SL22108-Prescribing in Pregnancy
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
CHALLENGES IN PREGNANCY
Consider mum ad fetus
entity as one
Pregnancy= childbearing potential
prescribing questions
Is the drug safe?
Is the drug necessary?
Are there alternatives that are as effective/ safer?
Effect of pregnancy on drugs and drugs on pregnancy
Assess need for extra monitoring of mum and baby
OFFER PRE - PREGNANCY COUNSELLING
pregnancy prescribing website
UKTIS
contains drug monographs
pregnancy trimesters
Pregnancy is divided into three trimesters
1st is up to 13 weeks
2nd is 13-28 weeks
3rd is after 28 weeks
1st trimester
1st trimester increase in blood volume but reduction in protein binding due to pregnancy steroids, therefore alteration of medications are required eg levothyroxine increase usually 25%.
teratogenic defects
vomiting in pregnancy
Risk of vomiting in pregnancy: slow transit time reduced or increased absorbtion, therefore repeat doses required.
Metabolism: activation of cytochrome p450 enzyme pathway: eg lamotrigine
which drugs should be avoided
uMETHOTREXATE
uRADIOACTIVE IODINE
u(LITHIUM)
uISORETINONIN
uSODIUM VALPROATE
uWARFARIN
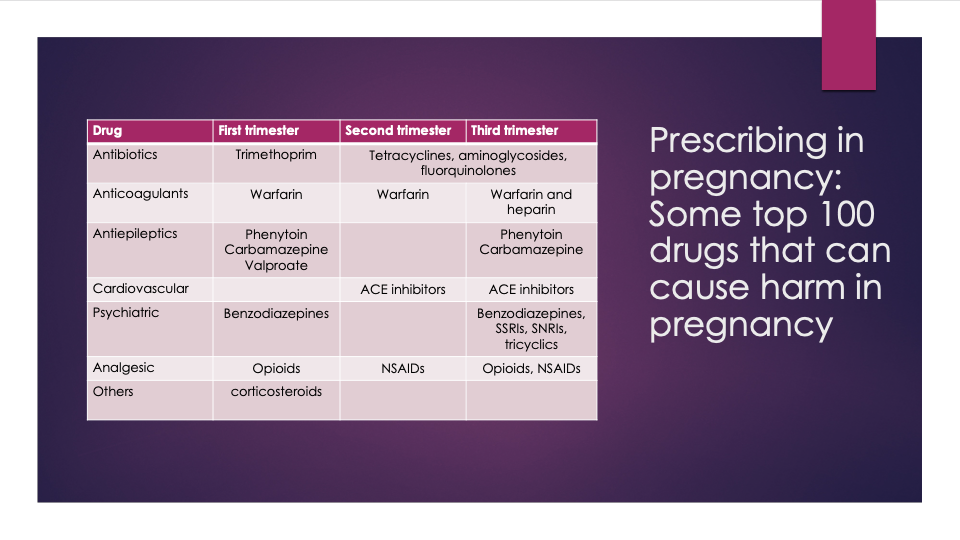
which medicines and which trimester do they affect
Within 20 days after fertilisation
All-or-nothing effect (death or no effect)
Highly resistant to birth defects
3-8 weeks after fertilization
Possibly no effect
Miscarriage
Obvious birth defect
Permanent but subtle effect only evident in later life
Organ development, particularly vulnerable to birth defects
2nd and 3rd trimesters
Changes in growth and function of normally formed organs and tissue
Unlikely to cause obvious birth defect
Unknown long-term effects
Organ development complete
pre pregnancy
uOnly switch drugs in pregnancy if meds unsafe and suitable alternative
uDifferent drugs at varying gestations
recreational drugs
Nicotine
Alcohol
Drugs of addiction
pregnancy pharmacokinetics
Plasma levels change, reduced absorption, dilution, excretion
Increase drug concentrations
Hyperemesis
morning sickness
caused by
uCyclizine
uMetoclopromide
uprochlorperazine
uOndansetron
uSteroids
teratogenesis
1-2% of babies born with a congenital abnormality
If a teratogenic agent is taken during the period of embryogenesis (up to 8 weeks) the result will be an anatomical malformation
Later in pregnancy function will be affected
seizure control in pregnancy
carbamazepine is contraindicated in pregnancy
it is teratogenic
patient must be counselled before medication switch as it can be difficult to make a switch when patient has good seizure control
also may need to delay pregnancy
recommended to take 5mg folic acid as anti-epileptics are weak folate antagonists
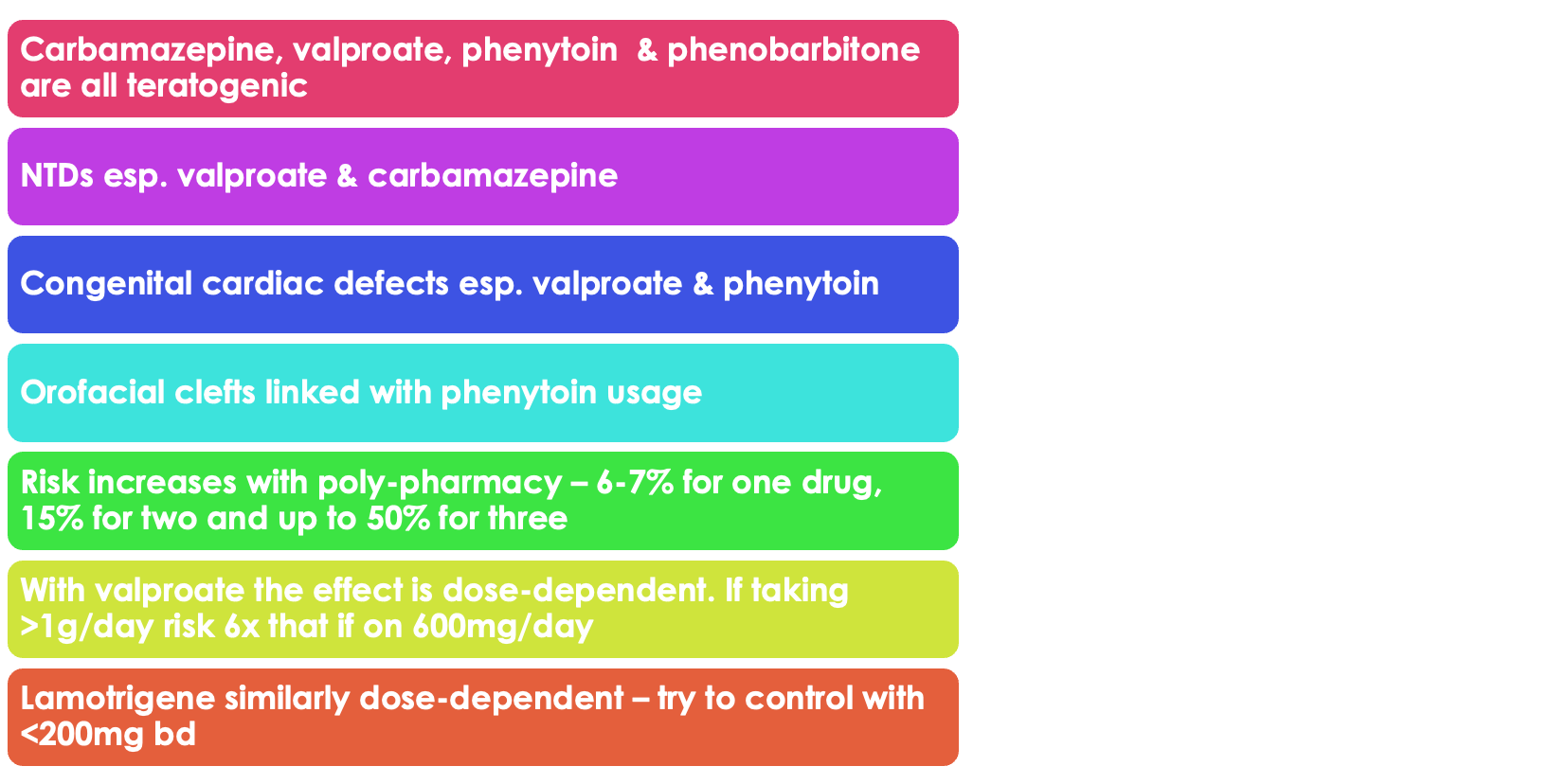
describe the consequences of antiepileptic drugs on fetus
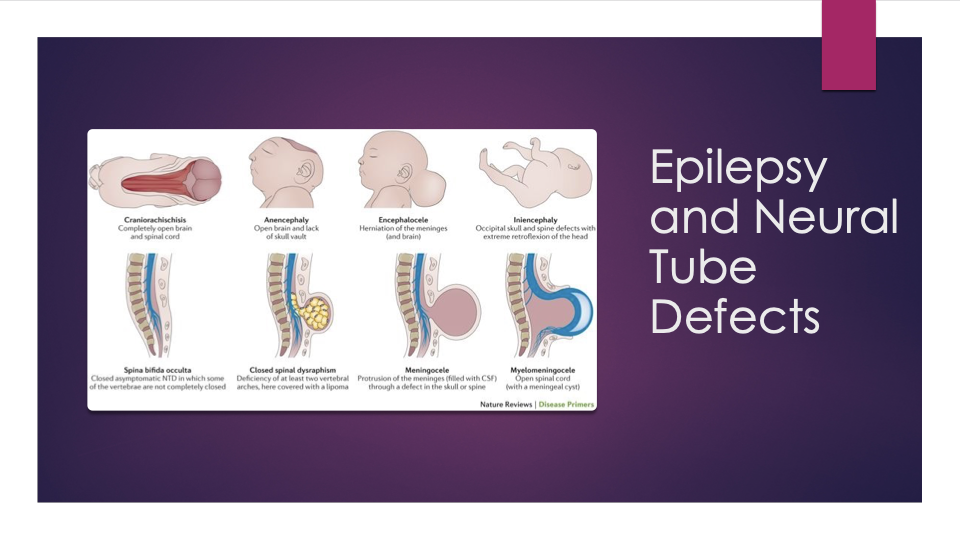
Neural tube defects
ulow-set ears
u broad nasal bridge
u irregular teeth
u hypoplastic nails and digits
gabapentin and pregabalin
•Newer anti-epileptics eg lamotrigene, gabapentin do not appear to be so risky but not entirely risk free
patient must have pre-natal screening
Asthma in pregnancy
Risk of uncontrolled asthma far outweighs small risk of harm to fetus.
Sometimes a short course of oral steroids, prednisolone may be prescribed in exacerbations
Pregnancy & Asthma: Risks
Fetal growth restriction, preterm birth, neonatal hypoxia, increased perinatal mortality, pre-eclampsia, and complicated labor.
Pregnancy & Asthma: Management
Use inhalers as normal, including short- and long-acting beta-2 agonists and corticosteroids. Oral corticosteroids should be used for exacerbations if needed.
Pregnancy & Diabetes: Primary treatment
Insulin remains the primary drug for Type 1, Type 2, and uncontrolled gestational diabetes.
Pregnancy & Diabetes: Risks of hyperglycemia
Structural abnormalities (CVS: 37%, CNS: 20%, GUS: 14%), spontaneous miscarriage, stillbirth, macrosomia, neonatal hypoglycemia, and childhood obesity.
Pregnancy & Hypertension: Treatment threshold
Blood pressure ≥140/90 mmHg (target: <135/85 mmHg).
Pregnancy & Hypertension: Safe antihypertensives
Methyldopa, nifedipine, labetalol, and hydralazine.
labetalol first line
but be aware in asthmatics, vasoconstriction
beta blocker
in most severe cases where hypertension can’t be controlled labour may be induced at an appropriate gestational age
Pregnancy & Hypertension: Contraindicated antihypertensives
ACE inhibitors, diuretics, and ATII receptor blockers.
Pregnancy & Analgesia: Preferred pain management
Paracetamol is the safest option. NSAIDs should be avoided, especially in the third trimester after 20 weeks
Pregnancy & Analgesia: Risks of opioid use
Neonatal withdrawal syndrome and potential fetal harm.
if taken prolonged
preclampsia
Medical emergency
organ damage
Pregnancy & Mental Health: Considerations before prescribing
Risks vs. benefits, teratogenic potential, and whether the medication can be safely switched or discontinued.
Pregnancy & Mental Health: Contraindicated psychiatric drugs
Lithium, sodium valproate, and some antipsychotics due to risks of congenital abnormalities.