SC5: Separate Chemistry 1
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
1
New cards
What is corrosion?
Corrosion refers to the process by which metals slowly rbreak down by reacting with substanaces within there environment
2
New cards
What is irons corrosion called?
Rusting
3
New cards
Rusting word equation
iron + water + oxygen → hydrated iron (iii) oxide
4
New cards
Rusting ionic equation
Fe → Fe (3+) + 3e(-)
O2 + 4e (-) → 2O(2-)
O2 + 4e (-) → 2O(2-)
5
New cards
What kind of reaction is rusting?
A redox reaction as iron is being oxidised (losing electrons) and the oxygen is being reduced (gaining electrons)
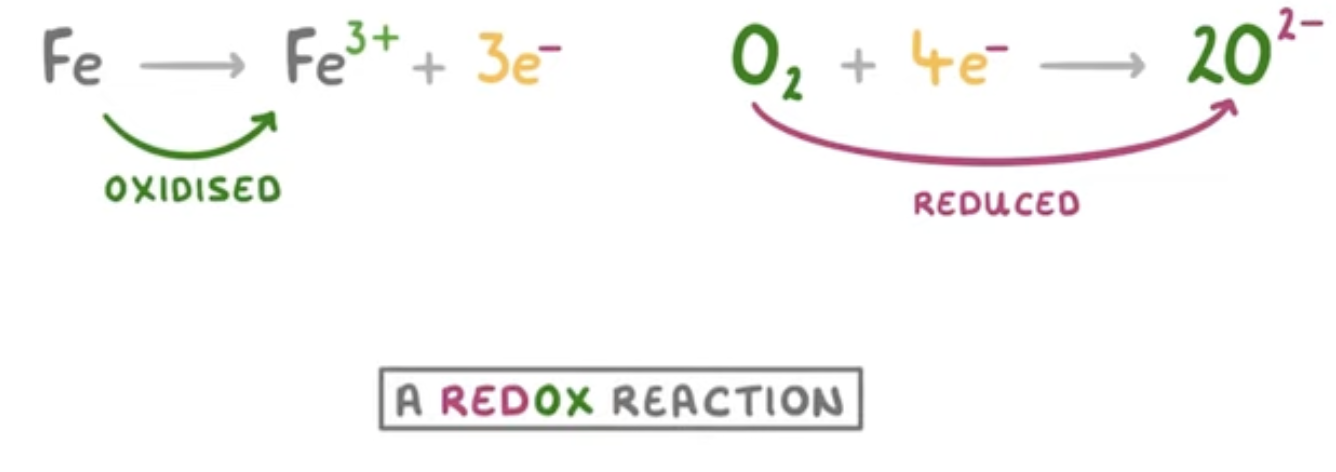
6
New cards
What are the conditions required for rusting to take place?
water and oxygen must be present
7
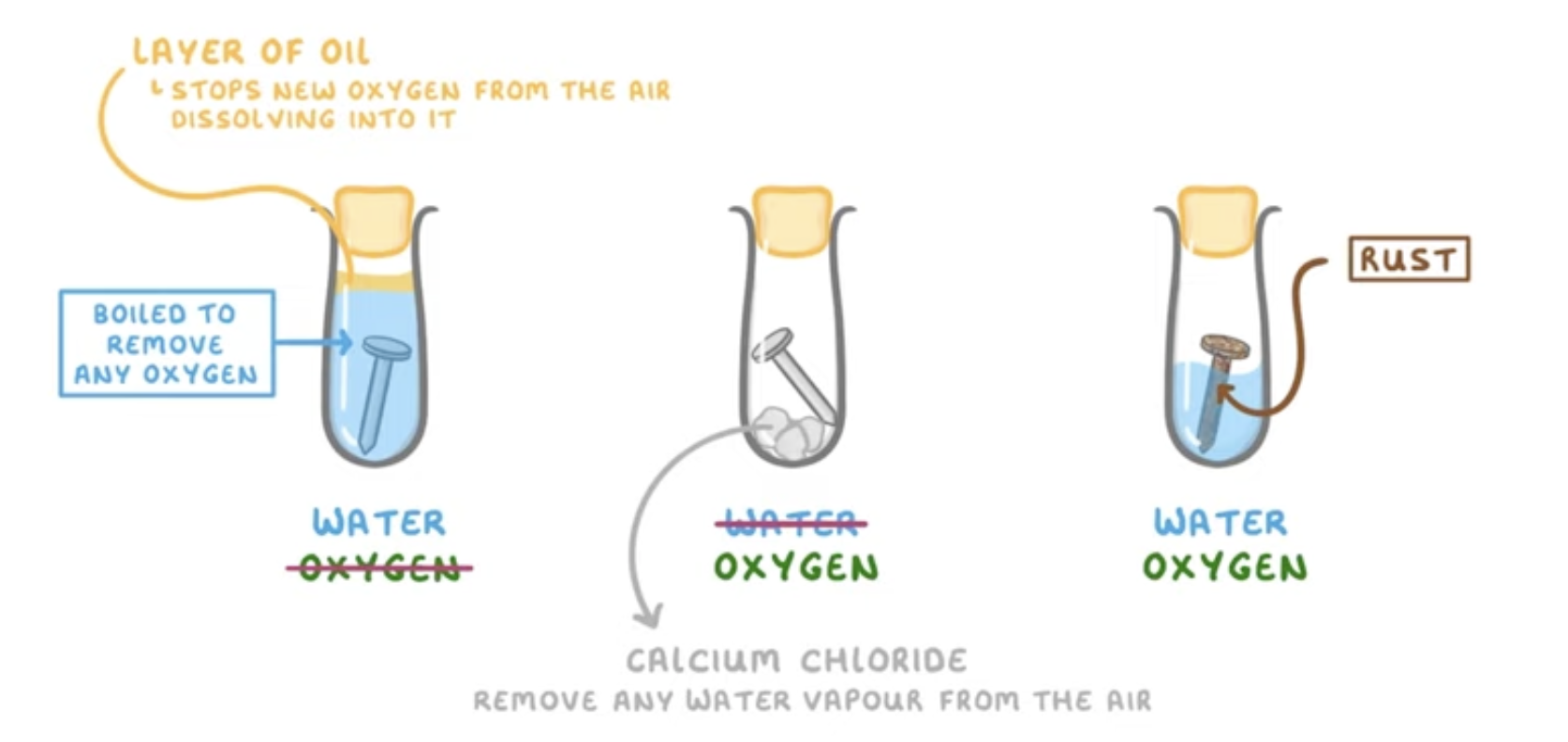
New cards
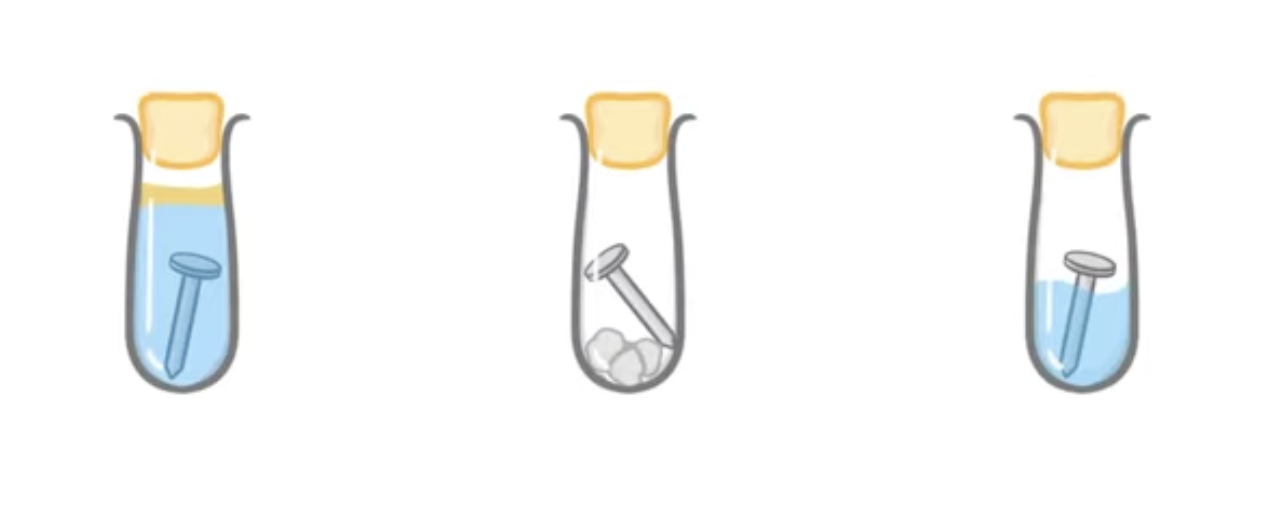
In these three test tubes which would rust (corrode)
8
New cards
What part of the metal corrodes?
Only the surface as this is the only part that is exposed
9
New cards
When iron rusts what occurs to the surface and then the next layer?
When iron rust the surface layer of rust will gradually flake off leaving a new layer of metal to rust. over a long period of time the entire metal can rust.
10
New cards
When aluminium corroded what occurs to the surface layer and the next layer?
Only the surface layer of atoms will corrode and then the top layer of atoms form aluminium oxide when in contact with oxygen which acts as a protective layer from the environment around the metal.
11
New cards
What are the two types of methods to prevent rusting?
1. barrier methods- prevents oxygen and air from touching the iron
2. sacrificial methods-adding another (more reactive) metal to the iron
12
New cards
Explain the three barrier methods
1. painting it for big pieces
2. oil and grease are it-necessary for moving parts
3. electroplating-using electrolysis to cover iron in a thin layer of another metal
13
New cards
Explain the sacrificial method
When you add a more reactive metal (aluminium or zine e.g.) to the iron, the more reactive metal will be oxidised instead of the iron.
14
New cards
What uses both types of methods?
Galvinizing- coating iron in zinc (barrier method), however if zinc gets scratched, it will still react with any oxygen (sacrificial method)
15
New cards
What is a titration?
A titration is an experimental technique used to find an unknown concentration of an acid or an alkali.
16
New cards
What equpiment is required for a titration?
1. white tile- to place the conical flask on
2. conical flask- to contain the liquid from the pipette
3. burette-to add alkali or acid to the the conical flask
4. pipette-accurately measure a certain volume of acid or alkali
17
New cards
What is the method of titration?
1. Use the pipette to add 25 cm3 of alkali to a clean conical flask.
2. Add a few drops of indicator and put the conical flask on a white tile.
3. Fill the burette with acid and note the starting volume.
4. Slowly add the acid from the burette to the alkali in the conical flask, swirling to mix.
5. Stop adding the acid when the end-point is reached (this is when the acid has neutralised the alkali and the indicator changes colour).
6. Note the final volume reading, and calculate how much acid you added in total.
7. Repeat the titration until you get 'concordant results', which means volumes of acid that are within 0.10 cm3 of each other.
18
New cards
Why do you have to swirl the solution?
Important to swirl as you add the acid from the burette to evenly distribute it, and ensure that the colour change occurs as soon as neutralisation takes place.
19
New cards
Why is the white tile significant?
Can more easily see when the colour change takes place.
20
New cards
What is atom economy?
The percentage of reactants which are put to making useful products
21
New cards
How do you calculate atom economy?
Atom economy=Mr of desired products/Mr of total reactants x 100 (%)
22
New cards
When there is only one product (which is desired) what is the atom economy?
100%
23
New cards
Why do you need atom economy?
* calculated profitability
* raw materials are expensive
* it is expensive to get rid of waste products
* This is then used to find more efficient methods of obtaining products or using the waste products as by products
* raw materials are expensive
* it is expensive to get rid of waste products
* This is then used to find more efficient methods of obtaining products or using the waste products as by products
24
New cards
What is yield
amount of product (measured in grams or moles)
25
New cards
What is actual yield
the yield obtained when experiment is carried out
26
New cards
What is theoretical yield
expected yield based on calculations
27
New cards
Why is actual yield less than theoretical?
1. Not all reactants may be used up to fully react
1. mainly occurs in slow reactions or reversible reactions
2. Side reactions may occur (reactants produce a different by product)
3. Some product may be lost in the process
1. gaseous products may escape in an open system
2. filtering can result in some loss of liquid as well
28
New cards
How do you calculate percentage yield?
actual yield/theoretical yield x 100
29
New cards
What is the Haber process?
Industrial production of ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen
30
New cards
What is the equation for the Haber process?
N2+3H2 ⇌ 2NH3
31
New cards
What are the conditions required for the Haber process?
1. 200 atm
2. 450° celcius
3. iron catalyst
32
New cards
Why is the Haber process important?
creates nitrogen based fertiliser used for growing crops
33
New cards
Is the haber process exothermic or endothermic?
Exothermic as it releases heat
34
New cards
Is the haber process reversible?
Yes this is a reversible reaction as some of the ammonia will break back down to nitrogen and hydrogen.
35
New cards
Why is the temperature of the Haber process 450°?
* the reaction is exothermic so a low temperature is required for more products and a higher percentage yield
* to achieve a higher RoR a high temperature is required as particles need kinetic energy to react
450° is an average in the middle as a higher temp than this would be too costly but this is hot enough for a fast RoR
* to achieve a higher RoR a high temperature is required as particles need kinetic energy to react
450° is an average in the middle as a higher temp than this would be too costly but this is hot enough for a fast RoR
36
New cards
Why is the pressure of the Haber process 200 atm?
* high pressure leads to more frequent collisions meaning the rate of reaction is higher
* higher pressure will favours the gaseous product than reactant as there are fewer molecules of product
While it has many benefits, this is extremely expensive and unsafe so 200 atm is a compromise.
* higher pressure will favours the gaseous product than reactant as there are fewer molecules of product
While it has many benefits, this is extremely expensive and unsafe so 200 atm is a compromise.
37
New cards
What is a fertiliser?
A fertiliser is a substance that is applied to soil, in order to supply plants with nutrients.
Fertilisers made by combining certain chemicals in a specific ratio are known as formulated fertilisers.
Fertilisers made by combining certain chemicals in a specific ratio are known as formulated fertilisers.
38
New cards
What three elements are usually found in fertilisers?
Fertilisers normally consist mainly of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium compounds as these are the three main elements that plants needs from the soil
39
New cards
What is a fuel cell?
**An electrochemical cell which can convert the chemical energy of a fuel and oxygen to electrical energy to power things.**
**Hydrogen-Oxygen fuel cells are the most common.**
**Hydrogen-Oxygen fuel cells are the most common.**
40
New cards
Electrolyte in the centre is a..
solution the ions can move through. An example is potassium hydroxide
41
New cards
What are the charges of cathode and anode in a fuel cell?
ANODE:NEGATIVE
CATHODE:POSITIVE
\
(this is the opposite of normal electrolysis)
CATHODE:POSITIVE
\
(this is the opposite of normal electrolysis)
42
New cards
What are the electrodes made of in a fuel cell?
porous carbons
43
New cards
Where does oxygen enter and where does hydrogen enter?
Hydrogen will enter from the anode compartment while oxygen enters the cathode compartment. When the reaction is over water and heat leave by cathode outlet.
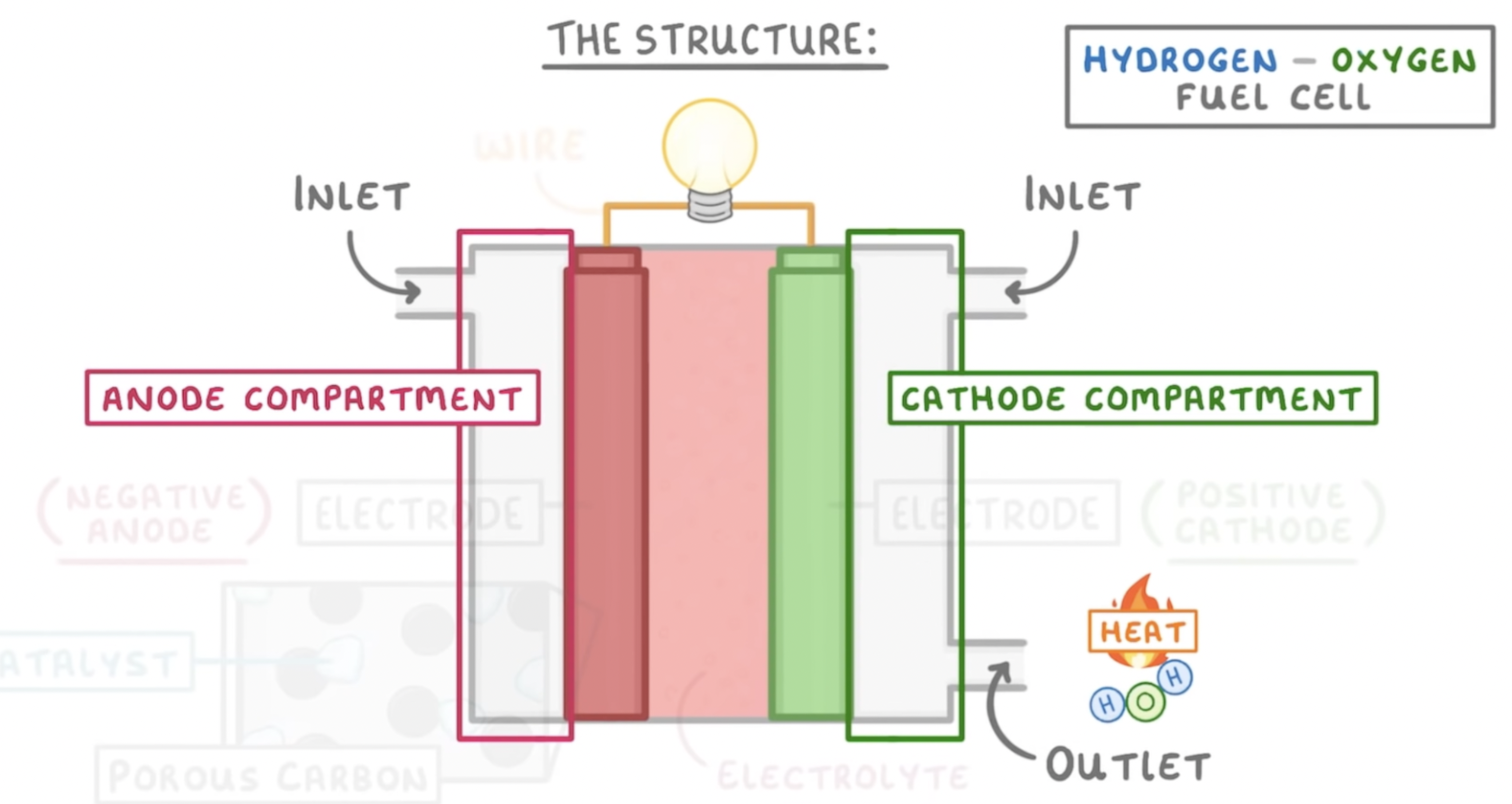
44
New cards
What is the process of using a fuel cell?
1. hydrogen comes into the anode compartment and is then oxidised by the anode
2. all hydrogens lose an electron to become hydrogen ions
1. H2 → 2H+ 2e
3. electrons pass around the wire to the cathode and hydrogen ions move through the electrolyte to the cathode.
4. this can then react with oxygen on right at the anode compartment
5. this will form water and 2 sets of hydrogen will react with one oxygen
6. Water leaves the fuel cell via the outlet
1. O2+ 4H+ + 4e → 2H2O
45
New cards
What is the overall equation of what occurs in a fuel cell?
O2 +2H2 → 2H2O
46
New cards
What are the pros of fuel cells?
Alternative energy source (fossil fuel engine and the battery is replaced) in vehicles
Can replace other not environmentally friendly items
Last longer than batteries
less pollution to dispose of
Can replace other not environmentally friendly items
Last longer than batteries
less pollution to dispose of
47
New cards
What are the cons of fuel cells?
hydrogen is a gas taking more space to store
explosive when mixed with air
energy is required to start the process
explosive when mixed with air
energy is required to start the process