[Module 5] Electric and Magnetic Fields in Life
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
What is the distinct characteristic of electric forces?
Repulsion and attraction, dependent on the charge of the body.
How is magnetism associated with electricity?
It involves two bodies moving relative to each other.
What does Maxwell’s Theory describe?
A unified description of electricity, magnetism, and light.
What do certain particles have that leads to long-range interactions?
An intrinsic and locally conserved property called charge.
Who is James Clerk Maxwell?
A physicist (1831-1879) known for his contributions to electromagnetism.
What do Maxwell’s Equations relate to?
The location and speed (v) of source charges and their density in space.
What do charged particles create in surrounding space?
A disturbance called the electromagnetic field.
What is the equation for the divergence of the electric field (E)?
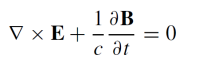
What is the equation for the divergence of the magnetic field (B)?
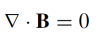
What is the equation for the curl of the magnetic field (B)?
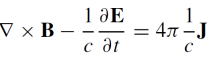
What is the equation for the force (F) on a charged particle?
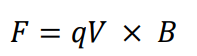
In Maxwell's equations, what do Q, E, B, and p' represent?
Q is the charge
E is the electromagnetic field
B is the magnetic field
p' is the momentum of particle q'.
What are electromagnetic waves?
Electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum and transfer energy.
What is the speed of electromagnetic waves in a vacuum?
They travel at the speed of light, c = 300,000,000 m/s.
Can electromagnetic waves be refracted and reflected?
Yes, they can be refracted and reflected.
What is electric charge (q)?
It is the unit of electricity that describes the size of force an object feels when exposed to other charged objects, measured in Coulombs (C).
What is an electric field (E)?
It is created by charged bodies and is where electric force is transferred (Can be thought as invisible lines). It is expressed in N/C (newtons per coulomb).
What is electric potential or voltage?
It describes the potential energy of electric attraction/repulsion, measured in J/C (joules per coulomb).
Who formulated Coulomb’s Law?
It is formulated by Charles Augustin de Coulomb.
What does Coulomb’s Law describe?
It described electric force.
What is the formula for Coulomb’s Law?
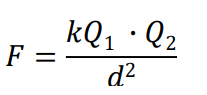
What is K in Coulomb’s Law?

What does the formula for Coulomb's Law represent?
The formula represents the electric force between two charged objects, where Q1 and Q2 are the charges, and d is the distance between them.
How does Coulomb's Law determine the direction of the electric force vector?
It illustrates how the direction of the electric force vector is determined based on the relative orientation of the two charges.
What is Ohm's Law considered in physics?
Ohm's Law is a fundamental concept in physics that serves as the foundation for understanding the behavior of electric circuits.
Who formulated Ohm's Law?
Ohm's Law was formulated by the German physicist Georg Simon Ohm.
What does Ohm's Law establish?
Ohm's Law establishes a mathematical correlation between voltage, current, and resistance within an electrical circuit.
What is the mathematical relationship in Ohm's Law?
Ohm's Law states that electric current (I) is equal to voltage (V) divided by resistance (R), or I = V/R.
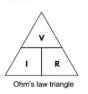
What are the three key variables in Ohm's Law?
The three key variables in Ohm's Law are electric current (I), voltage (V), and resistance (R).
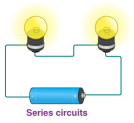
What is a series circuit?
A series circuit is one in which numerous resistances are linked one after the other, with a single current pathway.
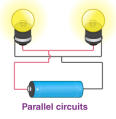
What is a parallel circuit?
A parallel circuit is one in which numerous resistances are linked across one another, with multiple current pathways.
How do series and parallel circuits differ?
In a series circuit, all components have the same current running through them, while in a parallel circuit, all components have the same potential difference across them.
What is the relationship between the sum of potential dips and the EMF in a series circuit?
In a series circuit, the sum of the potential dips across each component is equivalent to the EMF of the source.
What is the relationship between currents in a parallel circuit?
In a parallel circuit, the sum of the currents flowing into any point is equivalent to the sum of the currents flowing out of that point.
What is the charge state of the human body?
The human body is neutral in charge, but it uses electricity in biochemical and molecular processes.
What is the branch of physiology that deals with electric phenomena in living bodies?
Electrophysiology is the branch of physiology that deals with the electric phenomena associated with living bodies and their functional activity.
What are the major targets of electrophysiological studies?
The major targets of electrophysiological studies are the central nervous system, particularly the neuron cell type, as well as membrane and ion channels.
How does electrophysiology study ion channels?
The movement of ions across cell membranes allows the study of ion channels through electrophysiological techniques.
What is a key technique used in electrophysiology?
Patch clamping is a technique used in electrophysiology to study the behavior of ion channels and neurons.
What are the uses of electrophysiology in medicine?
Electroencephalograph (EEG)
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Defibrillators
Bone growth
What are magnetic fields?
Magnetic fields are visualizations of the distribution of magnetic force around an area.
Where are magnetic fields concentrated?
Magnetic fields are concentrated in areas with higher magnetic force.
What is the shape and direction of magnetic fields?
Magnetic fields form loops or circles, with the direction from north to south.
How are magnetic fields measured?
Magnetic fields are measured using magnetometers, with the SI unit being Tesla (T), which is equivalent to 10,000 Gauss.
What is the relationship between Tesla and Gauss?
The relationship between Tesla (T) and Gauss (G) is that 1 T = 10,000 G, so they are both units of measuring the force applied to a charge moving in a magnetic field.
What is the Lorentz Force Law?
The Lorentz Force Law states that the force (F) on a moving charge (q) in a magnetic field (B) is given by F = qVxB, where V is the velocity of the charge.
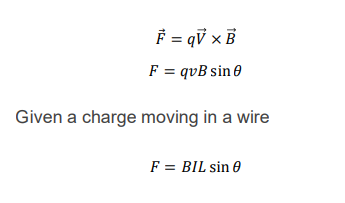
Who formulated Ampère's Law?
Ampère's Law was formulated by the French physicist André-Marie Ampère (1775-1836).
What is Ampère's Law?
Ampère's Law states that magnetic fields are related to the currents that produce them, provided that the electric field does not change over time.
What is the equation of Ampère's Law?
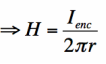
What is magnetic flux?
Magnetic flux is defined as the number of magnetic field lines given an enclosed space.
How is magnetic flux represented mathematically?
Magnetic flux is the integral of the normal component of the magnetic field (B) over an enclosed area, with the SI unit of weber (Wb).
What happens when the magnet is at rest near the coil?
When the magnet is at rest near the coil, there is no deflection in the galvanometer.
What happens when the magnet moves towards the coil?
When the magnet moves towards the coil, there is a deflection in the galvanometer in one direction.
What happens when the magnet is held stationary near the coil?
When the magnet is held stationary near the coil, there is no deflection in the galvanometer.
What happens when the magnet moves away from the coil?
When the magnet moves away from the coil, there is a deflection in the galvanometer but in the opposite direction.
What happens when the magnet is held stationary away from the coil?
When the magnet is held stationary away from the coil, there is no deflection in the galvanometer.
What did Michael Faraday formulate?
Michael Faraday formulated the basic law of electromagnetism, which helps predict how a magnetic field interacts with an electric circuit to produce an electromotive force (EMF).
What is the phenomenon described by Faraday's Law?
The phenomenon described by Faraday's Law is electromagnetic induction.
What is the mathematical expression of Faraday's Law?
The mathematical expression of Faraday's Law is E = -N(dΦ/dt), where E is the induced EMF, N is the number of turns in the coil, and dΦ/dt is the rate of change of the magnetic flux Φ.
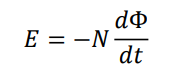
What is the formula for the magnetic flux Φ?
The formula for the magnetic flux Φ is Φ = BA cos θ, where B is the magnetic field, A is the area, and θ is the angle between the magnetic field and the normal to the area.
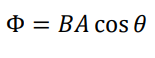
What are AC generators?
AC generators are machines that convert mechanical energy to electrical energy, typically from turbines.
What is the output of an AC generator?
The output of an AC generator is an alternating voltage and current.
What is Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) or Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (EPR)?
ESR/EPR is a phenomenon where an unpaired electron flips its spin upon exposure to a magnetic field, and this change in energy can be detected through spectroscopic techniques.
How is ESR spectroscopy used in biology?
ESR spectroscopy is used to study biochemical pathways and processes in biology, particularly those involving unpaired electrons.
What types of biological molecules can be studied using ESR?
ESR can be used to study free radicals, reactive oxygen species (ROS), and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) in biological systems.
What is Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy?
NMR spectroscopy is the study of molecules by recording the interaction of radiofrequency electromagnetic radiation with the nuclei of molecules placed in a strong magnetic field.
What does NMR spectroscopy rely on?
NMR spectroscopy relies on the phenomenon of nuclear magnetic resonance, providing detailed information about the structure, dynamics, reaction state, and chemical environment of molecules.
How is NMR used in biology?
NMR can be used for
drug screening
pharmacokinetics
to provide information in the design and discovery of new drugs.
What other biological applications does NMR have?
NMR can be used to
measure the translocation of ions and small molecules across lipid bilayers and membranes
to characterize the structure, phase behavior, and dynamics of membranes and membrane-embedded peptides and proteins.
What is Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)?
MRI is a technique used to create detailed images of organs and tissues within the body using a strong magnetic field and radiofrequency pulses.
How is an MRI image generated?
An MRI image is generated by placing tissue in a strong magnetic field with a gradient (field increasing in a direction) and passing a broad-band radio frequency pulse through it.
Why are magnetic nanoparticles being explored in medicine?
Researchers are exploring magnetic nanoparticles due to drug delivery problems, seeking alternative modes of drug delivery.
How can drugs be delivered using magnetic nanoparticles?
Drugs can be packaged into magnetic nanoparticles and then targeted to a specific area in the body.