Geology, land use and glaciation in the UK
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Landscape
The character of an area, resulting from the actions and interactions of natural and human elements.
Geology
The scientific study of the origin, history, structure and composition of the Earth.
Tees - Exe line
Imaginary line that stretches across the UK and splits it into Lowland & Upland.
Starts at the river Tees in the north to the river Exe in the south.
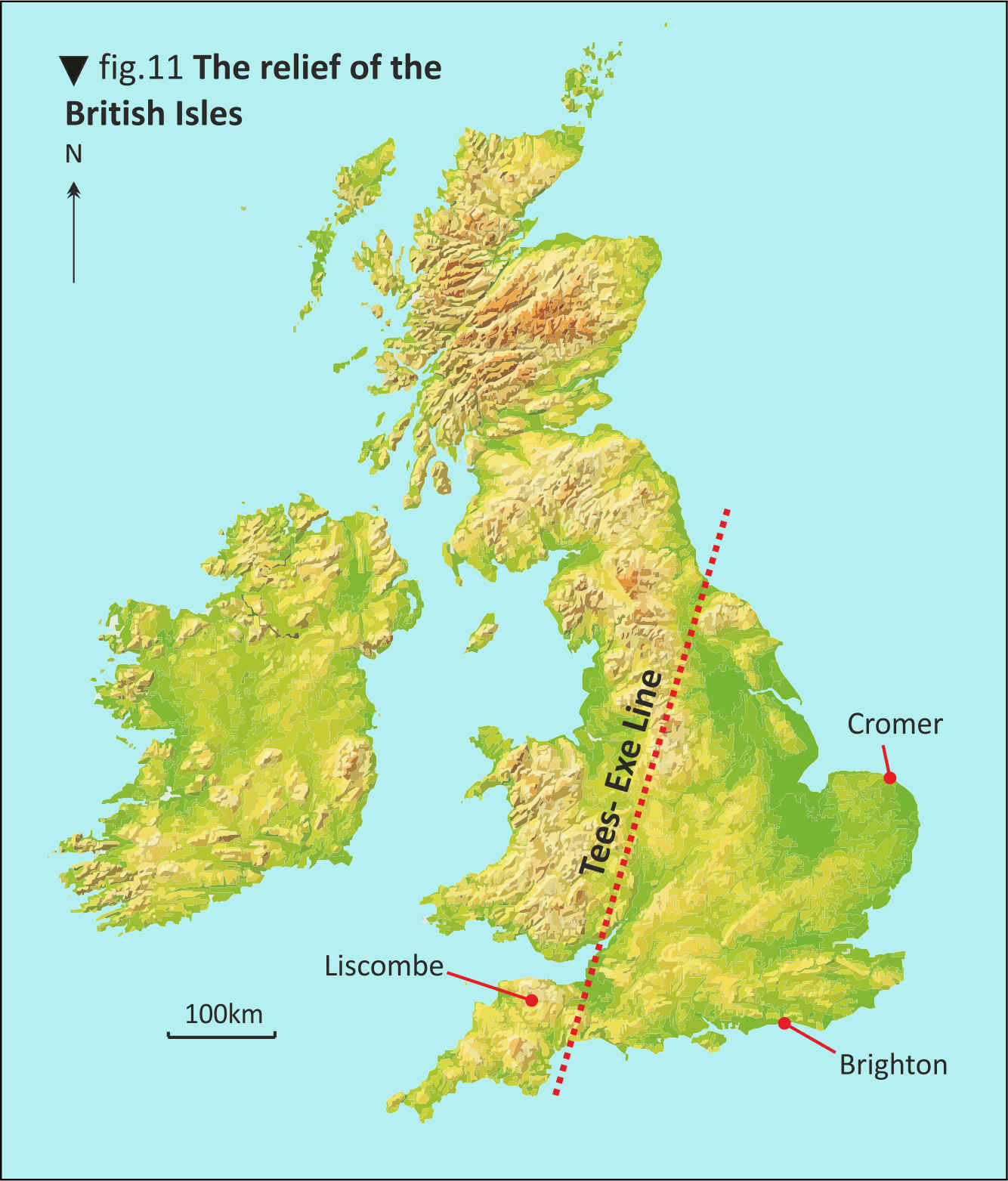
Where are Upland areas? What are they like?
North of the Uk, above Tees-Exe line. High above sea level and they are often but not always mountainous. They usually consist of metamorphic and igneous rock.
Characteristics of Upland areas:
Experience lower temperatures
High rainfall
Windy
Examples of Upland areas:
Scottish Highlands, Lake District, the Pennines
Where are Lowland areas? What are they like?
The south of the UK, below the Tees-Exe line. Not very high above sea level. Mainly consists of sedimentary rocks.
Characteristics of Lowland areas:
Often flat
Experience milder temperatures
Less rainfall
Examples of lowland areas:
Low weald Sussex, the London basin, the Midlands
Explain 3 differences between the climates of uplands and lowlands in the UK.
Uplands are colder, temperatures fall as altitudes rise, because mountains force air to rise and as it rises it expands & therefore cools
Uplands are wetter than lowlands because mountains force air to rise and therefore cool, which leads to condensation forming clouds and increasing rainfall
There is more snow in the uplands because of lower temperatures that means precipitation sometimes falls as snow and not rain
Erosion
The wearing away of rocks and displacement of materials by moving forces such as wind, water and ice.
Weathering
The decomposition of rocks, soil and minerals by direct contact with the atmosphere. Does not involve movement - different from erosion.
Mechanical Weathering:
Breakdown of rocks due to exertion of physical forces - e.g. freeze-thaw
Chemical weathering:
Breakdown of rocks due to chemical reactions. e.g. carbonation - acid rain reacts with calcium carbonate in rocks to form a chemical compound which can be dissolved.
Biological weathering:
The breakdown of rocks due to the actions of living things. e.g. as roots of plants grow bigger they can break up weaker rocks or burrows of species like rabbits can break down rocks.
What is glaciation?
It is the formation, movement, and melting of glaciers.
Glaciation starts with snow and ice accumulation, which turns into ice sheets or glaciers.
As glaciers move, they erode the land, shaping the landscape by carving valleys, creating U-shaped valleys.
What is a glacier?
A large accumulation of ice, snow, rock, sediment and water that slowly move downhill under the influence of their own weight.
How did glaciation shape the Upland areas of the UK?
Glaciation shaped Britain's highland areas during the Ice Age, creating sharp peaks and deep valleys. As glaciers move, they erode the land, shaping the landscape by carving valleys, creating U-shaped valleys.
Deposition
The laying down of sediment carried by wind, flowing water, sea or ice
How Tectonic activity shaped the landscape:
Caused mountains to form as land was pushed upwards - Scottish Highlands, Snowdonia.
Metamorphic rocks were formed when sedimentary rocks were heated and compressed during tectonic activity - e.g. slate & schist
Igneous rocks were formed when magma cooled, are more resistant to erosion so were pushed and folded upwards to form Upland areas
Volcanic cones formed by tectonic movement can still be seen in the UK landscape.
The three types of rocks
Igneous, sedimentary, metamorphic
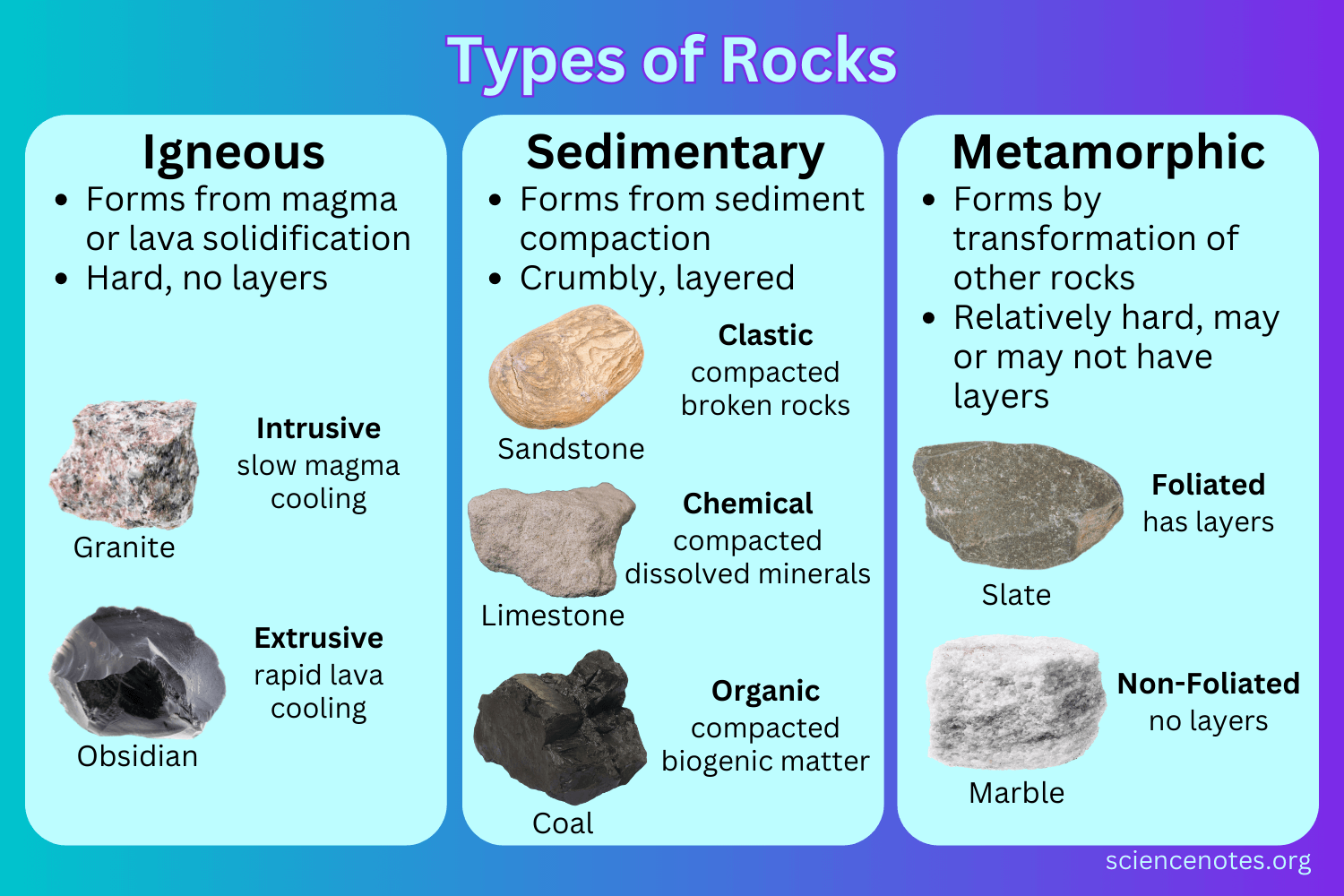
Igneous rock formation
They are a result of volcanic activity in the past when Britain was close to a plate boundary.
Magma from the mantle or lava cools and solidifies. As it cools crystals are formed in the rock which interlock and form hard crystalline rocks.
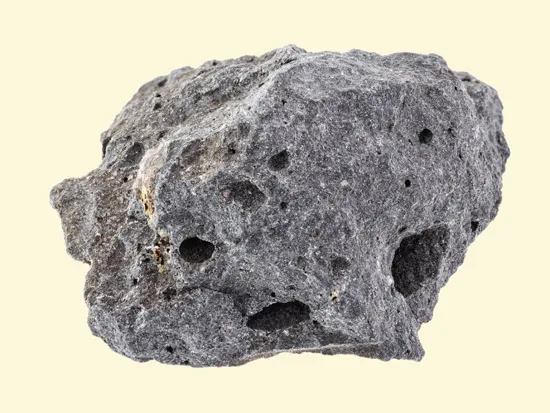

Igneous rock characteristics
Hard - because they are made of interlocking crystals
Resistant to erosion - because they are made of interlocking crystals that increase strength
Impermeable
Extrusive
Crystalline
Examples of igneous rocks:
Granite, Basalt, Obsidian
Sedimentary rock formation
Made up of small particles of sand and rock, which have been transported by the wind, rivers, and ice.
They are usually deposited in the bottom of a body of water and over millions of years, successive layers of sediments accumulate
These layers are compressed by the weight of the deposits above, into sedimentary rocks.
These rocks form in layers known as bedding planes.
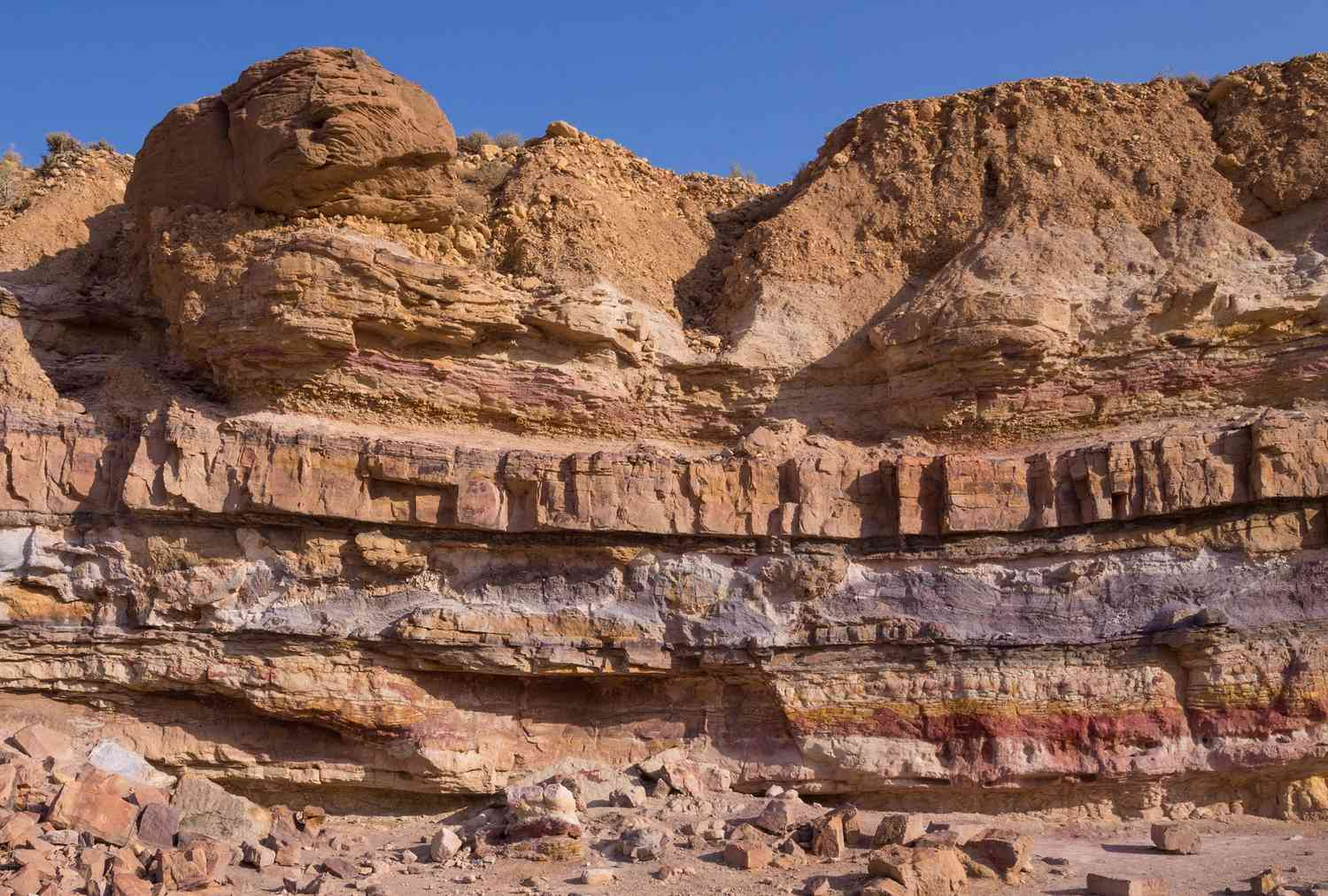

Sedimentary rock characteristics
Soft - because it is made up of layers that slide against eachother
Permeable
Examples of sedimentary rocks
sand forms sandstone
mud forms clay
limestone and chalk come from the remains of dead plant, animal, and marine species (rich in calcium carbonate)
Metamorphic rock formation
Rocks that have been changed in shape and form by intense heat and pressure at a plate boundary or along a fault line.
start either as igneous or sedimentary rocks and are crystallized under intense heat and pressure conditions. Becoming more compact & denser.
Change is sometimes caused by tectonic plate movement.
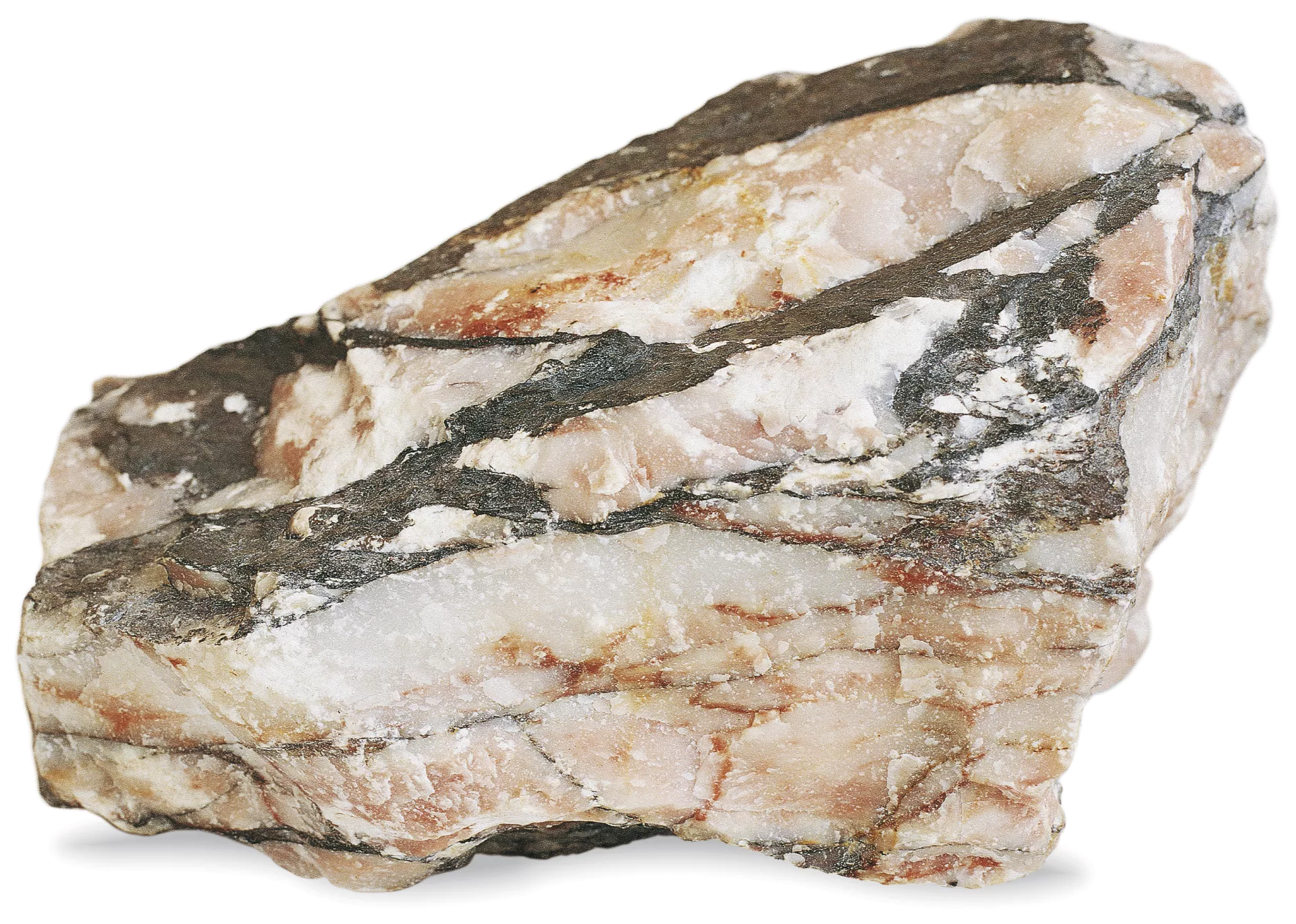

Metamorphic rock characteristics
Is the hardest rock type
Resistant to erosion
Impermeable
Metamorphic rock examples
Marble, Slate, Schist
What types of rocks are found in lowland areas in the UK?
Sedimentary rocks such as limestone, sandstone, and clay are commonly found.
What types of rocks are found in highland areas in the UK?
Mostly Igneous rocks such as granite and basalt, metamorphic rocks like slate and schist, and some sedimentary rocks such as sandstone and limestone.
Why are sedimentary rocks found in lowland landscapes?
Sedimentary rocks are less resistant to physical processes so can be more easily eroded leading to lower land.
Weaker rocks form…
Lowlands
Stronger, more resistant rocks form…
Highland/Upland areas.
Permeability:
Whether a rock allows water to pass through it.
Permeable: water will pass through
Impermeable: won’t let water through
How does permeability affect landscape?
Determines how wet or dry the surface of a landscape is.
Permeable rocks → dry upland areas
Impermeable rocks → wet lowland areas
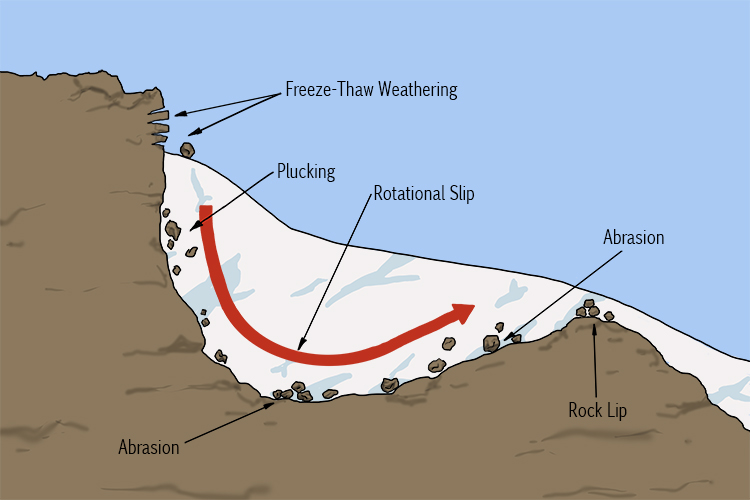
Examples of glacial erosion processes in Upland areas:
Abrasion, plucking
Abrasion (Upland)
As a glacier moves downhill, rocks that have been frozen into the base and sides of the glacier scrape the rock beneath, wearing away the underlying rock surface
These rocks scrape the bedrock (like sandpaper) leaves scratches called striations behind
Cause U-shaped valleys and hanging valleys.
Plucking (Upland)
Rocks become frozen to the bottom and sides of the glacier
As the glacier moves downhill its ‘plucks’ rocks frozen into the glacier from the ground
Cause U-shaped valleys and hanging valleys.
Freeze-thaw weathering (Upland)
Snow or water entering the cracks in a rock or sides of a glacier during the day
When the temp drops below 0, the water in the crack freezes and expands by 9%
Crack widens and process repeats through continual thawing and freezing
Rock eventually breaks off
Cause hanging valleys.
Examples of slope processes in Upland areas:
Rock falls, Landslides, mudflows
Rock falls (Upland)
Occurs on sloped cliffs over 40degrees once rocks have been exposed to freeze-thaw weathering.
Landslides (Upland)
Water between sheets of rock and the rock-face reduces friction, and allows large chunks of rock to slide down the cliff.
Mudflow (Upland)
Saturated soil flows down the face of a hill like fluids creating a lobe at the bottom
Examples of Weathering processes in Lowland areas:
Dip slopes, Escarpments, Low clay vales
Dip Slopes
Formed by the different rates of erosion of different rock layers. These rock layers will dip in a specific direction. Softer rocks will erode faster creating a gradual & gentler slope.
Escarpments (Lowland)
Results from the erosion-resistant rocks layers being left behind once softer rock layers have been eroded away

Low clay vales
Created by the deposition of clay and silt particles, carried by water. These low-lying areas form in areas with slow-moving rivers.
Rotational slip
Forms when the material on a slopes surface slides downhill along a curved surface.
Human activities in the Uk
Agriculture, Forestry, Settlements
Examples of location agriculture + why:
85% of the South downs national park is farmed (1100 farm businesses)
Chalk grasslands have short grass that is rich with nutrients, making it ideal for grazing sheep as well as arable farming
Clay grasslands are suitable for dairy cows as the grass is longer
How UK landscape has been changed by farming:
Drainage ditches built to drain water from low-lying land
Trees and hedges are cleared away to make room for large agricultural machinery
Small fields are combined to make farming more profitable and to use large machinery
Advantages of agriculture
Farming generates income for local economy through employment & profits
Farming supported by government can help support local wildlife as farmers are payed to plant wildflowers and hedgerows to allow wildlife to move around safely - Wildlife corridors
Disadvantages of agriculture
There has been a shift from arable farming to livestock farming in the UK as food is cheaper to import from central Europe/Asia/Africa, this has changed the types of plants available to pollinators in the UK - decline in biodiversity
Use of chemicals and pesticides has affected wildlife - further impacting ecosystems - also affecting soil
To be profitable, farming must take up a lot of space - invades protected areas
Examples of location of Forestry:
South downs woodland covers 23.8% of park
Human activity has increased, resulting in large areas being cleared
Change from primitive axes to machinery has improved efficiency
Advantages of forestry
Proper management of woodland allows wildlife to thrive - especially protected species
Allows for sustainable source of fuel, good building resources & heating for local areas
Proper management can boost tourism - paths for hikes - boosting local economy through investment & employment
Disadvantages of forestry
Removal of woodland by forestry to make way of new housing threatens ancient leaved lime woodland and has caused a decline in biodiversity
Poorly managed woodland disrupts biodiversity - overgrowth limits what species can live there
Poorly managed tourism can impact woodland through erosion of soil pathways and damage to trees
Examples of location of settlements:
Valley scenery in South downs, settlement were built on naturally formed slopes as it gives shelter
Flat land makes it easier for building infrastructure to be travelled on
Rivers - meanders provided good defence, transport links and freshwater
Natural harbours - fishing/trading
Natural springs - reliable freshwater