Modern physics
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Thermionic emission
The release of electrons from the surface of a hot metal
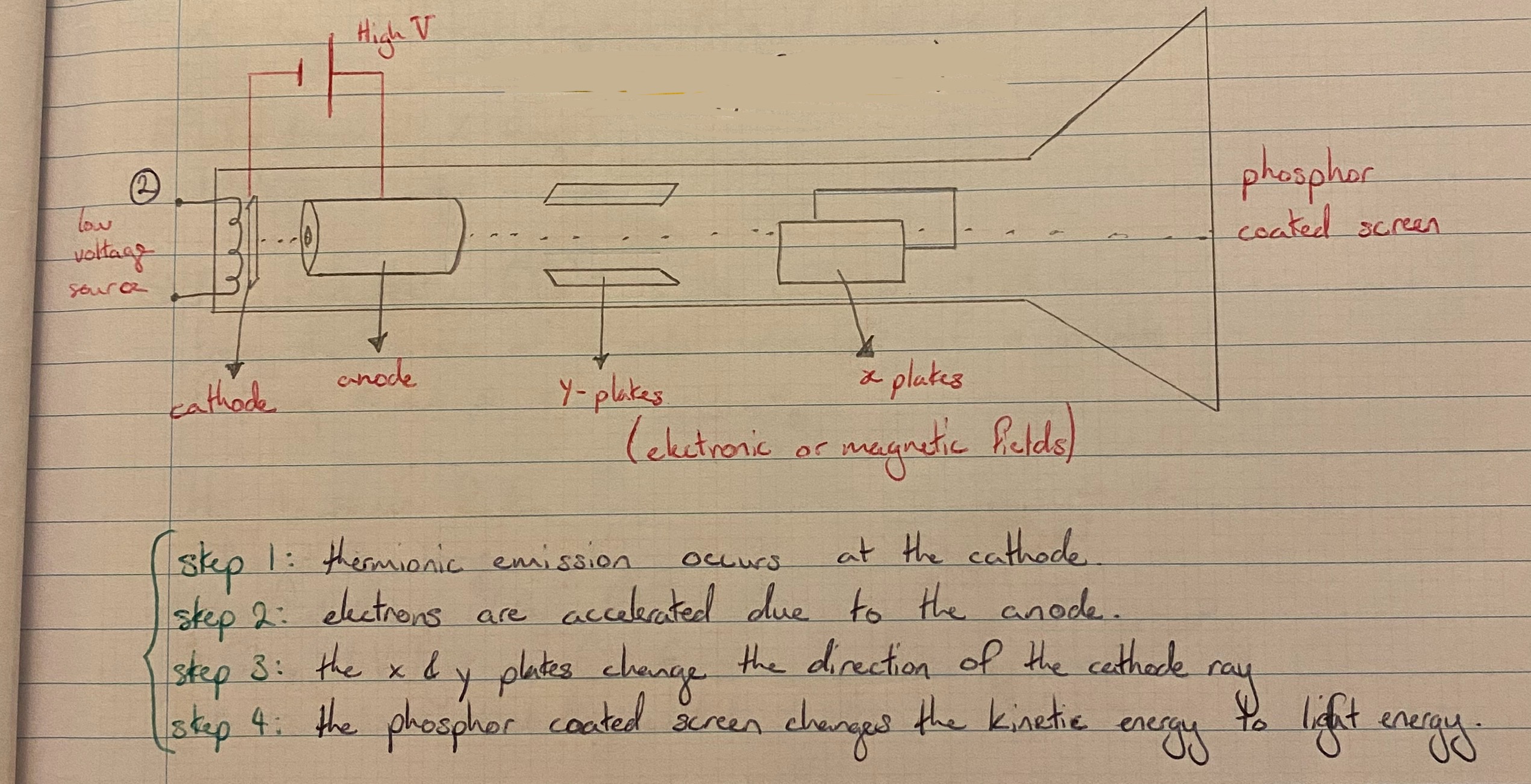
Cathode Ray Tube
Kinetic energy formula
1/2 mv²
Kinetic energy =
qV
q= charge on one electron
V= high voltage
X-rays
Are produced when high-energy electrons collide with a high density target. They are a high frequency form of electromagnetic radiation.
Who discovered x-rays?
Wilheim Rontgen
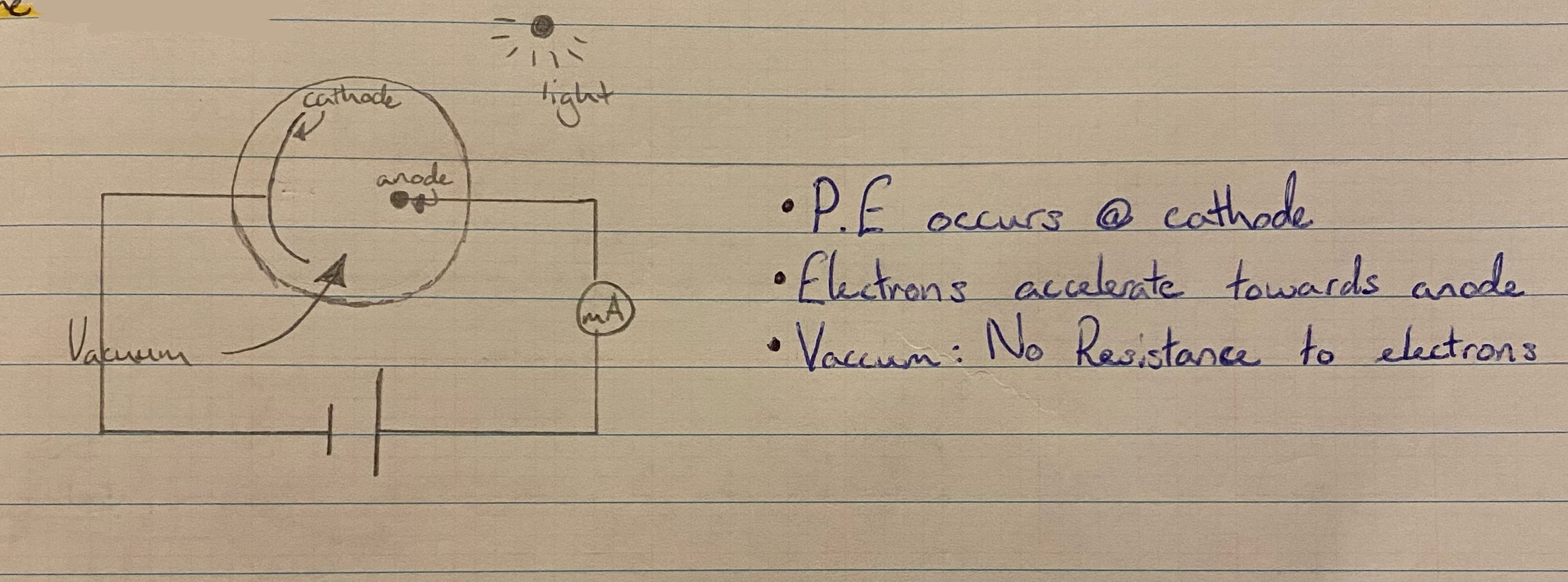
The photoelectric effect
The emission of electrons from the surface of a metal when light of a suitable frequency shines on it.
How to demo P.E.
1: negatively charge a G.L.E.
2: Shine U.V. Light on G.L.E.
3: leaves collapse → electrons emitted
The photocell
Einstein’s explanation of the photoelectric effect
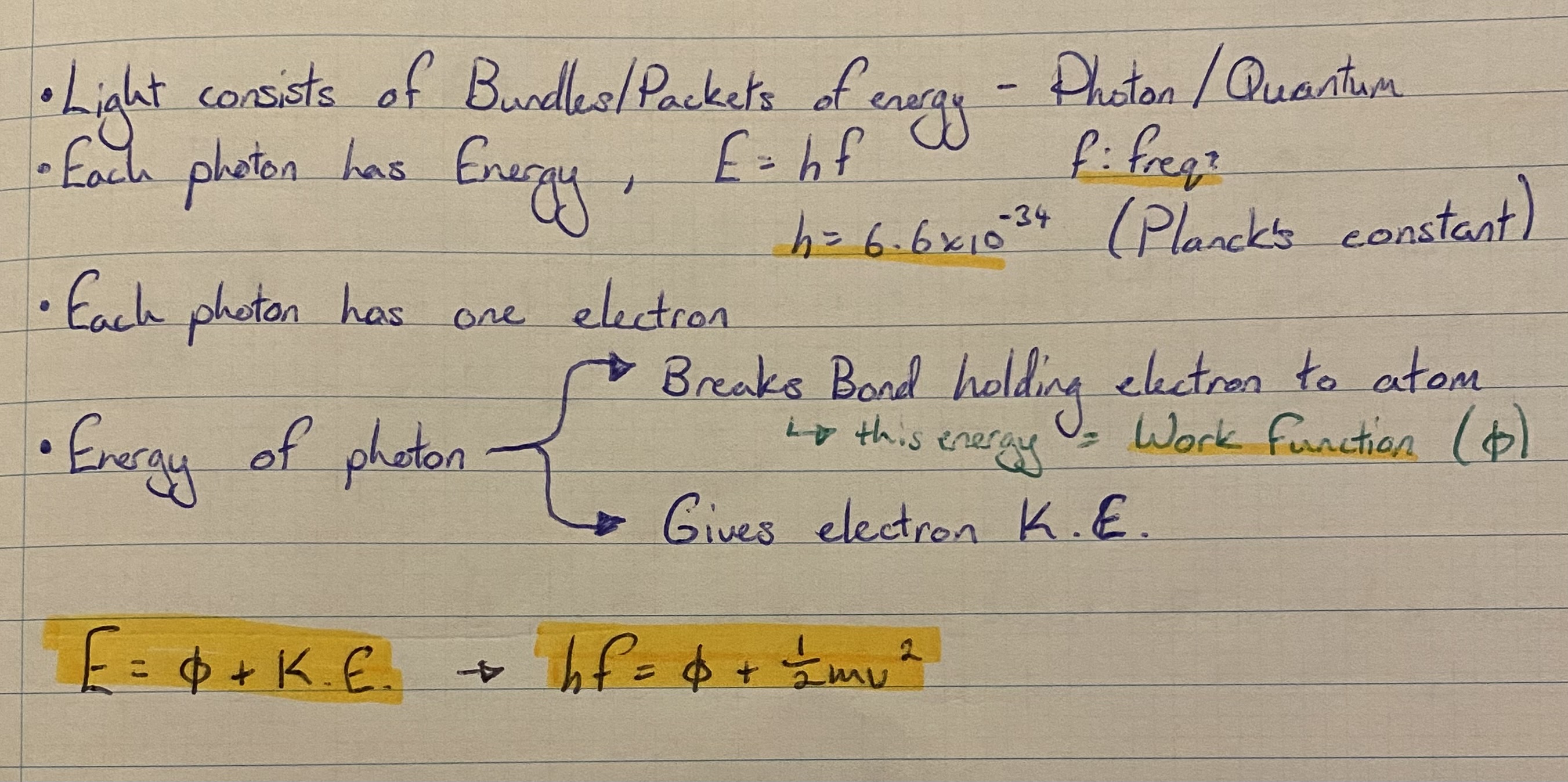
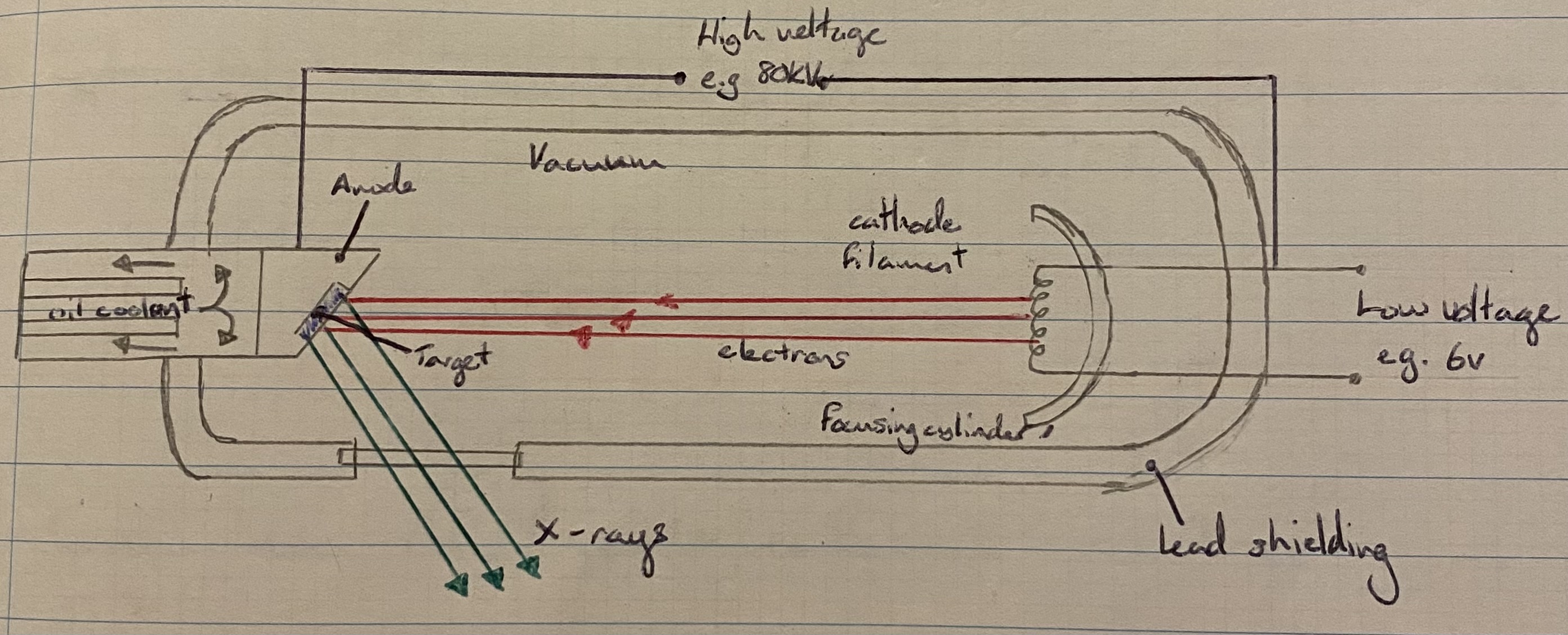
Diagram of an X-Ray tube
1. The low voltage supplies power to a filament. | |
2. Electrons are emitted from the filament due to thermionic emission. | |
3. They get accelerated across the vacuum due to the very high voltage and smash into the high-density anode (usually tungsten). | |
4. Most of the kinetic energy gets converted to heat, which must be removed with a coolant. | |
S. Sole in dod on into une can i ne a i pried in eve, tea quickly | |
6. These X-rays are emitted in all directions. | |
7. Most of these get absorbed by the lead shielding, but some exit through a narrow window, where they are then used for the required purpose. |