theory: vascular sonography lll
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
132 Terms
Which of the following is the first major branch of the aortic arch?
Brachiocephalic artery
Where is the Inferior Vena Cava (IVC) formed?
By the union of common iliac veins at L5
What anatomical structure does the IVC pierce to enter the thoracic cavity
Diaphragm’s central tendon
Which organ serves as an acoustic window to visualize the intrahepatic portion of the IVC?
Liver
Which vein drains directly into the IVC and not through the renal vein?
Right gonadal vein
What sonographic feature characterizes acute IVC thrombosis?
Anechoic or hypoechoic lumen material
What maneuver can cause the IVC to temporarily collapse during ultrasound evaluation
Valsalva
What is the maximum normal diameter of the IVC?
2.5cm
What is the most common origin of emboli that travel to the pulmonary system?
Deep vein thrombosis in lower extremities
Which imaging plane best visualizes the complete IVC course?
Sagittal
What is a Greenfield filter used for
Trapping emboli in the IVC
What structure does the abdominal aorta bifurcate into?
Common iliac arteries
Which branch of the abdominal aorta supplies the liver, stomach, and spleen?
Celiac trunk
The aortic arch gives rise to how many major arteries?
3
Which segment of the aorta is located between the diaphragm and the iliac bifurcation?
Abdominal aorta
The renal arteries typically arise from which portion of the aorta?
Abdominal aorta
Which of the following best describes the sonographic appearance of the aorta?
Anechoic with echogenic walls
What is the clinical significance of identifying aortic branches during sonographic evaluation?
To access stenosis or aneurysm
Which artery arises from the aorta just inferior to the origin of the celiac trunk?
Superior mesenteric artery
The descending thoracic aorta is located:
Between the diaphragm and aortic arch
Which of the following is the most common location for an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA)?
Infrarenal aorta
An aortic aneurysm is diagnosed when the aortic diameter exceeds:
3.0cm
What type of aneurysm involves all three layers of the arterial wall?
True aneurysm
Which of the following is a classic risk factor for the development of aortic aneurysms?
Smoking
Which pathology involves a tear in the intimal lining of the aorta?
Aortic dissectio
A pulsatile abdominal mass is a common clinical finding in:
Abdominal aortic aneurysm
Which sonographic sign is associated with an aortic dissection?
Íntimal flap
What measurement technique is used for AAA in ultrasound
Outer to outer wall
Which of the following complications is most life-threatening in AAA?
Rupture
Endovascular Aortic Repair (EVAR) is primarily used to treat:
Aortic aneurysm
Which segment of the aorta is typically evaluated during an abdominal ultrasound
Abdominal aorta
What patient preparation is required for optimal abdominal aortic imaging?
Nothing by mouth NPO for 6-8 hours
.What is the normal upper limit for the abdominal aorta diameter
3.0 cm
Which transducer is typically used for abdominal aortic ultrasound?
Curvilinear 2–5 MHZ
Which branch of the aorta is the first major unpaired branch?
Celiac trunk
An abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is diagnosed when the aorta measures:
>3.0 cm
What is the most common shape of an aortic aneurysm?
Fusiform (both sides )
A sonographic finding of an intimal flap within the aorta is indicative of:
Dissection
In transverse imaging, the aorta is typically located:
Left of the spine
Why is it important to measure the aorta in both long and transverse views?
To ensure accurate diameter assessment
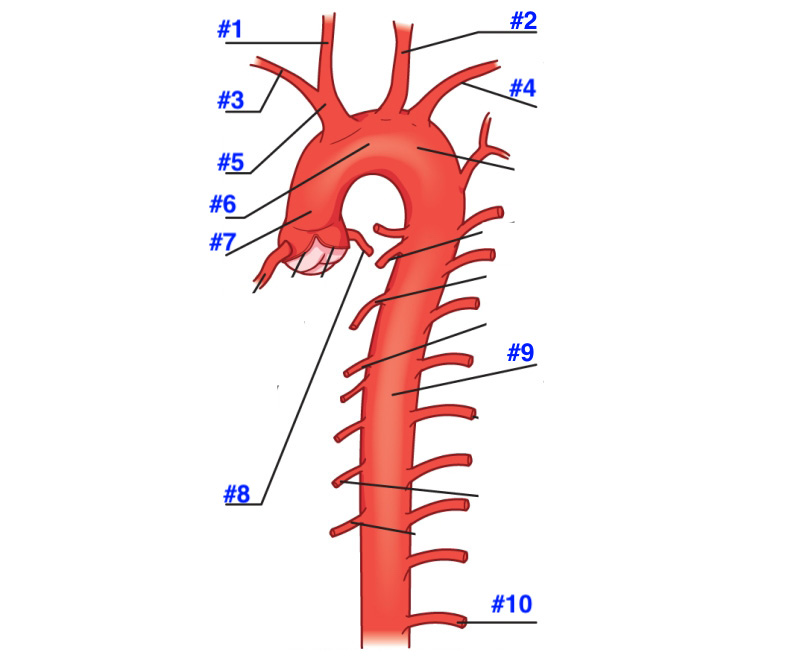
1- right common carotid artery
2-left common carotid artery
3-right subclavian artery
4-left subclavian artery
5-brachiocephalic branch
6-aortic arch
7-ascending aorta
8-left coronary artery
9-descending aorta
10- subcostal artery
When performing a median arcuate study, the Doppler waveforms are obtained from
above the origin of the celiac axis
Doppler waveforms in the abdomen should be obtained at an angle of ______________________.
Less than 60 degrees
To calculate the resistive index the Doppler waveform is measured at peak systole and ___________________.
End diastolic
An example of a low-resistance signal is the ___________________.
Renal artery
Which control needs to be adjusted to measure the velocity of the blood flow?
Angle correction
Where is the Inferior Vena Cava (IVC) formed?
By the union of common iliac veins at L5
What anatomical structure does the IVC pierce to enter the thoracic cavity?
Diaphragm’s central tendon
Which organ serves as an acoustic window to visualize the intrahepatic portion of the IVC?
Liver
Which vein drains directly into the IVC and not through the renal vein?
Right gonadal vein
What sonographic feature characterizes acute IVC thrombosis?
Anechoic or hypoechoic lumen material
What maneuver can cause the IVC to temporarily collapse during ultrasound evaluation?
Valsalva
What is the maximum normal diameter of the IVC?
2.5cm
What is the most common origin of emboli that travel to the pulmonary system?
Deep vein thrombosis in lower extremities
Which imaging plane best visualizes the complete IVC course?
Sagittal
What is a Greenfield filter used for?
Trapping emboli in the IVC
What two veins unite to form the main portal vein?
Splenic vein and superior mesenteric vein
Where does the main portal vein enter the liver?
At the porta hepatitis
What is the normal flow direction of the portal vein?
Hepatopedal
The echogenic walls of the portal vein on ultrasound are due to:
Connective tissue sheath of the portal triad
What is the normal diameter of the portal vein?
Less than 13 mm
Which vessel courses posterior to the pancreatic body and tail?
Splenic vein
Which Doppler finding is most indicative of portal hypertension?
Loss of respiratory variation
What structure is involved in cavernous transformation of the portal vein?
Multiple periportal collaterals
Which vein drains the left third of the colon and ascends retroperitoneally?
Inferior mesenteric vein
The most common site of spontaneous portosystemic shunting is:
Gastroesophageal region
Which of the following is the most common cause of kidney transplant?
Diabetes mellitus
Where are most kidney transplants placed?
Extraperitoneally in the right iliac fossa
What is the primary modality used for initial screening of suspected vascular complications in transplant patients
Ultrasound
What is a normal resistive index (RI) in a transplanted kidne
<0.7
Which of the following is a common postoperative fluid collection following a kidney transplant?
Hematoma
When does acute transplant rejection typically occur?
About 2 weeks post op
Portal vein stenosis following liver transplant most commonly occurs at the
Anastomotic site
Which of the following is a sonographic finding of hepatic artery thrombosis?
Absence of flow
What is the normal direction of flow in the portal vein
Hepatopetal
What is the most common cause of liver transplant dysfunction?
Rejection
The aorta continues to flow in the _____________________ cavity anterior and slightly left of the vertebral column.
Retro peritoneal
Capillaries definition
Minute vessels that connect the arterial and venous systems
Tunica Íntima define
Inner layer of the vascular system
Tunica media define
Middle layer of the vascular system
Anastomosis define
Communication between two blood vessels without any intervening capillary network.
Vasa vasorum define
Tiny arteries and veins that supply walls of the blood vessels
Túnica adventitia define
Outer layer of the vascular system
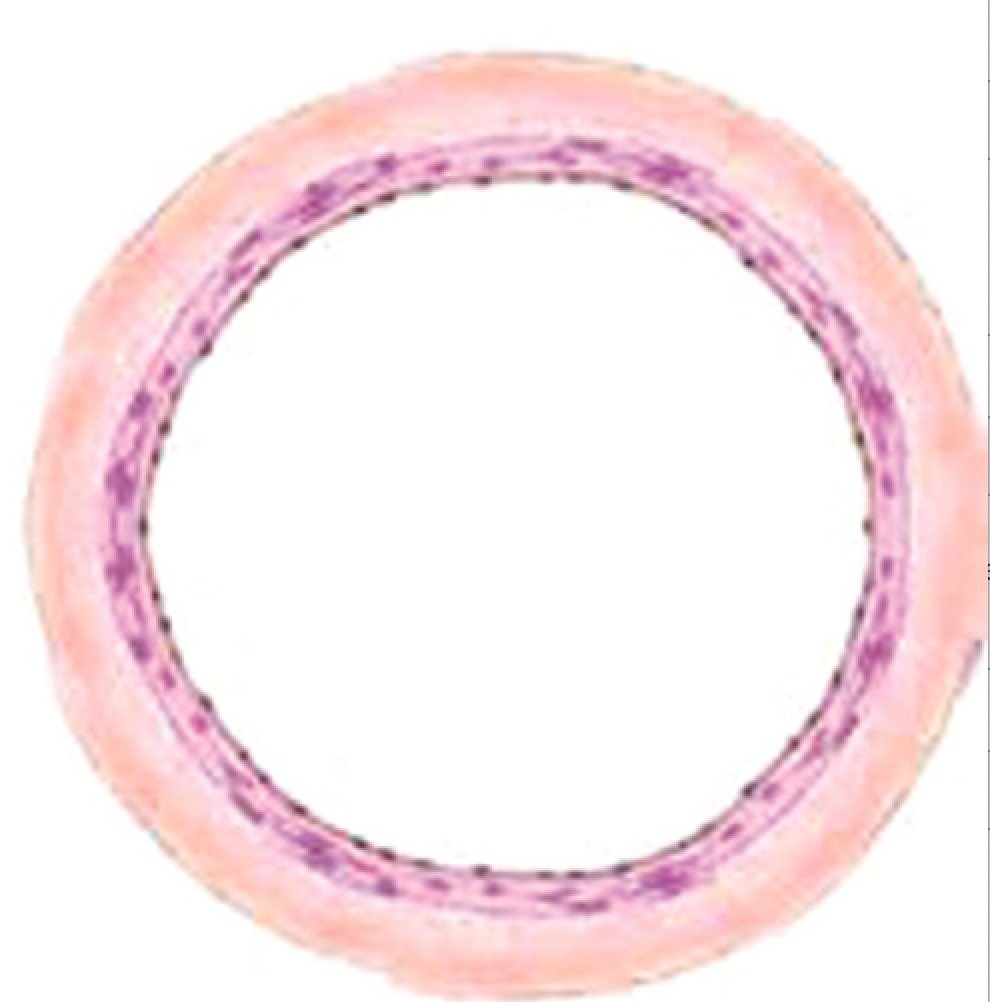
Vein
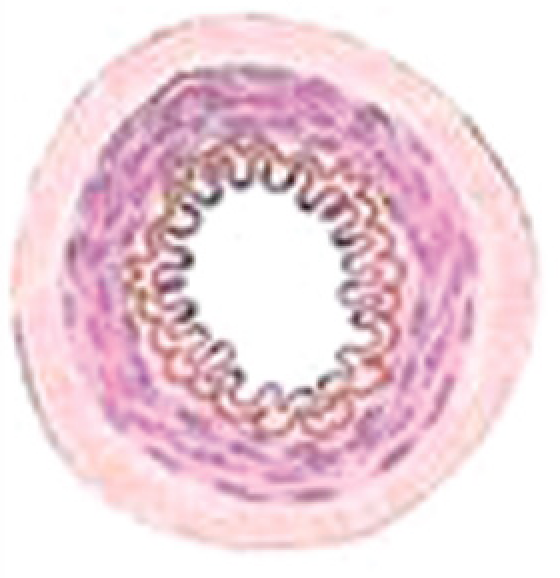
Artery
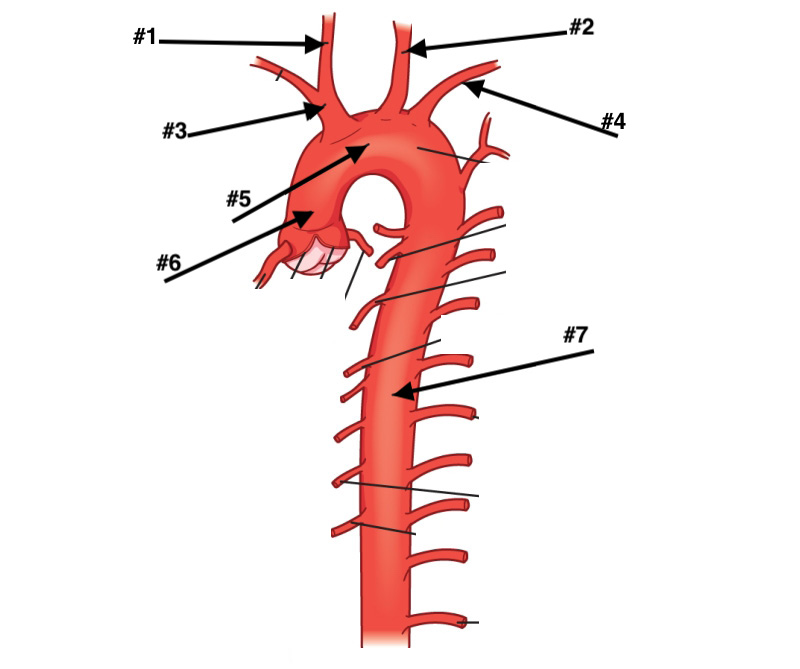
#1 ,2,3,4,,5,6,7
R common carotid, L common carotid , brachiocelephic trunk, L subclavian artery, aortic arch, ascending aorta, descending aorta
The normal diameter of the aorta is less than __________________ millimeters (mm) in men.
23 mm
The inferior mesenteric artery distributes blood to the ______________________.
left transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, and rectum.
The right renal artery passes _________________________ to the inferior vena cava (IVC).
Posterior
The vessel that arises from the anterior aortic wall and takes a parallel course to the aorta is the _______________________.
Sma
Which one of the following vascular structures courses between the aorta and SMA?
Left renal vein
Where do the renal arteries branch from the lateral wall of the aorta?
Inferior to the sma
The IVC courses anteriorly to enter the ________________________.
Correct Answer
Rt atrium
Which vascular structure is used as a landmark in locating the celiac trunk?
SMA
The most common cause of abdominal aneurysms is _____________________.
arteriosclerosis
In patients with massive swelling of the lower trunk and leg edema and a dilated IVC, a(n) _______________ should be suspected
arteriovenous fistula
Choose the tumor that invades the IVC from a connecting vein.
Renal cell carcinoma
The clinical signs of leg edema, low back pain, pelvic pain, gastrointestinal complaints, and renal and liver problems may represent _________________.
Ivc thrombosis
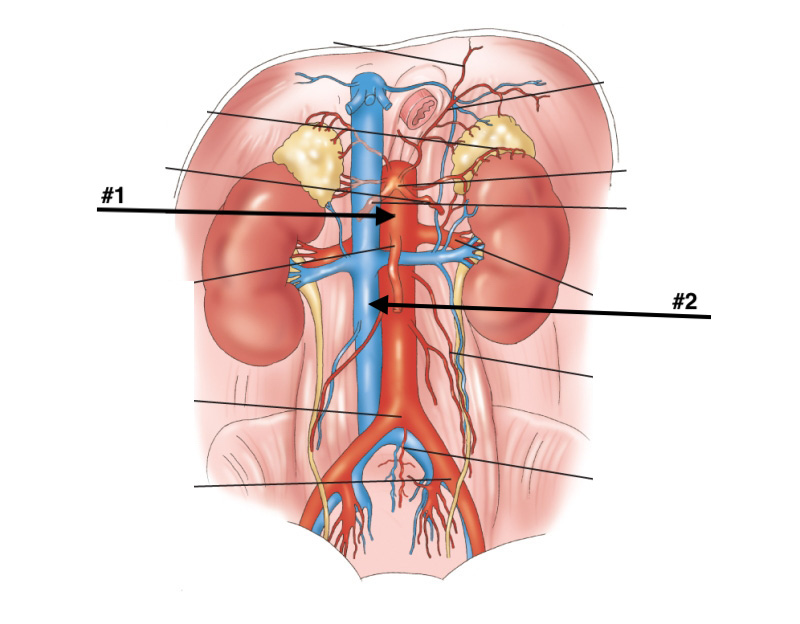
#1?
Abdominal aorta