Geography - Environmental
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
Evidence for Climate Change
Sea-floor sediments - Indicate previous ocean temperatures
Ice Cores - CO2 Levels have fluctuated - Indicate previous gaseous composition of the atmoshphere
Lake Sediments - Pollen grains indicating the vegetation types from the past
Tree rings - the width of the annules vary depending on the temperature
Fossils - Indicates the plants and animals that were able to survive in the conditions
Glacial and Inter-Glacial periods - we have not entered one
Human Causes for Climate Change
Fossil Fuels - releases CO2 from the lithosphere into the atmosphere
Agriculture - cattle farming releasing methane
Deforestation - releasing CO2 from the biosphere into the atmosphere
Natural Causes for Climate Change
Solar output - measured using sunspots
Orbital changes - the ellipse of the earth’s orbit changes, so does the angle of the axis and it wobbles
Volcanic activity - emit clouds of dust and gas that reflect the short waves from the sun back out of the atmosphere, cooling the planet
Global Circulation System (tri-cellular model)
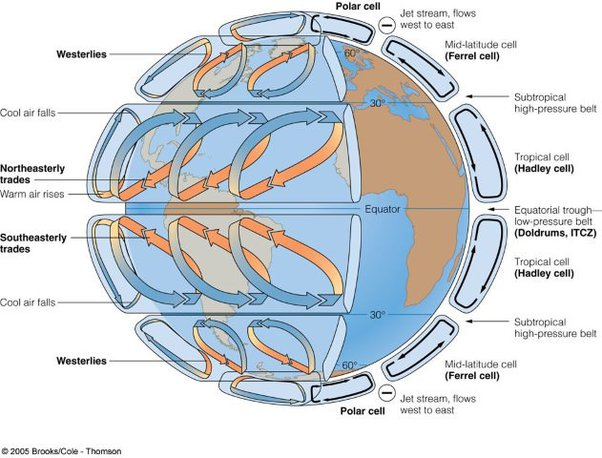
Low Pressure Hazards and Formation
Tropical storms (Hurricane):
A strong upward movement of air draws water vapour up from the warm ocean surface
This evaporated air cools as it rises and condenses to form towering thunderstorm clouds
As the air condenses it releases heat which powers the storm and draws up more and more water from the ocean
Several small thunderstorms join to form a giant spinning storm
As the storm is carried across the ocean by the prevailing winds it continues to gather strength
The storm now develops an eye at its centre where air descends rapidly
On reaching land the storm’s energy supply is cut off and friction with the land slows it down
High Pressure Hazards and Causes
Droughts and Heat Waves:
Weather
Global Warming
El Nino
Overpopulation
Overcultivation
Overextraction
Deforestation
Distribution of: Low Pressure Storms
Found over warm oceans (27 degrees +) - the tropics
Form 5-15 degrees north and south of the equator as there is not enough ‘spin’ at the equator
The intense heat in tropical climates makes the air unstable causing air to rise rapidly
Distribution of: High Pressure Systems
Higher risk in:
LICs
Places with overpopulation
Places with hotter climates
Change overtime of: Low Pressure Systems
Form in the summer and autumn when sea temperatures are at their highest
Increased due to climate change
Change overtime of: High Pressure Systems
Increase in drought in the last 100 years due to climate change
Low Pressure System Case Study
What: Hurricane Matthew
Where: Caribbean, SE Coast of USA
When: October 2016
Consequences: Homelessness, Displacement, Separation of families, Death, Flooding, Destruction of property, Contaminated water (LICs),
Responses: Evacuation, Money donation from other countries and NGOs, Donation of resources from this places (LICs)
High Pressure System Case Study
What: California’s Drought and Wildfires
Where: California
When: 2012-2015
Causes: Jet stream that usually brings precipitation to California was too high up
Consequences: Lower precipitation → dry soils → wildfires, fires engulfed many homes, housed pipe bans, property damage, loss of crops, vegetation dies
Responses: Mass Evacuation
Factors that create Weather Variation in the UK
Latitude
Altitude (+ relief rainfall)
Ocean Currents - North Atlantic Drift (warm)
Continentality - land heats up and cools down quickly whereas water does so slowly
Air Masses
Distribution of Biomes (Tropical Rainforests, Tundra and Savanna)
Tropical Rainforests: Grow in a band around the equator where the equatorial climate is hot and wet.
Tundra: Found where Winters are cold and Summers are short (arctic areas)
Savanna: Found in regions that have a tropical semi-arid climate (above and below the equator)
Tropical Rainforests (Climate and Distinctive Features)
Climate: Hot and wet - humid
Distinctive Features: Hot climate and abundant rainfall allow for rapid plant growth and trees that can reach very high heights
Savannas (Climate and Distinctive Features)
Climate: Hot with wet and dry seasons
Distinctive Features: An open tree canopy (i.e., scattered trees) above a continuous tall grass understory
How humans impact the ecosystems of: Tropical Rainforests
Deforestation:
Exposes soil to erosion
Takes carbon dioxide out of the biosphere and then lithosphere contributing to global warming
Creates ecological islands - separating groups of animals from others
Nutrient cycles are broken
The use of heavy machinery damages shrubs → derives insects of food → disrupts the food chain
How humans impact the ecosystems of: Savanna
Desertification:
Slash and burn of trees → reduces evapotranspiration levels → reduces rainfall levels → reduces water for people who rely on rivers for water
The removal of vegetation → leaf litter can no longer fall into the soil → the nutrient cycle is broken → shrubs no longer replace nutrients or help to maintain a healthy soil structure by adding organic material to the soil
The destruction of the tree canopy → exposes the soil to rain splash erosion + during heavy rainfall the water flows over the surface of the ground in sheets, eroding all the organic material from the upper layers of the soil. On steeper slopes the power of the water picks up and carries soil particles and smaller rocks → it uses these to erode downwards into the soil in a process known as gulley erosion.
Sustainable Management of: Tropical Rainforests
Wildlife corridors - planting strips of forest to connect the remaining fragments of forest together. Allows animals to move freely from one area of forest to another without coming into conflict with people.
Buffer zones - encourages the local people to use the zone sustainably rather than just banning the usage of forests altogether - helps to make a living and educate people
Sustainable Management of: Savannas
Great Green Wall of Africa - involves planting a wall of native trees and shrubs across the width of Africa:
Increase biodiversity
Reduce soil erosion
Reduce time women spend collecting firewood
Grow medicinal plants
Diversify plant incomes
Improve soil fertility
Increase fodder for livestock
Provide shade for crops and increase their yield
Increase capability of coping with climate change
How humans affect small scale ecosystems in the UK: Studland Bay Sand Dunes
BBQs - Burns vegetation
Dog waste - fertilises the soil so unwanted plants also grow
Walking - tramples vegetation and kills it
Can be managed by: Land-use zoning, dog waste bins
Weather
Day to day conditions/changes in the atmosphere
Climate
Weather over a long period of time (30 years)
Affect of: Latitude on Temperature
Temperature: Greater curvature = Greater area of land to heat up
Affect of: Altitude on Temperature and Rainfall
Temperature: Density decreases as altitude increases.
Rainfall: Air is forced to rise over areas of high altitude causing relief rainfall
Affect of: Ocean Currents on Temperature and Rainfall
Temperature: Warm and cold ocean currents bring different temperatures
Rainfall: Brings in different pressure systems
Anticyclones
High pressure
Air sinks in the lower atmosphere
In the Summer: brings hot and sunny weather with light wind
In the Winter: Anticyclones cause cold weather including fog and frost
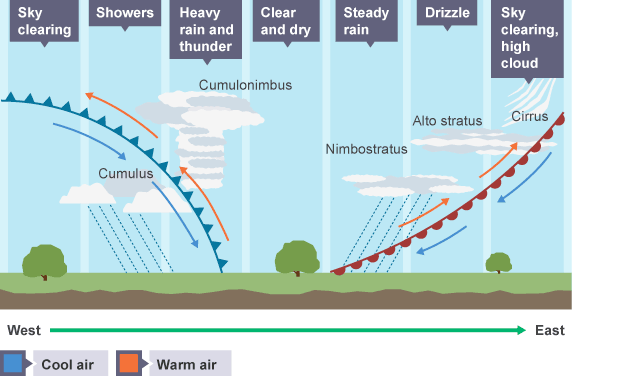
Depressions
Low Pressure
When a warm front meets a cold front
Air rising causes the formation of clouds, which brings rainfall. Depressions often move eastwards across the UK, bringing changeable weather as they travel.
There are usually frontal systems associated with depressions. The diagram below shows the changing weather that the warm and cold fronts bring as they move towards the east.
Urban micro-climates
The buildings and traffic in a large city influence the local climate - creates temperatures that are warmer than in the surrounding rural area.
Factors of: Urban micro-climates
Concrete, brick and tarmac all absorb heat from the Sun during the day. This heat is then radiated into the atmosphere during the evening and at night.
Buildings that are badly insulated lose heat energy, especially through roofs and windows. Heat is also created by cars and factories, which is lost to the air from exhausts and chimneys.
Tall buildings in a city affect local patterns of wind - act as a shelter so average wind speeds in cities are lower than in the surrounding countryside. However, rows of tall buildings can also funnel the wind into the canyon-like streets between them and cause high wind speeds. This may cause hazards for pedestrians and, in some extreme weather conditions, has led to the collapse of scaffolding.
During the summer months, the extra heat due to the urban heat island causes air to rise over larger cities - this can lead to convectional rainstorms.
Urban areas have 10 times the dust particles in the atmosphere than rural areas leading to higher amounts of rainfall - when water vapour condenses in the air to form water droplets it does so by attaching itself to a dust particle.
How has water demand changed over the past 50-100 years?
Increased in all usages and all areas due to:
industrialisation
rise in population
cost of living crisis
climate change
Water Footprints
A measure of humans use of water and our impacts on natural water resources
Water Security
People have enough and affordable water to stay healthy. There is sufficient water for agriculture, industry and energy. People are protected from water related hazards.
How do people manage water?
Construction of reservoirs
Water transfer schemes
Abstraction of groundwater
Construction of reservoirs and dams
Put in place to raise water levels upstream and also provides hydraulic power:
Displaces people
Causes other places to get less water causing political tensions
Water transfer schemes
Transferring water from countries with water surplus to a country with water shortage from reservoirs through pipes and canals.
Abstraction of water
Abstracting less polluted water from the ground:
Abstracting too much and not allowing it to replenish
Social, economic and environmental consequences of: Lesotho Highlands Water Project (Management of water resources at an international scale where rivers cross national boundaries)
Positives:
Makes a lot of money as it is an important source of income
Provides a lot of energy for Lesotho
Provides a lot of water
Provides a lot of electricity
Creates a lot of job
Some aquatic animals benefit from them
Negatives:
Flooding
Displacement of people
Creates conflicts between the local validity
Some people are not being supplied the jobs or compensation they were promised
Endangers animals and vegetation
Social, economic and environmental consequences of: South Africa and Limpopo Fog Harvesting small scale water management where appropriate levels of technology are used)
Positives:
Nets and poles are relatively cheap
Repairs are easy to make and require little training
Ground water is contaminated
Fog harvesting technology does not need any electrical energy
Many rural areas do not have piped supply from a reservoir
Negatives:
It is not foggy everyday
Repairs are essential and nets are easily torn by the wind
Some of the foggiest sites are some distance from rural communities
Social, economic and environmental consequences of: Over-Abstraction of Groundwater (Over-abstraction of groundwater where alternate futures are considered)
Positives:
Groundwater is believed to be less polluted than surface water as surface water is often contaminated with human waste
Water vendors also often sell water for high prices therefore building a well to abstract ground water is believed to be cheaper in the long term
Farmers have been encouraged to grow more food to keep up with the growing population therefore require more water
There are long dry periods and monsoon season can often be unpredictable
Negatives:
Over-abstraction means that, in the long term there will be limited water to abstract
Crops are unable to grow due to the dehydrated soil
Development
An improvement in a number of characteristics
HDI
Looks at people and their capabilities as well as economic measures
GNI
Calculated by adding up the value of output by resident producers + primary income from abroad + any product taxes
GDP
Includes national income, output and expenditure
Measures of Development
GNI, GNI Per Capita, GDP, HDI, Literacy Rate, People per doctor, Access to safe water, Infant Mortality, Life expectancy
Brandt Line
A line that divides the “poor south” and the “rich north”
Limitations of the Brandt Line
There are countries with higher middle GNI, GDP and HDI below the Brandt Line especially as LICs and MICs further develop
Limitations with using national wealth as a comparative measure of development
Only shows economic development and says nothing about whether people in a country have a good standard of living. It is an average and may hide differences in wealth within a country.
The development continuum
A sliding scale from least to most developed countries, with lots of intermediates such as the newly-industrialised countries.
Causes of Uneven development
Climate
Corruption
Geography
Culture → Religious beliefs that limit development
Colonisation
Exports
Goods and services produced in one country and shipped to another
Imports
Goods and services brought into one country from another
Tariffs
Taxes imposed on imports
Quotas
Limits on the amount of goods imported
Subsidies
Benefits given by the government usually in the form of cash payment or tax reduction
Trading blocs
Groups of countries that work together to promote free trade between the members
Interdependent
Where countries are linked together in a complex web so that they are dependent on each other
Primary industry
Extracting raw materials (LICs)
Secondary industry
Manufacturing raw materials into goods (NICs)
Tertiary
Provision of a service (HICs)
Quaternary
Intellectual/knowledge-based products and services
Why do the different industries cause uneven development?
Raw products tend to sell for very little and the price can fluctuate overtime whereas the price of manufactured goods, services and intellectual knowledge is higher and tends to rise
How do trade blocs contribute to the development gap?
LICs are often excluded from trade blocs therefore HICs in the same trade bloc trade freely and easily between each other whereas LICs outside of the trade blocs do not have such easy access to these goods as tariffs would have to be paid therefore HICs can continue to develop whereas LICs cannot, causing the development gap.
How do tariffs on imports contribute to the development gap?
Some poorer countries cannot afford to pay these tariffs in order to export their goods into other countries, reducing their sales.
Trade deficit
More imports than exports
Gambia (LIC): Trade leading to uneven development: Problems with Exports
Gambia relies heavily on travel and tourism as an export → very vulnerable industry as demand can decrease quickly leaving the country’s economy severely depleted
Gambia also relies heavily on agriculture as an export → a disagreement in supply and demand/extreme weather events that negatively affect agricultural land such as flooding or droughts may reduce agricultural activity and therefore exports, significantly impacting the economy.
Gambia (LIC): Trade leading to uneven development: Problems with Imports
35% Of Gambia’s imports are agricultural therefore, if something happens to their suppliers, they will have a massive depletion in resources
India (NIC): Trade leading to uneven development: How has India Reduced the Development Gap?
Large portion of exports are services
Decreasing the number of people in and the size of the agricultural industry
Increasing the number of people in and the size of the services industry
Exporting more products unique to India’s culture and resources therefore they are less likely to face competition
MNC
Multinational Companies
Global Shift
The movement of manufacturing and outsourcing of services from west to east
Globalisation
People and places around the world are linked by the process of globalisation. Close links are made between countries through trade, migrations and the investment of MNCs. This is helped by improving communication technology. Globalisation helps to create economic growth.
What factors drive globalisation?
Trade
MNCs
Transport
Communication
Why do MNCs locate plants in less developed countries? (Pull and Push factors)
Pull Factors:
Cheap labour
Large profit margin
Location of factories
Cheap land
Less competition
Cheaper materials
Push Factors:
Expensive labour
More robust worker’s rights (workers rights are often exploited in LICs)
Expensive land
High competition
Advantages of MNCs in NICs
Investment of MNCs creates the multiplier effect driving the country’s economic development:
Factories are built for the MNC creating jobs and further investment → creates demand for housing → creates demand for shops and services → leads to the multiplication and the improvement of them too → businesses grow and pay more tax → enables the government to spend more money on roads, other services etc. → creates recognition for the country → attracting more businesses to invest there
Companies provide expensive machinery and introduce modern technology
Improves levels of education and technical skills of local people
Disadvantages of MNCs in NICs
Money could be spent elsewhere than on encouraging foreign countries to invest
Big schemes can end up increasing national debt
Decisions are being made outside of the country that might not always be in the best interest of the country
Insufficient attention to health and safety can lead to unsafe working conditions
Local labourers have to work long hours and worker’s rights may not always be enforced
Poor environmental regulations can lead to exploitation of the environment
MNCs may leave if stricter worker’s rights are enforced, leaving a gap in the local economy
Outsourcing
When a business gets some of its goods, components or services from an outside supplier
How do MNCs grow?
Merging with consolidation → forming a new company
Acquisition → when a bigger company buys a smaller company
Opening more branches around the world therefore reaching new markets
SEZ
Special Economic Zone: An area in which the business and trade laws are different from the rest of the country. SEZs are located within a country’s national borders and their aims include increasing trade balance, employment, increased investment, job creation and effective administration. To encourage businesses to set up in the zone, financial policies are introduced.
Case Study: India and Tata Steel: Why has it grown so quickly?
Globalisation
Headquarters are in Mumbai:
60th Largest Company
700,000 employees worldwide
Owns 38 companies in the UK
Case Study: India and Tata Steel: Impacts on HICs as they deindustrialize
Even though the EU imposed tariffs on Chinese Steel, the UK steel industry could not compete with the lower cost of Chinese steel.
This resulted in TATA losing a lot of money in lost profits. As a consequence, many jobs were lost in the UK Steel Industry.
Many indirect jobs were also lost, resulting in a Negative Multiplier Effect within some regions of the UK
Dependency Theory
Resources flow from a “periphery” of poor and underdeveloped states to a “core” of wealthy states, enriching the latter at the expense of the former
Neo-colonialism
A foreign power indirectly controlling or influencing a territory and its people, usually through financial means
Tourism
Commercial organisation and operation of holidays and visits to places of interest
Enclave tourism
Tourism development that generally operates within a clearly demarcated, self-contained environment
Causes of growth in tourism
Advancement in transport links/modes of transport
Tourism is advertised more/ease of booking → packages
More disposable income as places develop
More development in the tourist sector in NICs
What opportunities does tourism create?
Employment → provides 1 in 10 jobs worldwide
Economic development
Economic diversification
Biodiversity conservation → sustainable tourism
What challenges does tourism create?
Environmental degradation → puts pressure on resources/environment
Leaky tourism → Money from international travel associations goes back to the HIC in which it is set up rather than benefitting the local economy
Foreign gentrification → countries become what tourists want/exploitation of culture
Concept of enclave tourism
Travel companies often sell ‘all inclusive’ holidays.
Tourists pay one price for transport, accommodation, food, drinks and entertainment.
Cruise ships offer a similar type of holiday.
Tourists are reluctant to leave the hotels/cruise ship in order to buy food and drink as they feel they have ‘paid for everything’ already
Consequences of enclave tourism
The consequences of this are that the economy of the local destinations benefit very little from tourism as most of the money is kept by MNCs like TUI or Royal Caribbean
Positives and Negatives of tourism in Gambia (LIC)
Negatives:
Tourism is seasonal → leaves many people unemployed or underemployed for several months → forcing them to turn to work in the informal sector → do not pay tax → economy does not benefit → income is not reliable → people cannot provide for themselves or their families
Increases cost of living
Leaky tourism
Deforestation/destruction of other natural sites
Disrespecting of cultures/religious beliefs
Positives:
Creates jobs
Benefits economy
Attracts MNCs
Conservation of environment
Conservation of cultural sites, skills and events
Improvement/Development in infrastructure due to its high demand and increased disposable income
Positive multiplier effect
Positives and Negatives of tourism in Goa (NIC)
Negatives:
Deforestation and destruction of sand dunes and mangrove swamps to make room for hotels, water is extracted for hotels to run → decreases biodiversity and protection from soil erosion
Increased waste management issues
Commercialisation and destruction of tradition for tourist benefit
Disrespect also occurs in places such as religious buildings where people do not where the correct clothing
Leaky tourism
Tourism has increased crime
Tourism has caused overcrowding in honeypot sites
Cost of living has increased
Positives:
Provides jobs and increases GDP→ increased standard of living by 70%
Allows women to get jobs and increase their wealth
Infrastructure has developed massively due to increase in demand and disposable income → better and more services are provided
Positive multiplier effect
Emergency Aid
Immediate/short term aid to preserve life
Long-term aid
Aims to preserve/improve quality of life
Why do countries give aid?
Extreme weather events/Natural disasters that cause destruction
Strengthen alliances
To sustain being part of an organisation such as WHO
Encouraging education and healthcare
Providing military support
Bi-lateral aid
Direct aid given from one country to another
Multi-lateral aid
Many countries providing aid which is then distributed by a central body/organisation
Causes of inequality in India
Some groups of people remain poor because they are excluded from part or all of their education or better jobs: women, people with disabilities, Muslims, Dalits and tribal groups
Huge numbers of Indians work in very low paid jobs
Extreme weather events
Climate change
Government rule
Consequences of Inequality in India
Health → low life expectancy in some areas
Education → low literacy rate in some areas
Economic → people unable to find jobs
Examples for Inequality in India
Bihar:
Very rural → less work opportunities
30+% of people live in poverty
Less than 50% of people can read and write
Government has only recently started to invest in public health and education
Kerala:
Government is generous in funding public health and education
Very low poverty rate
Very high literacy rate
Very high life expectancy
Policies to help reduce birth rate → Low birth rate
Focus on girls attending school
North/South divide in the UK
Better standard of living in the south than in the North:
Higher life expectancy in the south for both males and females
Higher earnings overall for both men and women in the south
There are still some areas of that earn higher in the north and lower in the south