Somatosensation: Mechanoreception and Proprioception
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Somatosensation
Sense of touch and body position awareness.
Sensory modality
Type of sensory information processed by receptors.
Transduction
Conversion of physical stimulus to neural signal.
Mechanoreception
Detection of touch and pressure stimuli.
Proprioception
Awareness of body position in space.
Nociception
Detection of pain and tissue damage.
Adequate stimulus
Specific stimulus type for receptor activation.
Tuning curves
Graphs showing receptor specificity for stimuli.
Receptive fields
Area where a stimulus affects neuron activity.
Conduction velocity
Speed of neural signal transmission.
Adaptation
Decrease in response to constant stimulus.
Plasticity
Neural reorganization based on experience.
Serial processing
Sequential information processing through neural pathways.
Parallel processing
Simultaneous processing of different sensory modalities.
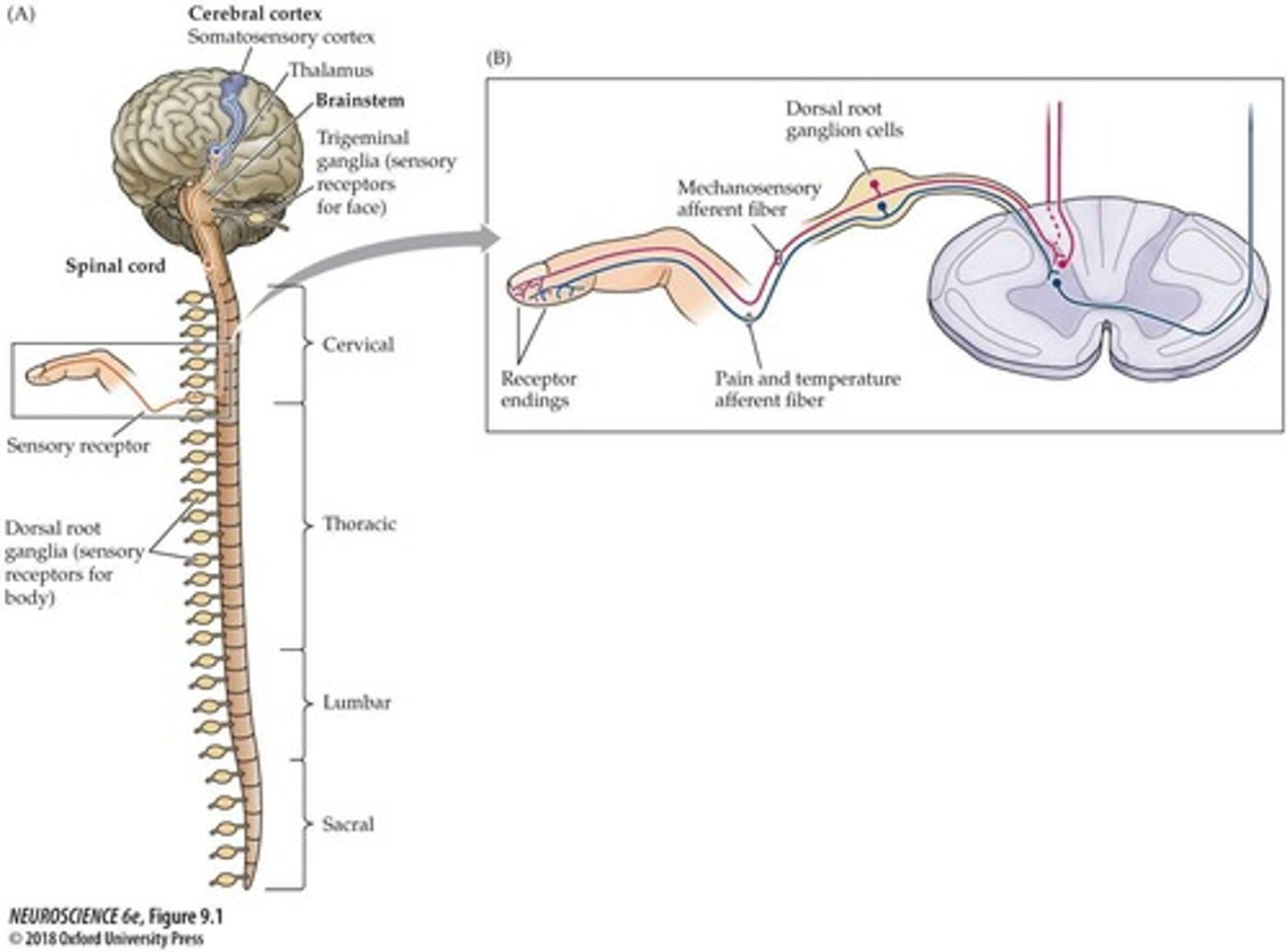
Dorsal root ganglia
Cluster of sensory neuron cell bodies.
Afferent fibers
Nerve fibers carrying signals to the CNS.
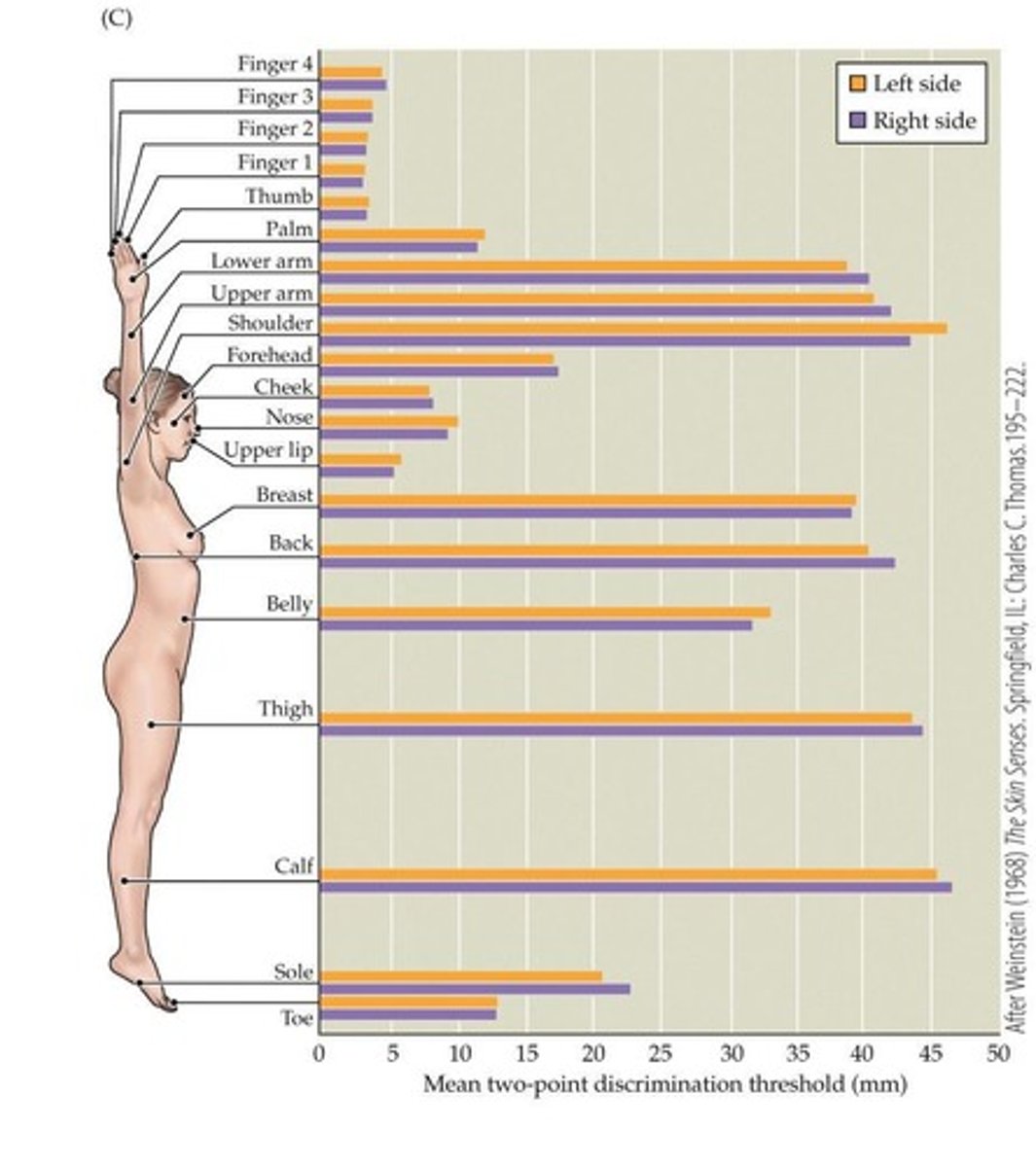
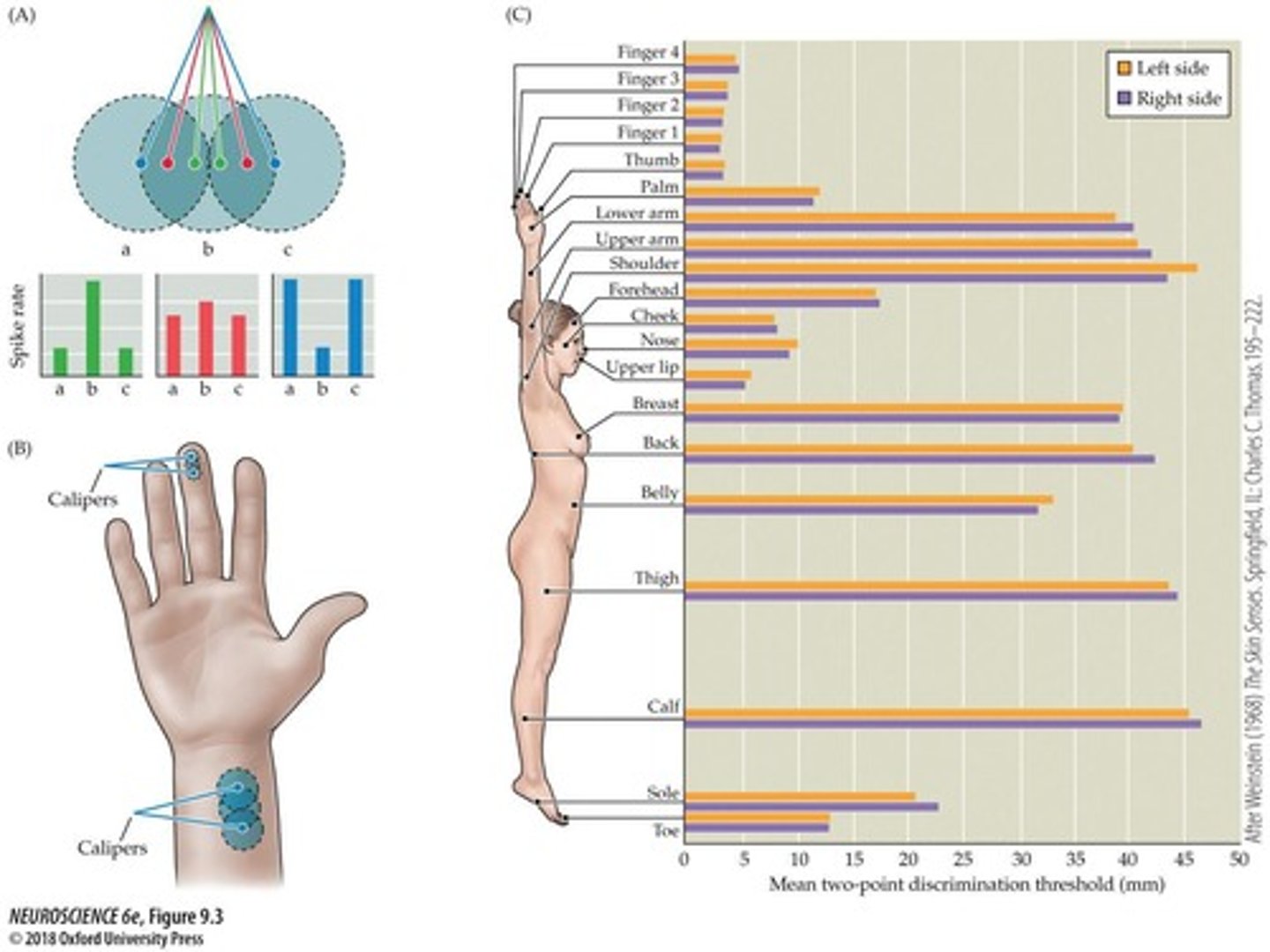
Two-point discrimination threshold
Minimum distance to distinguish two stimuli.
Receptive field properties
Characteristics determining sensory receptor response.
Ipsilateral
Same side of the body.
Contralateral
Opposite side of the body.
Conduction time calculation
Time taken for signal to reach CNS.
Conduction Velocity
Speed of signal transmission, 1m/s in example.
Temporal Fidelity
Rate of adaptation affects touch information quality.
Receptive Fields
Areas where sensory receptors respond to stimuli.
Two-Point Discrimination
Ability to distinguish two stimuli points on skin.
Dermatomes
Skin areas innervated by specific spinal nerves.
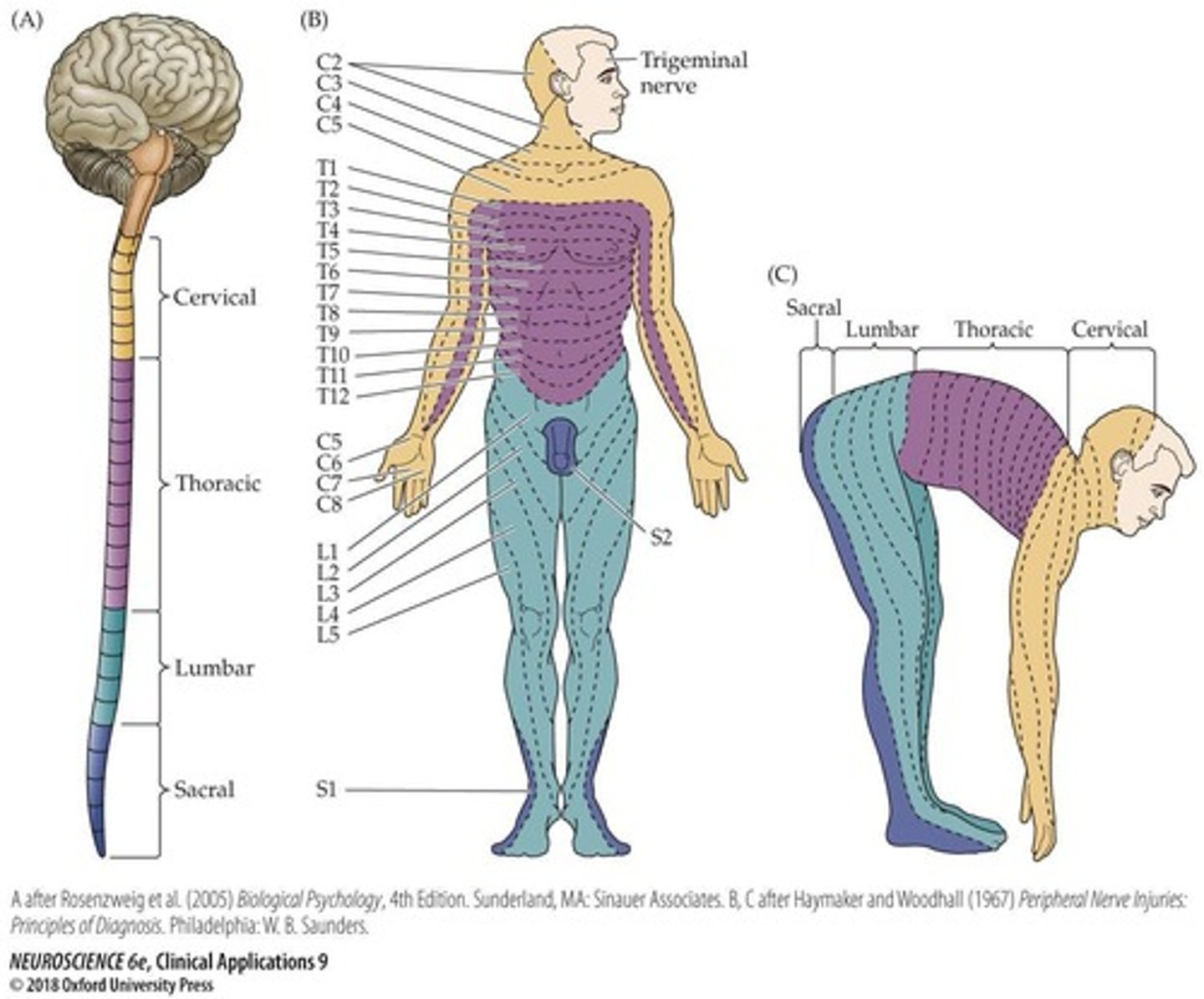
Shingles
Viral infection affecting specific dermatomes.
Somatoform Disorders
Physical symptoms without identifiable physical cause.
Dorsal Column-Medial Lemniscus (DCML)
Pathway for touch and proprioception signals to brain.
Ipsilateral
Same side of the body in neural pathways.
Contralateral
Opposite side of the body in neural pathways.
Primary Somatosensory Cortex
Brain area processing tactile information, areas 1-3b.
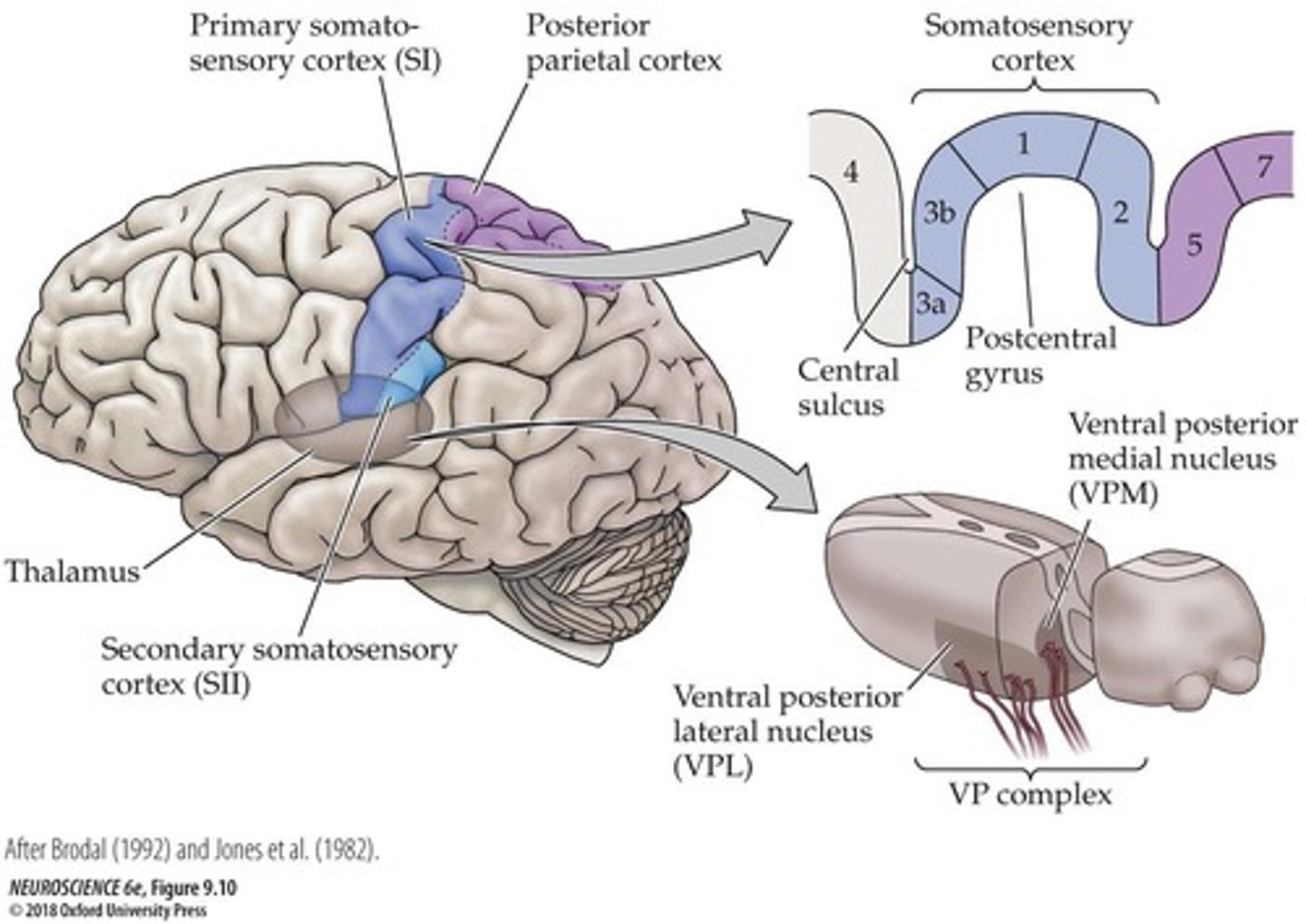
Somatotopic Map
Representation of body layout in the brain.
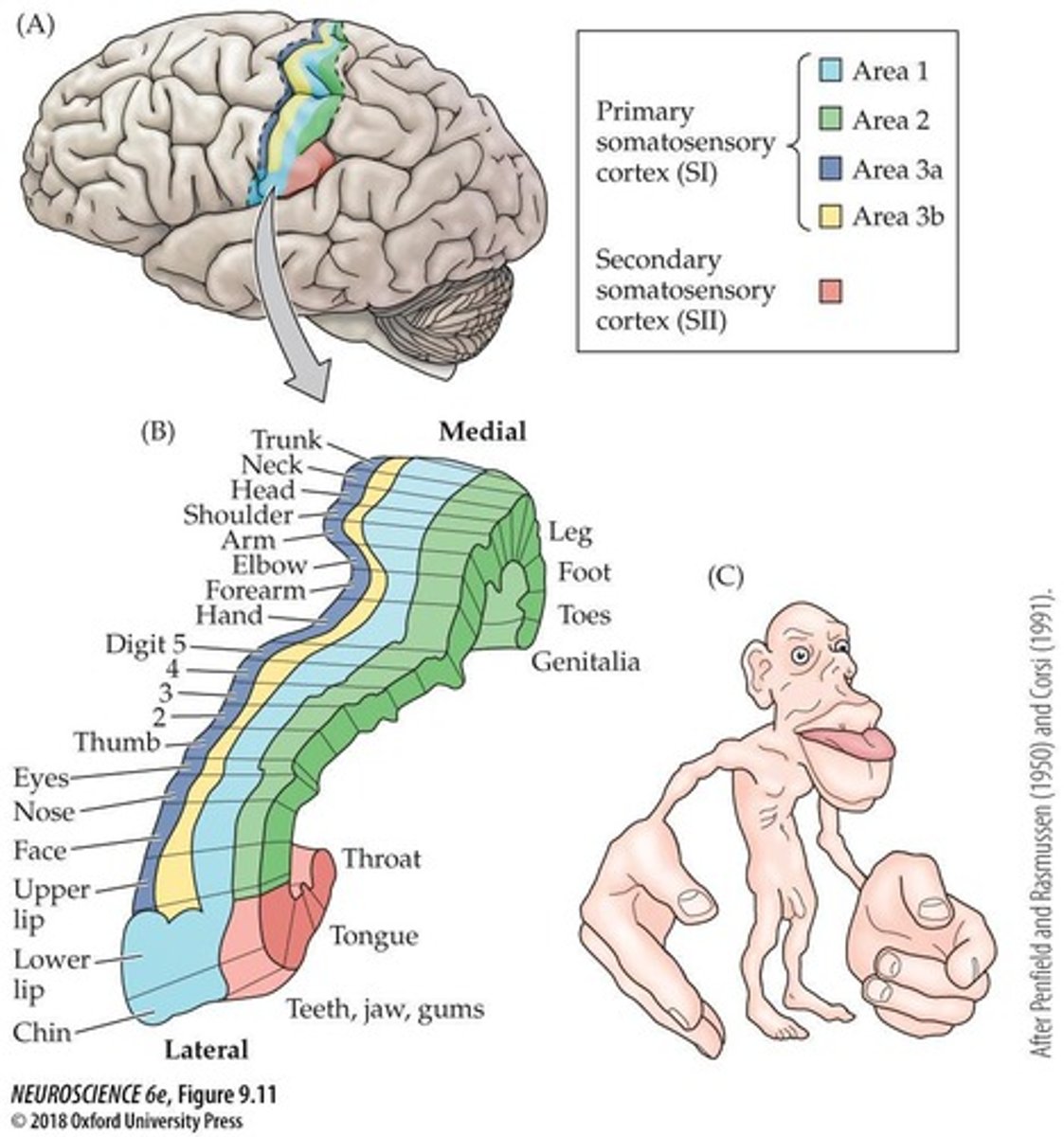
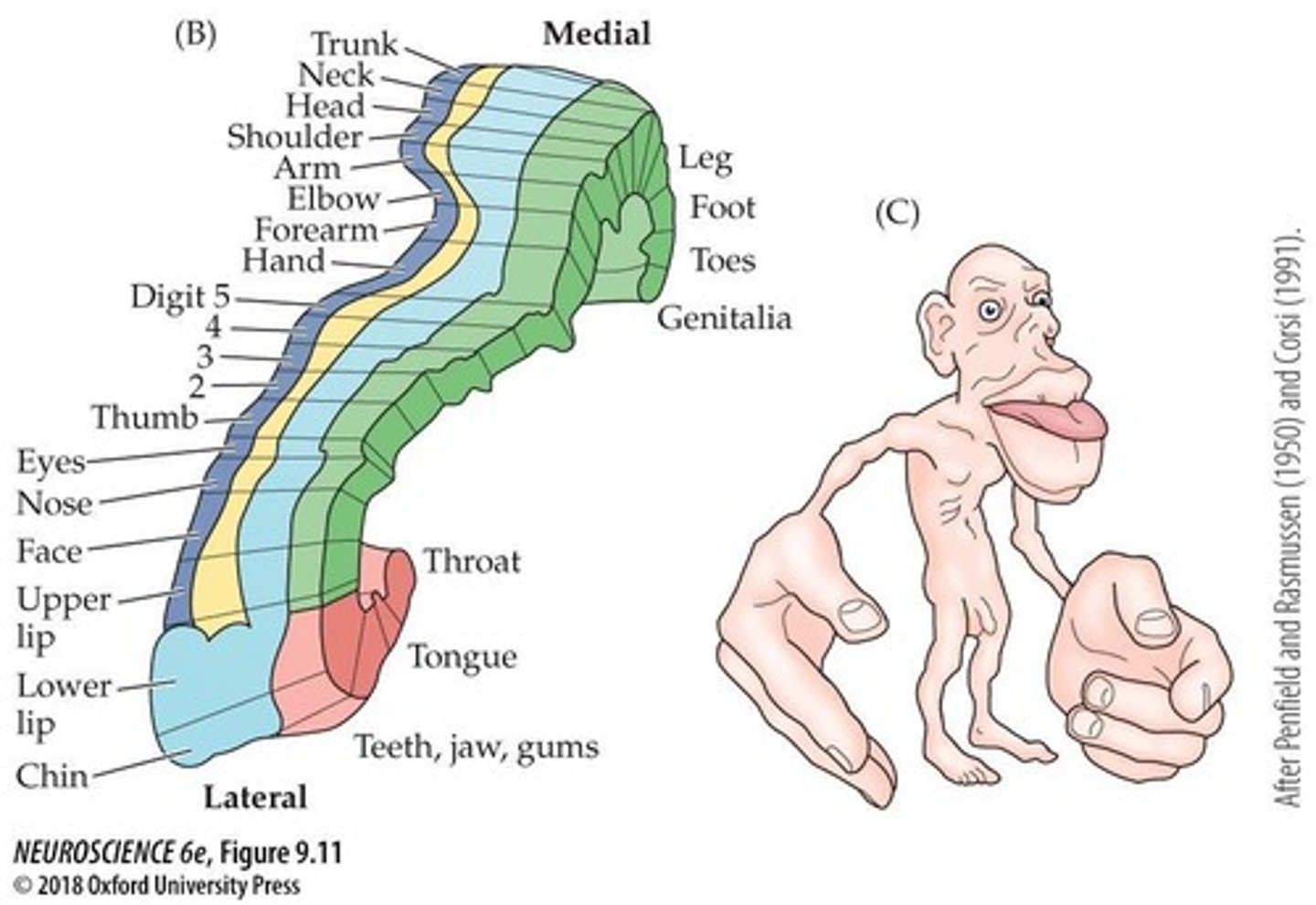
Receptive Field Size
Influences sensitivity and discrimination ability.
Evolutionary Benefit of Distorted Map
Enhanced sensitivity in critical body areas.
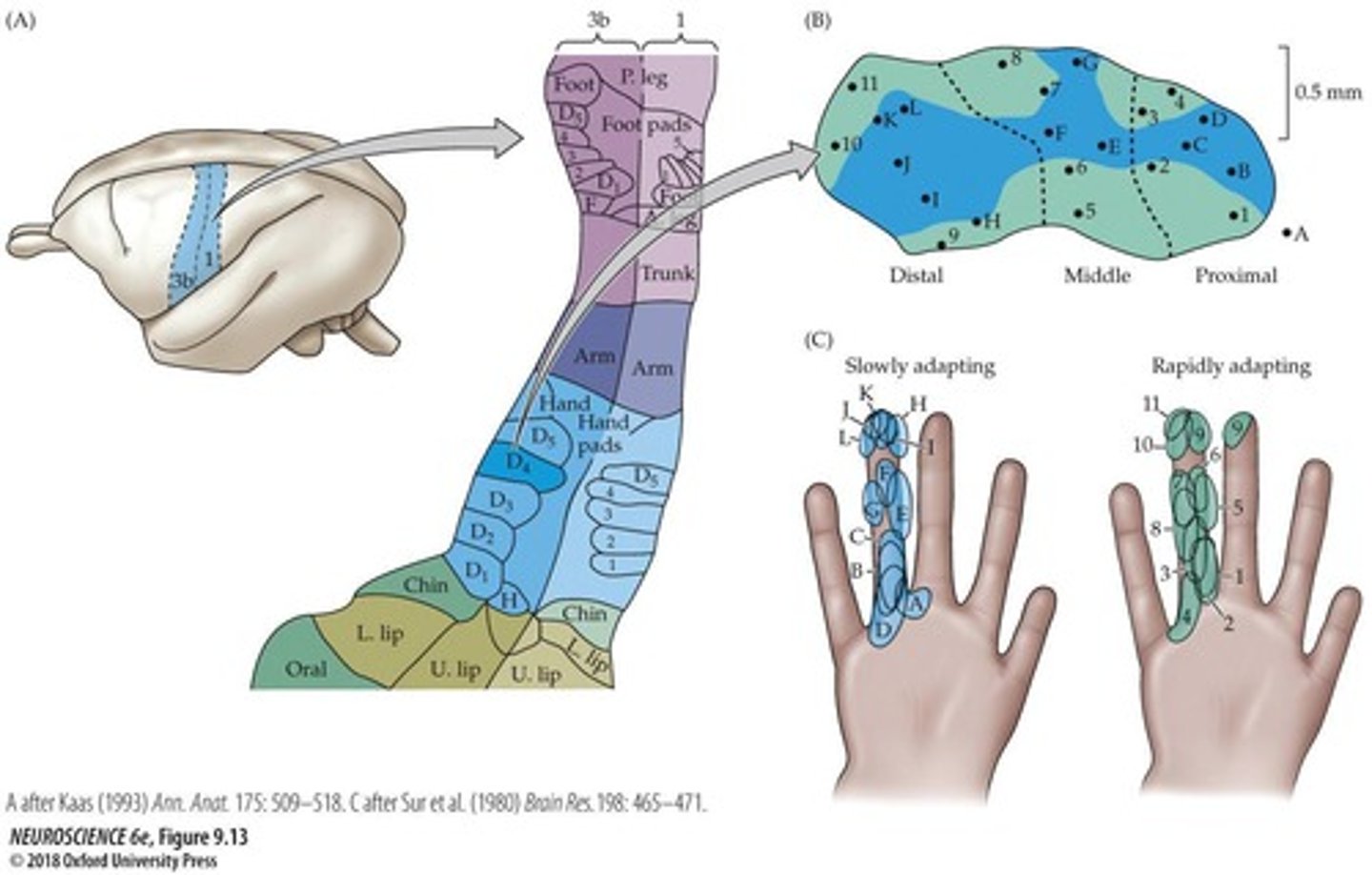
Mechanoreception
Detection of pressure and vibration on skin.
Slow-Adapting Receptors
Respond to constant pressure over time.
Fast-Adapting Receptors
Detect changes or movements in stimuli.
Plasticity in Mechanoreception
Adaptability of sensory representation in the brain.
Deafferentation
Loss of sensory input affecting cortical representation.
Tactile Sensitivity
Heightened sensitivity to touch stimuli.
Sensory Input Gain
Increased representation due to more sensory experience.
Background Noise Sensitivity
Overreaction to ambient sounds or stimuli.
Tactile Sensitivity
Sensitivity to touch, often requiring treatment.
Reorganization of Somatosensory Map
Brain's remapping after injury or sensory changes.
Phantom Limb Syndrome
Sensation of a missing limb post-amputation.
Case Study
Research method involving detailed individual examination.
Proprioceptors
Sensors in muscles and tendons for body position.
Dorsal Column-Medial Lemniscal Pathway
Pathway for proprioceptive and fine touch information.
Clarke's Nucleus
Nucleus involved in proprioceptive signal processing.
Somatosensory Map
Brain representation of body surface sensations.
Conduction Velocity
Speed of nerve signal transmission, 35-120 m/s.
Slow-Adapting Receptors
Detect constant pressure over time.
Fast-Adapting Receptors
Detect changes or movement in pressure.
Parallel Processing
Simultaneous processing of sensory information.
Somatotopic Organization
Spatial arrangement of sensory input in the brain.
Mechanoreception
Detection of mechanical pressure or distortion.
Vibration Sensation
Perception of oscillating pressure on skin.
Pressure Sensation
Perception of force applied to skin.
Receptive Fields
Area of skin where stimuli affect neuron response.
Tactile Objects
Items used for sensory stimulation, e.g., sandpaper.
Tight-Fitting Clothes
Clothing used to enhance tactile sensitivity treatment.
Remapping
Brain's adaptation to changes in sensory input.