DPT II Exam IV
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
STEMI infraction
transmural MI (entire thickness of the heart wall), ST segment elevation and pathologic Q waves
NSTEMI
subendocardal MI (affects the inner third of the heart muscle), non St segment
best biomarkers for outcome are
tropin I and T
how to tx STEMI
MONA
what does MONA stand for
morphine, oxygen, nitrate, aspirin
moriphine
analgesic and anxiolytic
statins
reduce LDL and have anti inflammatory effects
fibrinolysis
repercussion for STEMI
b blockers
decrease in HR, contractility, BP , and subsequently myocardial oxygen demand
ca channel blockers
arterial vasodilation, coronary vasodilation, decreasing peripheral resistance, after load, BP, and myocardial oxygen demand
arteriosclerosis
Chronic vascular disease characterized by abnormal thickening and hardening of the vessel wall
atherosclerosis
fat and fibrin deposits that harden over time
atherosclerosis is a BLANK disease
inflammatory with lesion progress
numerous factors are involved in atherolscleoris
non modifiable and modifiable
oxidized LDL plays
central role in the formation of fatty streaks
Ath-1 gene controls
oxidation and inflammatory process
HDL associated proteins apoj and paraoxonase may minimize
LDL oxidation
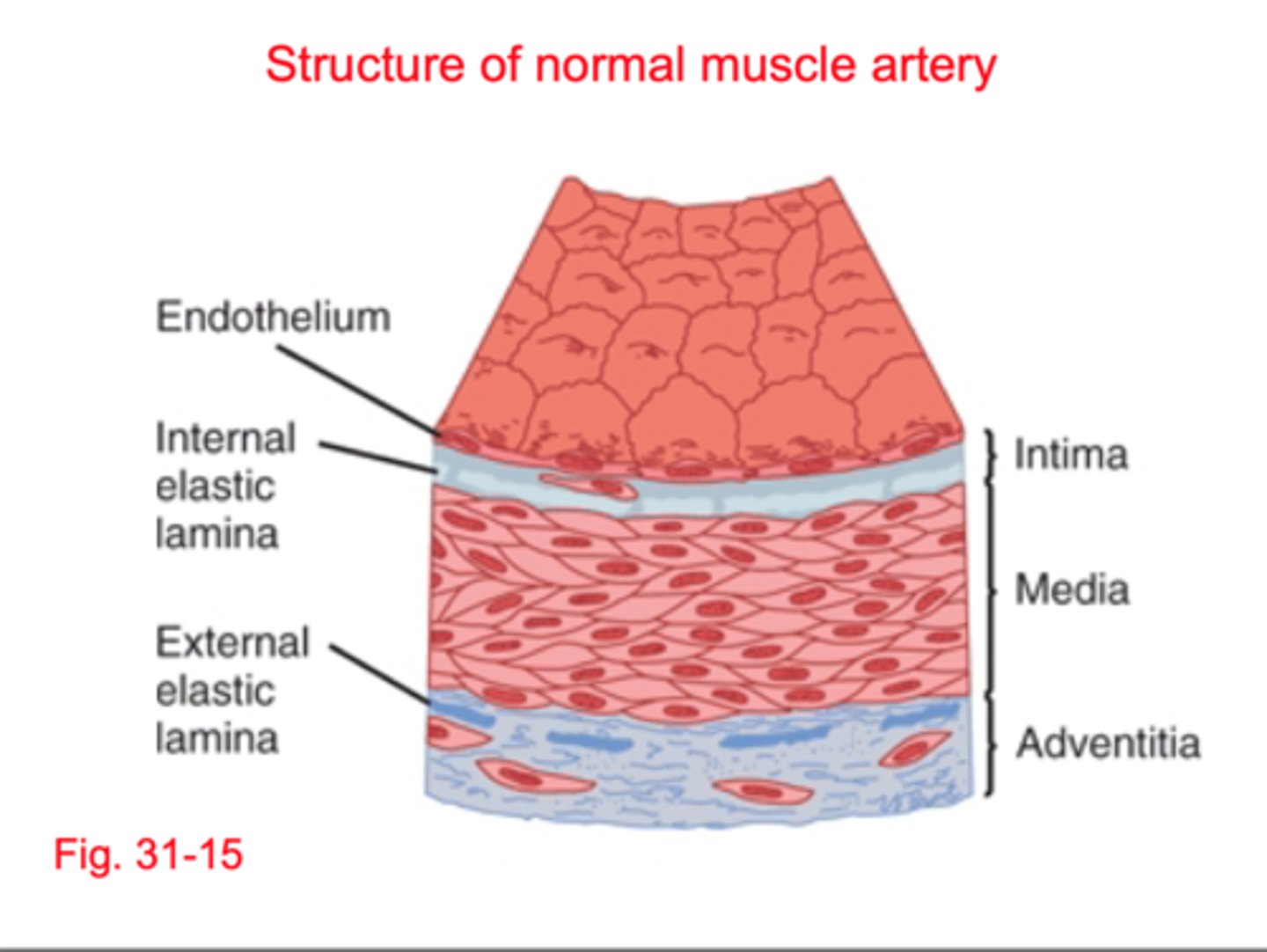
normal artery structure
1) intima (inner most layer)
2) media (middle layer)
3) adventitia (outer)
primary cause of SIHD
atherosclerosis, lesions decrease vessel diameter reducing perfusion in normal state when demand increases
microvascular angina
summer resistance sized vessels exhibit abdominal constriction resulting in ischemia
loss of endothelial integrity
structure and function, key to lesion development
the location of atherosclerotic lesion influences
extent of muscle involvement and clinical manifestation
collateral vessel development involves what growth factors
VEGF and BFGF
classical angina is due to
transient episode
MI is due to
response to significant or prolonged ischemia
what metabolic abnormalities are present in SIHD
lactate production, decreased IC pH, depletion of ATP, impaired cell transport
ECG abnormalities in SIHD
T wave inversion and or ST depression
chronic stable angina is caused by
transiet myocardial ischemia (exertion)
when can chronic stable agina occur
during rest and at night
what typically results from exertion/emotion and is relieved by rest?
chronic stable agina
chronic stable aging ECG is
normal in 50% at rest, changes in ST segment (depression) and T wave inversion occurs during episodes
are changes in cardiac enzymes resent in chronic stable angina?
no
primary indicators of chronic stable angin
left ventricular function as well as severity of stenosis
silent ischemia ECG
ST elevation or depression
why is there lack of symptoms in silent ischemia
altered pain afferents, pain perception, or less inflammation during episode
coronary vasospasm in SIHD
presence of mild/moderate fixed obstruction with occasional spasms at/near site of plaque, usually in the morning
Prinzemetal's Variant Angina
coronary vasospasm, no coronary artery obstruction (younger pts)
Prinzemetal's Variant Angina ECG
ST segment elevation
organic nitrates
NO activates guanylyl cyclase GC, increases cyclic GMO levels in cells, reduces phosphorylation of myosin light chain (MLC), decreases IC Ca and relaxation/vasodilation
ranolazine
selective inhibition of late Na current
all patients with PAD need
non pharmacist intervention, statin therapy, htn/diabetes management
what is beneficially in PAD symptomatic pts
antiplatelt +/- rivaroxaban/vorapaxar
stable
elicited by exertion or emotion
ischemic heart disease
artherosleoritc disease of coronary arteries, coronary artery disease
SIHD
chronic coronary disease
SIHD is a condition of
imbalance between myocardial oxygen supply and demand most often caused by atherosclerosis of the coronary artery.
prinzmetal
vasospastic angina without coronary artery obstruction
SNS intervention to the coronary arteries regulates
blood flow
determines the oxygen demand by the heart
contractility
LDL
oxidized during the first step of atherosclerosis
endothelin
potent vasoactive substance that c an cause vasoconstriction in the coronary circulation
abciximab
Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor
APOJ
minimized LDL oxidation
intima
endothelial cells, NO PGY12
media
middle layer containing smooth muscles causes constriction/ contraction
adventitia
collagen rich that hardens connective tissues
ApoJ and paraoxonase
minimize LDL oxidation
direct effects of SNS intervention
smooth muscle dilation
indirect effects of SNS intervention
stimulate cardiac muscle beta receptors to increase HR and increase metabolic activity
coronary flow is greatest during
diastole
aortic pressure
important factor for perfusion to the coronary arteries (assist in blood flow)
radius of the vessel
primary determinant of overall flow
metabolic factors
adenosine, K ion, CO2, H+, prostaglandin, NO
endothelium
vasodilation through NO and PG12
grade I
ordinary physical activity does not cause aging, but strenuous work
Grade II
slight limitation of ordinary activity
Grade III
marked limitation
Grade IV
inability to carry any physical activity without discomfort, may be AT REST
what is the primary cause of SIHD
artherosclerosis
classic amnia is due to
transiet episodes
MI occurs in response to
significant or prolonged ischemia
SIHD metabolic abnormalities
low pH, depletion of ATP, lactate production
SIHD EKG
T wave inversion and ST depression
chronic stable angina
caused by transit myocardial ischemia and resolves at rest
silent ischemia
detected on routine exams, pain receptors or less inflammation during episode
PAD
most common form of peripheral vascular disease
caused by progressive narrowing of arteries due to atherosclerosis
characterized by stenosis and or occlusion of medium and large sized arteries excluding arteries that supply the heart and brain
PAD is due to
the oxygen demand greater than the oxygen demand
risk factors for PAD
Cigarette smoking
Hyperlipidemia
Hypertension
Diabetes mellitus
symptoms of PAD
intermittent claudication, fatigue, discomfort, cramping, relieved by rest, pain at lower extremities
claudication
pain within a specific group of muscles that is exacerbated by exercise and received by rest
clinical limb ischemia
pain at rest or tissues, limb loss
ABI
highest of DP or PT/ highest of brachial (take the lowest number)
ABI 0.7-0.99
mild
ABI 0.4-0.69
moderate
ABI under 0.4
severe
what vaccinations should patients either PAT receive
flu and covid
when should sympathetic patients receive surgery
imitating claudication or inadequate response to GDMT
what medications should PAD pts be on?
- high intensity statin
- diabetes management
- HTN management
- anticoagulant or antiplatlet
is antithromboric therapy recommended for asymptomatic pts?
No, unless other disease
is anti platelet therapy recommended for asymptomatic pts?
yes if there's other factors
clopidogrel
blocks P2Y12 receptor on platelet preventing GPIIb/IIIa activation leading to reduced platelet aggregation
what is vorapaxar C/E
stroke, ICH, TIA, bleeding
is warfarin indicated in PAD
no
when Is rivoraxaban indicated in PAD
symptomatic pts to reduce MALE/MACE
cilostazol MOA
inhibits PDE3 to increase cAMP to reversibly inhibit platelet aggregation and promotes vasodilation
Cilostazol C/E
Heart failure
Cilostazol used for
improvement of walking distance in claudication but NOT associated with benefit for MACE
pentoxifylline MOA
improves tissue oxygenation through improved blood flow (less blood viscosity and improved RBC flexibility)
what is petoxifylline used for
same as cilostazol, just less effective
what trial states that PAD is under diagnosed
PARTNERS