polysaccharides - chapter 1.2
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
how are polysaccharides made
made from many monosaccharides joined by condensation reaction
3-10 molecules are called
polysaccharides
11+ molecules are known as
true polysaccharides
how does there structure make them ideal for storage
-compact molecules
-glycosidic bonds are easily Brocken
-not very soluble in water (no osmotic movements)
how are glycosidic bonds broken
hydrolysis
how does hydrolysis work
water is added and the bonds break down shorter and shorter until only simple sugars are left
why is starch important
energy storage in plants
sugars from photosynthesis = starch (insoluble, compact and broken down rapidly)
is amylose branched or unbracnched
unbranched
what glycosidic bonds are amylose made of
1,4 - glucose
why is amylose compact
as the chains lengthen the molecule spirals
what glucose is amylose made from
a-glucose
amylose diagram
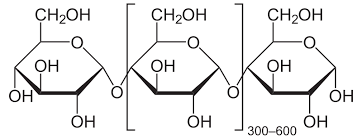
what percentage of starch is amylose
10-30%
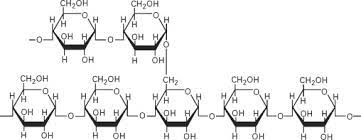
is amylopectin branched or unbranched
branched
what glycosidic bonds are amylopectin made of
1,4 - glycosidic bonds and 1,6 - glycosidic bonds
what is amylose useful for
storage
what is amylopectin useful for
can be broken down rapidly
what percentage of starch is amylopectin
70-90%
amylopectin diagram
where can you find glycogen
found in animals and fungi
what glucose is glycogen made from
a-glucose
how is glycogen broken down so rapidly
many 1,6 - glycosidic bonds
in what tissue is glycogen most commonly found
muscle and liver tissues
what is cellulose used for
structural support - many of them
high tensile strength
freely permeable
what glucose are cellulose made from
long chains of b-glucose