audiology final
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
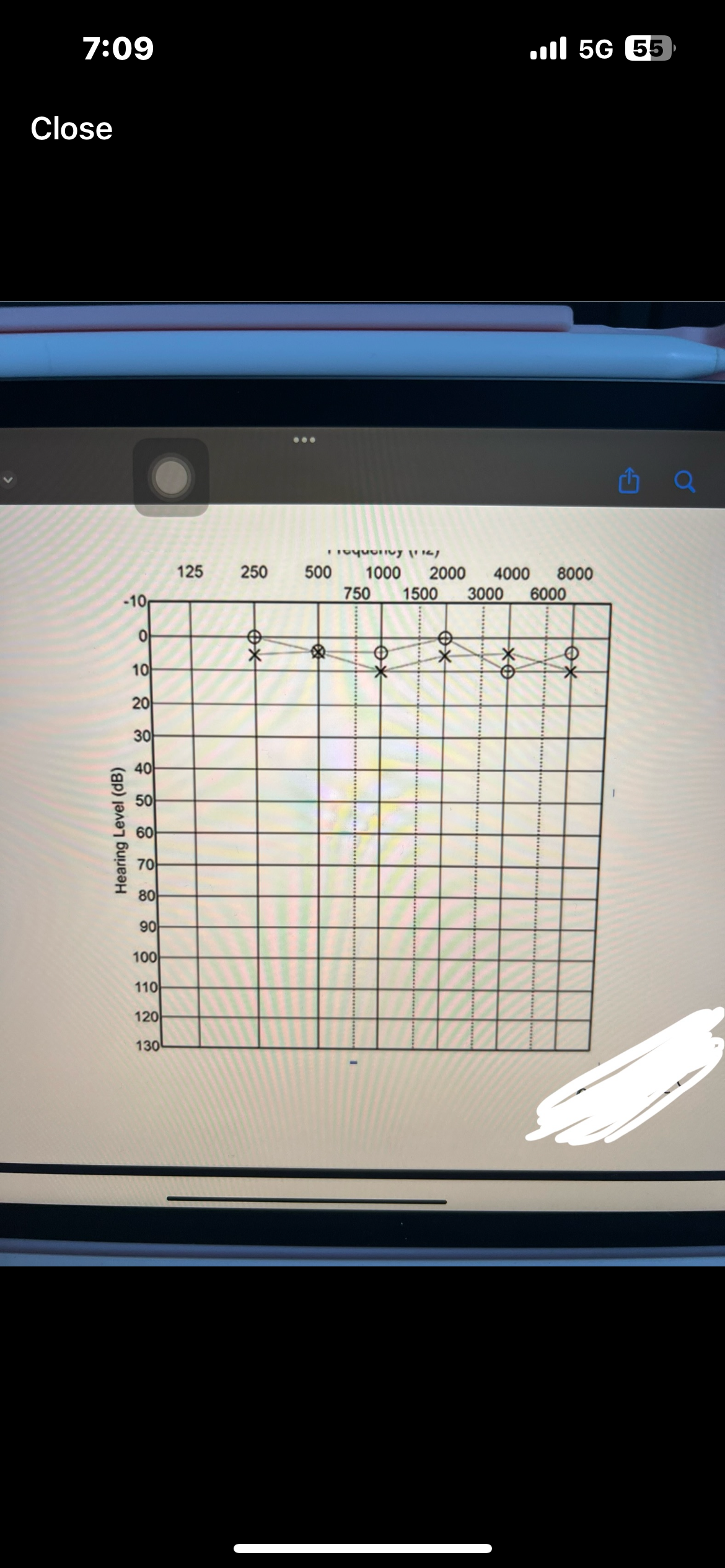
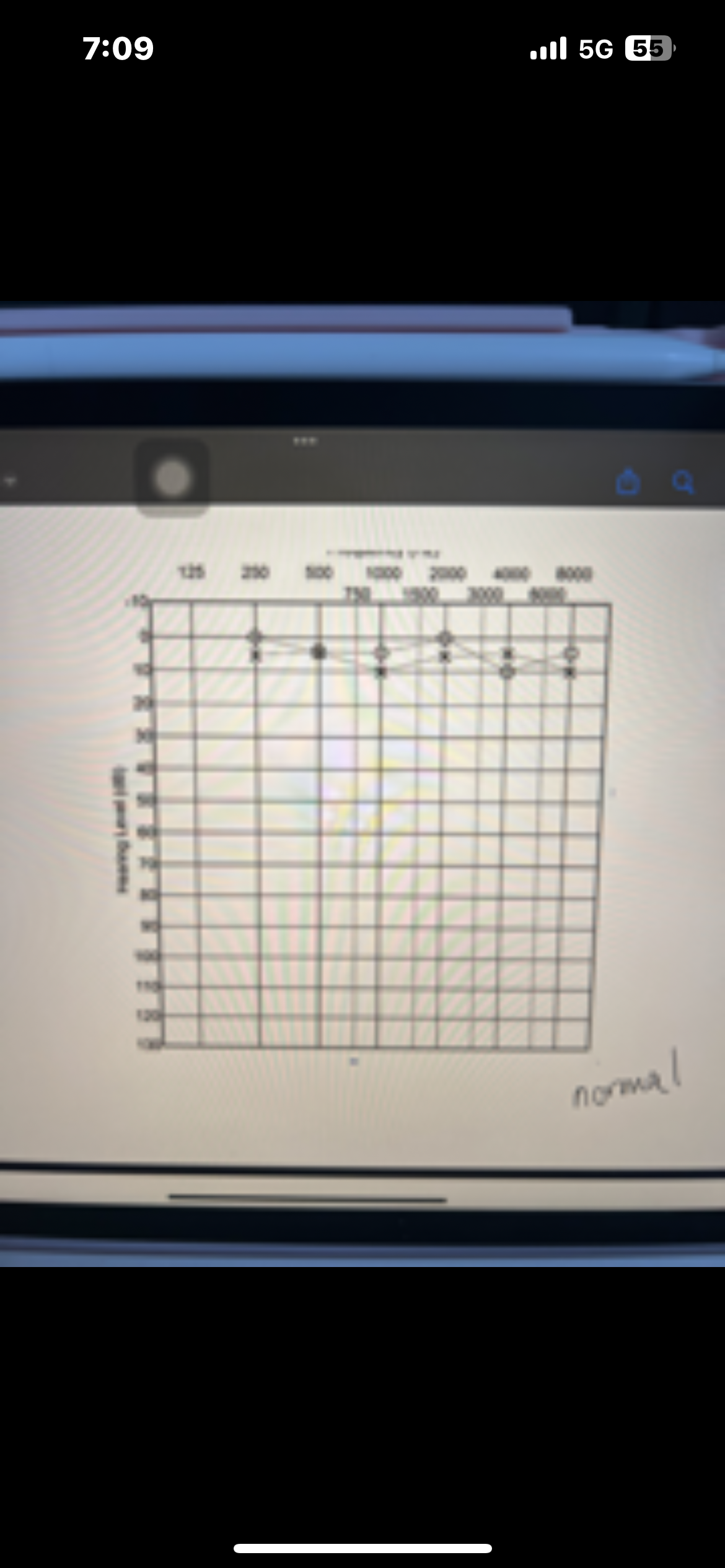
What is tonotopic organization
Frequency specific organization. Every frequency/tone gets represented at a specific place on the basilar membrane
The high frequencies occur at the ___ of the cochlea
Base
The low frequencies occur at the ___ of the cochlea
Apex
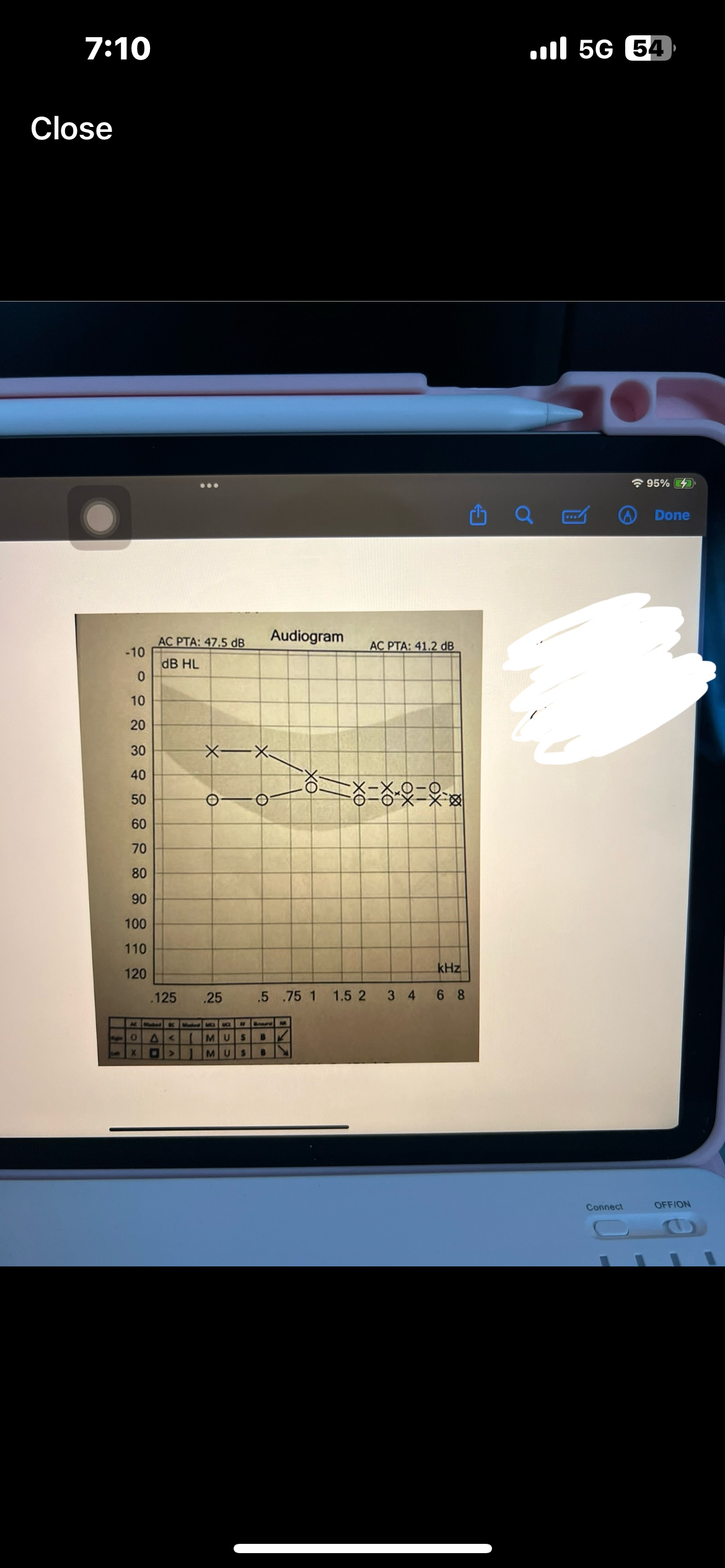
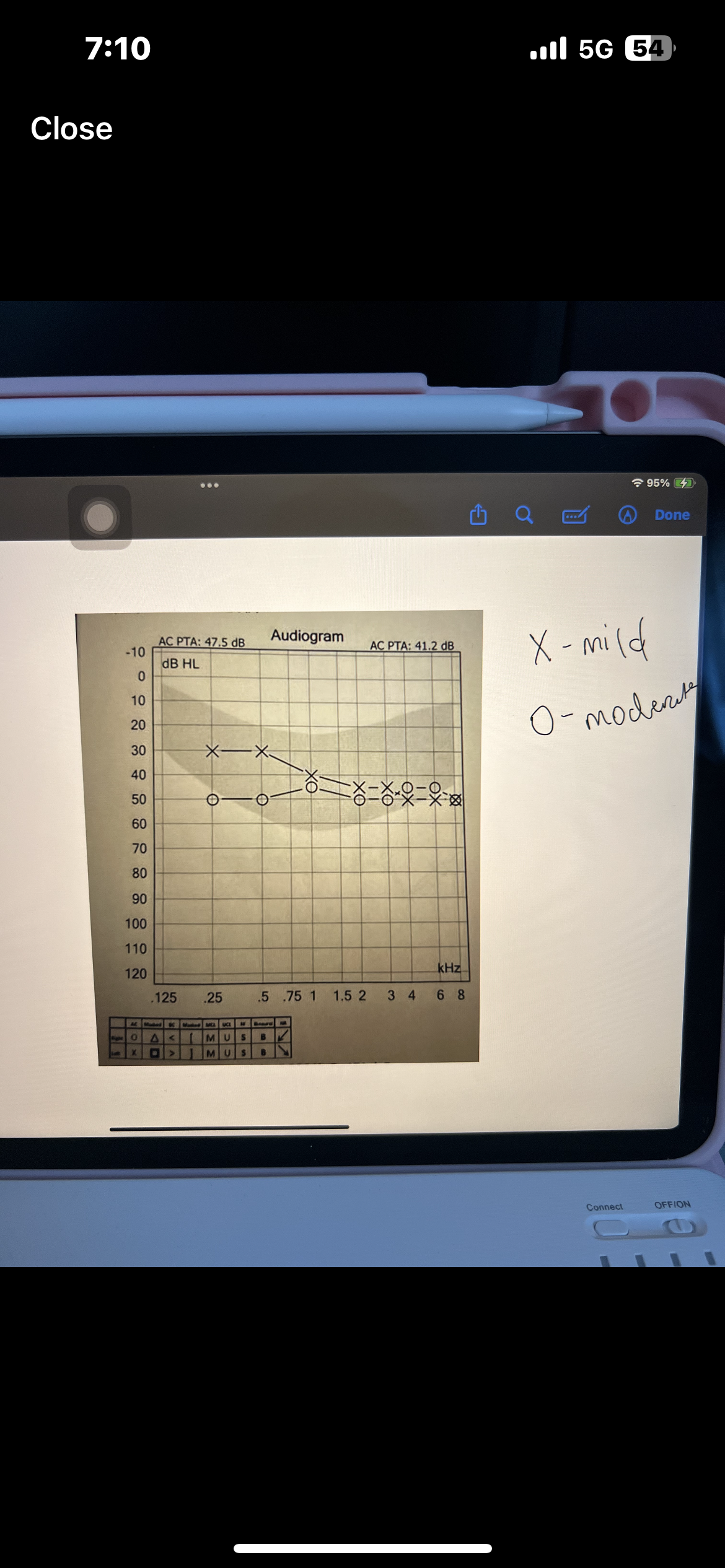
What is the purpose of pure tone (air+bone)
Purpose is to determine the lowest intensity that a pure tone is heard
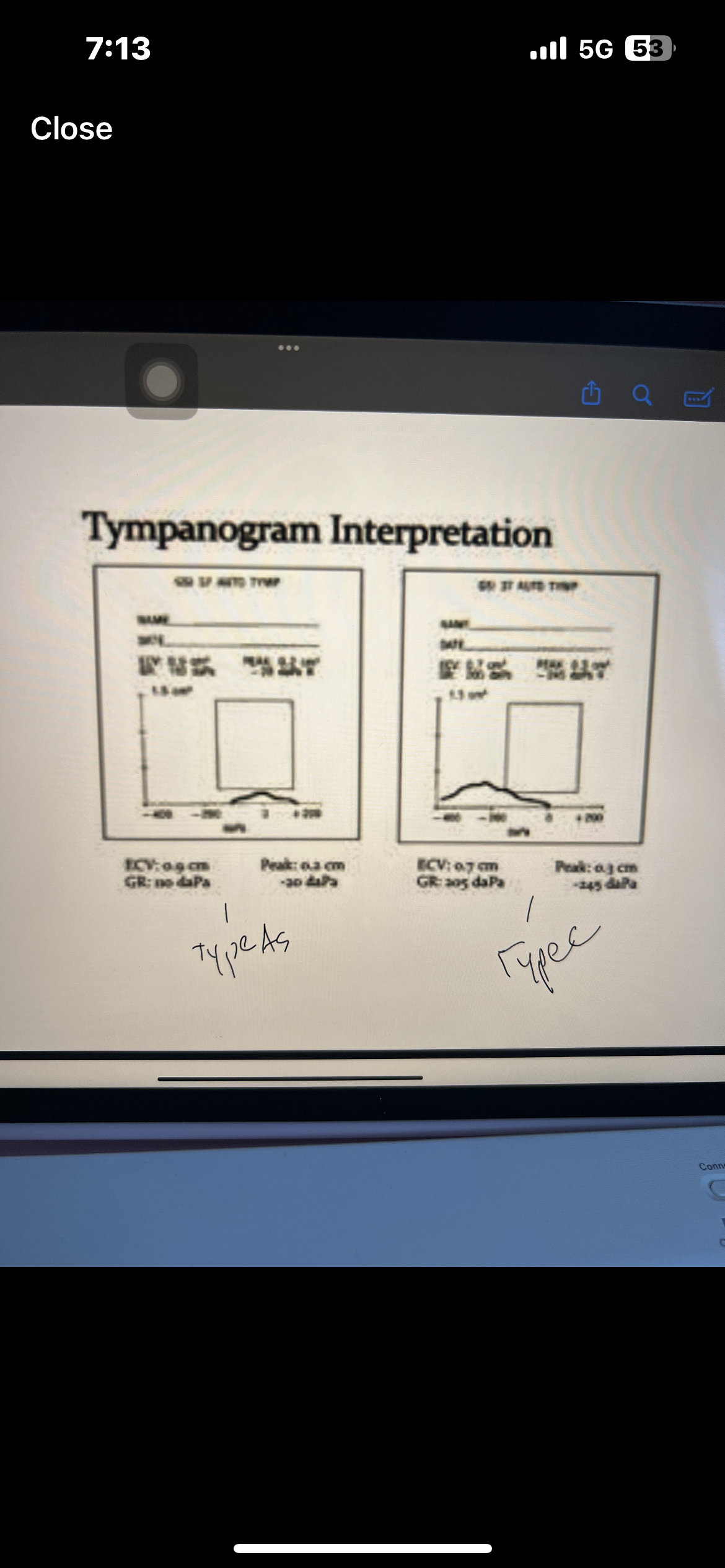
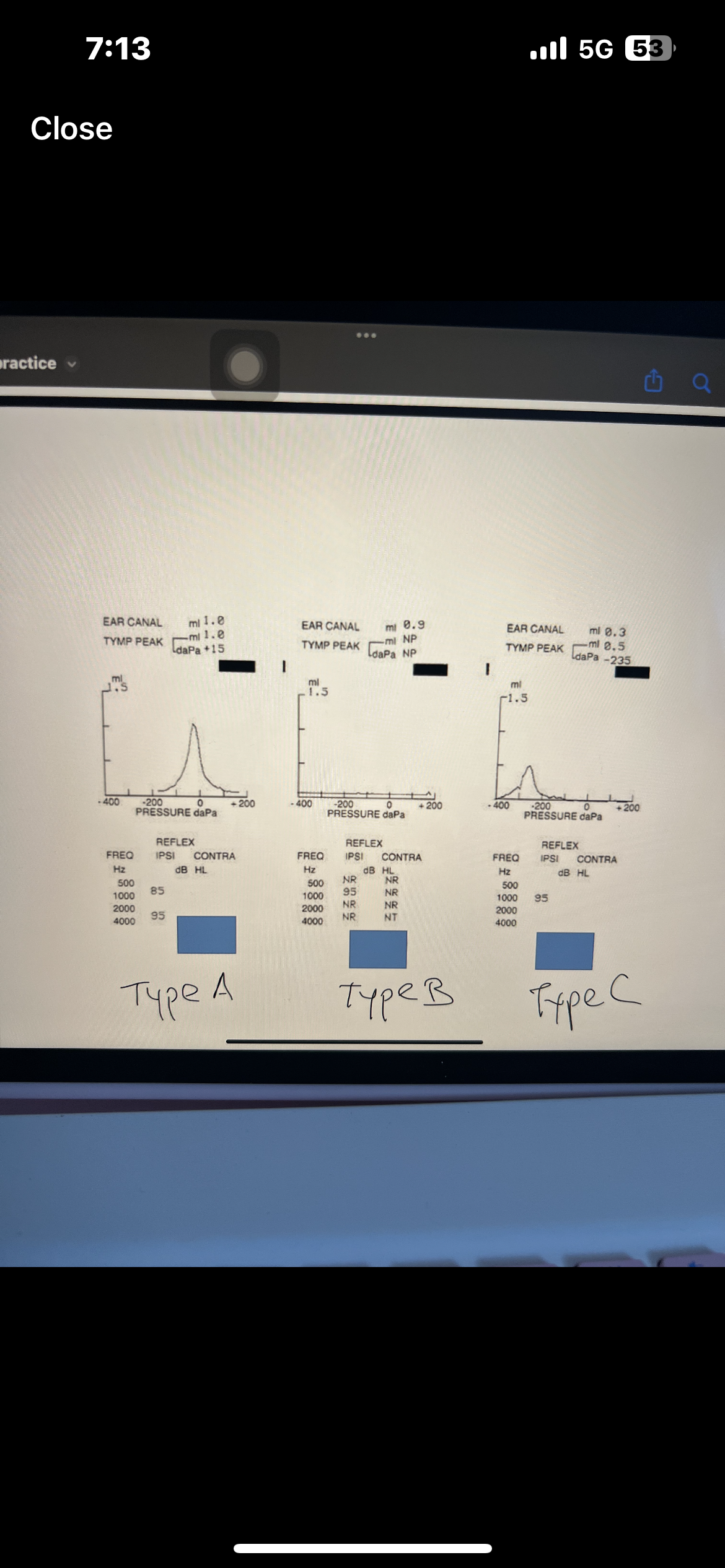
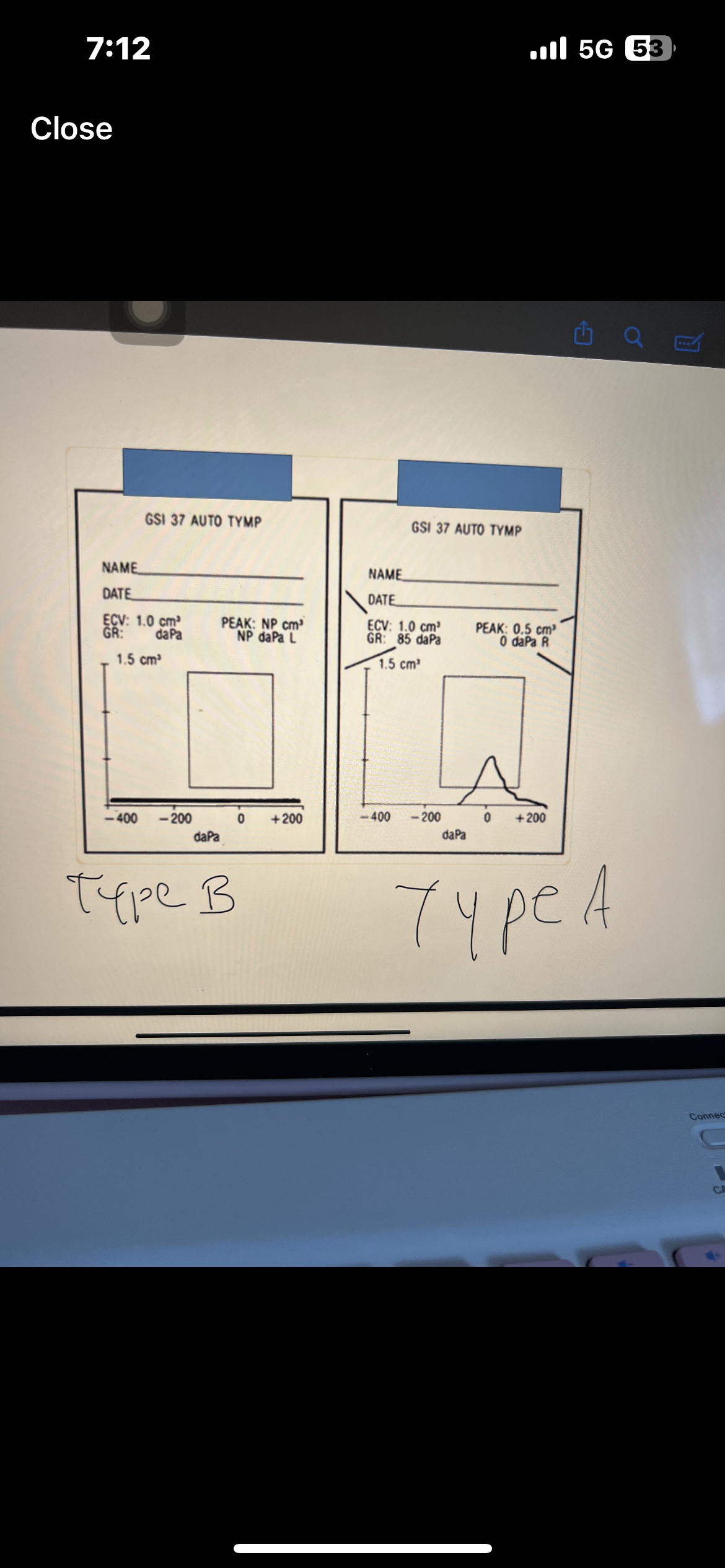
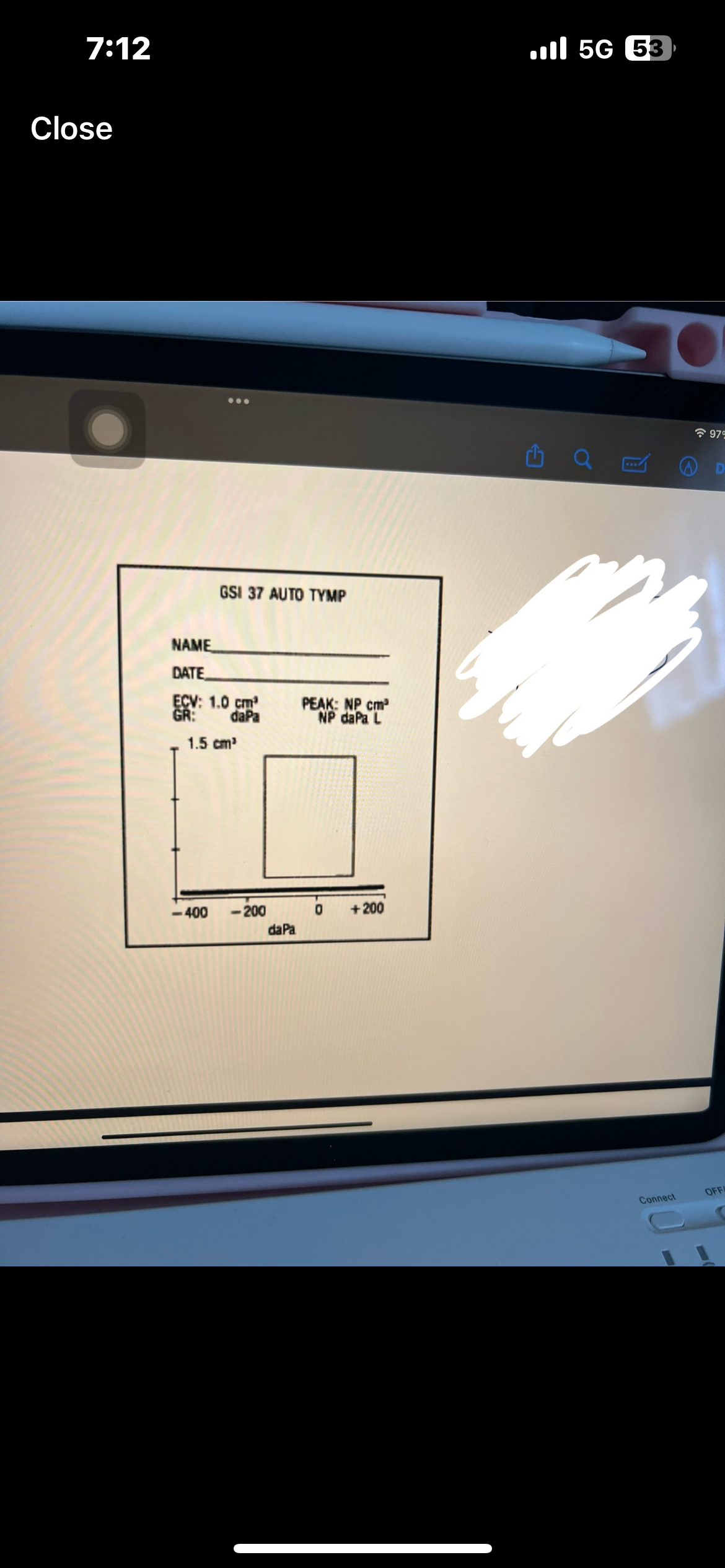
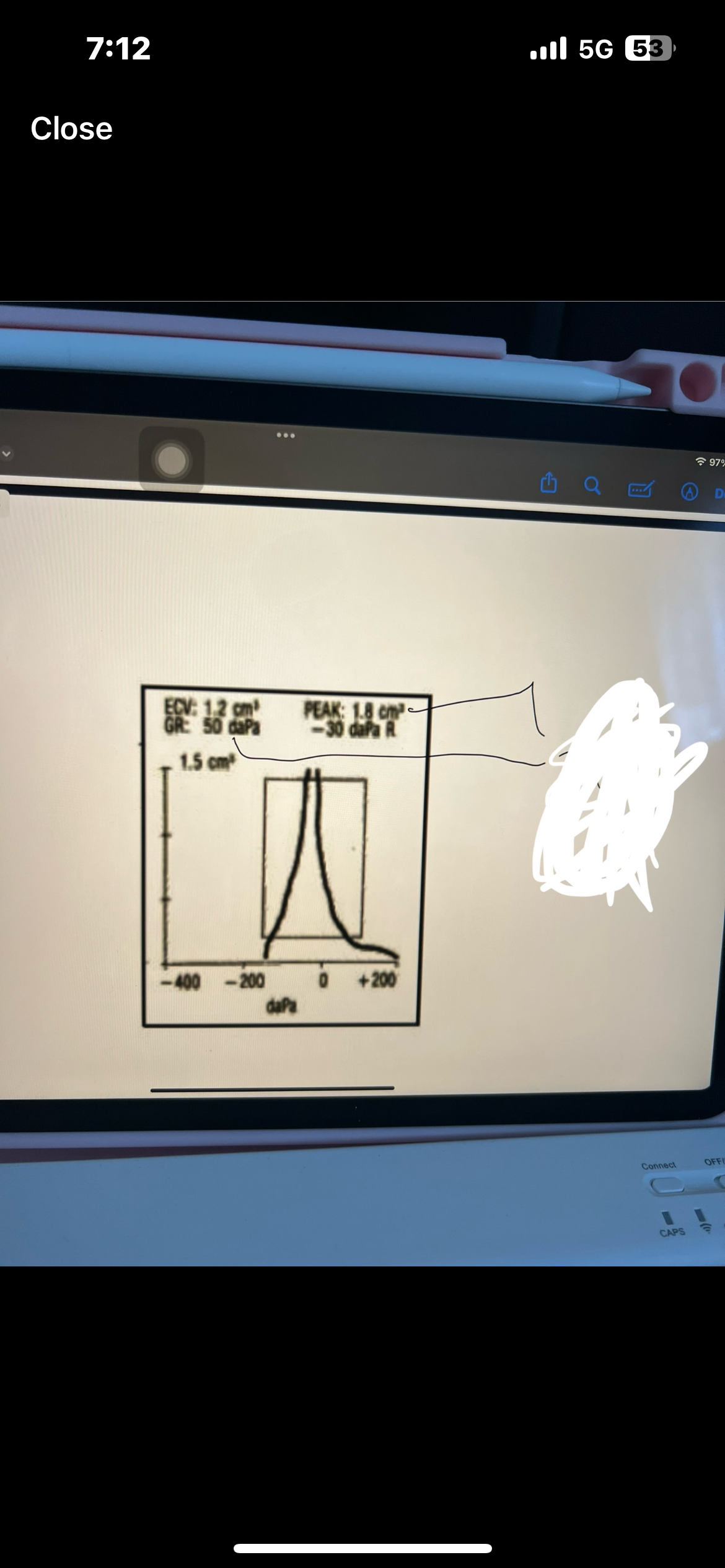
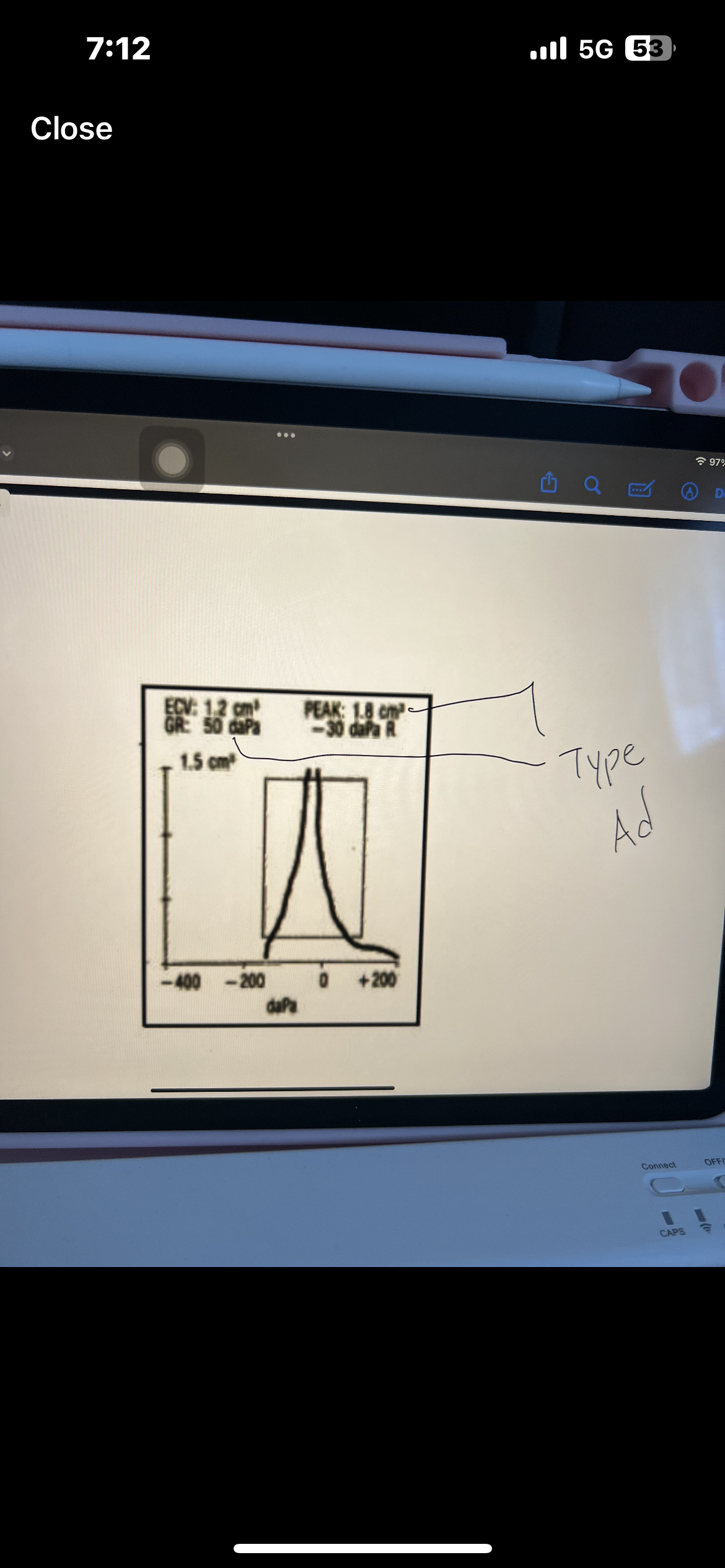
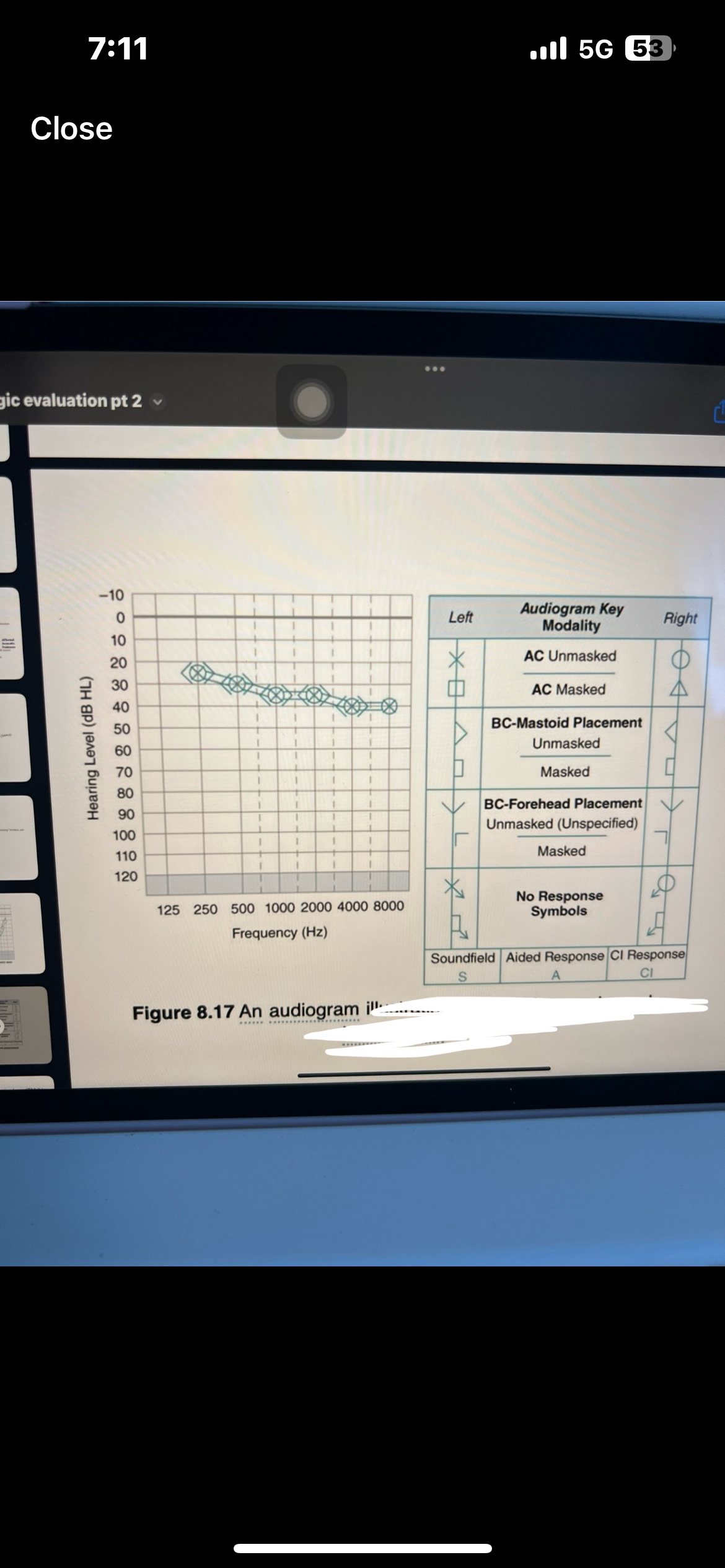
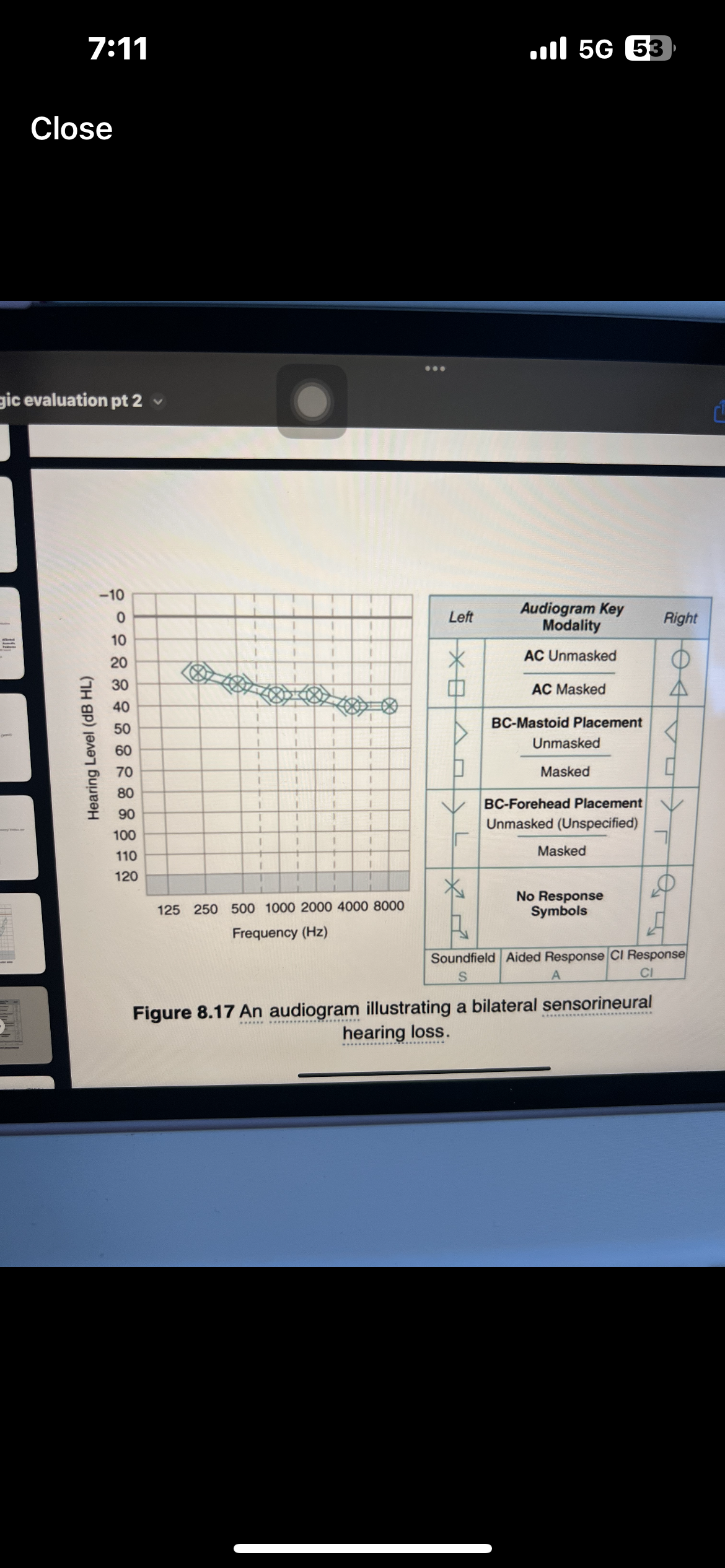
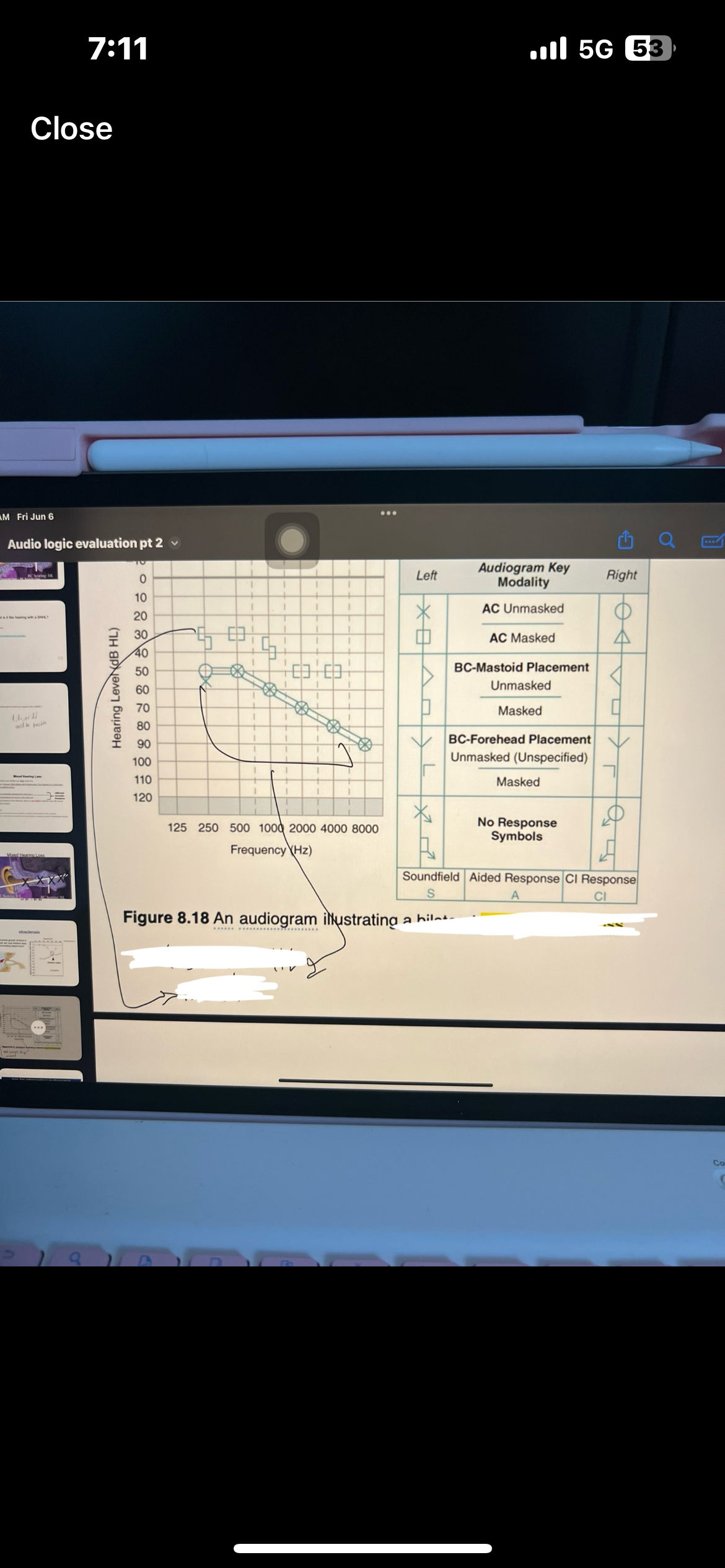
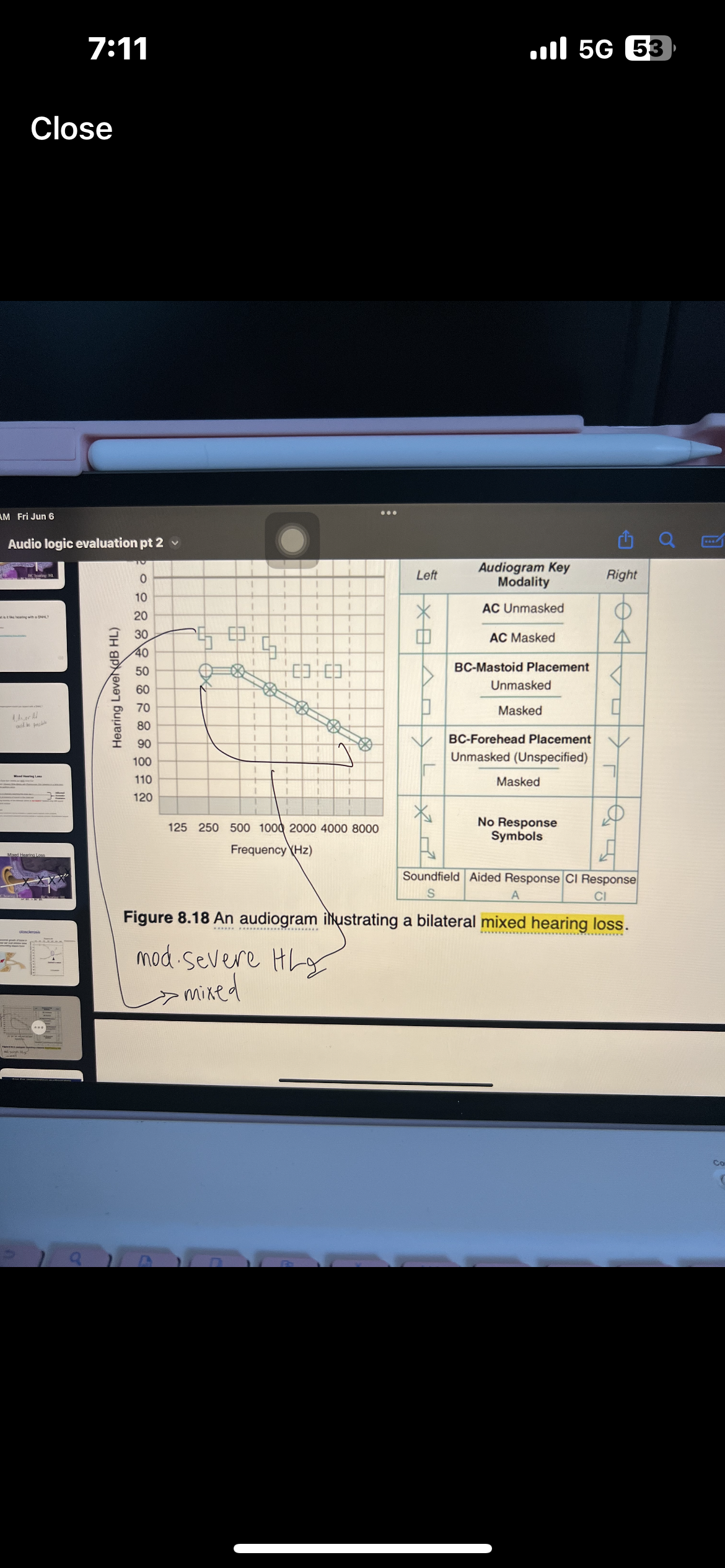
Pure tone interpretation
Use both AC and BC testing to make statement
Degree, configuration, type
Which ones are AC used for
AC is used for degree and configuration
Degree, configuration, type
Which ones are BC used for
BC is used for type
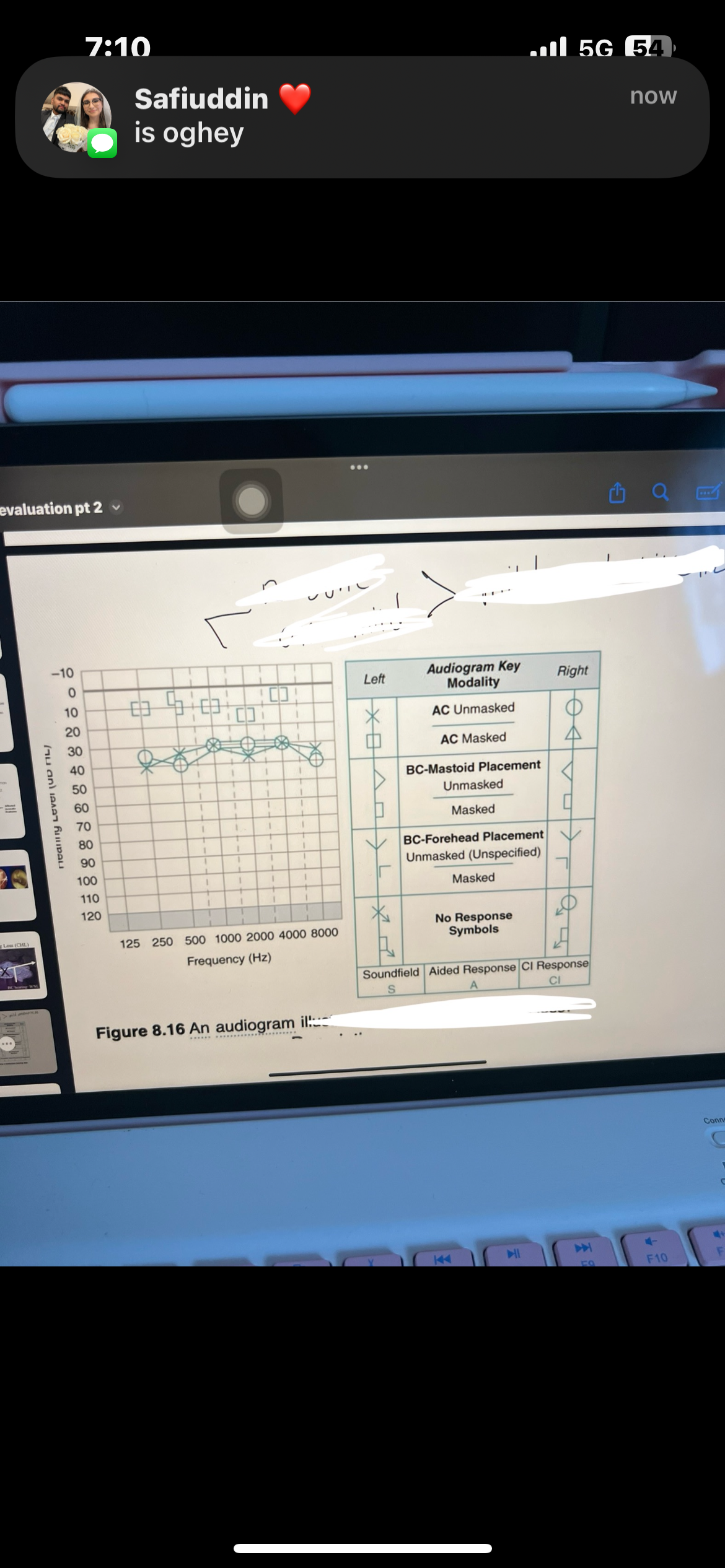
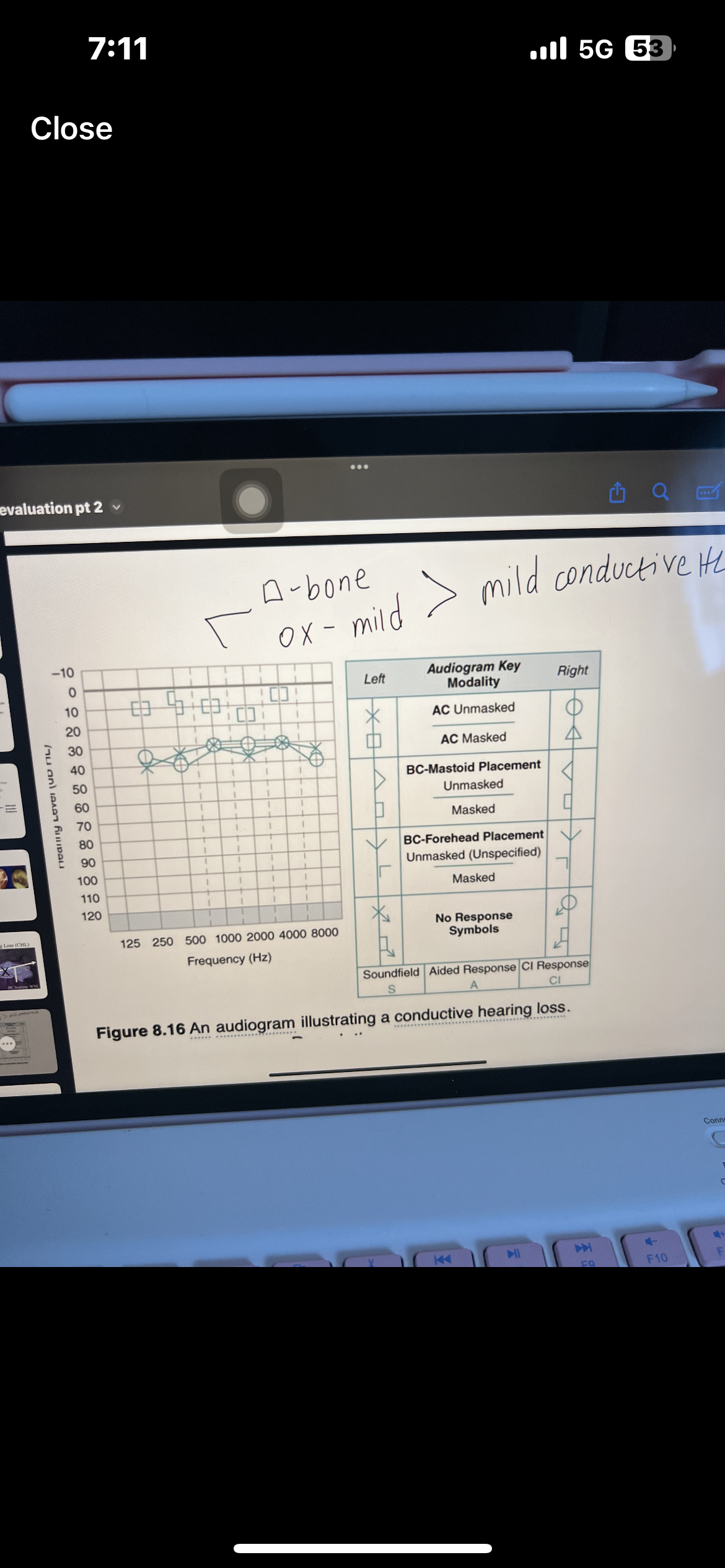
Purpose of masking vs unmasked
Masking BC reflects the cochlea of that specific ear, unmasked BC represents the better cochlea on which mastoid it was placed
If both masked and unmasked BC are on the Audiogram, which do you use for interpretation
Masked BC
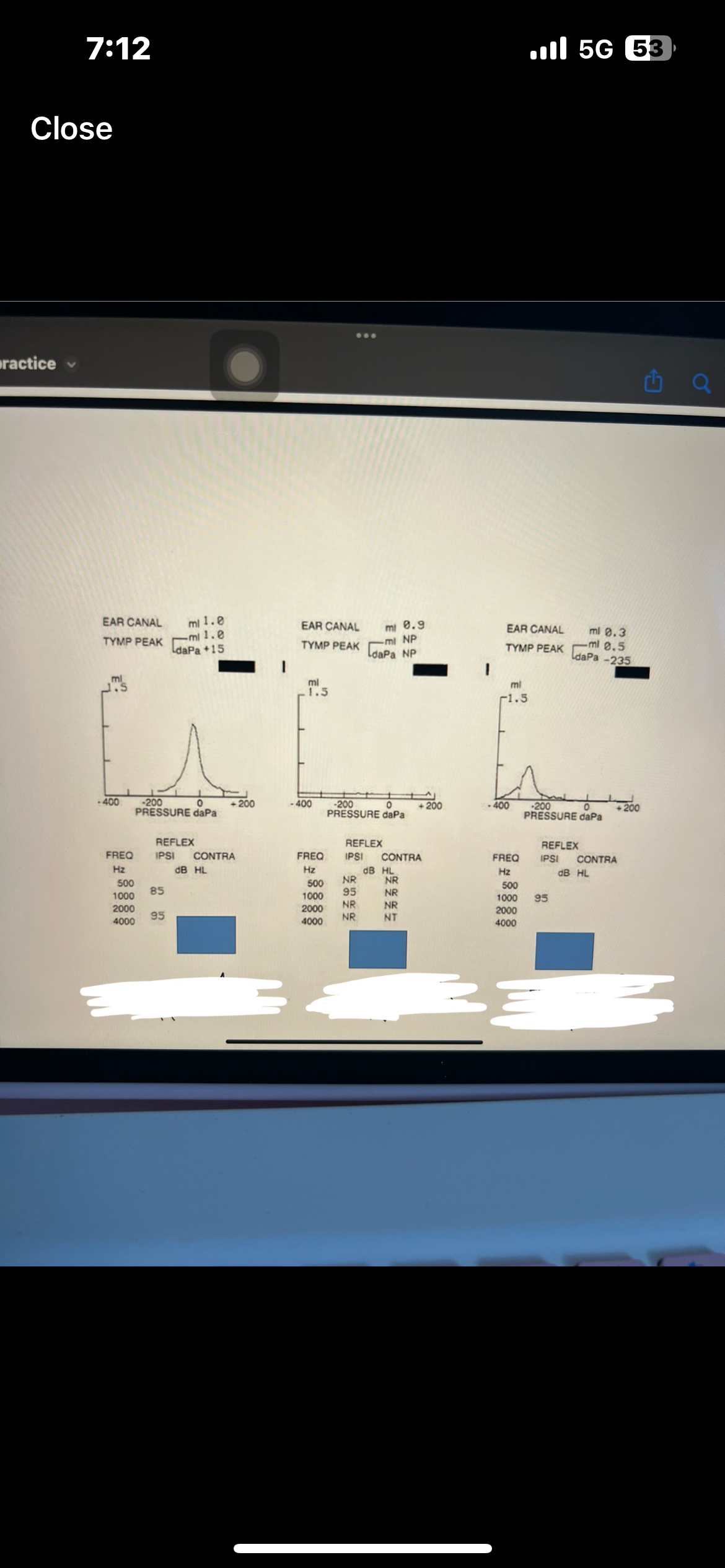
Speech recognition threshold SRT
Lowest level at which speech words are recognized on average
Speech recognition score SRS
Percent score of correctly heard words
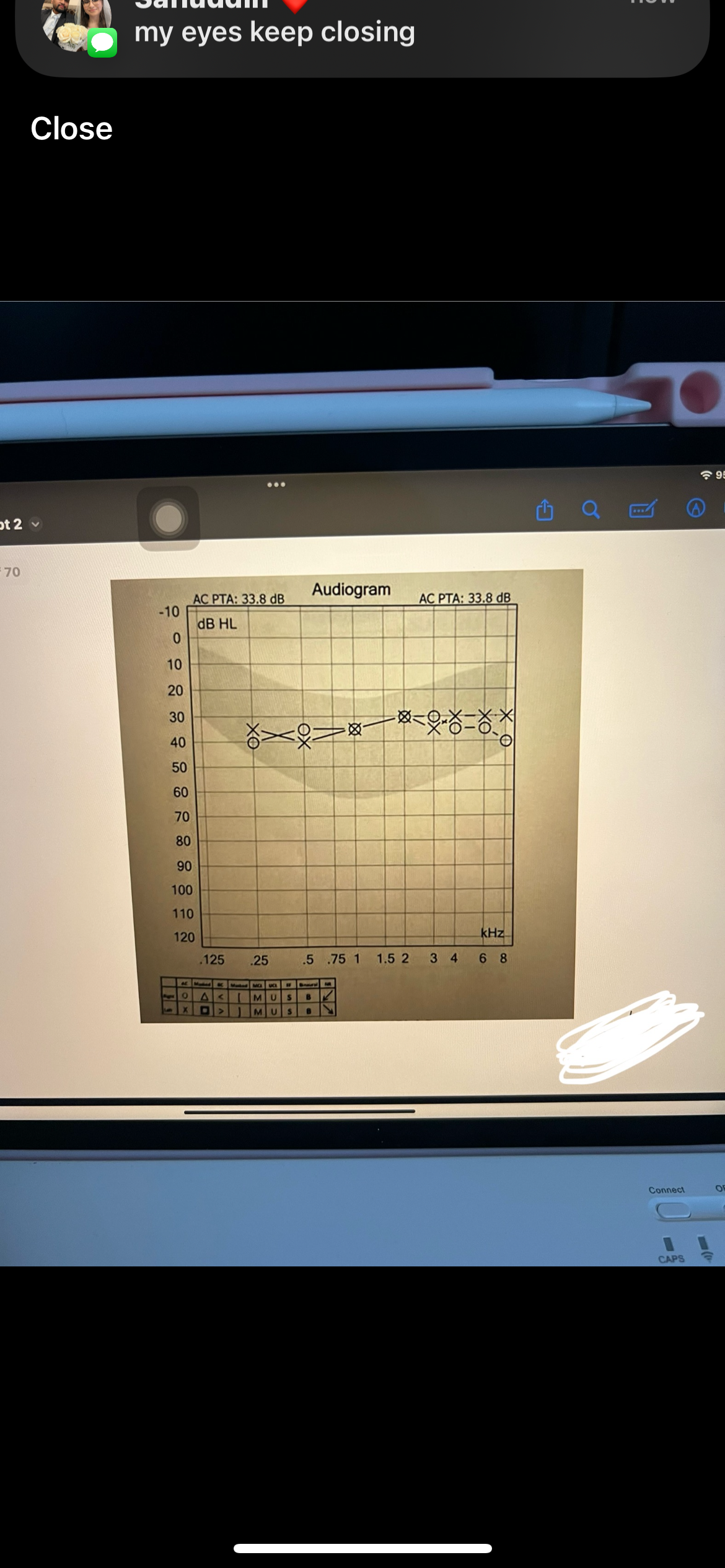
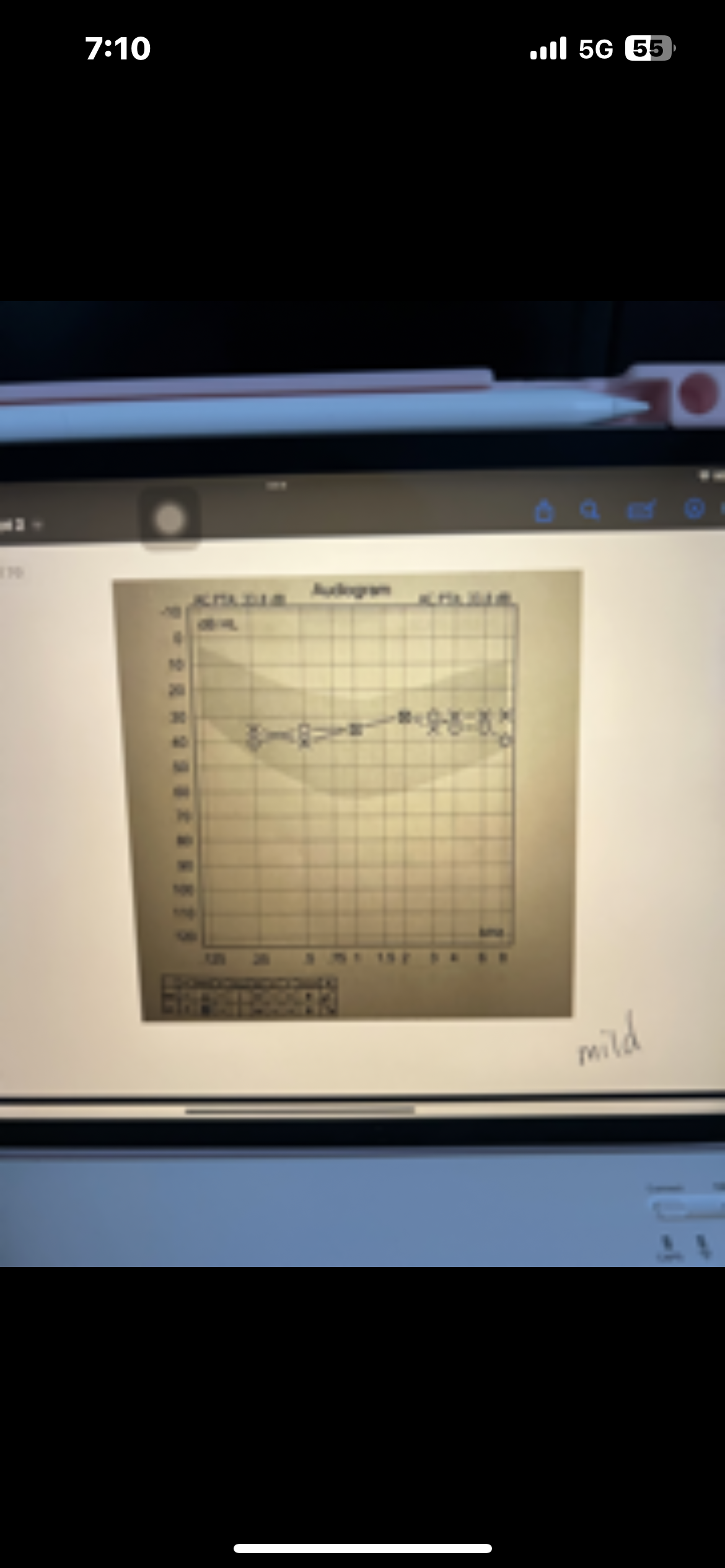
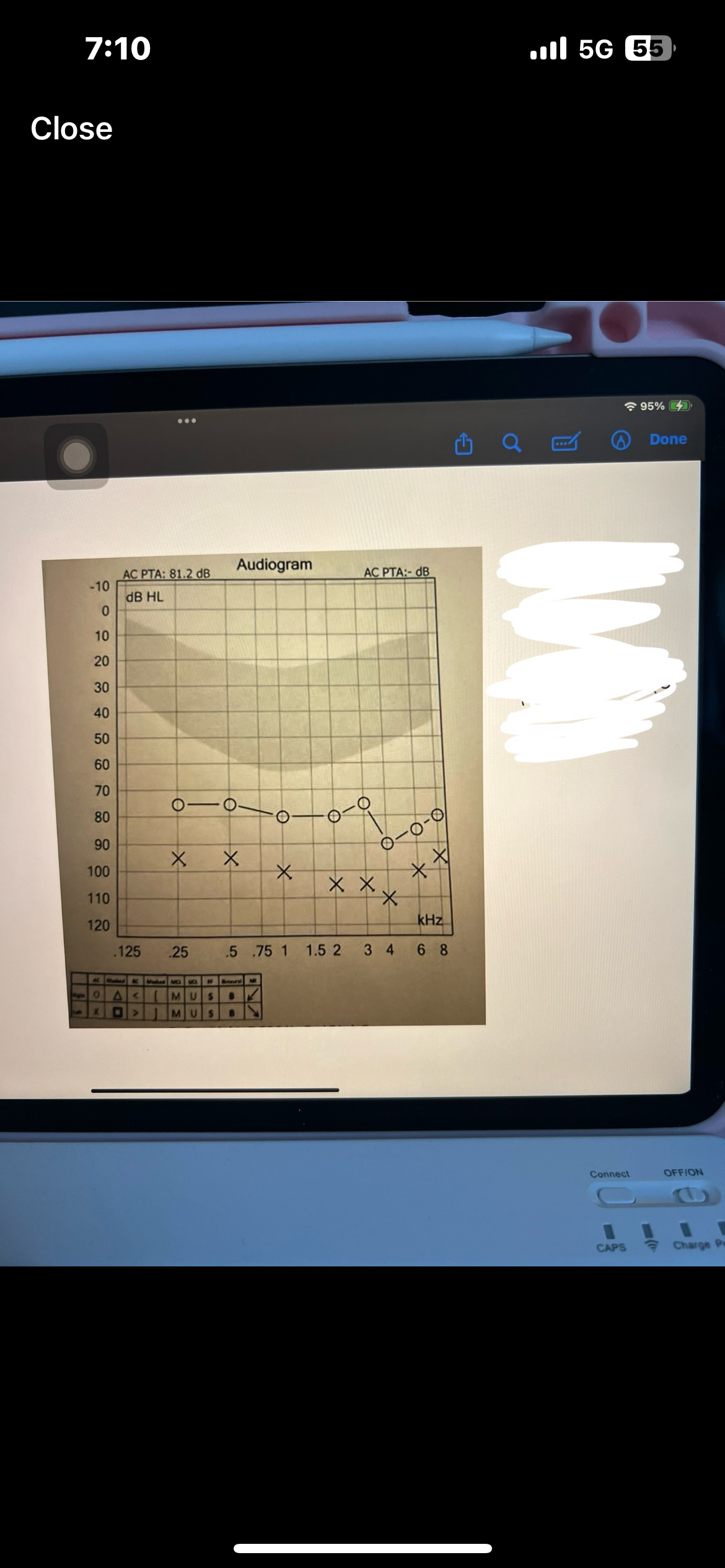
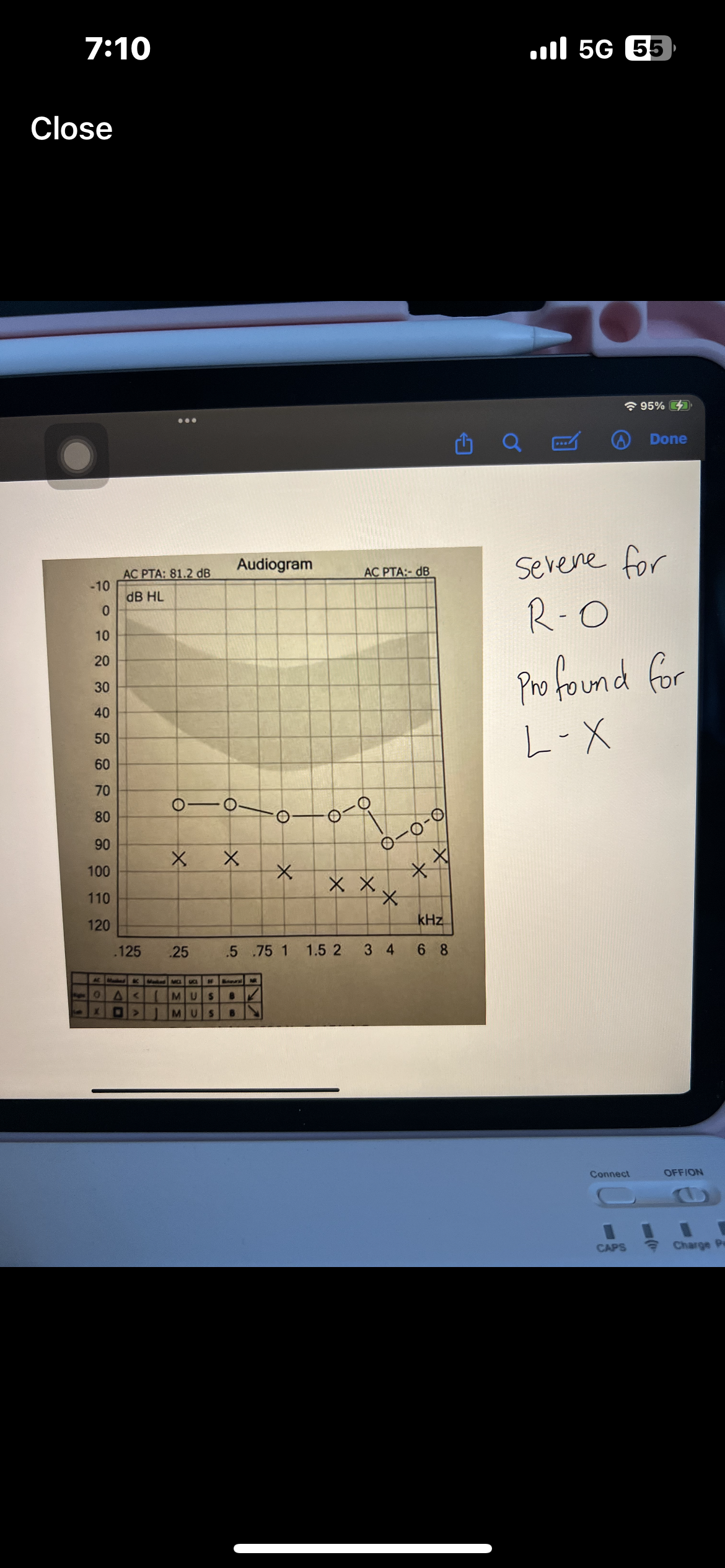
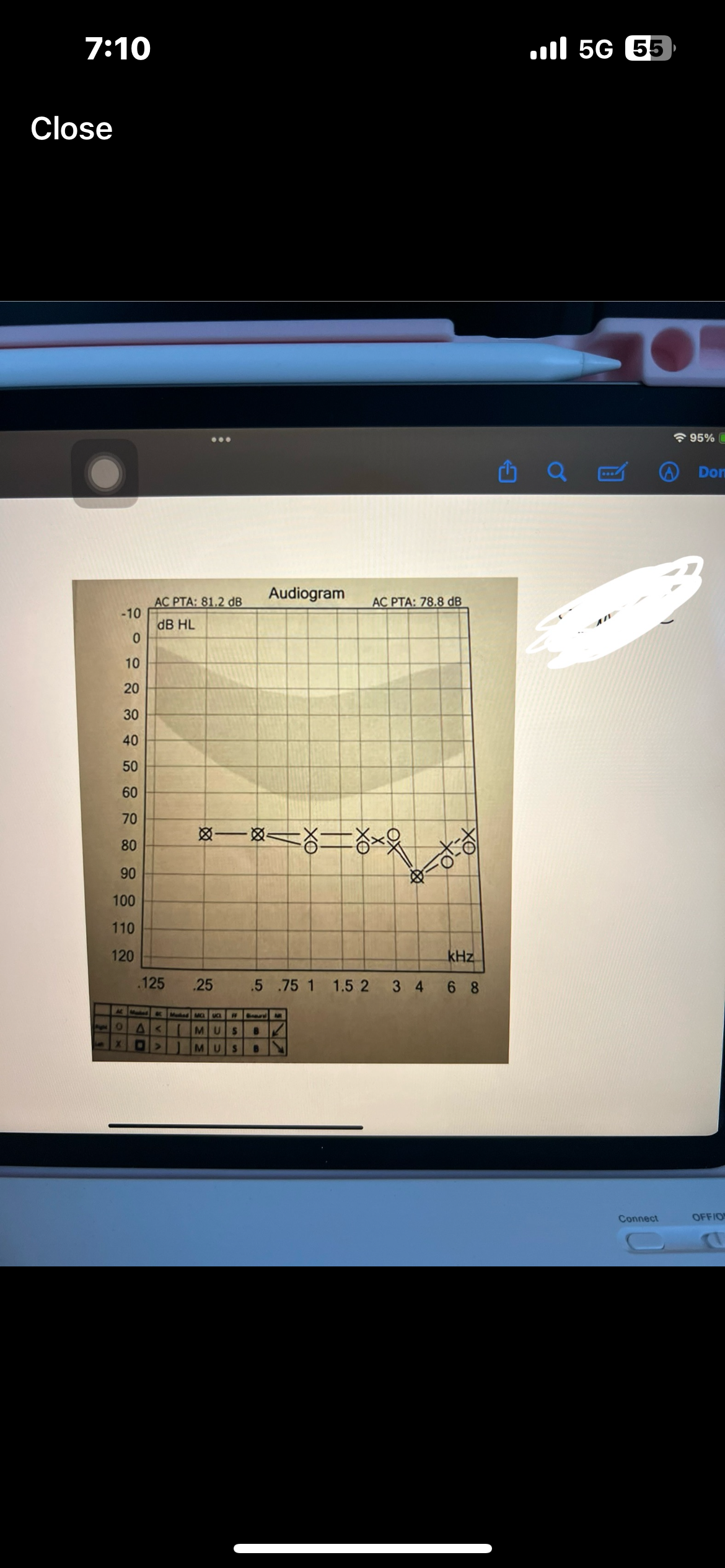
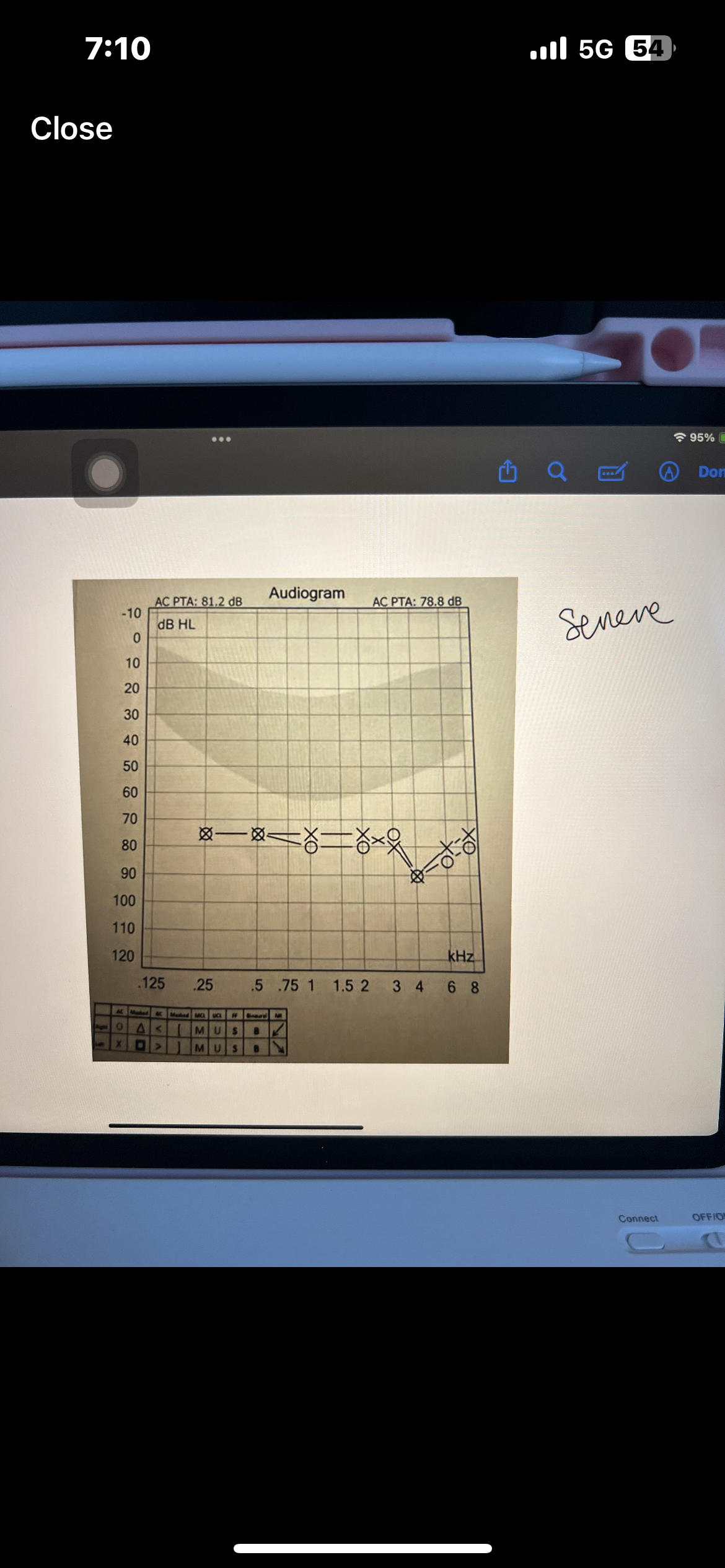
Pure tone average PTA
Average of 3 frequencies (500,1000,2000 Hz)
Ménière’s disease is caused by
Caused by overproduction of endolymph in the inner ear
Ménière’s disease characteristics
Fluctuating low frequency SNHL, vertigo, “roaring” tinnitus, ear fullness
Effects of hearing loss
communication, education, vocational and economic potential as they age into adulthood, social connections
Central auditory processing disorder CAPD
Impaired ability of the central auditory nervous system to manipulate and use acoustic signals. Difficulty interpreting or comprehending auditory information
HL impact on speech: low vs high frequency
May not use sounds like s, sh, f, t, or k due to HL at high frequencies. May not hear their own voice due to HL at low frequencies responsible for: vowel perception, quality of voice, prosody (rhythm/timing)
Conversational speech: ____ dB SPL at ____ Hz to _____ Hz
60 dB SPL at 1000Hz-8000Hz
Most energy for conversational speech
<1000 Hz
Auditory input is best accessed during the years of the greatest
Neural plasticity
Levels of auditory skill development
Detection
Discrimination
Identification
Comprehension
Listening and spoken language: 2 approaches
Auditory verbal approach
Aural/oral
Auditory-verbal approach (AVT)
Family center, evidence based approach for the development of listening, speech, and spoken language in infants and children who are hard of hearing.
Parent-professional partnership is developed: professional teaches parent how to teach their child to communicate using listening for spoken language development.
Nothing other than oral language should be used to stimulate child with HL
Aural/oral approach
Method to help children develop the spoken language and academic skills they need to be successful in a “regular” classroom and work and live in a predominantly hearing society.
Focuses on listening to speech and speaking
Primary mode of speaking should be through ears
Developing speech naturally, speech reading and gestures are normal
3 types of manual communication
ASL
Bilingual-bicultural
Manually coded English
American Sign Language ASL
Visual-spatial language used by deaf/Deaf people in US
Has own grammar, syntax
Uses space, direction, speed of movement, facial expressions to convey meaning
Rule bound
No spoken or written form
Bilingual-bicultural
ASL taught as first language (bilingual)
Information about Deaf life and culture is addressed (bicultural)
Manually coded English (MCE)
Uses some combination of ASL signs, special vocab, and English grammar to visually communicate
Used in educational settings to bridge between sign and English
Speech reading
Person attempts to both the auditory and visual signals, facial expressions, gestures, and cues
EHDI
Public health initiative for UNHS funded by both state and federal
Enrollment in EI
Family support services
All infants should be screened by _____, diagnosed by ____, and those w confirmed HL should receive intervention no later than _____
Screened by 1 month
Diagnosed by 3 months
And receive intervention no later than 6 months
JCIH
Aspires to meet new 1-2-3 timeline
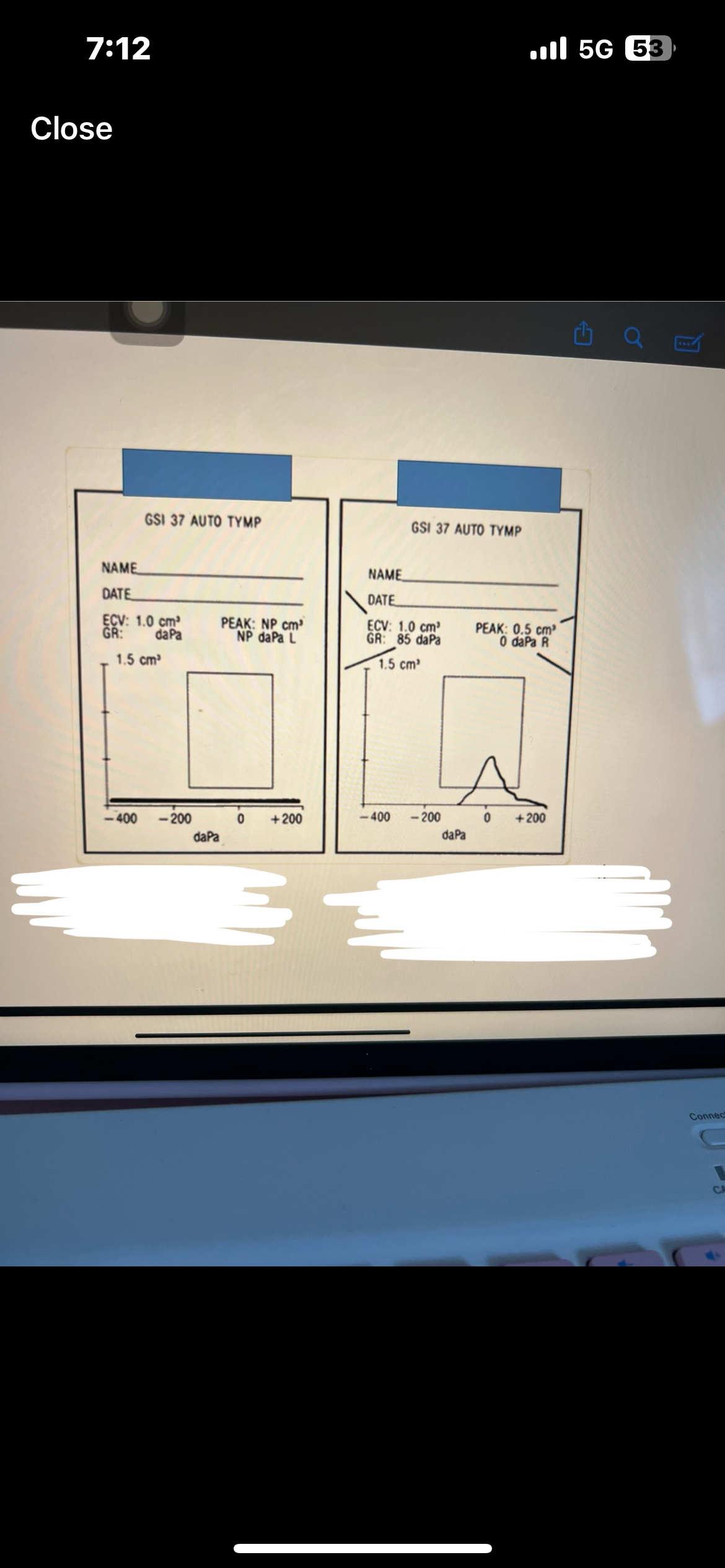
Frequency specific ABR (air and bone)
Click evoked ABR w both rarefaction and condensation
OAE screening
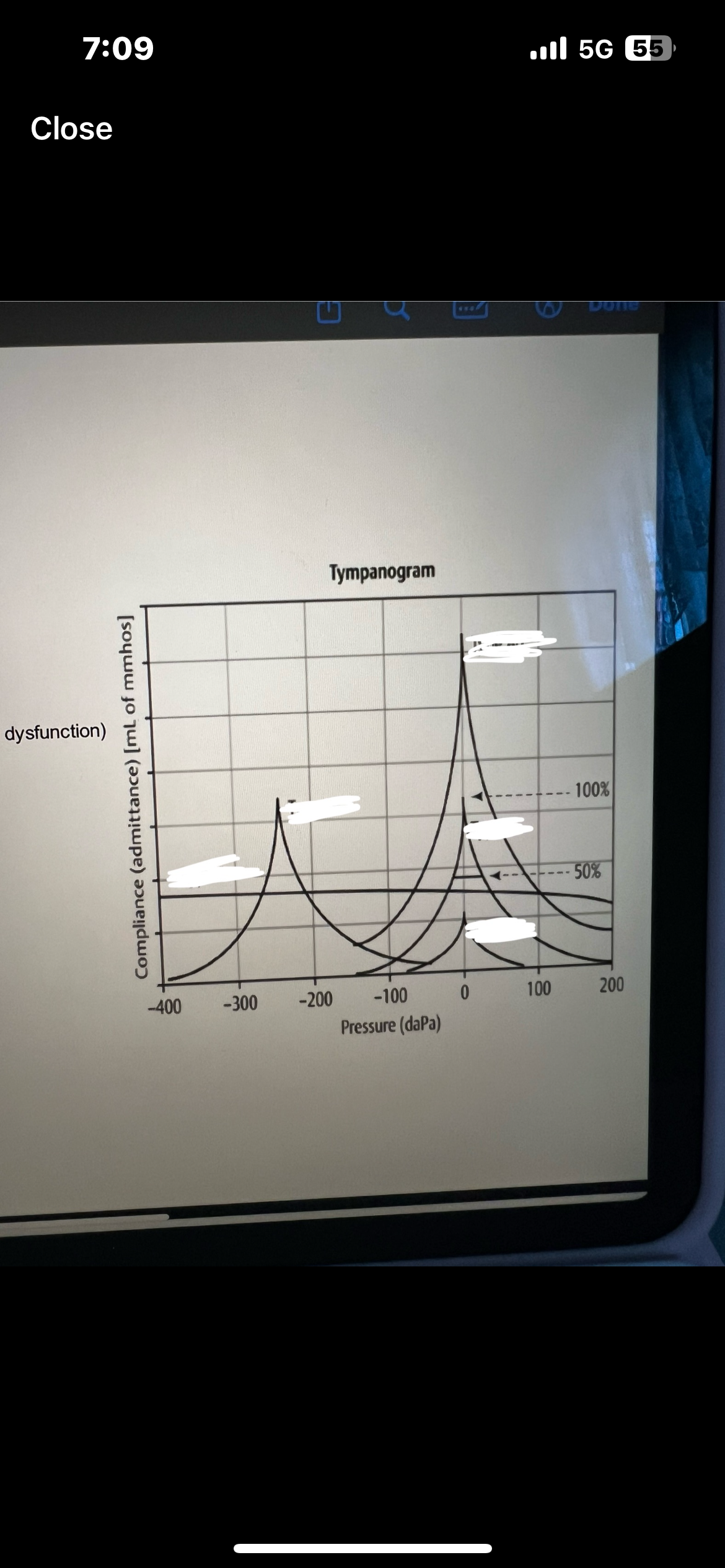
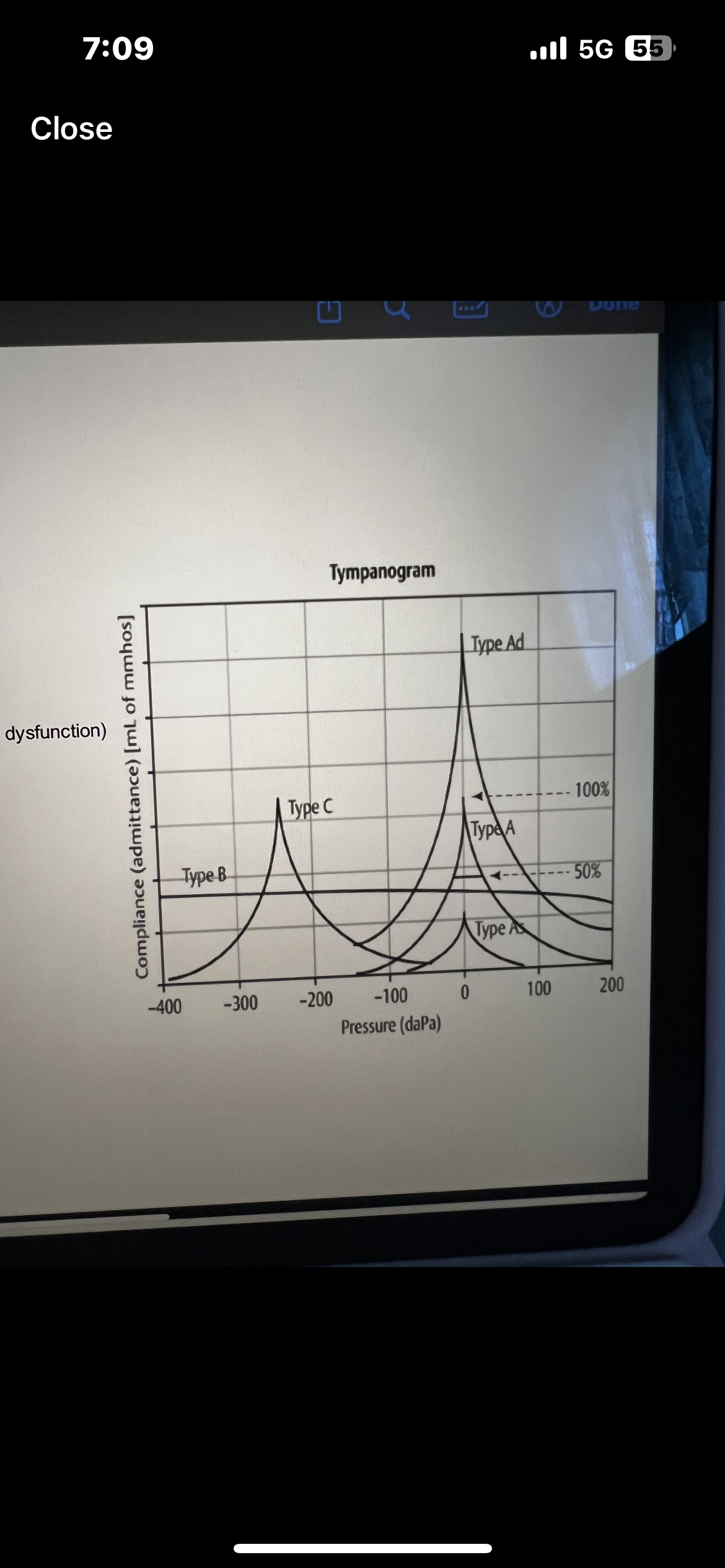
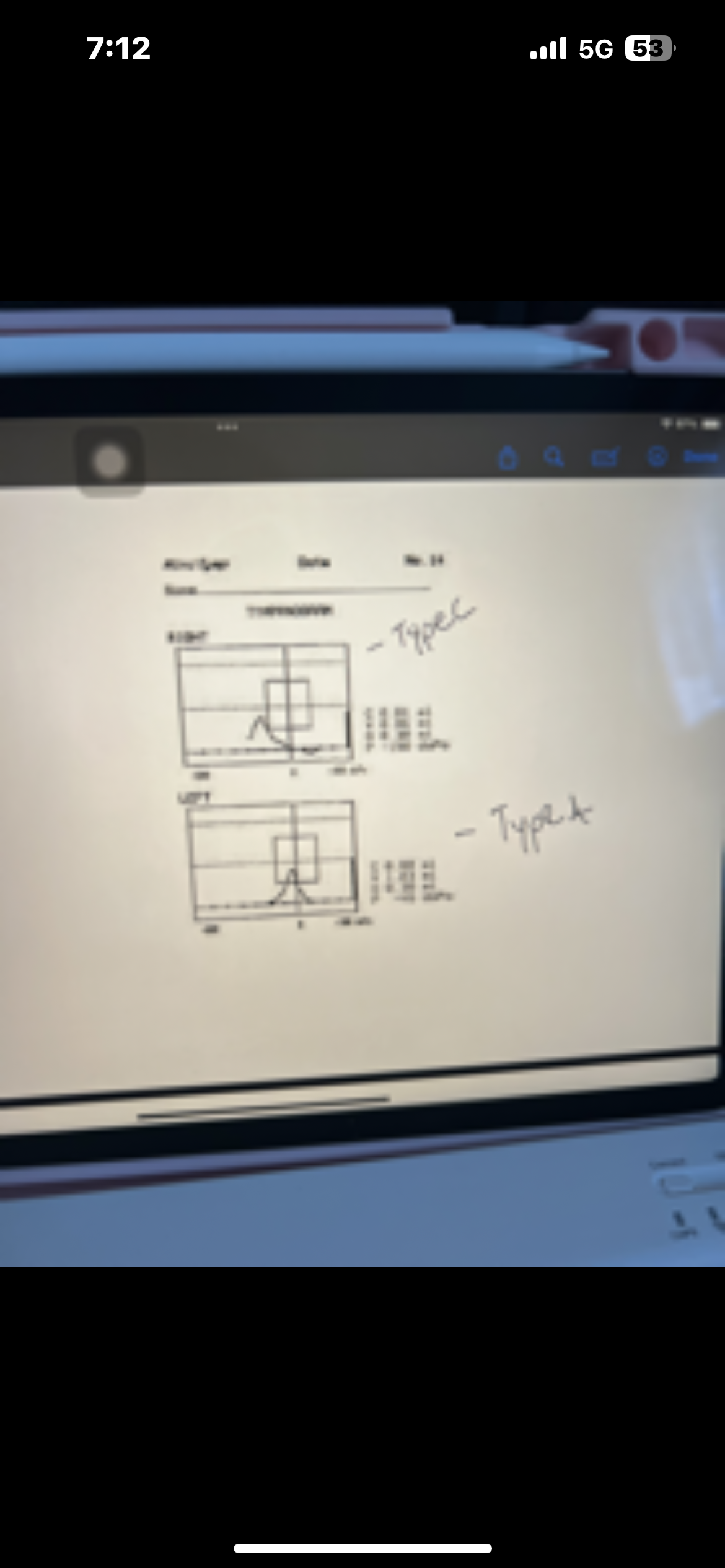
High frequency tympanometry 1000Hz
Individuals w disabilities education act IDEA
Federal initiative to provide early intervention and free and appropriate public education FAPE to all children w developmental/health impairments
Part A- lays foundations and rules/guidelines
Part B- children ages 3-21
Part C- birth to 3
Part D- national support programs administered at federal level
Components of hearing aid
Microphone
Amplifier
Receiver
Battery
Electroacoustic characteristics of hearing aid
Gain - amount of amplification
Frequency response - amount of gain across frequency range of HA
Output sound pressure level - max. output level of HA
Linear sound processing - equal dB increase for all incoming sounds
Non linear sound processing - amount of gain is dependent on intensity of incoming sound (most commonly used)
Styles of hearing aids
BTE, mini BTE, receiver in canal RIC, in the ear ITE, digital hearing aids
Fitting formulas for children
DSL v5
What causes feedback in HA
Volume is too high, earmold not sitting properly/too small, tubing cracked, ITE casing cracked
Ling 6 sound test
Quick listening check that uses 6 speech sounds (m, a, oo, ee, sh, s) to assess if a child w HL can detect sounds across the frequency range
Verification HA
Objective process to ensure HA is programmed correctly for user’s specific HL
Validation HA
Subjective experience and benefits from HA
Questionnaires, interviews, real world performance
Cochlear implants
Surgically implanted device that enhances hearing and speech abilities for individuals w severe to profound HL who demonstrate limited benefit from HA
Bone conduction HA BAHA
For conductive or mixed HL
Greater than 5 yo
Bypasses outer and middle ear
Can be used for unilateral HL
Deaf w capital D
Cultural identity within Deaf community
Own language ASL
Shared values
Pride in Deaf identity
Many prefer not to use amplification
deaf lowercase d
Term that refers to individuals w little to no hearing
May or may not use sign language
More likely to use HAs or CIs