by 124L - NS & senses
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
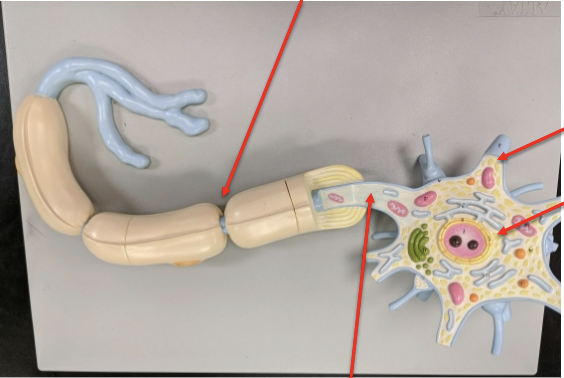
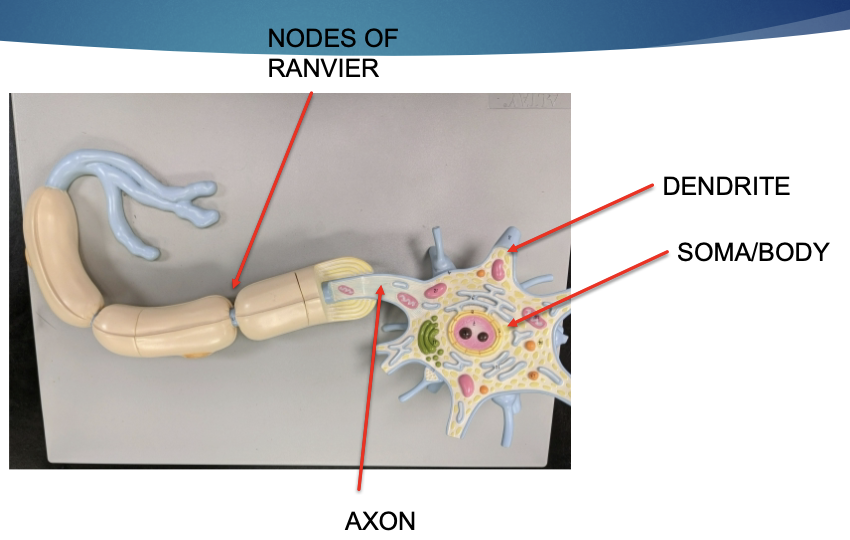
label the structures the arrows are pointing to.
neuron
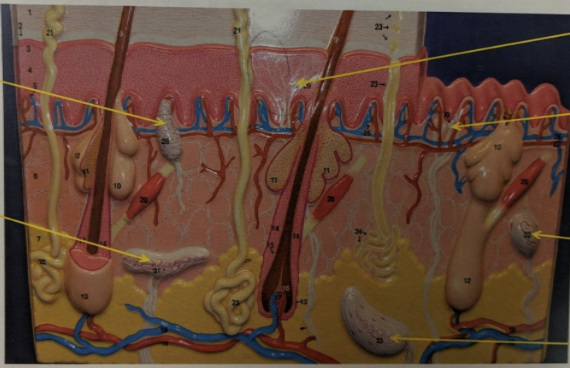
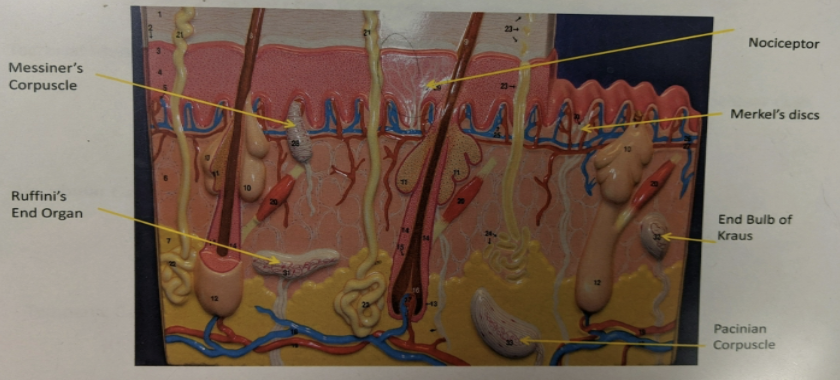
label the structures the arrows are pointing to.
skin
label the structures the arrows are pointing to.
tongue
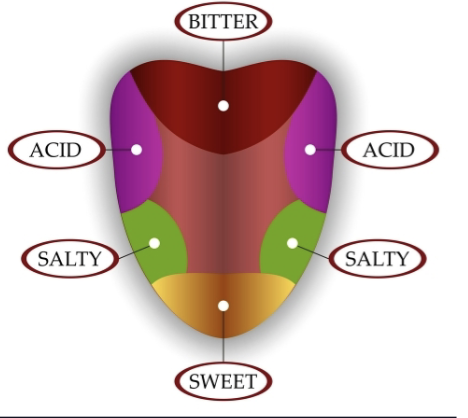
describe the difference between the old school version of the taste map and the new school version.
old school: each taste receptor is concentrated in dif. areas on the tongue
new school: all taste receptors are scattered everywhere
what characteristics does the sweet taste receptor have?
has a sugar content
multiple types of sugars
the sweetest natural sugar to humans is fructose
what characteristics does the salt taste receptor have?
has a “salt” NaCl content
what characteristics does the sour taste receptor have?
has a low pH level (acids)
what characteristics does the bitter taste receptor have?
has a high pH (basic)
what characteristics does the umami taste receptor have?
new taste receptor
savory
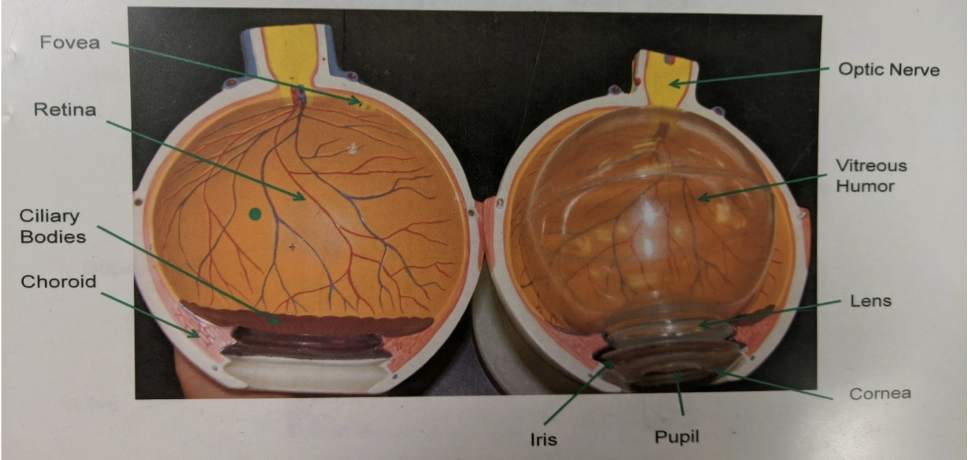
label the structures the arrows are pointing to.
eye
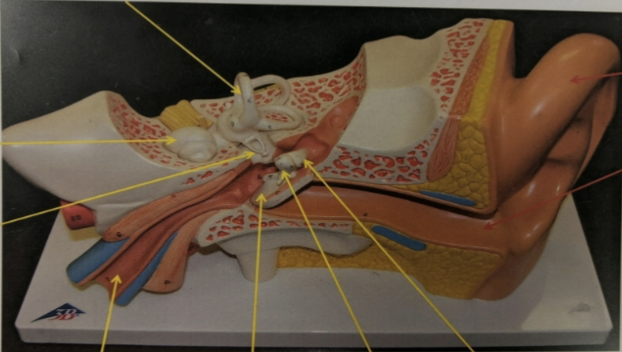
label the structures the arrows are pointing to.
ear
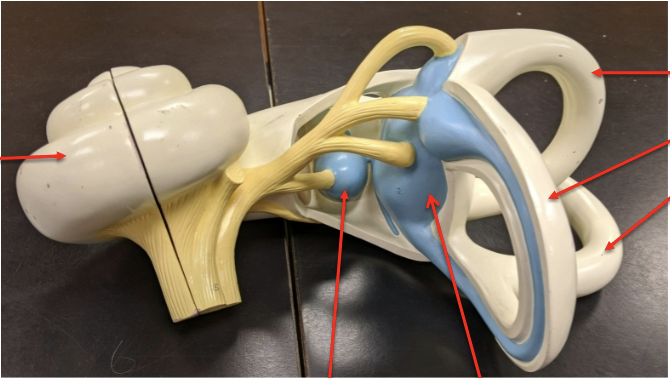
label the structures the arrows are pointing to.
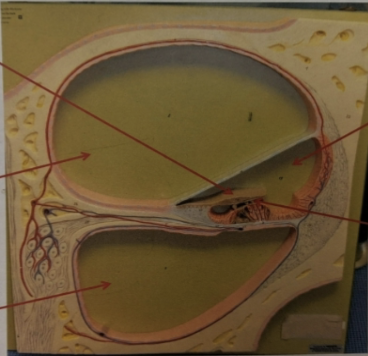
label the structures the arrows are pointing to.
label the structures the arrows are pointing to.
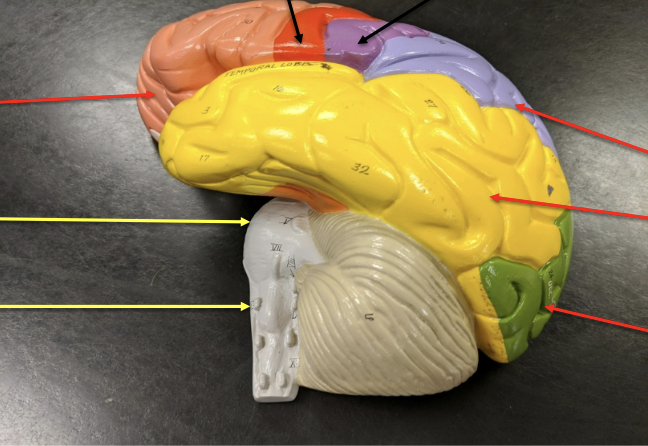
label the structures the arrows are pointing to.
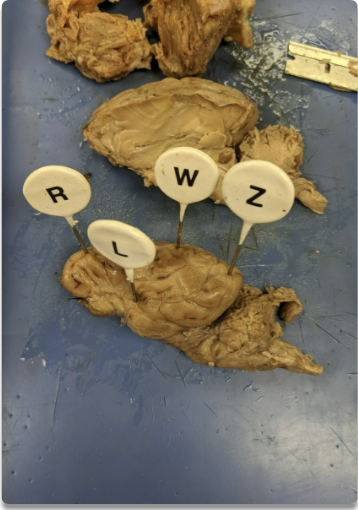
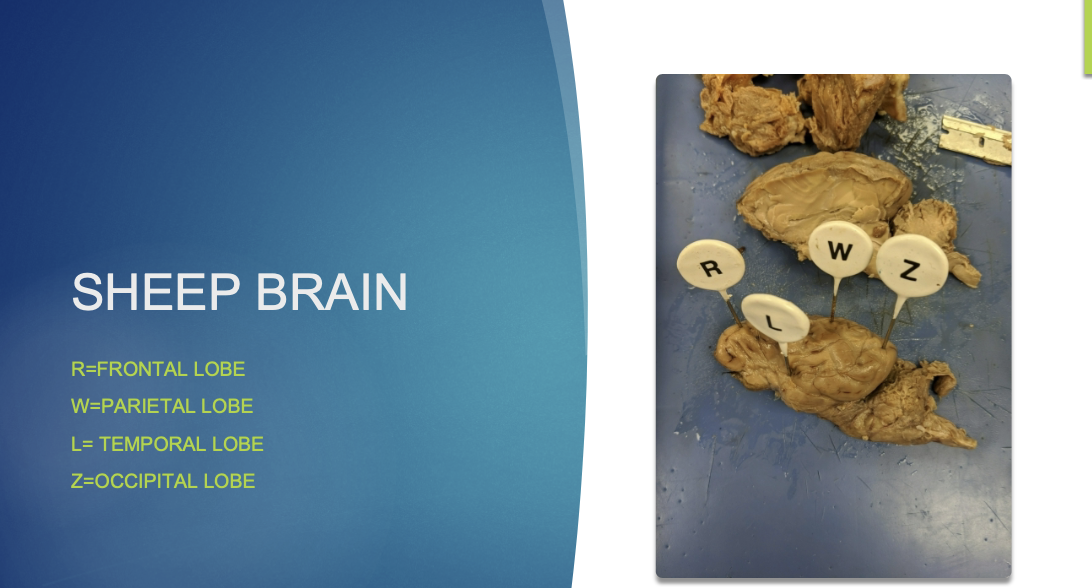
label the structures the pins are pointing to.
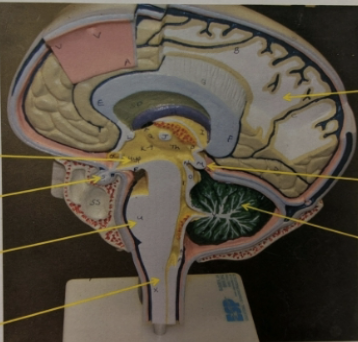
label the structures the arrows are pointing to.
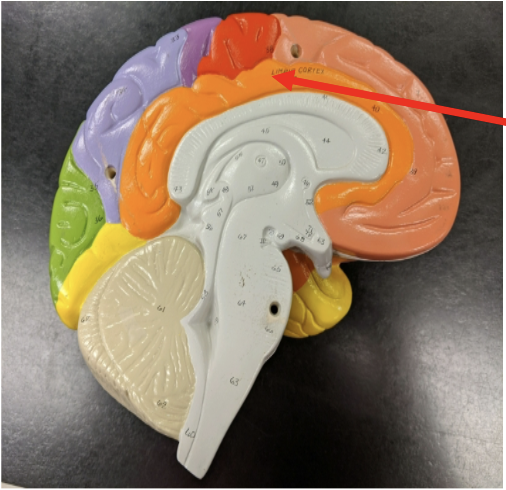
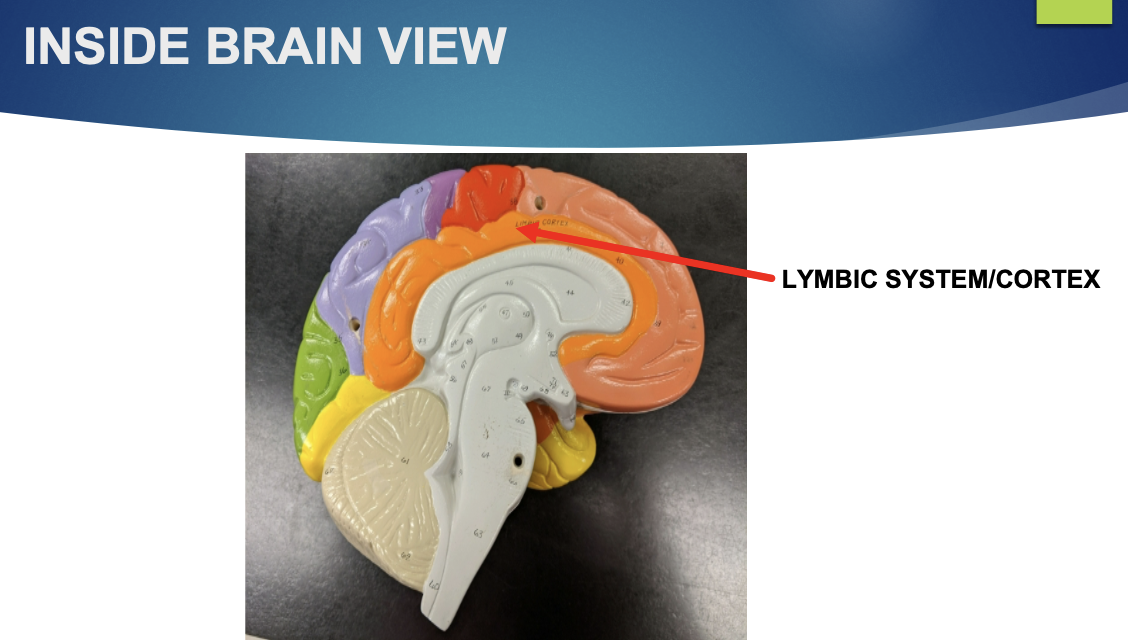
longitudinal section of the brain
what are pacinian corpuscles?
a mechanoreceptor that’s onion shaped and used for pressure
more of a sustained touch, felt over a larger area that regular touch
what are messiner’s corpuscles —> merkel’s light discs (aka tactile discs)?
a mechanoreceptor that’s responsible for discriminative touch (light touch)
what are nociceptors?
a pain receptor that’s naked/free dendrites in the epidermis of the skin that respond to pain
what are the mechanoreceptors?
pacinian corpuscles
messiner’s corpuscles —> Merkel’s light discs (aka tactile discs)
what are the pain receptors?
nociceptors
what are the chemoreceptors?
gustatory
olfaction
what are gustatory receptors?
a chemoreceptor that’s responsible for the sweet, sour, salt, and bitter taste sensations
what are olfaction receptors?
a chemoreceptor that’s responsible for smell sensations
what are the thermoreceptors?
end bulb of Krause
Ruffini’s end organ
what are the end bulb of Krause receptors?
a thermoreceptor responsible for cold sensations
what are the Ruffini’s end organ receptors?
a thermoreceptor responsible for heat sensations
what is the function for proprioceptors?
gives sensations about body positions and movement
where are proprioceptors located?
located in muscles, joints and inner ear
what is the sclera?
tough, white, outer covering of the eye
what is the cornea?
front of the eye where the sclera becomes transparent
what is the choroid?
pigmented inner layer of the eye
what is the function of the choroid?
responsible for “night shine” in nocturnal mammals
what is the conjunctiva?
a delicate layer of epithelial cells that cover the sclera
what is the function of the conjunctiva?
helps keep eye moist
what is the iris?
pigmented outer layer of the eye which surrounds the pupil
what is the function of the iris?
gives the eye its color
what is the lens?
a hardened structure located behind the cornea
what is the function of the lens?
helps focus light
what is the function of the ciliary body?
produces a clean watery fluid that fills the space between the cornea and the lens
what is the aqueous humor?
the clear, watery fluid produced by the ciliary bodies
what is the function of the aqueous humor?
occupies space between the cornea and lens
what is the vitreous humor?
jellylike material that occupies the area behind the lens
what is the function of the vitreous humor?
fills up the majority of the volume of the eye
what is the retina?
innermost layer of the eyeball
what does the retina consist of?
2 types of photoreceptors (rods and cones)
what are cones?
one of 2 types of photoreceptors in the eye
list out characteristics and function of cones
takes more light to stimulate
less numerous in human eye
most numerous in fovea region
function: gives color vision
what are rods?
one of 2 types of photoreceptors in eye
list out characteristics and function of rods
more numerous in the eye
located more on the periphery of the retina
completely absent from the fovea
function: gives night (black and white) vision
what is the fovea?
center of visual field
list out characteristics and function of the fovea
has the densest concentration of cones
function: point where humans see sharpest (directly in front of viewer)
what is the blind spot?
point on the retina whereby the optic nerve leaves the eye
contains no photoreceptors
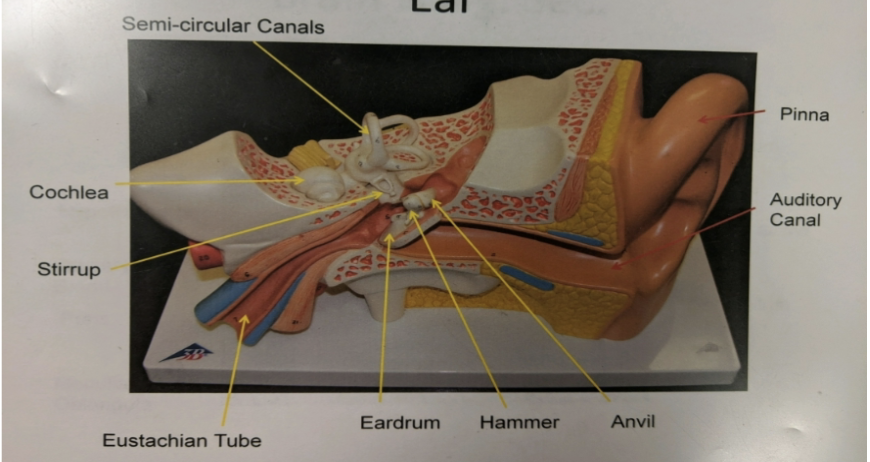
what are the regions the ear is divided into?
outer
middle
inner
what is the pinna?
structure in the outer ear that’s the external surface
what is the auditory canal?
structure in the outer ear that’s the passage from outside to eardrum
what is the tympanic membrane (eardrum)?
structure in the outer ear that’s the membrane which vibrates in response to sound waves
what is the malleus (hammer)?
structure in the middle ear that’s the 1st in a series of ossicles (tiny bones) and attaches directly to the eardrum
what is the incus (anvil)?
structure in the middle ear that’s the 2nd in a series of ossicles and lies betwixt malleus and stapes
what is the stapes (stirrup)?
structure in the middle ear that’s the 3rd in a series of ossicles and attaches to the oval window (membrane leading to the inner ear)
what is the eustachian tube?
structure in the middle ear that serves as canals that connect the middle ear with the pharynx (back of the throat)
when open, equalizes air pressure of the middle ear with that of the atmosphere —> “popping” of ears
what regions of the ear are air filled and fluid filled?
outer - air
middle - air
inner - fluid
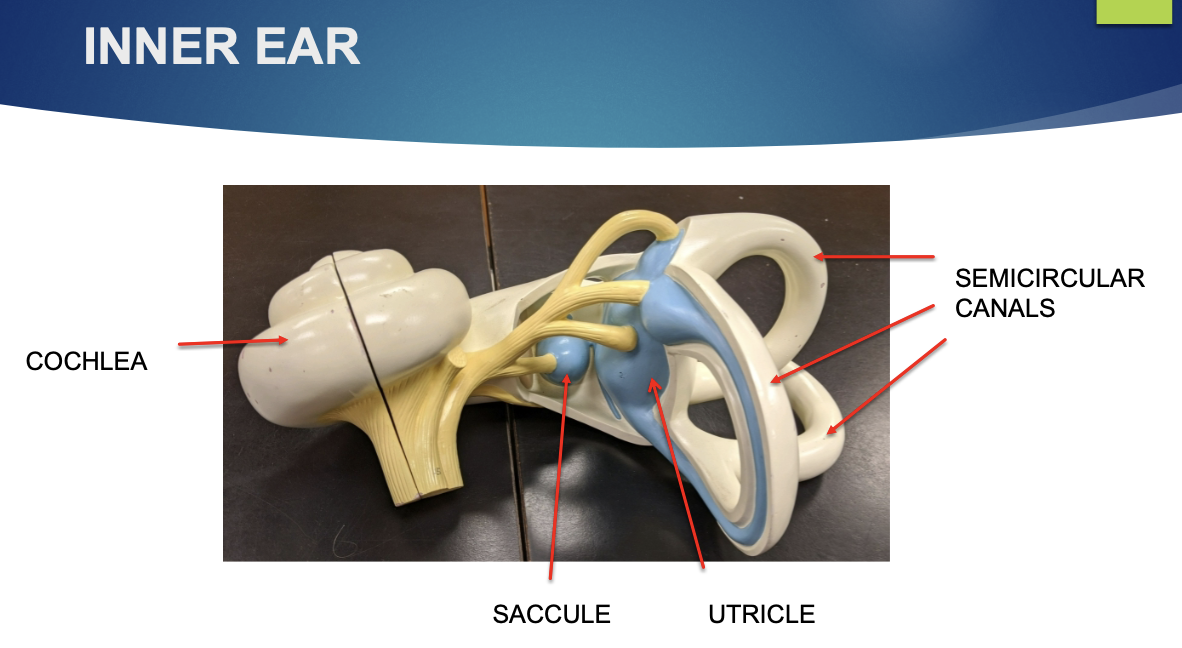
what is the utricle?
one of 2 chambers in the vestibule behind the oval window
what are the functions of the utricle?
opens into 3 semicircular canals which are responsible for equilibrium
gives body sense of forward to backward movement
what are the semicircular canals?
a series of 3 structures which are located in 3 spatial planes
what is the function of the semicircular canals?
to detect position of the head
what is the saccule?
one of 2 chambers in the vestibule
what is the function of the saccule?
opens into the semicircular canals and gives the body a sense of up or down movement
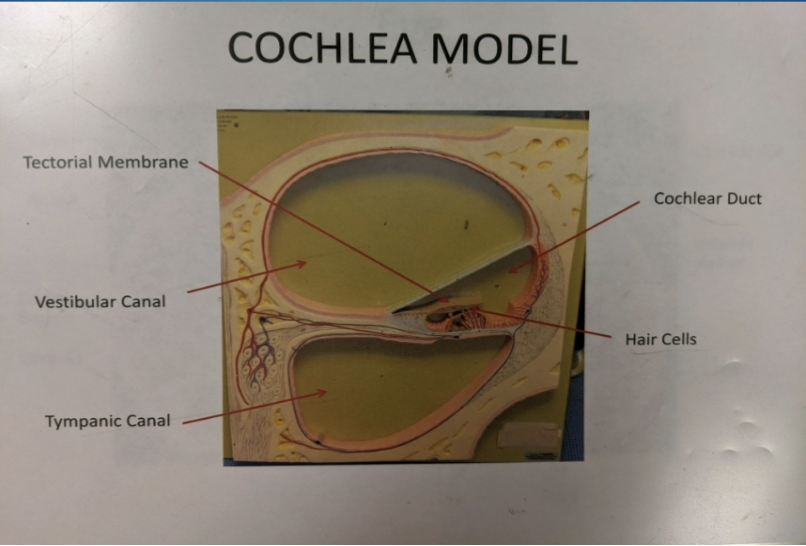
what is the cochlea?
coiled (snail) shaped structure
what is the function of the cochlea?
the hair cells within the structure are used for the detection of sound
what is the vestibular canal?
the upper canal of the cochlea
what is the tympanic canal?
the lower canal of the cochlea
what is the organ of corti?
contains the receptor cells, hair cells whose hairs project into the cochlear duct of the ear
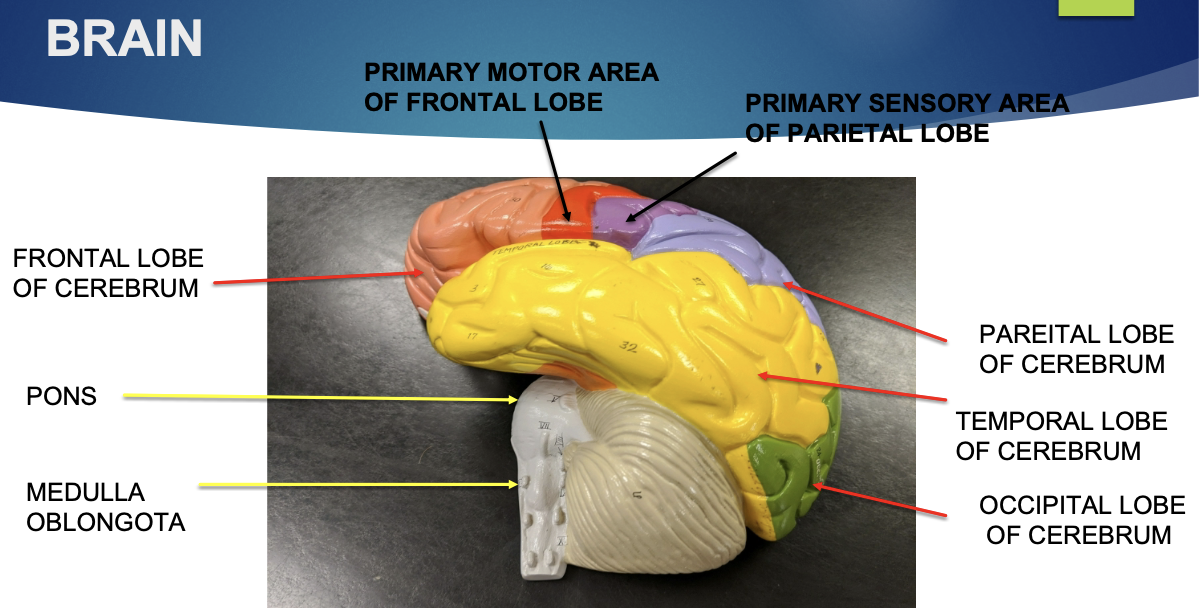
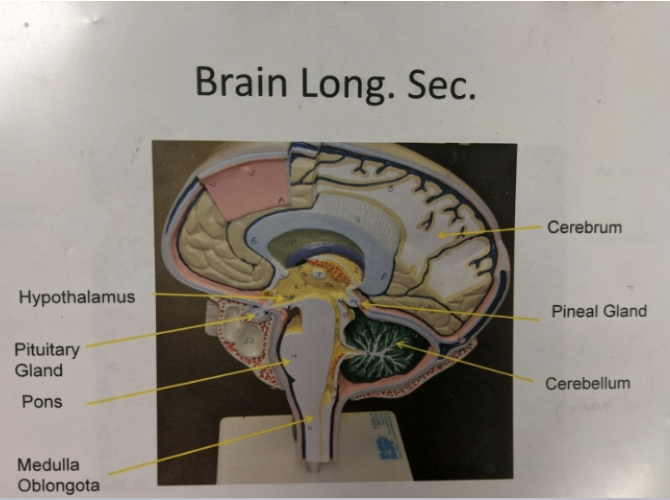
what is the cerebrum?
largest region of the brain
what regions is the cerebrum divided into? what are the general functions for each?
frontal - primary motor area and thought center
parietal - primary sensory area, areas for speech and reading, taste
temporal - hearing and olfaction
occipital - vision
what is the corpus callosum?
area along the internal, mid-line of the cerebrum, only area where the 2 hemispheres of the cerebrum connect
what is the function of the corpus callosum?
acts as a relay center betwixt the two sides
what is the cerebellum?
smaller, more compact than cerebrum
what is the function of the cerebellum?
coordinates movements and balance
what is the function of the pons?
helps medulla oblongata with its functions
what is the medulla oblongata?
combines with pons to make brainstem
what is the function of the medulla oblongata?
controls autonomic/homeostasis functions: swallowing, breathing, digestion, heart rate, vomiting
what is the limbic system?
older part of the brain
what is the function of the limbic system?
contains areas which govern emotions such as laughter, crying, sexuality, feeding, and aggression