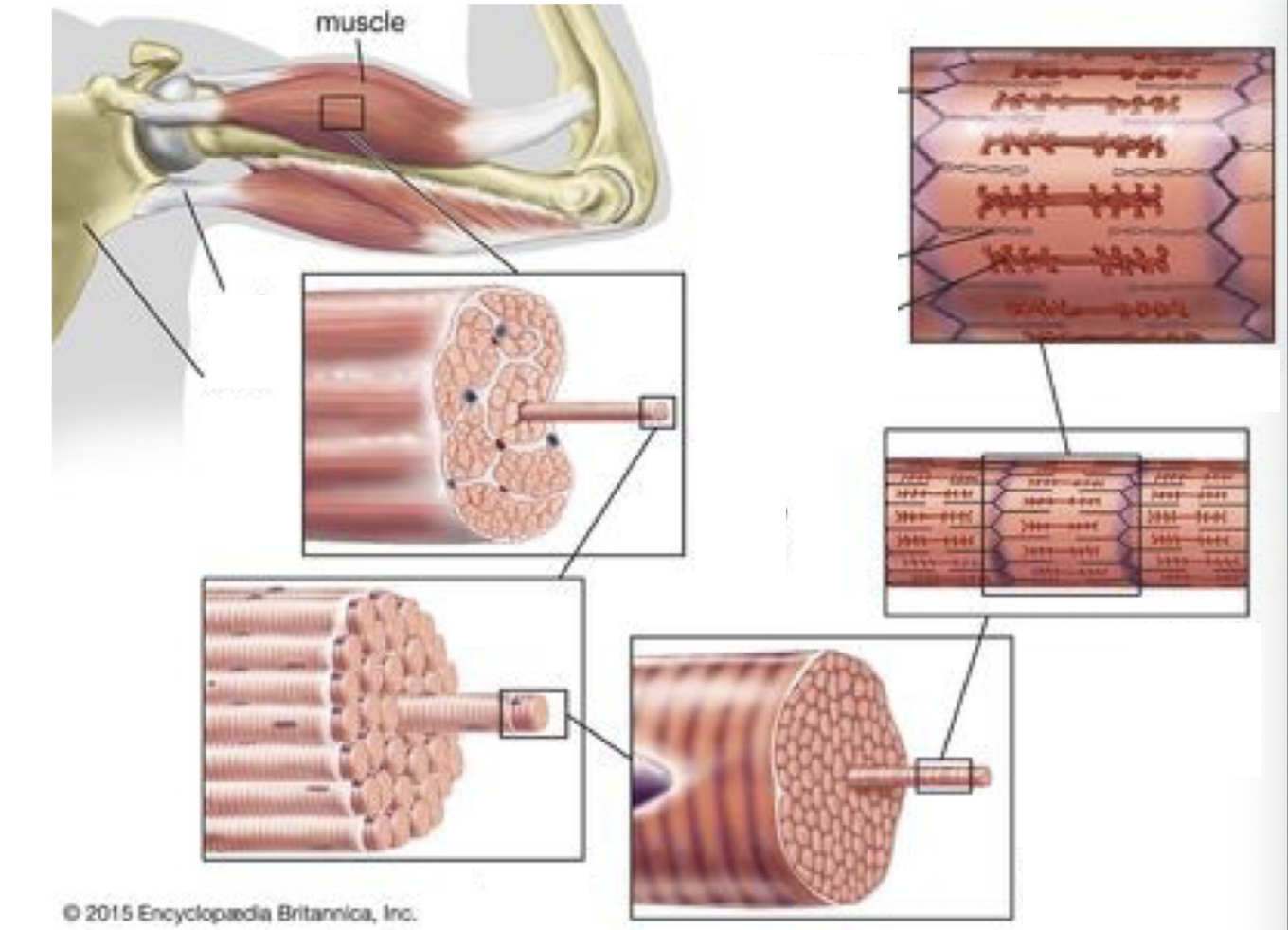
label
What causes the membrane potential to begin rising toward threshold?
A stimulus causes a graded potential and opens ligand-gated cation channels.
What happens when the membrane potential reaches the threshold?
Voltage-gated Na⁺ channels open and Na⁺ rushes into the cell (depolarization begins).
what happens during depolarisation
Voltage-gated Na⁺ channels are closed, K⁺ channels are open, and K⁺ rushes out of the cell.
what causes hyper polarisation
V-gated K⁺ channels are slow to close, and K⁺ continues to leave the cell, making the membrane potential more negative than the resting level.
When does the membrane potential return to resting state?
When all voltage-gated K⁺ channels are closed, and only K⁺ leak channels are open.
What is the correct order of events in the generation of an action potential?
Resting potential (–70 mV), Stimulus causes graded potential, Threshold reached (~–55 mV), Depolarization – Na⁺ channels open, Na⁺ rushes in, Peak of action potential (~+30 mV) – Na⁺ channels close, K⁺ channels open, Repolarization – K⁺ rushes out, Hyperpolarization – K⁺ channels slow to close, Return to resting potential – all channels reset
define hyperpolarisation
the membrane potential becomes more negative than the resting level due to continued k+ leaving the cell
define action potential
rapid temporary change in a cells membrane potential that allows negative signals to travel
define depolarisation
the membrane potential becomes less negative as Na+ ions enter the cell
define repolarisation
the membrane potential returns to a negative value as k+ ions exit the cell
define refractory period
a short time after an action potential when a neutron can’t fire another one or is less likely to
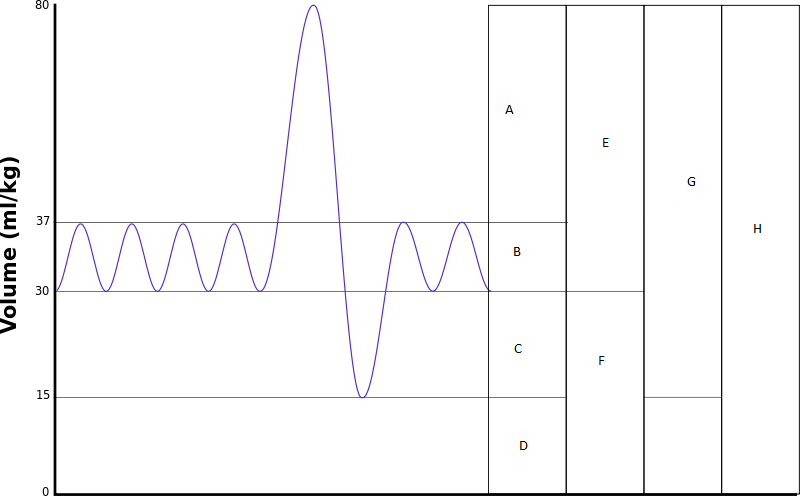
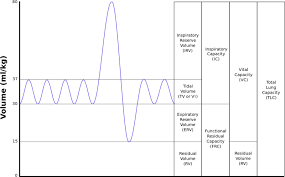
define resting tidal volume
amount of air breathed in or out during a normal breath
what is inspiratory reserve volume
the extra air you can breathe out after a normal inhalation
define expiratory reserve volume
extra air you can breathe out after a normal exhalation
define residual volume
the air that stays in your lungs after full exhale - cannot be voluntarily breathed out
define inspiratory capacity
total air you can breathe In after a normal exhale (TV + IRV)
define functional residual capacity
air left in lungs after normal exhale (ERV +RV)
define vital capacity
total amount of air you can forcefully exhale after a full inhale (IRV + TV +ERV)
Define total lung capacity
the total volume of air your lungs can hold (VC + RV)
what is the pathway of the cardiac conduction system
Sinoatrial node, atrioventricular node, bundle of his, purkinje fibres
function of the SA
the pacemaker; starts the impulse
function of the AV
delays the impulse for 0.1 seconds to allow the atria to fully contract
function of bundle of his
carries the impulse to the ventricles
function of purkinje fibres
spread the impulse through the ventricles causing contraction
effects of adrenaline on the heart
interacts with beta-adrenergic receptors to accelerate heart rate and increase force of myocardial contraction
effects of adrenaline on blood vessels
vasoconstriction in skin and gastrointestinal tract, vasodilation in the musculature, coronary and hepatic circulation
effects of adrenaline on respiratory tract
increased respiratory rate and bronchodilation
effects of adrenaline on gastrointestinal tract and liver
reduced gut motility, reduced blood flow to gastrointestinal tract, reduced digestion, increased breakdown of glycogen to glucose in liver
effects of adrenaline on central nervous system
activation of the sympathetic branch of the autonomic nervous system
what is the first step of ATP yield
glycolysis
glucose is broken down into pyruvate
2 ATP are made
2 NAD produced (via electron transport chain)
what is the second step of ATP yield
link reaction
pyruvate converted into Acetyl coA
2 NAD produced
what is the third step of ATP yield
Krebs cycle
Acetyl coA enters the Krebs cycle
produces 6 NAD, 2 FAD, 2 ATP
what is the total ATP yield
32
define rate limiting enzymes
an enzyme in the metabolic pathway that determines the speed and direction of a reaction and often catalyses the metabolically irreversible step
example of rate limiting enzymes in cellular respiration
glycolysis (glucose - pyruvate)
body mass index calc (kg.m2)
normal value for male and female
mass (kg) / [height (m)]2
fat mass
(% body fat / 100) x body mass
Fat free mass
(% non-body fat / 100) x body mass
waist to hip ratio
waist circumference / hip circumference
mean arterial pressure (mmHg)
(systolic bp + (diastolic bp x2))/3
cardiac output (L.min-1)
HR (bpm) X SV (ml)
FEV1/ FVC ratio (%)
(FEV1/ FVC) X100
minute ventilation (L.min-1)
respiratory rate x tidal volume
absolute haemltocrit from blood volume (ml)
(relative haematocrit / 100) x blood volume
daily resting metabolic rate (kcal.min-1)
resting metabolic rate (per min) x 60min x 24hrs