NUR 201 CONHP Nursing Philosophy & Conceptual Framework EXAM 1
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Nurse
The roles of the baccalaureate generalist include provider of care (physical care, teaching, advocating), leader and manager (manage and coordinate care, consume research), and member of profession (change agent, life-long learner).
Nursing Practice
The nurse incorporates interprofessional collaborative practice, research/EBP/quality, patient-centered care, communication, education, ethics, and informatics in the nursing process and clinical judgment.
Nursing Process
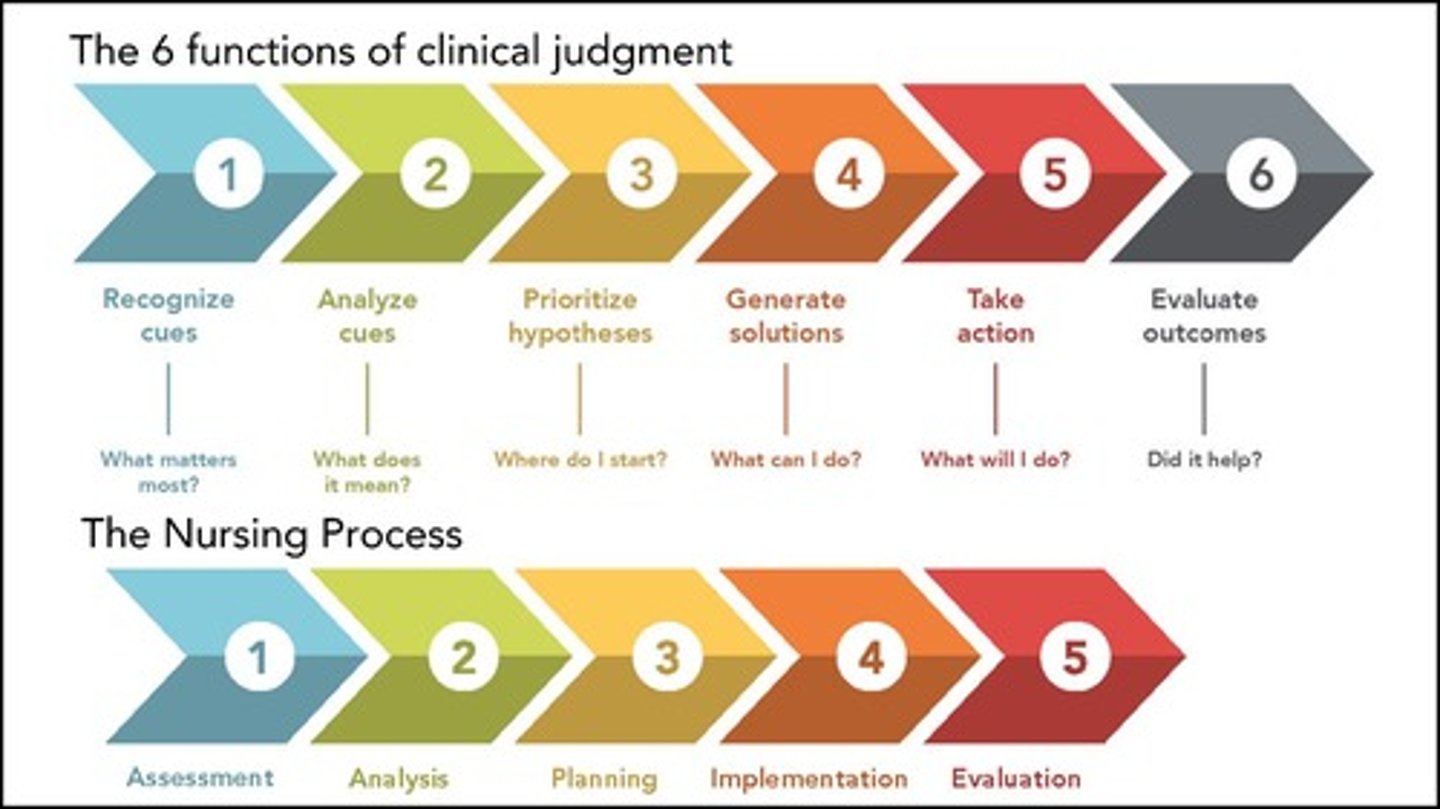
A critical thinking model used by nurses that is represented as the integration of the singular, concurrent actions of these steps: assessment, analysis/diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation.
Clinical Judgment
Recognize Cues, Analyze Cues, Prioritization, Plan, Implement, Evaluate.
Person
Persons are individuals, families, communities, or populations. Individuals are holistic beings with biological, psychological, social, cultural, and spiritual dimensions. Families are self-defined intergenerational systems of individuals who share biological, psychological, social, cultural, and/or spiritual dimensions. Communities are groups of individuals or families who share common characteristics and work toward a common goal. Populations are composed of aggregates and communities.
Health and Well-being
Health is a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity (WHO, 1948). An experience that is often expressed in terms of wellness and illness, and may occur in the presence or absence of disease or injury (ANA, 2015b, p. 87). Well-being generally includes global judgments of life satisfaction and feelings ranging from depression to joy (CDC, 2018).
Environment
The surrounding habitat, context, milieu, conditions, and atmosphere in which all living systems participate and interact. It includes the physical habitat as well as cultural, psychological, social, and historical influences.
Provider of Care
A role of the professional nurse that includes physical care, teaching, and advocating.
Leader and Manager
A role of the professional nurse that involves managing and coordinating care and consuming research.
Member of Profession
A role of the professional nurse that includes being a change agent and a life-long learner.
Interprofessional Collaborative Practice
A practice that involves collaboration among professionals from different disciplines to provide comprehensive care.

Research/EBP/Quality
The integration of evidence-based practice and quality improvement in nursing care.
Patient-Centered Care
An approach to care that respects and responds to individual patient preferences, needs, and values.
Communication
The process of exchanging information effectively between the nurse and the patient.
Education
The process of providing knowledge and skills to patients and nursing students.
Ethics
The principles that guide the professional conduct of nurses in patient care.
Informatics
The use of information technology in nursing practice to improve patient care.
Social Determinants of Health
Conditions in which people are born, grow, live, work, and age that affect health outcomes.
Professional Values
Values that epitomize the caring, professional nurse, including altruism, autonomy, human dignity, integrity, and social justice.
Historical Background of VU College of Nursing
Opened in 1968, first class of 55 freshman students in BSN program, Master's program began 1989, Post Masters FNP 1994, DNP program began 2008, Post Masters BSN-DNP, College of Nursing and Health Professions (CONHP) 2015.
Mission & Purpose
The purpose of the College of Nursing and Health Professions is to prepare beginning and advanced professionals of nursing and to provide an educational base for graduate study based on professional standards.
Objectives for CONHP's BSN Educational Program
To define the major concepts of CONHP's Nursing Philosophy and Conceptual Framework.
Major Concepts of CONHP's Nursing Philosophy
Nurse, nursing practice, nursing process, person, health & well-being, and environment.
Social Determinants of Health (SDH)
The conditions in which people are born, grow, work, live, and age, and the wider set of forces and systems shaping the conditions of daily life.
Evidence-based Practice (EBP)
EBP integrates best current evidence with clinical expertise and patient family preferences and values for delivery of optimal health care.

Quality Improvement (QI)
QI uses data to monitor the outcomes of care processes and uses improvement methods to design and test changes to continuously improve the quality and safety of health care systems.
BSN Program Outcomes
Integrate the role components of the nurse as provider of care, leader and manager, and member of profession.
Impact of Environment on Health
Describe the impact of environment on health and well-being of persons and nurses.
Nursing Perspective in Interprofessional Practice
Communicate the nursing perspective within the process of interprofessional collaborative practice.
Principles of Evidence-based Practice
Apply principles of evidence-based practice to deliver quality care in a diverse, global society.
Listening
An essential component of communication that involves actively understanding and interpreting spoken messages.
Oral Communication Skills
The ability to express thoughts and ideas verbally in a clear and effective manner.
Nonverbal Communication Skills
The use of body language, facial expressions, and gestures to convey messages without spoken words.
Written Communication Skills
The ability to convey information effectively in written form.
Digital Communication Skills
The ability to communicate effectively using digital platforms and technologies.

Compassionate Care
Care that is provided with empathy, respect, and consideration for the patient's feelings and needs.
Coordinated Care
Care that is organized and integrated across different services and providers to ensure continuity.
Decision Making in Care
The process of making choices regarding patient care based on evidence, preferences, and values.
Disease Prevention
Actions taken to prevent the occurrence of diseases and promote health.
Promotion of Healthy Lifestyles
Encouraging behaviors and practices that contribute to overall health and well-being.