Principles of Marketing Exam 2 - Moore
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
Consumer buying behavior
Buying behavior of final consumers
Consumer market. What are the three words?
All the individuals and households that buy or acquire goods and services for personal consumption
ACQUIRE, USE, DISPOSE
Is this an S-R model? What does S-R mean?
Yes. S-R means stimulus-response
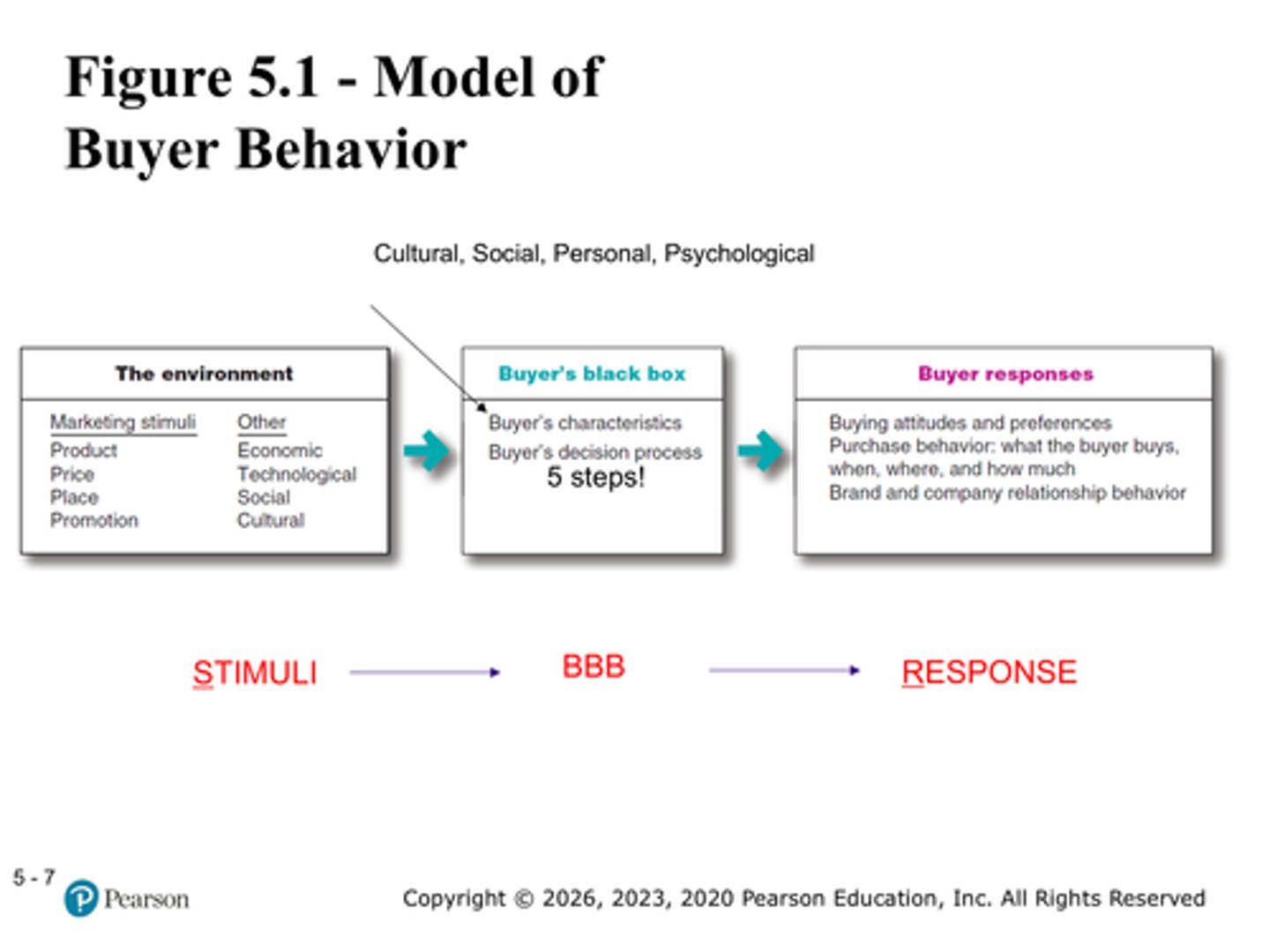
What is the BBB (what are the two parts)?
Buyer's Black Box
1. Buyer's characteristics
2. Buyer's decision process
What are the four characteristics that influence consumer purchases" See figure 5.2. Be able to list and define
Cultural, Social, Personal, Psychological
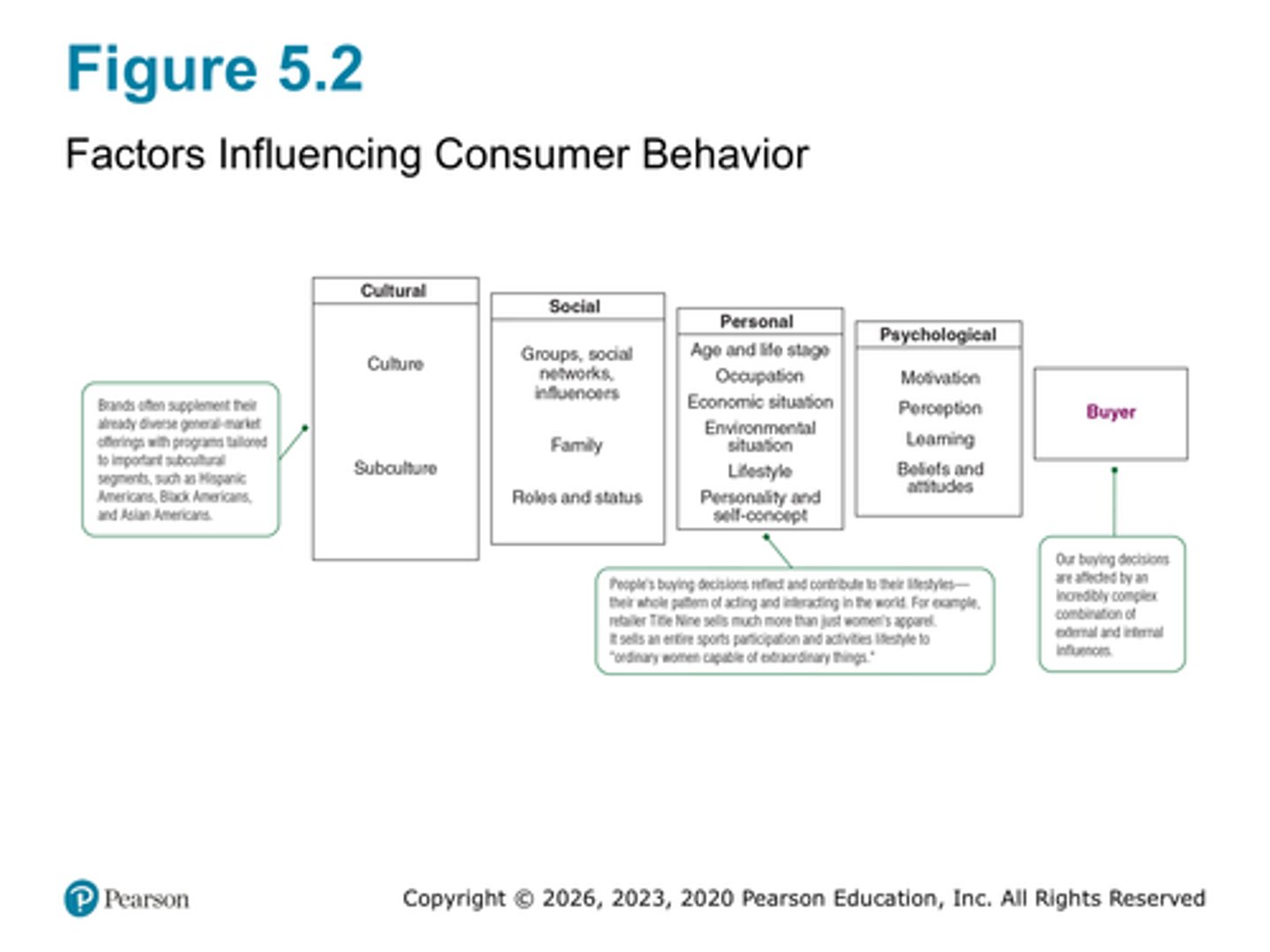
Define culture, subculture
Culture - •Set of basic values, perceptions, wants, and behaviors learned by an individual from family and other important institutions
Subculture - Group of people with shared value systems based on common life experiences and situations
What are the key elements of social factors.
- Membership groups
- Reference groups
- Word-of-mouth
- Opinion leaders
- Influencer marketing
- Online social networks
- Family
- Roles and status
Opinion leader
Person within a reference group that exerts influence due to special skills, knowledge, personality or other characteristics
Influencer marketing
Enlisting established influencers
Reference groups
direct or indirect point of comparison
-Aspirational groups: wish to belong
What do roles and status mean?
Is family important?
People usually choose products appropriate to their roles and status
Family is important
List the personal factors.
•Occupation
•Age and family life cycle
•Economic situation
•Environmental situation
•Lifestyle: involves AIO (activity, interest, opinions)
•Personality and self-concept
What does AIO stand for?
activities, interests, opinions
List the key psychological factors
•Motivation
•Perception
•Learning
•Beliefs and Attitudes
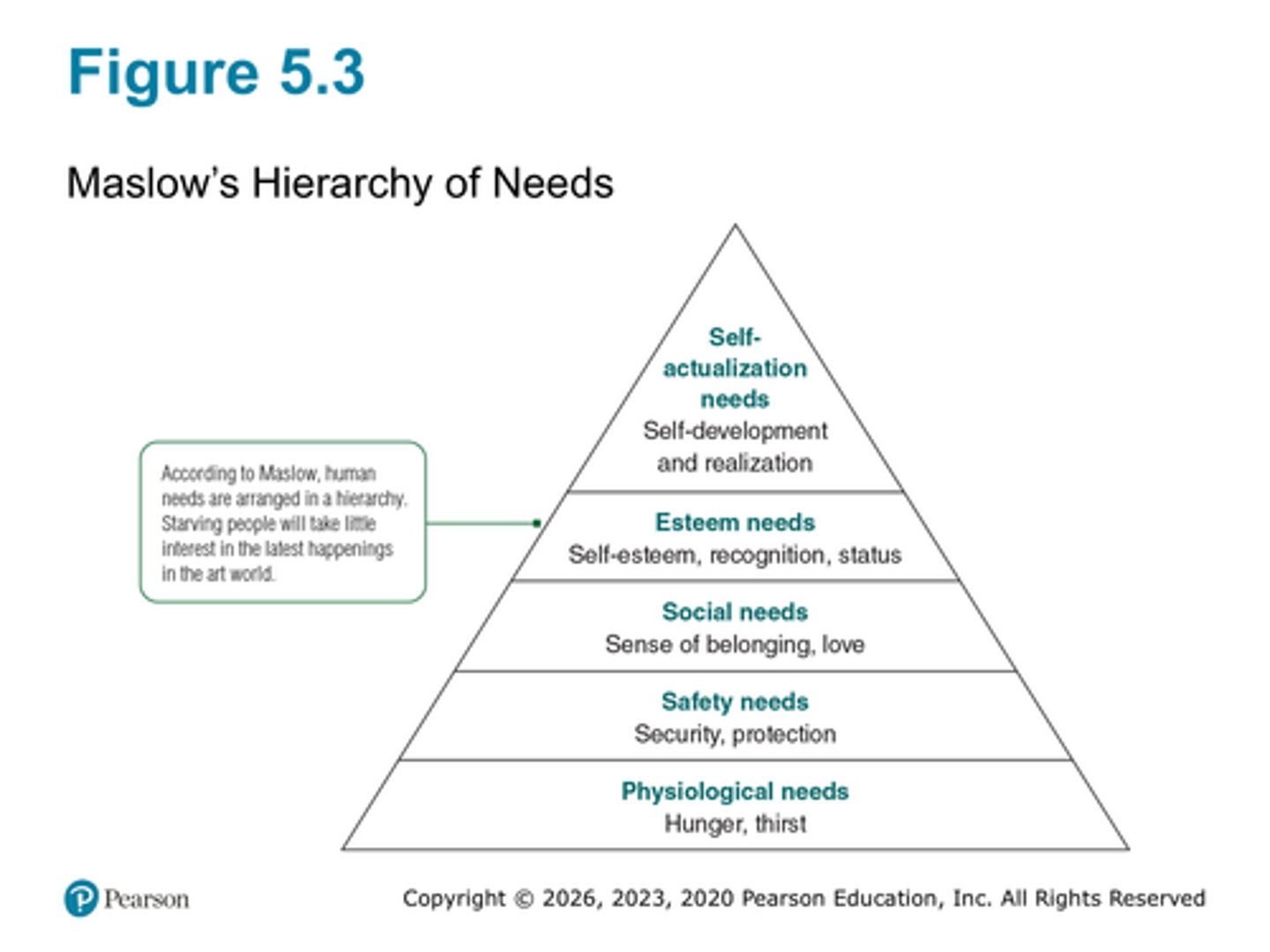
Know Maslow's Hierarchy of needs (figure 5.3)
Define perception
Selecting, organizing, and interpreting information to product meaning
Define subliminal advertising
advertising in which the consumer doesn't realize they are being affected by an ad
What is JND?
Just Noticeable Difference
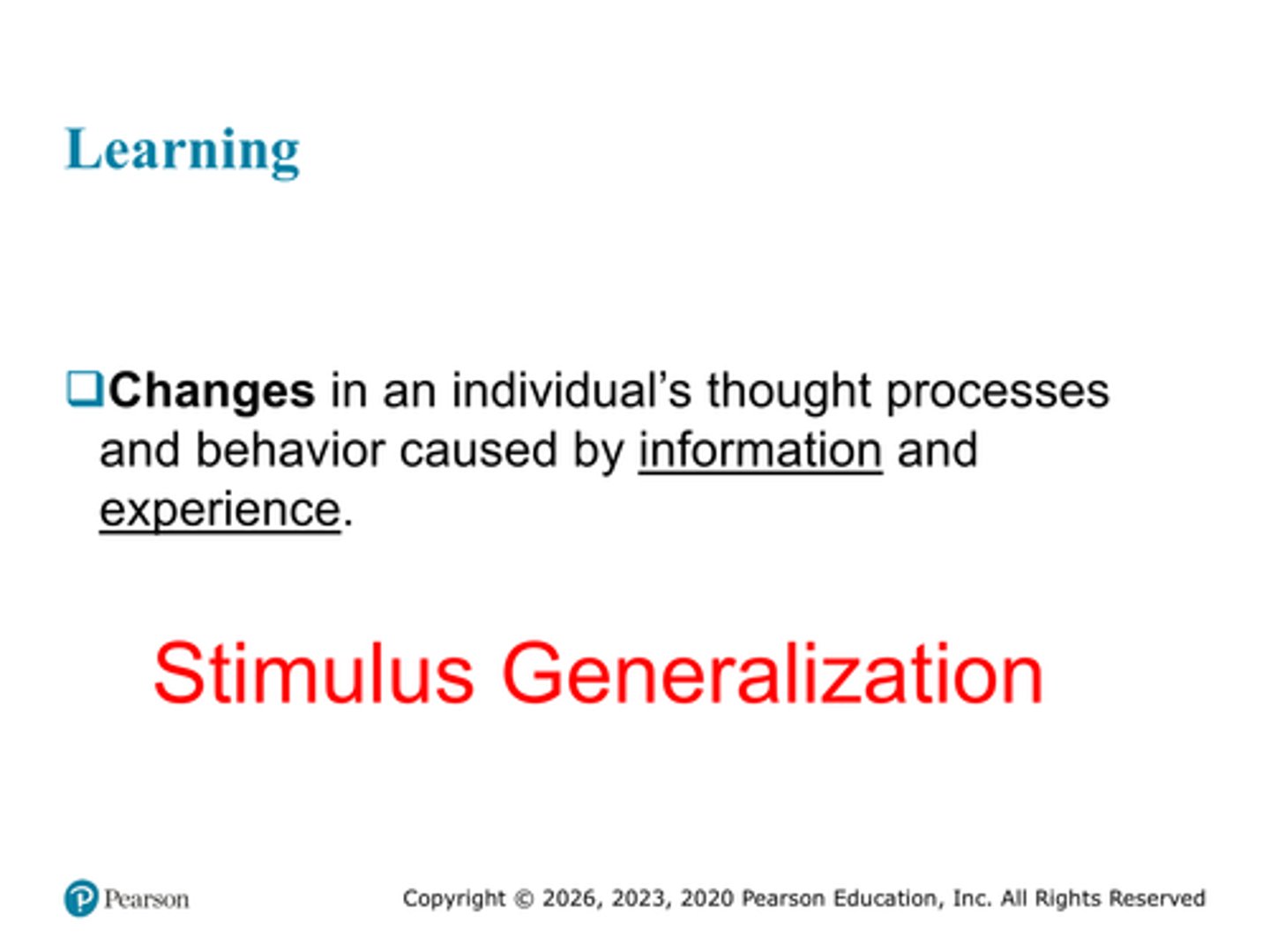
Is stimulus generalization part of learning? What were our examples?
Yes, it is
Examples include Arm and Hammer, and Ritz
Attitude
An individual’s enduring evaluation of feelings about and behavioral tendencies toward an object or idea
Parts of attitude
Cognition
Beliefs, knowledge, information
Affect
feelings, emotions
Behavior
intentions
KNOW figure 5.4 (steps in buyer decision process)
Need recognition
Information search
Evaluation of alternatives
Purchase decision
Post purchase behavior
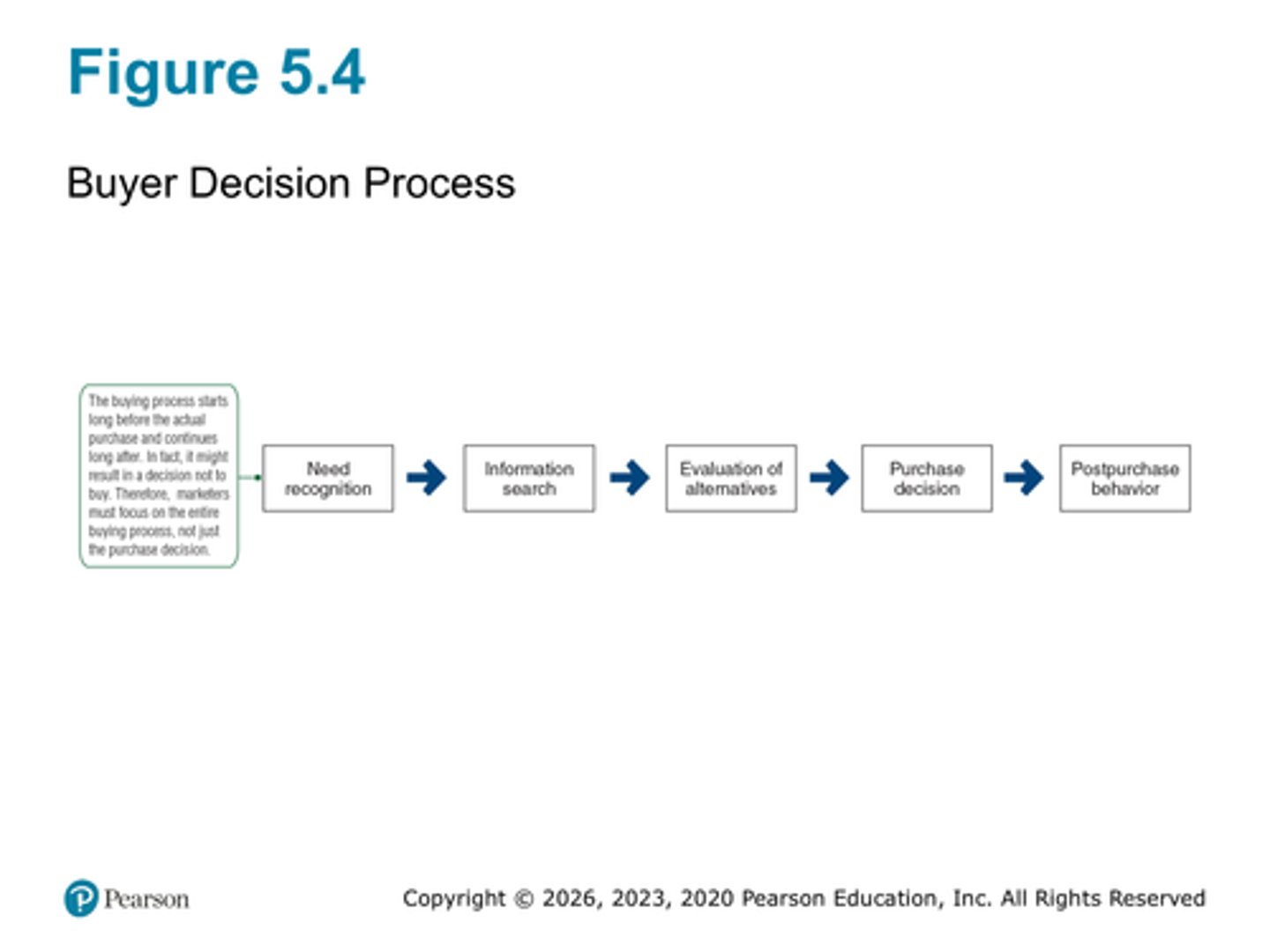
A need occurs when there is enough tension and distance between what and what (see slide)? How can a need be triggered?
Can be triggered through internal and external stimuli

Do we always engage in information search? What types are there? Which is the least biased?
Yes, we do. External is the least biased

What is universal, retrieval, consideration, choice set
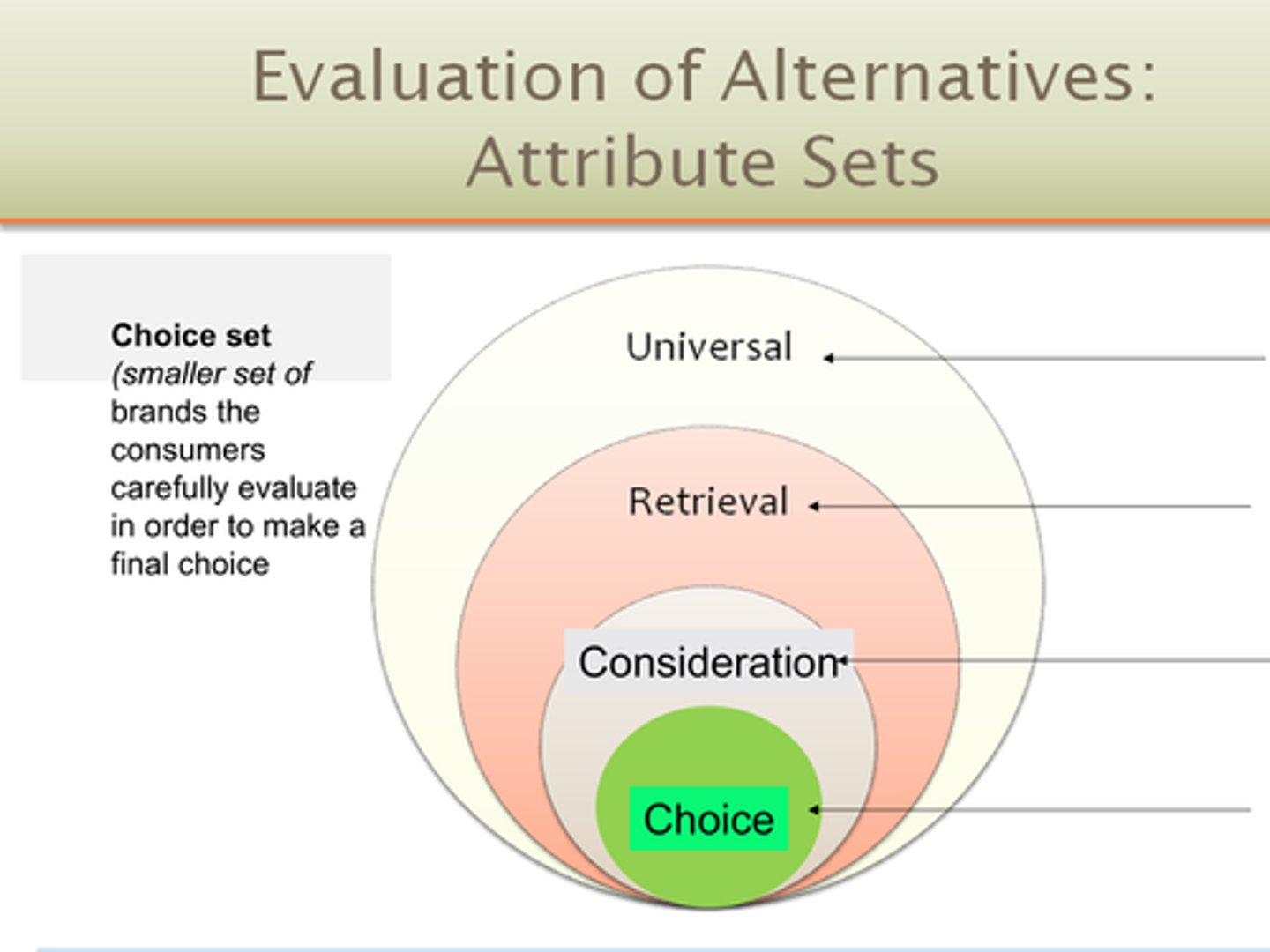
What two things get in the way during purchase decision stage?
-Attitudes of others
-Unexpected situational factors
In post-purchase, why is cognitive dissonance a concern? Define it.
A buyer's doubts shortly after a purchase about whether the decision was the right one
Often occurs after expensive, high-involvement purchases
Define Customer Journey.
the sum of the ongoing experiences consumers have with a brand that affect their buying behavior, engagement, and brand advocacy over time
List the steps in the adoption process. Define adoption process.
Adoption process: A mental process through which an individual passes from first learning about an innovation to final adoption
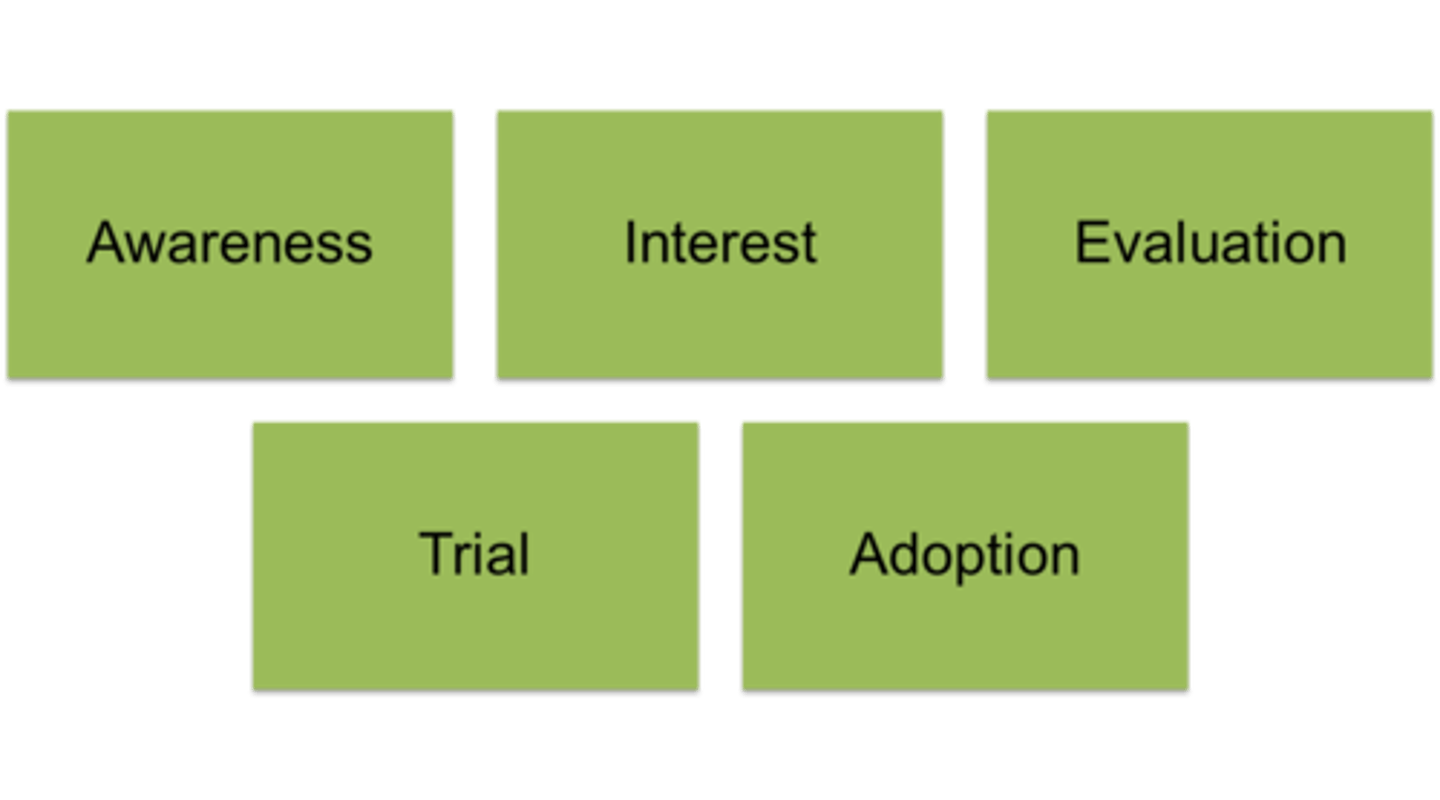
Trial (The quickest route to adoption)
In this stage, the consumer tries the new product on a small scale to improve his or her estimate of its value
know the difference between trial and adoption.
Trial is small scale test of a product, adoption is full and regular use of the product
Know figure 5.5
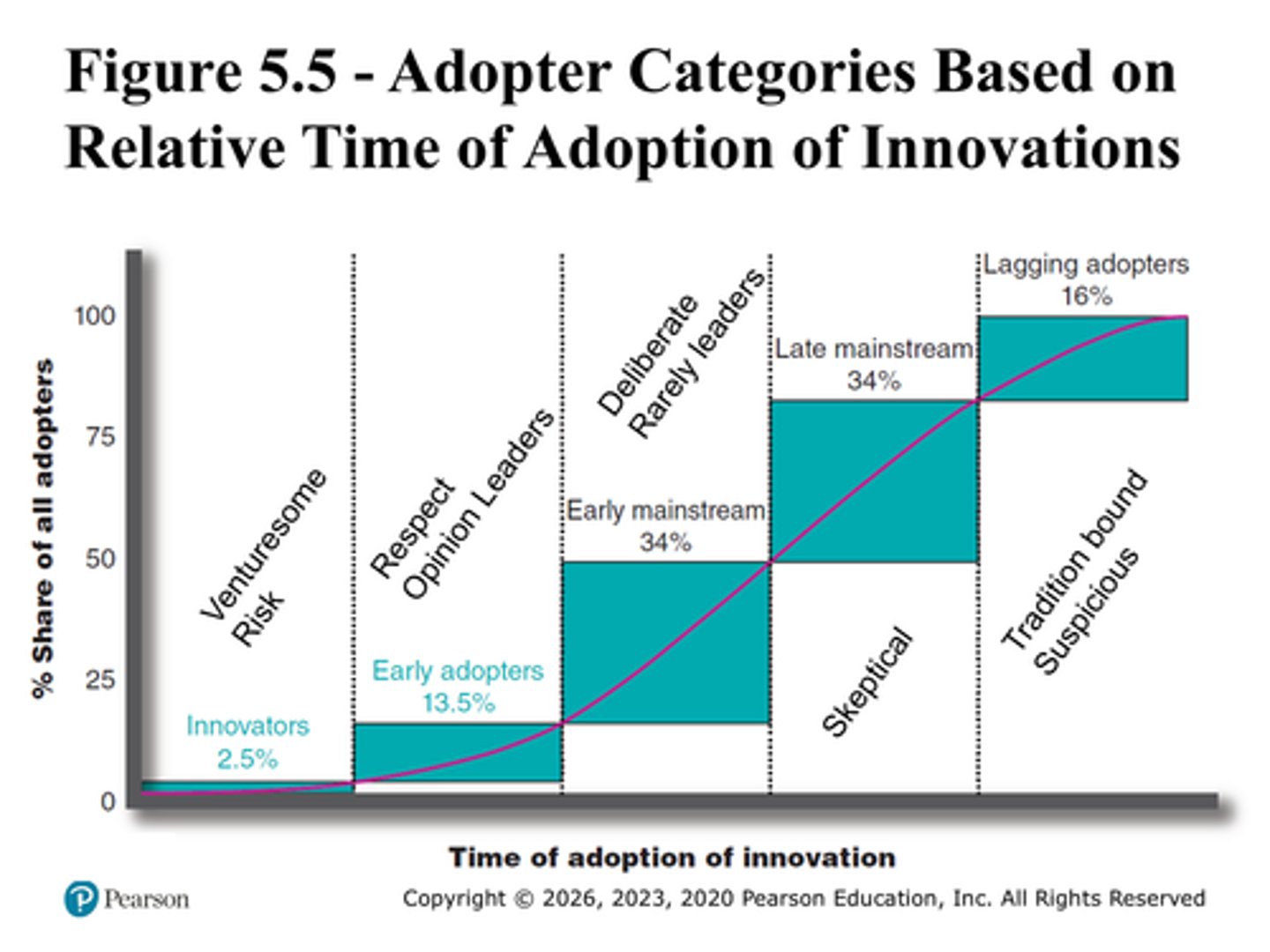
Innovators and Lagging adopters.
Innovators: Try new ideas at some risk.
Lagging: adopt the innovation only when it has become something of a tradition itself
What are the five characteristics that impact the rate of adoption?
•Relative advantage
•Compatibility
•Complexity
•Trialability
•Observability
•Risk
Relative Advantage
The degree to which the innovation appears superior to existing products.
Compatibility
The degree to which the innovation fits the values and experiences of potential consumers
Complexity
Refers to the degree to which the innovation is difficult to understand or use
Trialability
The degree to which the innovation may be tried or sampled on a limited basis
Observability
The degree to which the use of the innovation and the potential outcomes of usage can be observed by or communicated to others
Risk
The degree to which the customer perceives risk in purchasing the product
Business buyer behavior
-Purchasing goods and services that are used in the production of other products and services
Business-to-business B2B
must understand business markets and business buyer behavior
Business buying process
•Determining which products and services to purchase
-Finding, evaluating, and choosing among alternative suppliers and brands
What are the three main differences between consumer and business markets?
Business markets are
huge and involve more money and items than consumer markets.

What is meant by derived demand?
Business demand that comes from the demand for consumer goods. It is inelastic
Are there more buyers in this (business) market than in the consumer market? Are they larger or smaller?
Fewer but larger buyers
Is this market more professional? Are there more decision makers? (see slide).
Couldn't find anything for this
Know figure 5.6. Is this like the consumer model?
Yes (S-R)
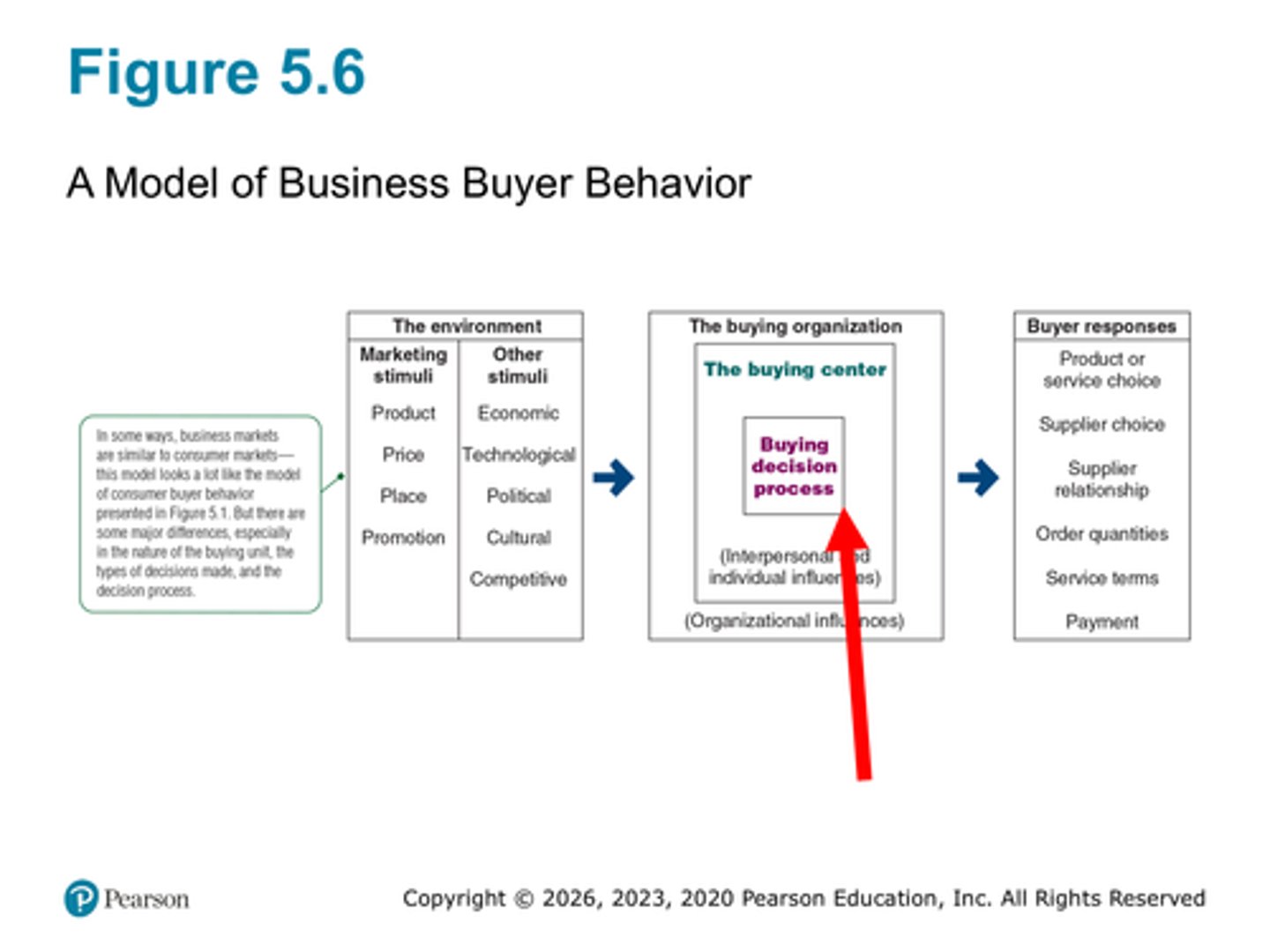
What is the difference between a straight rebuy, modified rebuy, new task?
Straight rebuy
•Buyer routinely reorders something without any modifications
Modified rebuy
•Buyer wants to modify product specifications, prices, terms, or suppliers
New task
•Buyer purchases a product or service for the first time
What are the different roles in the buying center?
Actual users of the product or service
People who make the buying decision
People and units influencing the buying decision
People who do the actual buying
Individuals and units controlling the buying information
What are the four broad influences on business buying behavior?
Environmental, Organizational, Interpersonal, Individual
How many stages are there in the business buyer decision process? (Is it more or less than the consumer buying process?)
There are 8
It is more
Define market segmentation
Divide the total market into smaller segments
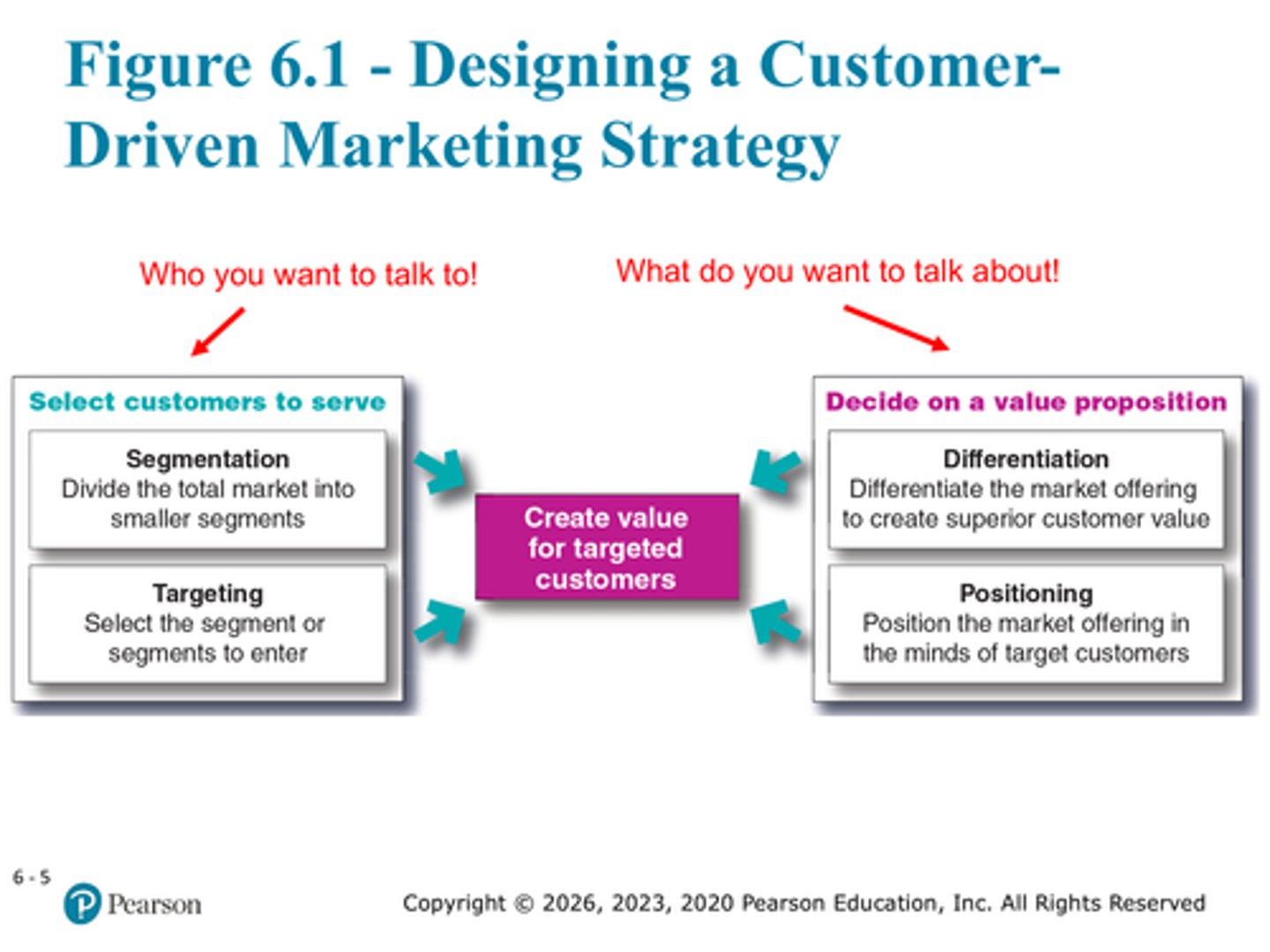
Define market targeting
Select the segment or segments to enter
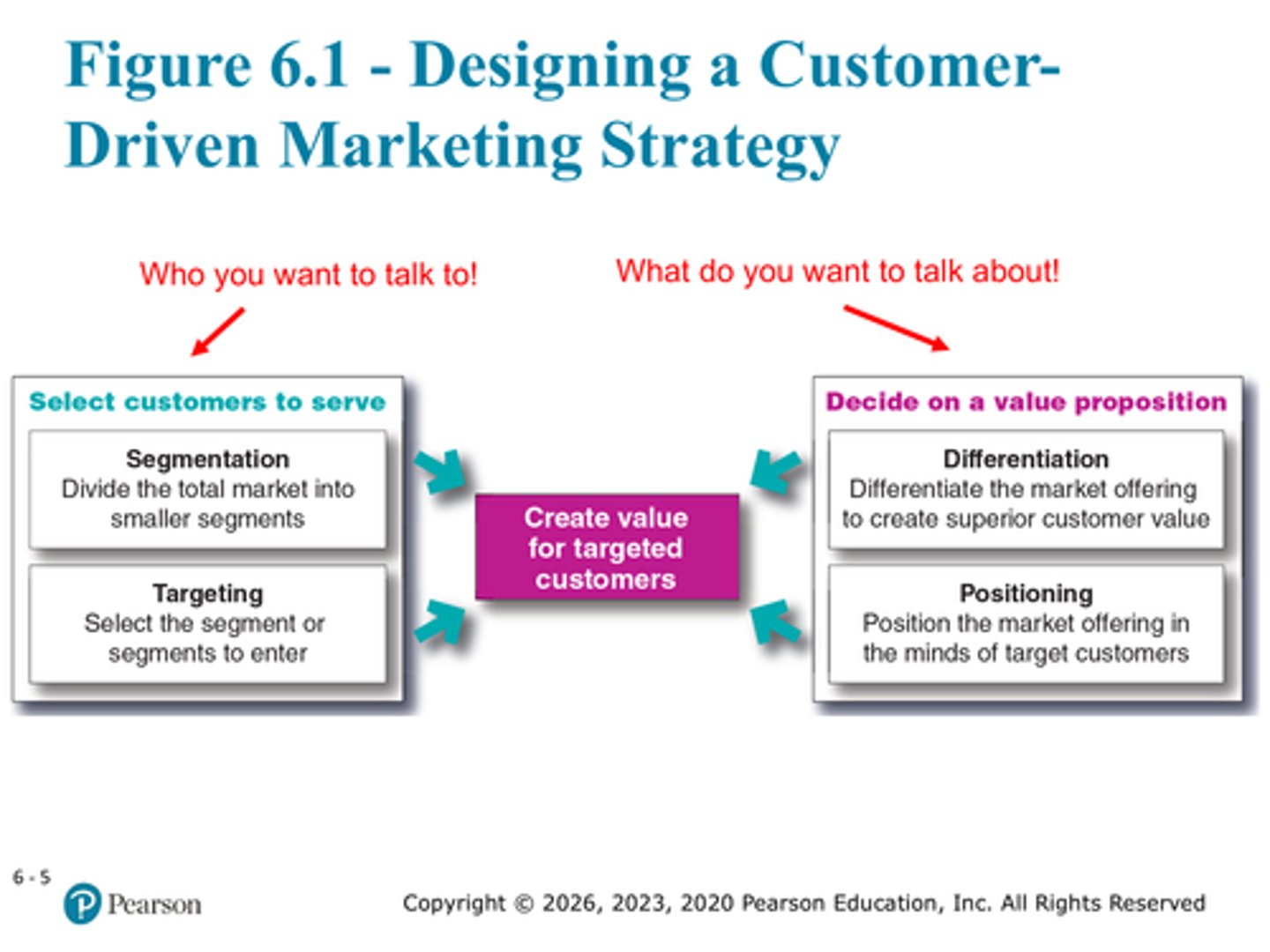
Define market differentiation
differentiating the market offering to create superior customer value
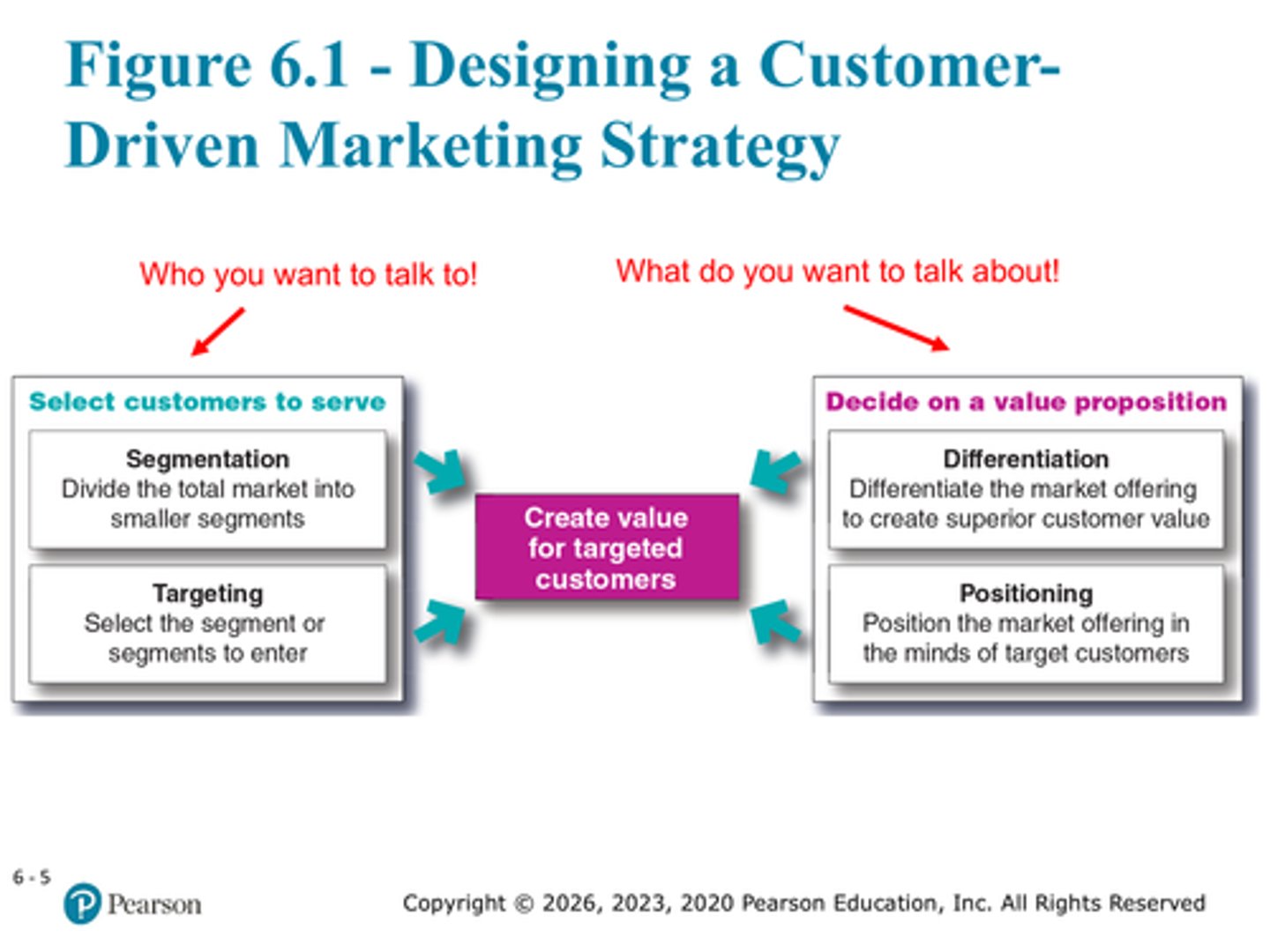
Define market positioning
position the market offering in the minds of target customers
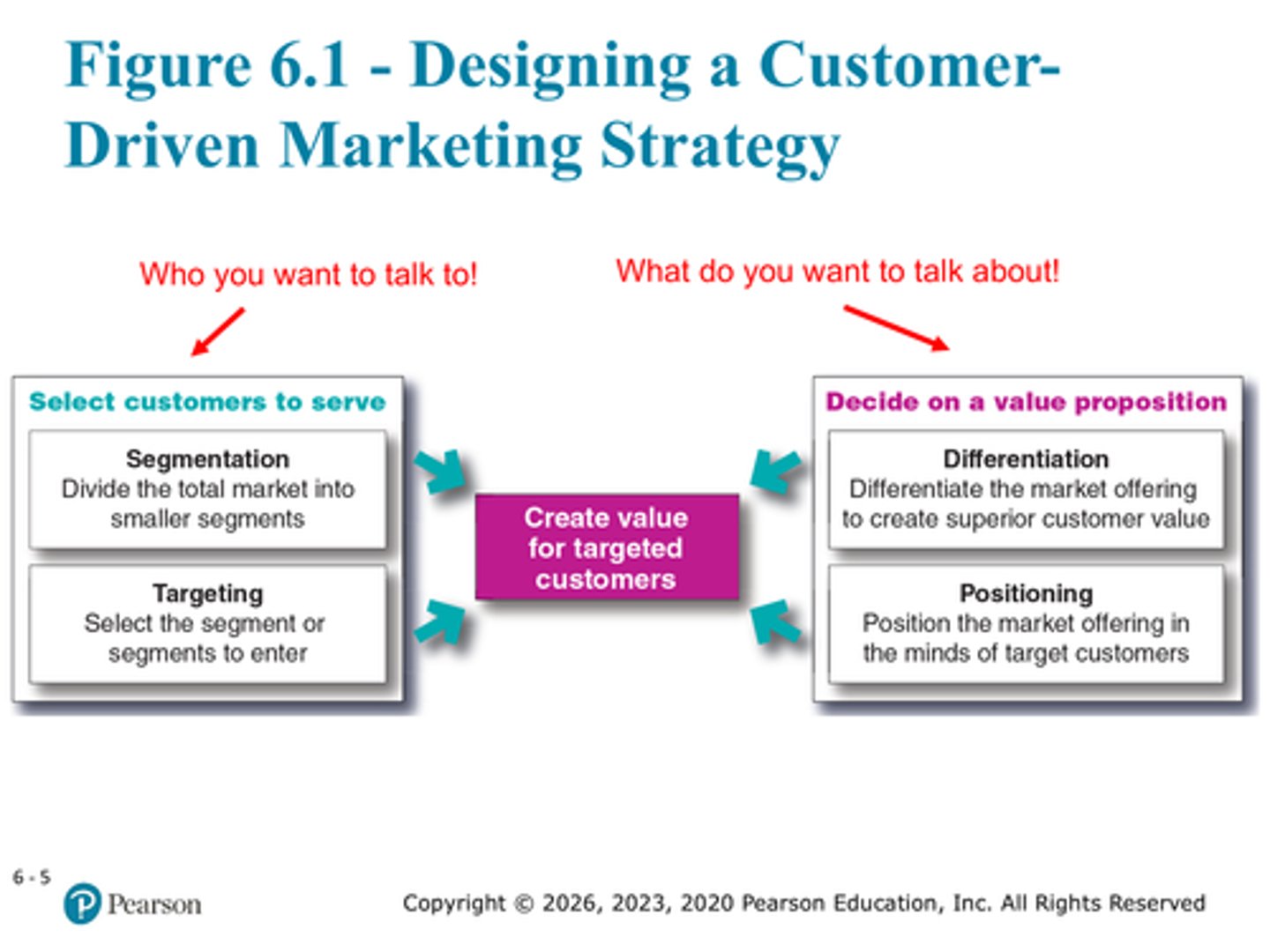
Correct order of the market strategy
Market segmentation, targeting, differentiation, positioning
What are the four major segmentation variables and examples?
Geographic, Demographic, Psychographic, Behavioral

Geographic segmentation
dividing a market into different geographical units, such as nations, states, regions, counties, cities, or even neighborhoods
Demographic segmentation
dividing the market into segments based on variables such as age, life-cycle stage, gender, income, occupation, education, religion, ethnicity, and generation
Psychographic segmentation
dividing a market into different segments based on social class, lifestyle, or personality characteristics
Behavioral segmentation
dividing a market into segments based on consumer knowledge, attitudes, uses of a product, or responses to a product
What are the key requirements for effective segmentation?
-Measurable, accessible, substantial, differentiable, and actionable

What are the four different targeting approaches? Define and provide examples. (figure 6.2)
Undifferentiated, Differentiated, Concentrated, Micromarketing

Undifferentiated marketing
a market-coverage strategy in which a firm decides to ignore market segment differences and go after the whole market with one offer
Differentiated
a market-coverage strategy in which a firm decides to target several market segments and designs separate offers for each
Concentrated
market-coverage strategy in which a firm goes after a large share of one or a few smaller segments or niches
Micromarketing
Practice of tailoring products and marketing programs to suit the tastes of specific individuals and locations
Define competitive advantage. What are some?
An advantage over competitors gained by offering greater customer value, either by
-Having lower prices, or
-Providing more benefits that justify higher prices
Which differences to promote?
•Important
•Distinctive
•Superior
•Communicable
•Preemptive
•Affordable
•Profitable
What is a perceptual map? Consider the example from class and the in-class activity.
•created by questioning a sample of consumers about their perception of products, brands, and organizations with respect to two or more dimensions
The full positioning of a brand is called the brand's v_________ p___________.
Value Proposition
Which are the 'winning' value propositions. What is ALDI's?
More for more
more for the same
more for less
The same for less
Less for much more (ALDI)

What is a positioning statement?
Summarizes company or brand positioning
Define product. Is it the same as a service?
ANYTHING that can be offered to a market for attention, acquisition, use, or consumption that might satisfy a want or need
It is the same as a service
What is a market offering?
It is both tangible goods and services
Know figure 7.1 What example did we use back in chapter 5 to discuss this?
Pool tables
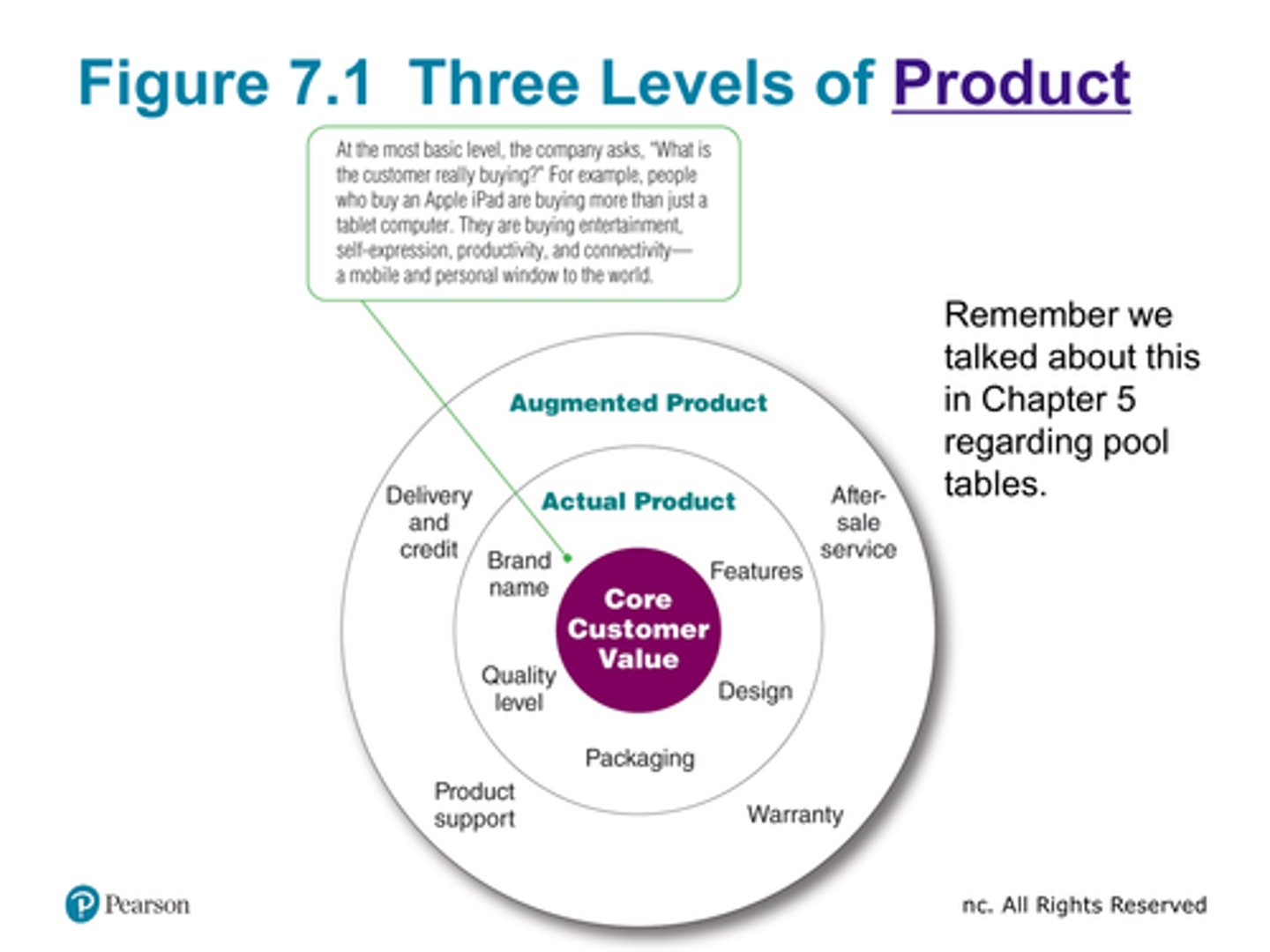
List the four types of consumer products. Define/example.
Convenience, shopping specialty, unsought
Convenience def
are usually bought frequently, immediately, with low customer involvement, and with minimal comparison and buying effort. Examples include laundry detergent, soft drinks, and city subway or bus transport
Shopping def
Are less frequently purchased consumer products and services that customers gather information about and compare carefully on suitability. Examples include furniture, clothing, major appliances, and hotel services.
specialty def
products have unique characteristics or brand identifications for which buyers are willing to make a special purchase effort. Examples include high-end cars, high-priced photography equipment, designer clothes, and medical or legal services
unsought def
are those that a consumer either does not know about or knows about but does not normally consider buying.
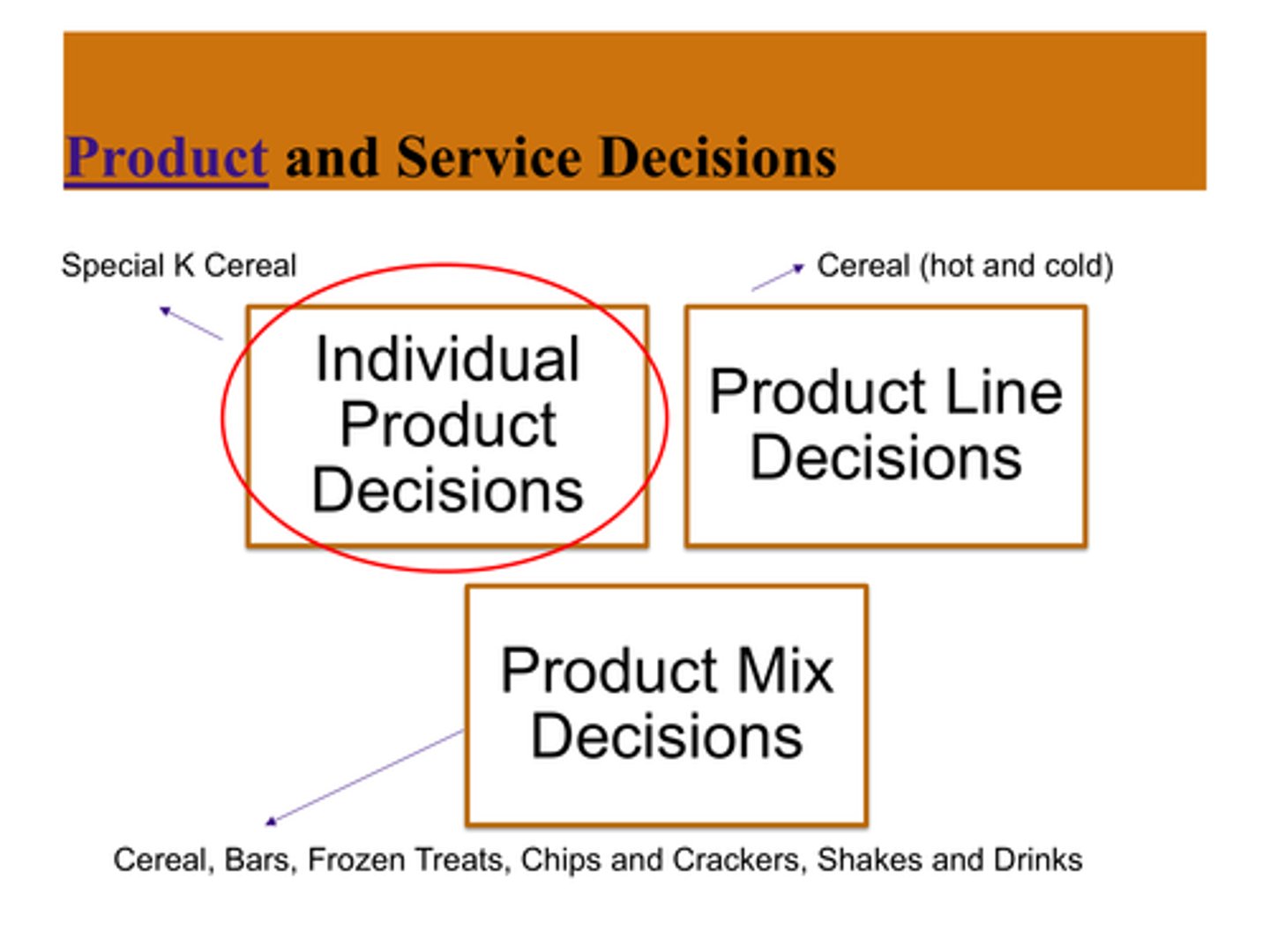
What are the three product/service decisions?
individual, product line, product mix
List the 5 individual product decisions.
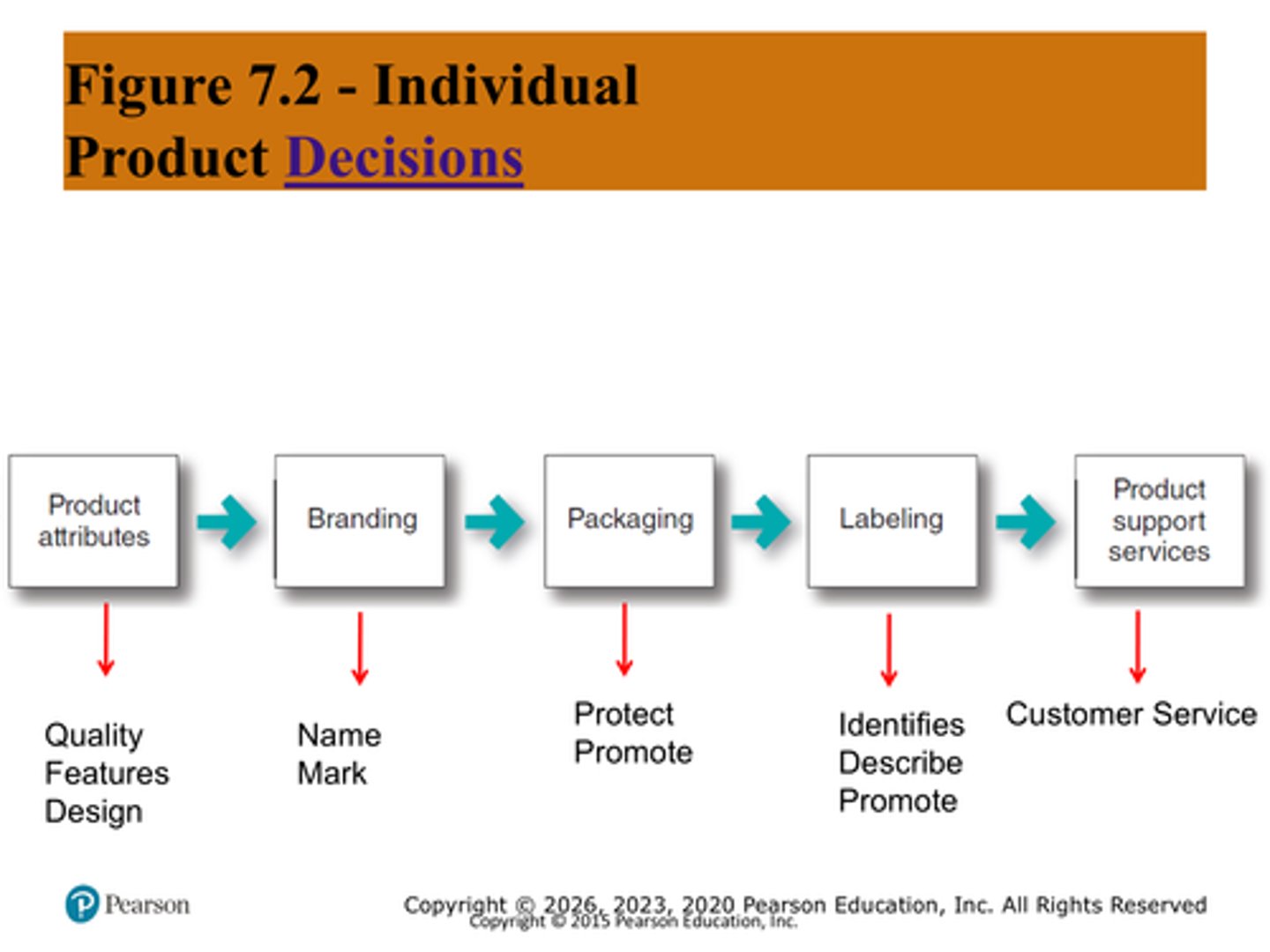
Define product quality, feature, design.

What is branding? Define brand, name, mark, trademark.

What does the package do? What does the label do?
Packaging protects and promotes,
Labeling identifies, describes, and promotes
List and define the 5 determinants of service quality.

Reliability
The ability to perform the service dependably and accurately
Responsiveness
The willingness to help customers and provide prompt service
Assurance
the knowledge of and courtesy by employees and their ability to convey trust and confidence
Empathy
The caring, individualized attention provided to customers
Tangibles
The appearance of physical facilities, equipment, personnel, and communication materials
What is the CREST method for?
-CALM the customer
-REPEAT the problem
-use EMPATHY statements
-SOLVE the problem
-make a TIMELY RESPONSE
What is a product line? What is stretching? Filling?
•closely related products that:
–Have similar functions and customer groups
–Are sold through similar outlets or fall within given price ranges
What is stretching
A company lengthens its product line beyond its current range
What is filling
Adding more items within the present range of the line
What (and define) are the 3 key product mix decisions (mix, length, width)?

What are the four service characteristics (figure 7.3)? Define and provide examples.
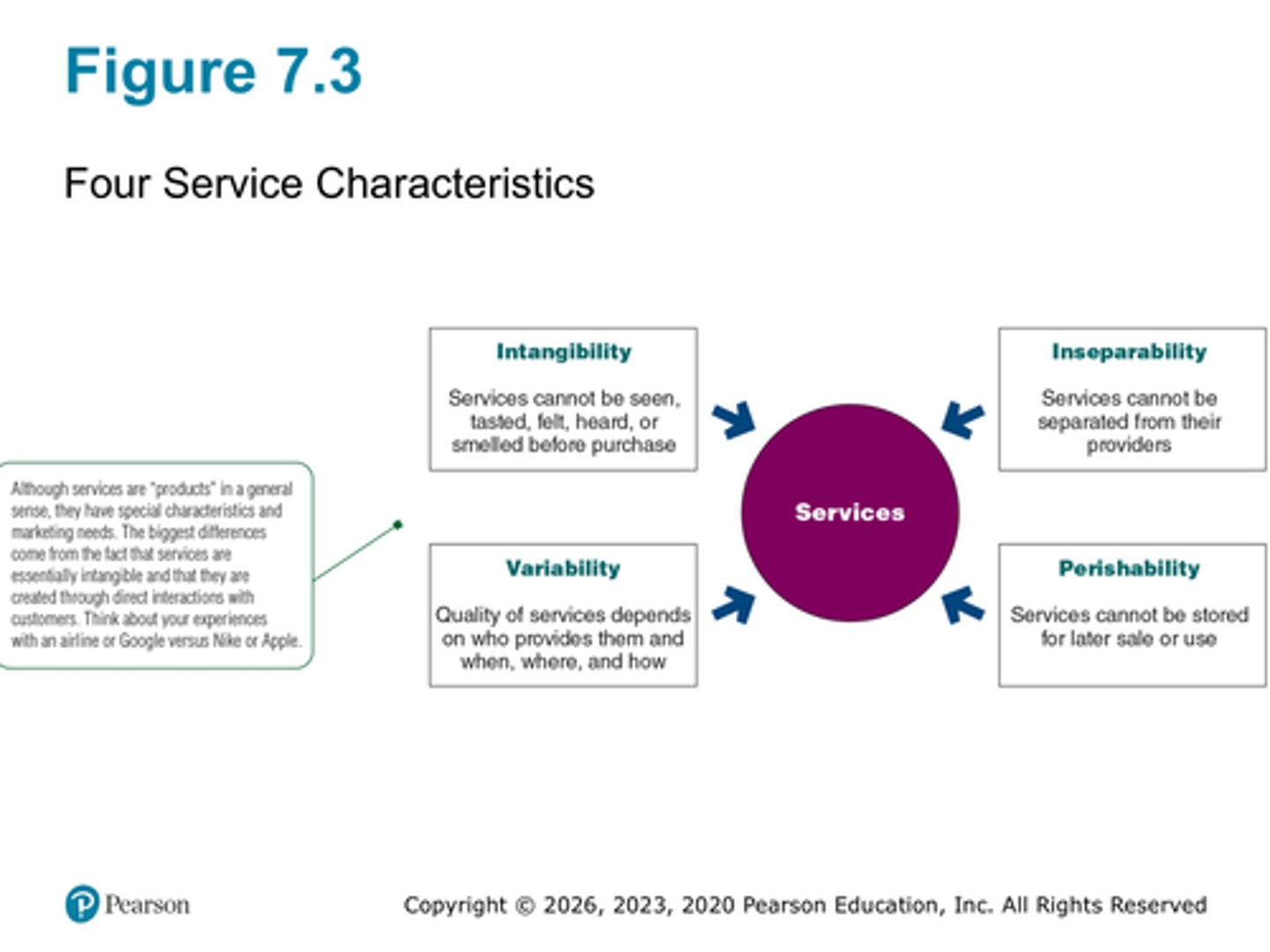
Service intangibility
Service intangibility means that services cannot be seen, tasted, felt, heard, or smelled before they are bought