Heart, Blood and blood vessels
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Blood is **tissue** consisting of plasma, in which the red cells, white blood cells and platelets are suspended.
* veins
* capillaries
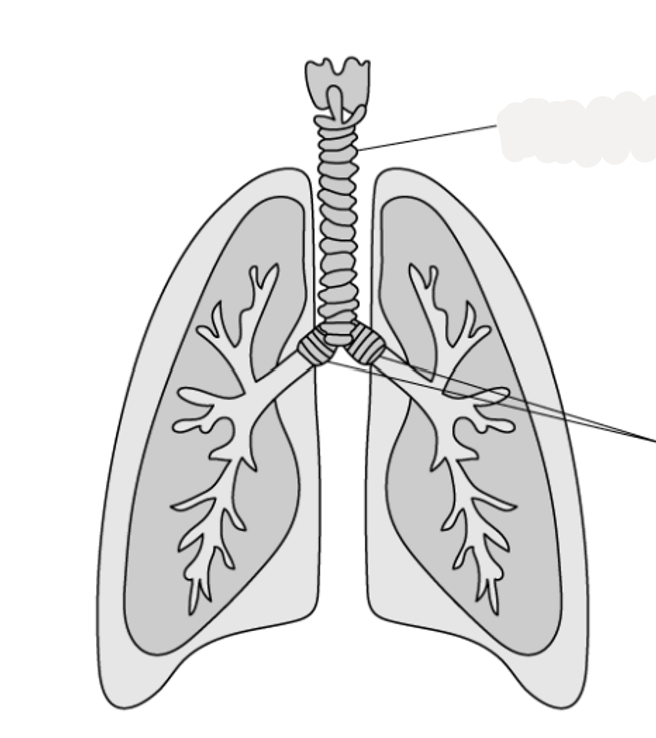
y= bronchi
\
\
* Moist surface- allows oxygen to readily dissolve
\
* capillaries are thin (one cell thick)- minimizes diffusion distance/short diffusion pathway
\
* large capillary network (provides good blood supply)- for efficient gas exchange with red blood cells/ to maintain a concentration gradient/ to remove oxygenated blood and bring carbon dioxide to lungs quickly
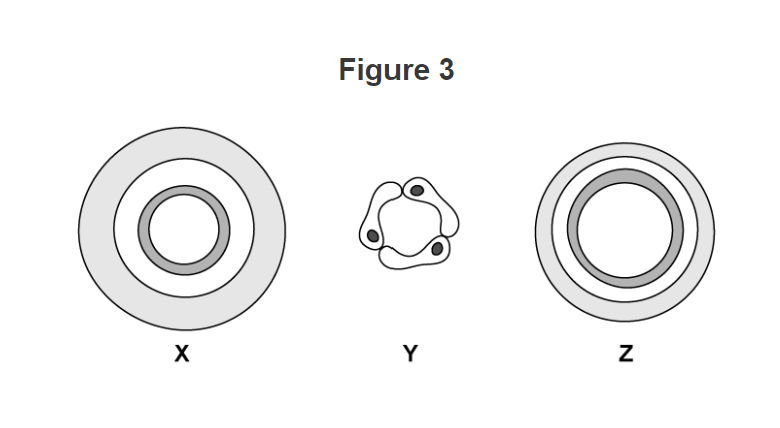
The wall of arteries is very thick compared to the size of the hole (lumen). Their walls are thicker than walls of veins to withstand high blood pressure.
\
* They have elastic fibres, allowing them to stretch and spring back.
\
Arteries transport blood away from the heart. (usually at a high pressure)
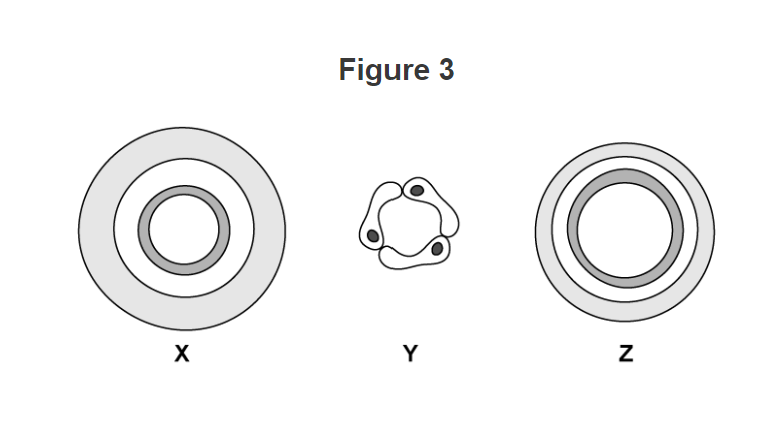
**Z** They have a large lumen and doesn’t need thick walls because the blood is at low pressure. \ Veins transport blood to the heart (usually at a low pressure)
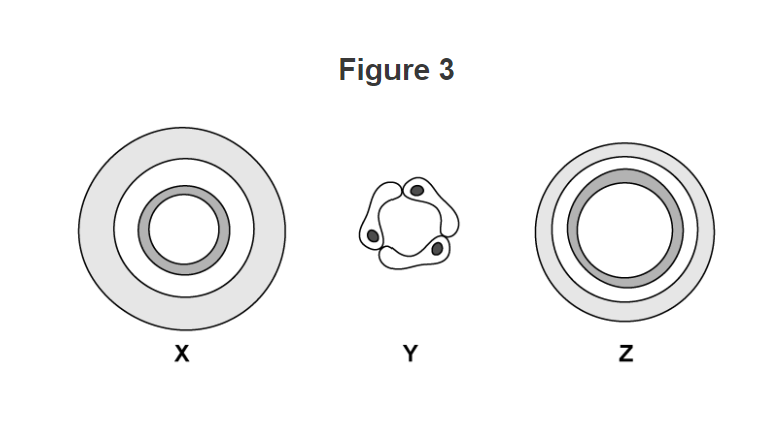
Capillaries are very small with walls that are usually only one cell thick.
\
Capillaries have thin walls which allows substances to leave the blood to reach the body’s tissue.
which can close/shut
which prevents the black-flow of blood
\-gives a large surface area
\-allows the cell to bend/squeeze against the capillary walls
* No nucleus to allow more space for carrying oxygen
* Contains hemoglobin which binds oxygen
* they stop blood loss
* prevents bacteria from entering
* stops bleeding
some produce **antibodies** to fight pathogens
some produce **antitoxins** to neutrilise any toxin produced by the pathogen
\
* The oxygenated and deoxygenated blood is separated so its more efficient
* Oxygen is carried by RBCs which contain haemoglobin to bind oxygen and have no nucleus so there is more space available to carry oxygen.
* thin walls allow for easy diffusion to cells
* large surface area of capi
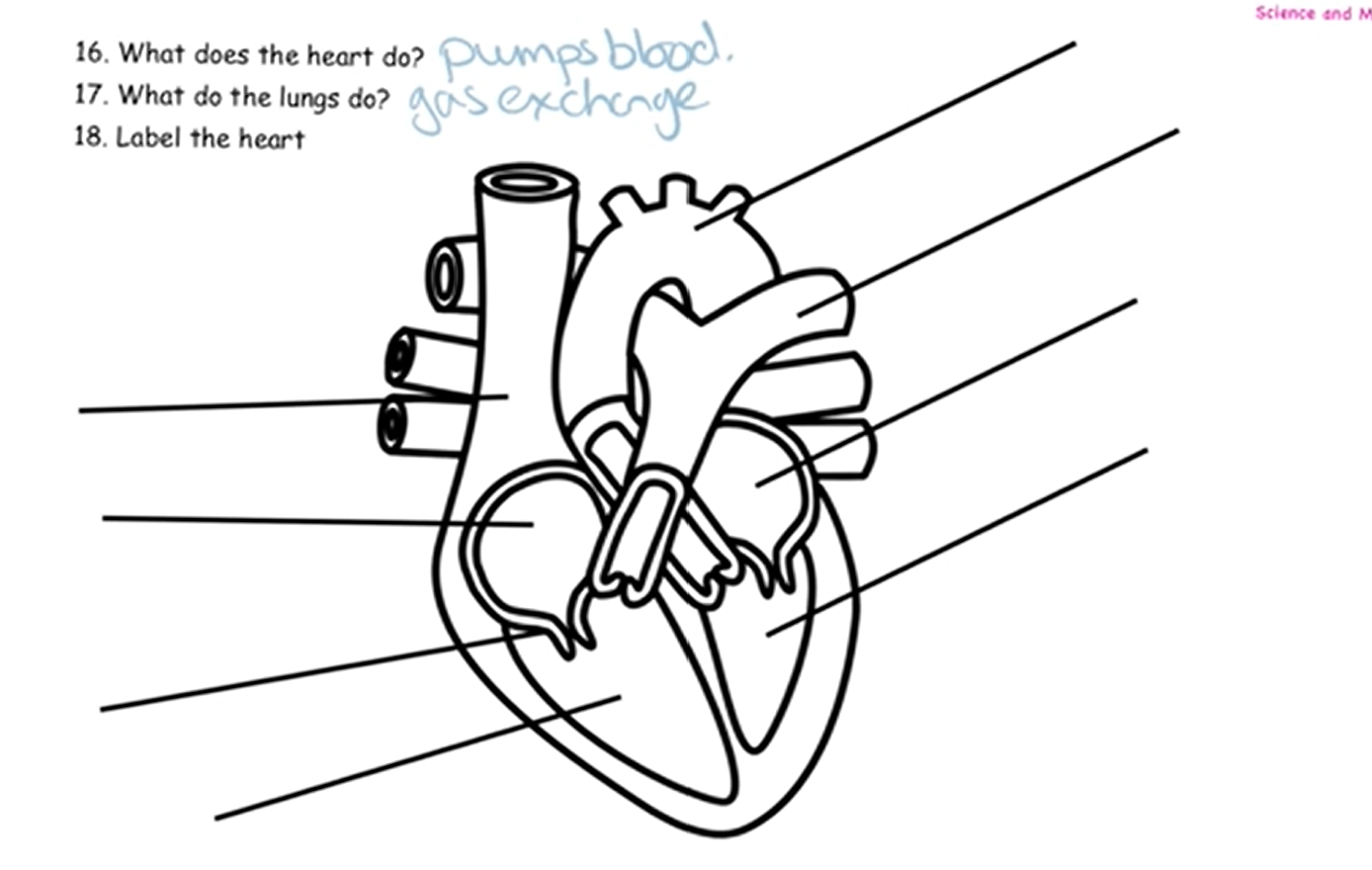
what are the processes in the heart which allows it carry out its function of supplying oxygen to the body and removing waste products?
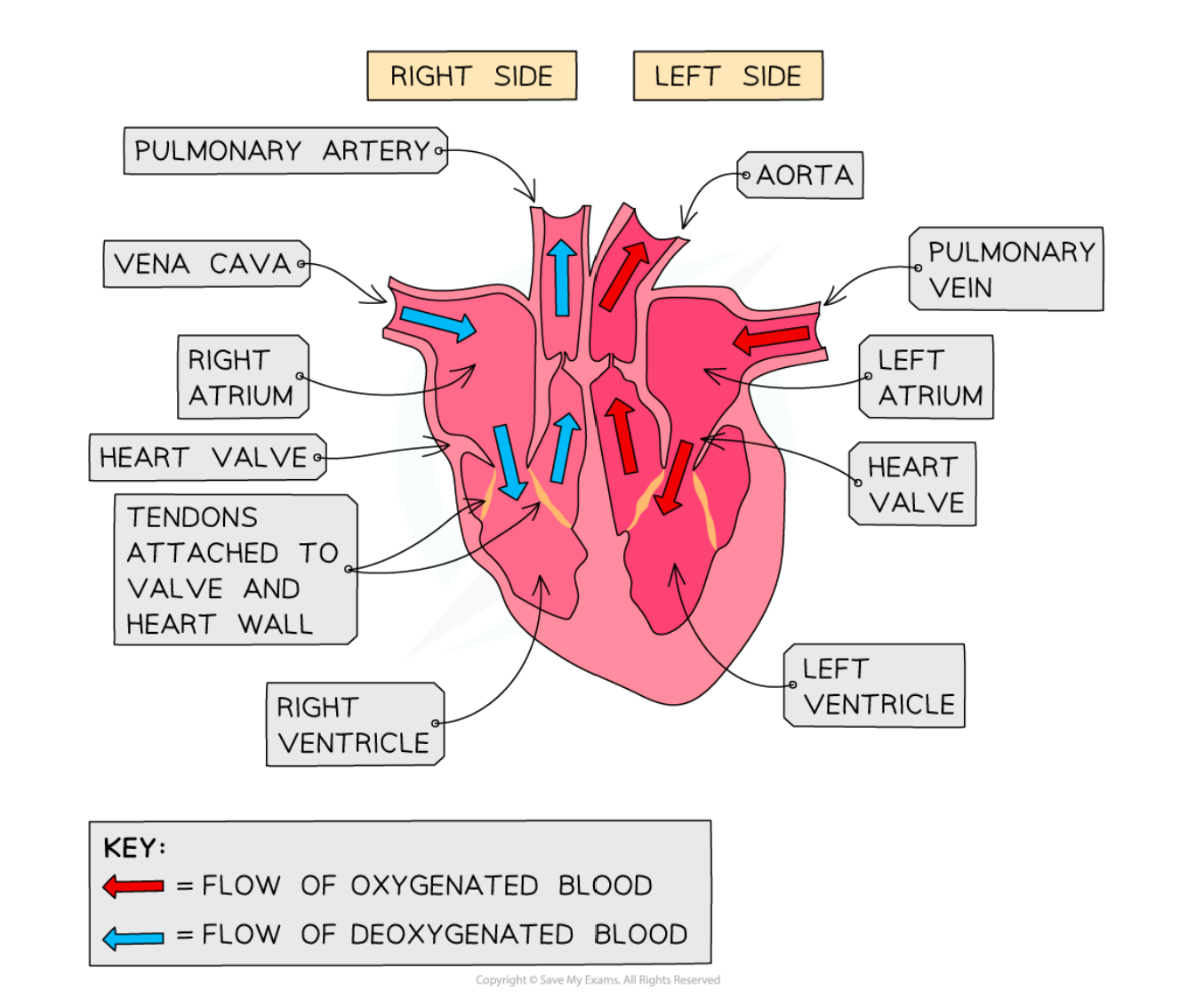
* The heart pumps blood to the lungs via the pulmonary artery so that oxygen can diffuse into the blood from the air in the alveoli
* blood returns to the heart via pulmonary vein where muscles pump blood to the body via aorta
* arteries carry oxygenated blood to tissues where capillaries deliver oxygen to cells for respiration and energy release.
1. Arteries branch into much smaller vessels, called capillaries. Capillaries have thin walls and pass very close to the body cells.
2. In capillaries, food and oxygen move out of the blood and into the cells.
3. In capillaries, waste products, such as carbon dioxide, move out of the cells and into the blood.
The heart pumps out oxygenated blood to the body through the aorta.
The blood becomes oxygenated in the lungs.