Composites
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What is a composite material?
A multiphase material made from two or more dissimilar constituents to achieve improved properties
What are the two main phases of a composite?
Reinforcement and Matrix
What is the role of the reinforcement?
Provides strength and stiffness; generally high quality and flaw-free
What is the role of the matrix?
• Transfers load
• Protects reinforcement
• Absorbs damage
• Provides environmental protection
What factors define the properties of a composite?
• Material choice
• Reinforcement distribution
• Design
• Processing route
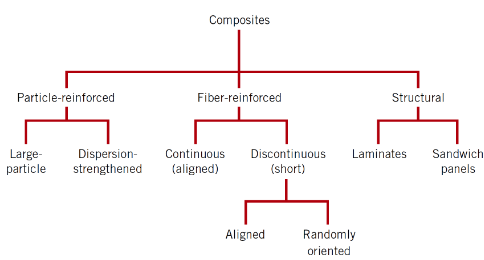
How are composites classified?
By the combination of material types (metal, ceramic, polymer), for example:
• Metal/Metal (B–Al)
• Metal/Ceramic (SiC–Ti)
• Ceramic/Polymer (Glass–polyester)
• Polymer/Polymer (Aramid–epoxy)
Which material is named first in a composite pairing?
The more expensive (reinforcement) material
What is a particle-reinforced composite?
A composite where particles are dispersed in a matrix to improve properties
What are the 3 types of fibre reinforcement arrangements?
(a) Continuous and aligned
(b) Discontinuous and aligned
(c) Discontinuous and randomly oriented
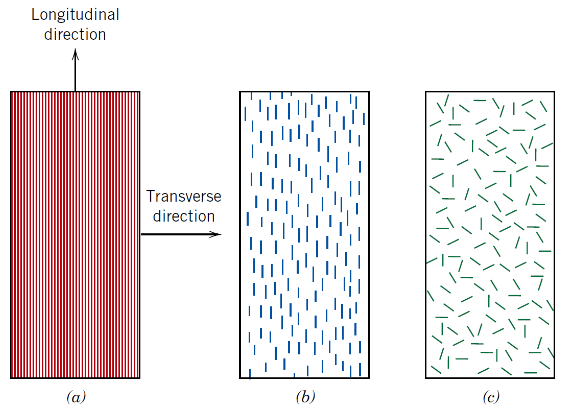
Which fibre arrangement gives the highest stiffness in one direction?
Continuous and aligned fibres
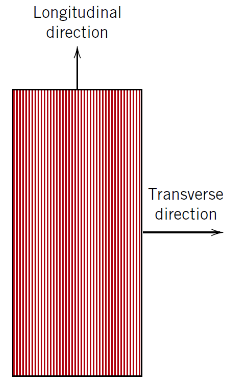
What loading condition applies along the direction of the fibres (longitudinal direction)?
Isostrain condition
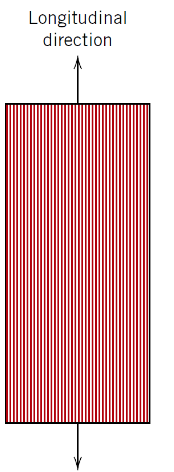
What does Isostrain mean?
Fibre, matrix, and composite all experience the same strain
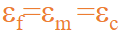
Formula for the Young’s Modulus for continuous fibre reinforcement in the longitudinal direction
• Ec = Young’s modulus of the composite (the overall stiffness of the composite material)
• Em = Young’s modulus of the matrix (the softer material, e.g., polymer)
• Ef = Young’s modulus of the fiber (the stiffer reinforcement, e.g., carbon fiber)
• Vm = Volume fraction of the matrix (proportion of the matrix in the composite)
• Vf = Volume fraction of the fiber (proportion of the fiber in the composite)
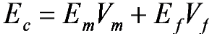
What loading condition applies transverse to the direction of the fibres (transverse direction)?
Isostress condition
What does Isostress mean?
Fibre, matrix, and composite all experience the same stress
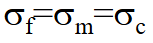
Formula for the Young’s Modulus for continuous fibre reinforcement in the transverse direction
• Ec = Young’s modulus of the composite (the overall stiffness of the composite material)
• Em = Young’s modulus of the matrix (the softer material, e.g., polymer)
• Ef = Young’s modulus of the fiber (the stiffer reinforcement, e.g., carbon fiber)
• Vm = Volume fraction of the matrix (proportion of the matrix in the composite)
• Vf = Volume fraction of the fiber (proportion of the fiber in the composite)
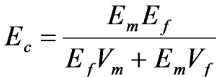
Why is transverse stiffness lower?
Load transfer is limited by the weaker matrix
Which assumptions are used in fibre mechanics?
• Isostrain for longitudinal loading (loading along the fibres)
• Isostress for transverse loading (loading transverse to the fibres)
What is anisotropy in composites?
Direction-dependent mechanical properties
How do longitudinal and transverse moduli compare?
Elongitudinal > Etransverse (significant anisotropy in stiffness and strength)
Name 3 natural composite materials
• Bone
• Wood
• Feathers