Unit 7 Flashcards (AP Biology)
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
What were Darwin's observations in South America?
1. Organisms had features suited to diverse environments
2. Organisms were similar based on proximity, not climate
3. Fossils resembled local living organisms
Why were the Galapagos Islands influential to Darwin?
-Animals on islands resembled those on SA mainland
-Hypothesized that Galapagos was colonized by mainland -> diversification on islands
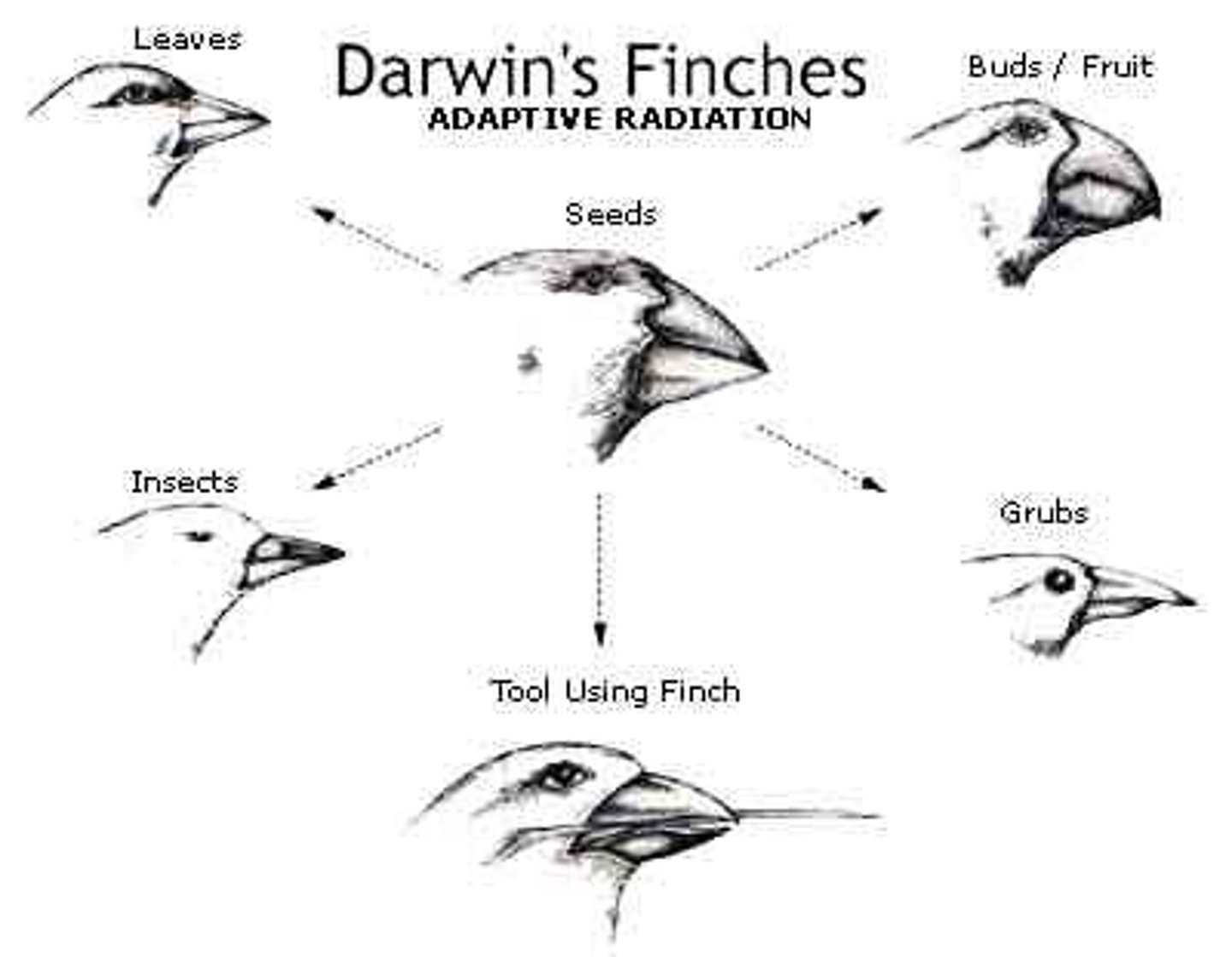
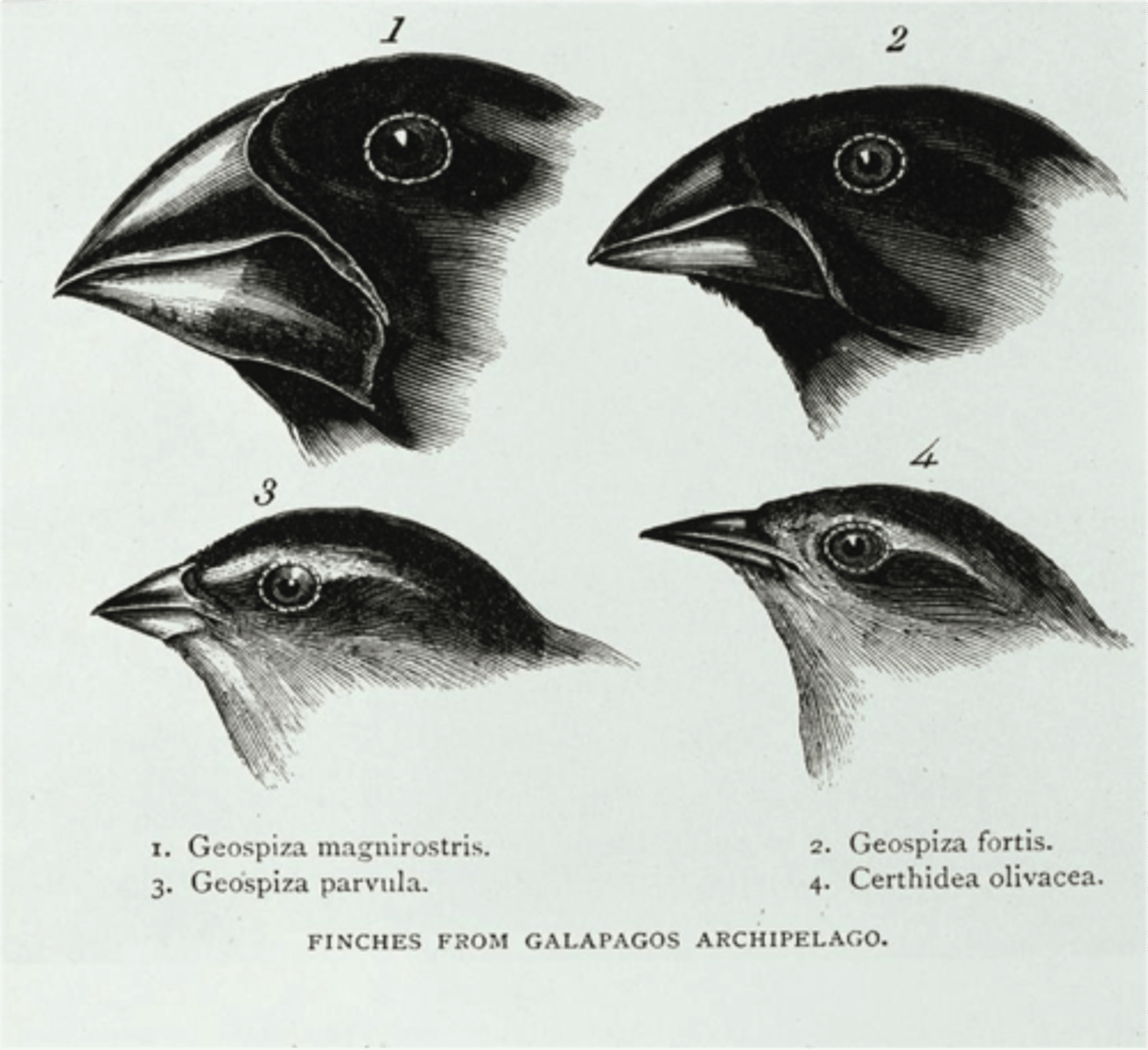
What was Darwin's conclusion on the finches?
-Common ancestor from SA mainland colonized islands
-Birds evolved traits specific niches (like food)
Adaptation vs. Niche?
Adaptation: inherited trait that increases fitness
Niche: role of organism/species in ecosystem
What is natural selection?
Process where individuals with favourable traits are more likely to survive/reproduce
**Driving force of evolution
What is artificial selection?
Process where humans change a species by breeding it for certain traits
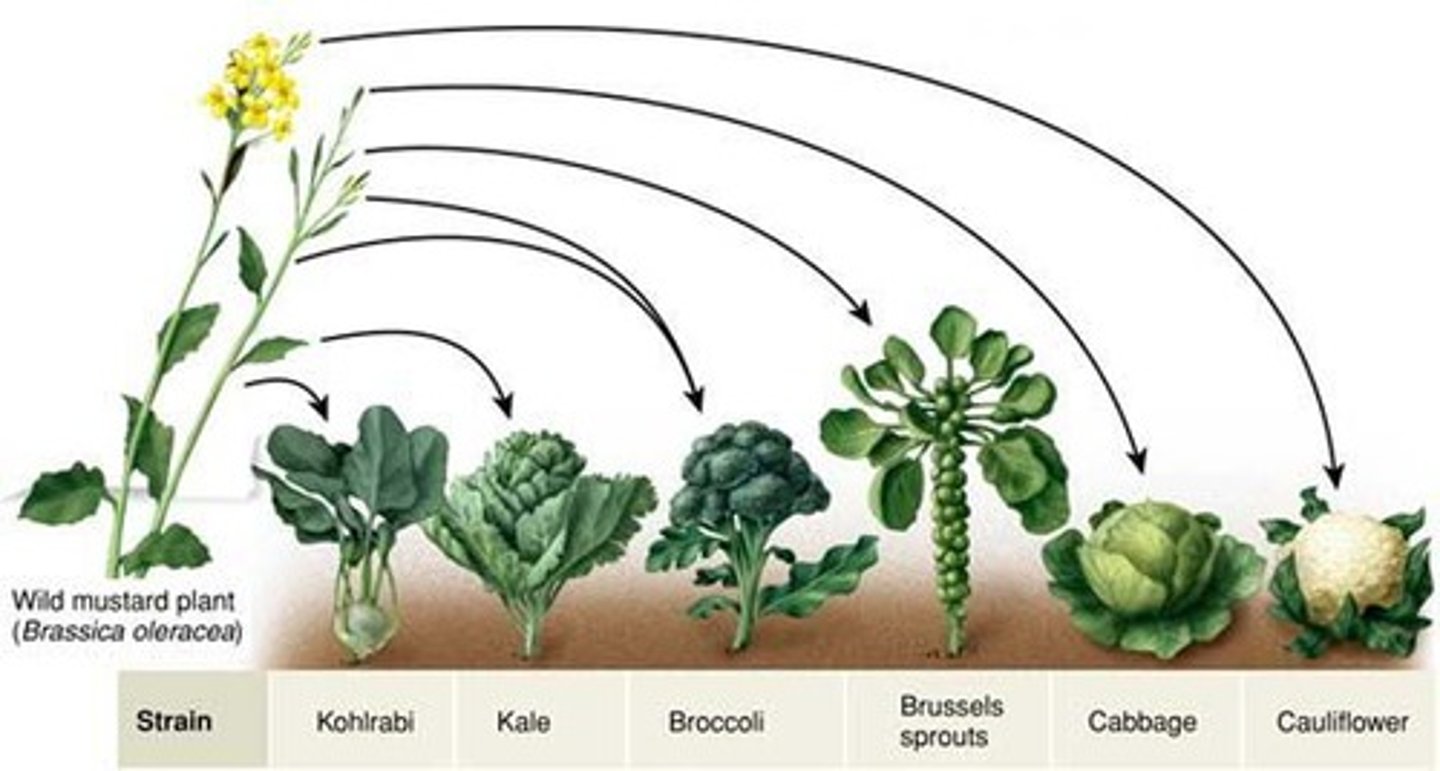
What are the 7 key features of natural selection?
-Members of population vary in inherited traits
-More offspring than environment can support
-More advantageous traits = more offspring.
-> Unequal fitness = more favourable traits over time
-Populations, not individuals, evolve.
-Natural selection only modifies existing traits
-Adaptive traits differ across environments
What are the requirements for natural selection?
1. Competition - too many offspring
2. Variation
3. Adaptation - more/less advantageous traits
4. Heritability - favourable trait must be genetic
What is the evidence that supports evolution?
1. Comparative anatomy
2. Fossil record
3. DNA sequencing
4. Documented observations
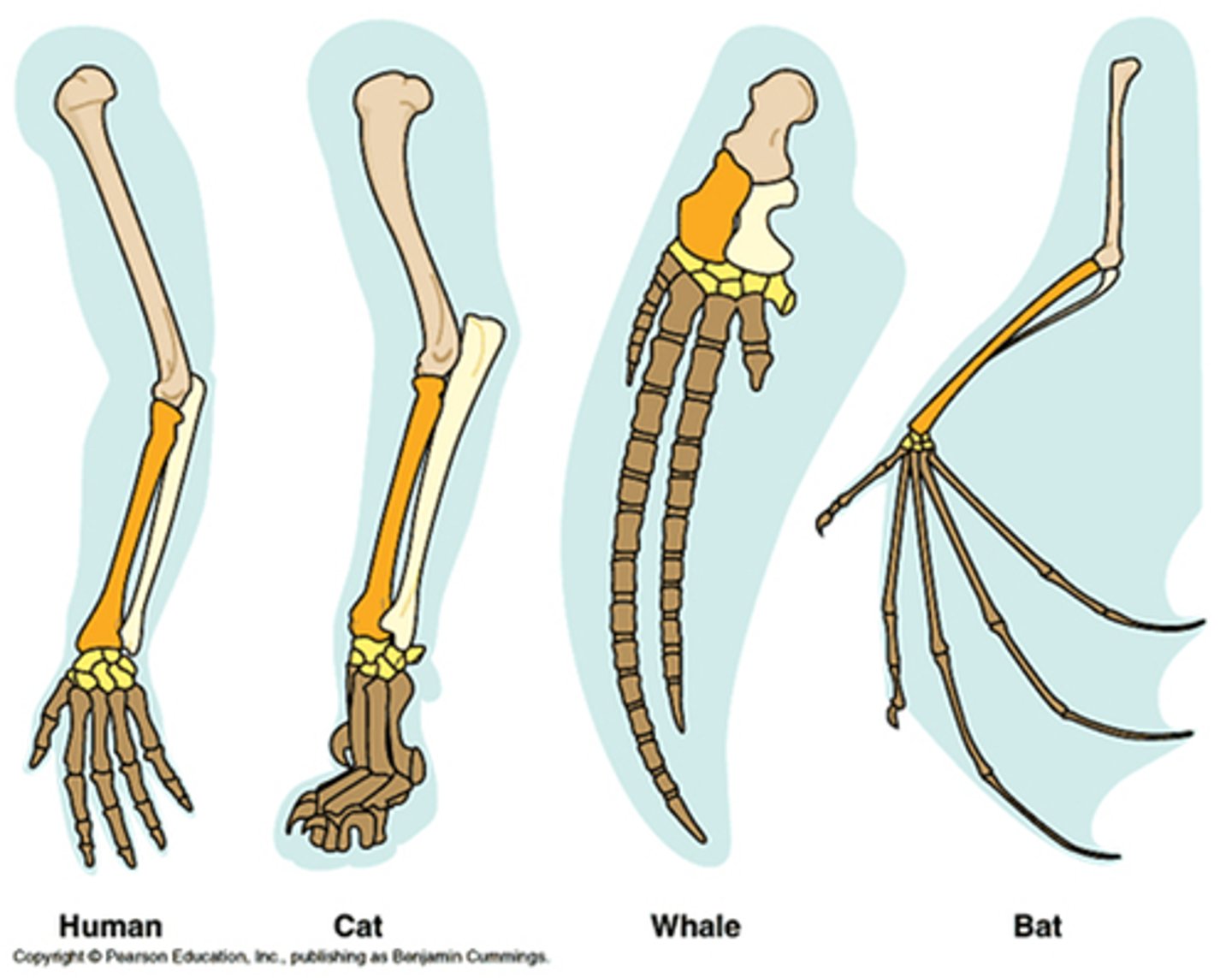
(C.A.) What are homologies/homologous structures?
Homologies: similarities between species from common ancestry
H structures: SAME STRUCTURE, different function
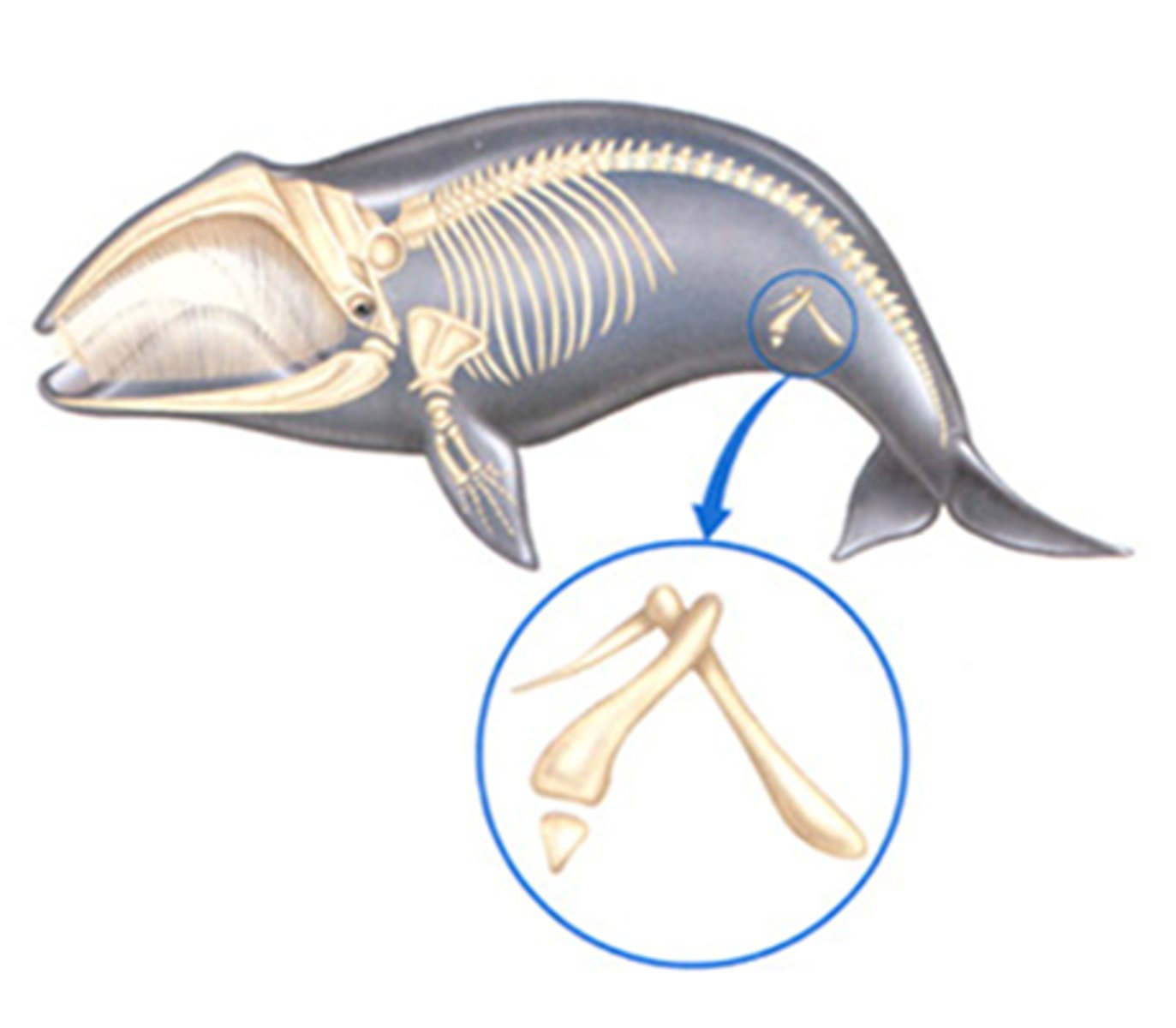
(C.A.) What are vestigial structures?
Once useful, now nonfunctional in living species
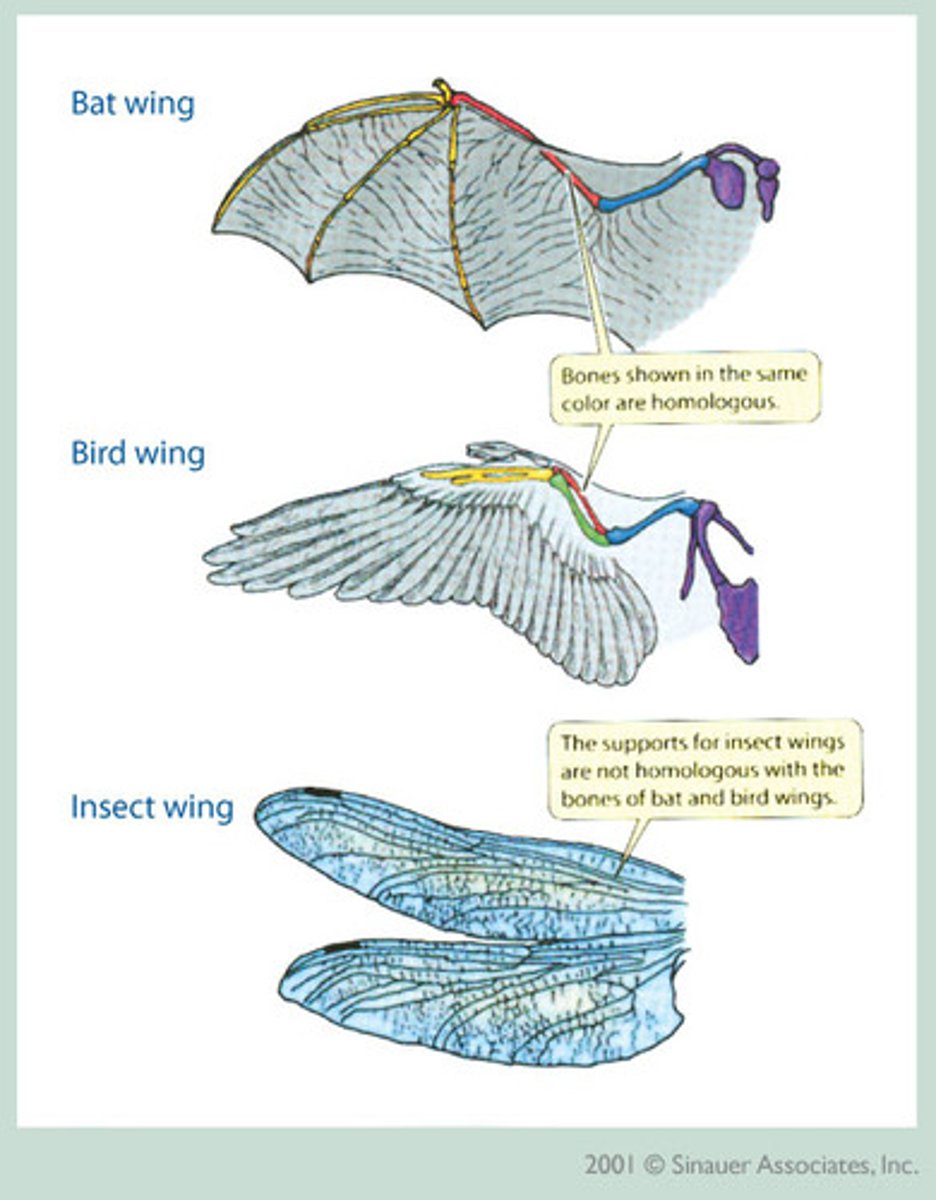
(C.A.) What are analogous structures?
SAME FUNCTION, different structure (no common ancestry)
(C.A.) Convergent vs. Divergent evolution?
Divergent = homologous
Convergent = analogous
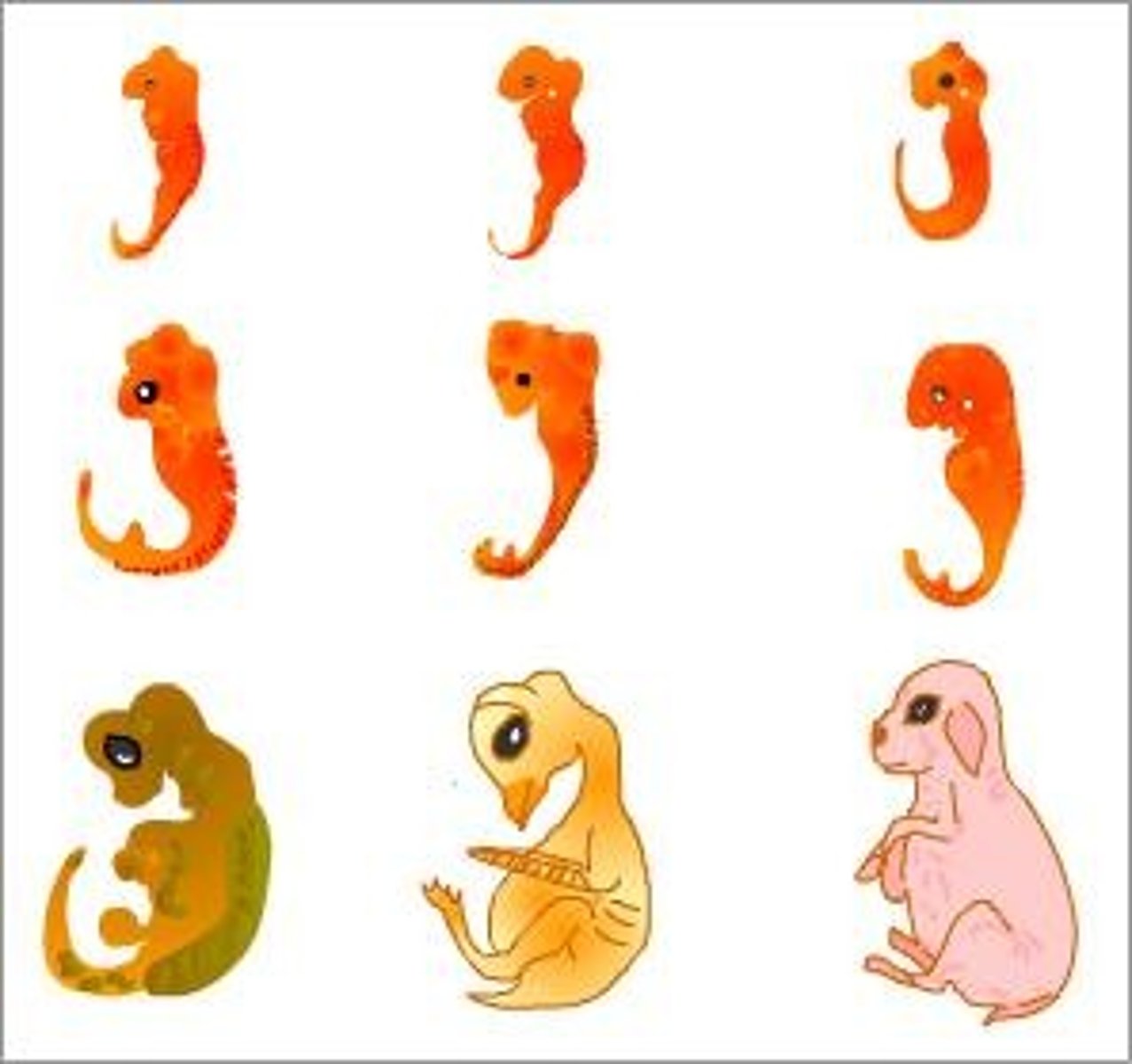
(C.A.) What is comparative embryology?
Shows homologies not visible in adults

What 3 things do fossil records show?
1. extinction
2. origins
3. changes
What is DNA sequencing and what does it show?
-Sequence nucleotides and amino acids
-Shows homologies between species
What are some important documentations of evolution?
1. Finches on the Galapagos Islands (beak changes)
2. E. coli evolution/efficiency
Gene pool vs. population?
Population: group of individuals that can breed
Gene pool: all the alleles of every gene in a population
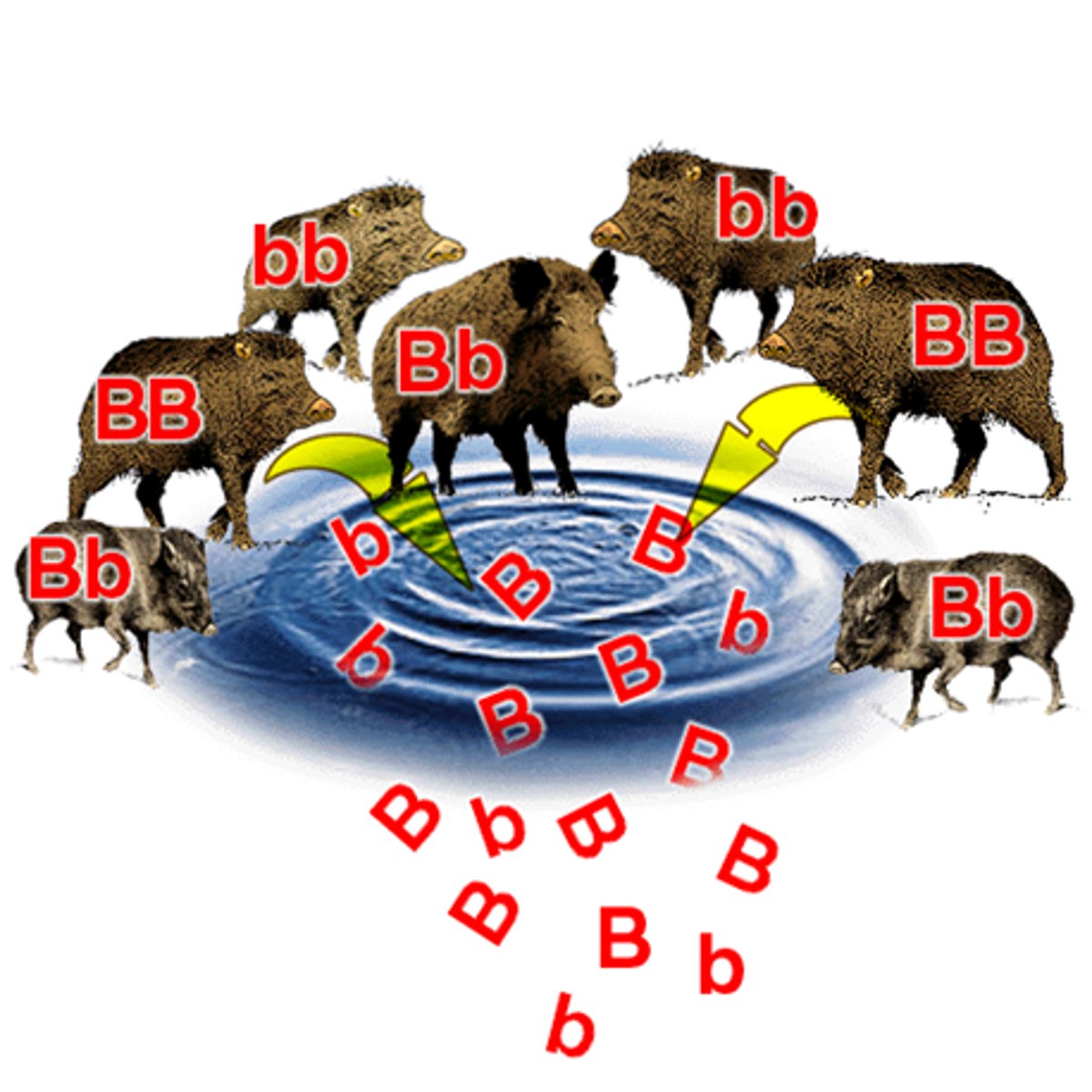
What does the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium represent?
Genetic makeup of a population NOT evolving
-> allele/genotype frequencies are constant in HW equilibrium
What are the conditions of HW equilibrium?
1. no mutations
2. random mating
3. no natural selection
4. extremely large population size
5. no gene flow
What are the factors that cause microevolution?
1. genetic drift
2. gene flow
3. natural selection
What is genetic drift and its 2 types?
Allele frequencies change by random chance (less variation)
1. Founder effect
2. Bottleneck effect
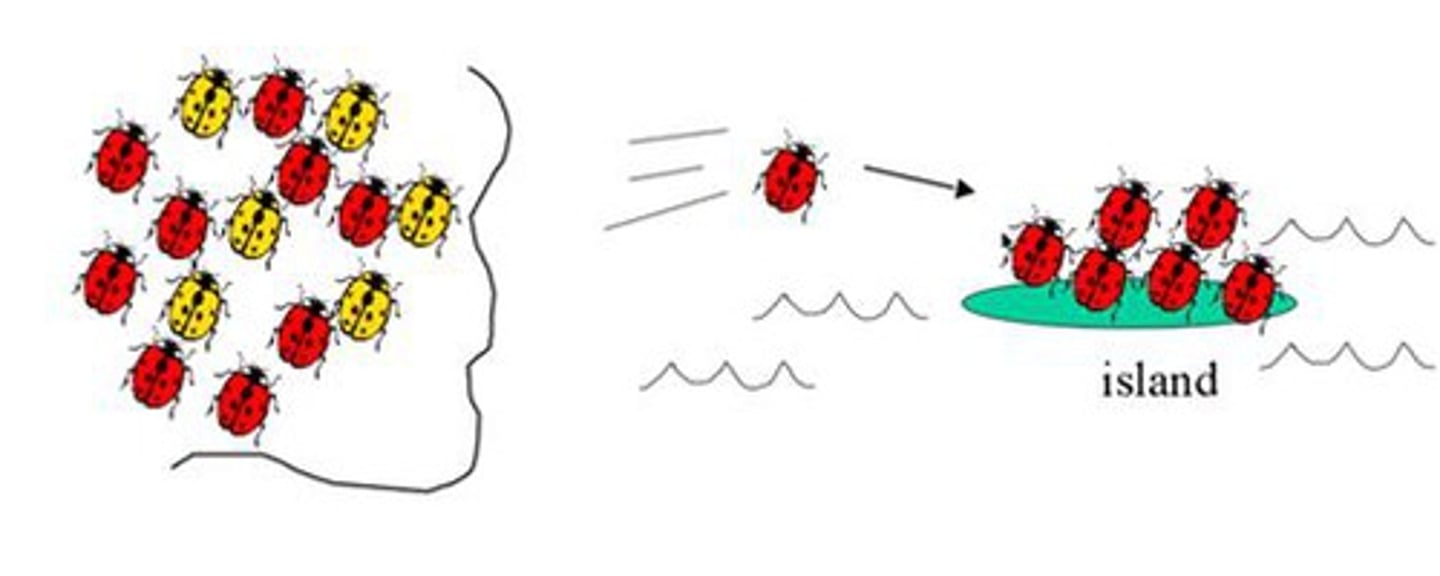
What is the founder effect?
-Few individuals break off from pop. and form a new one
-Gene pool in small pop. are different (random chance)
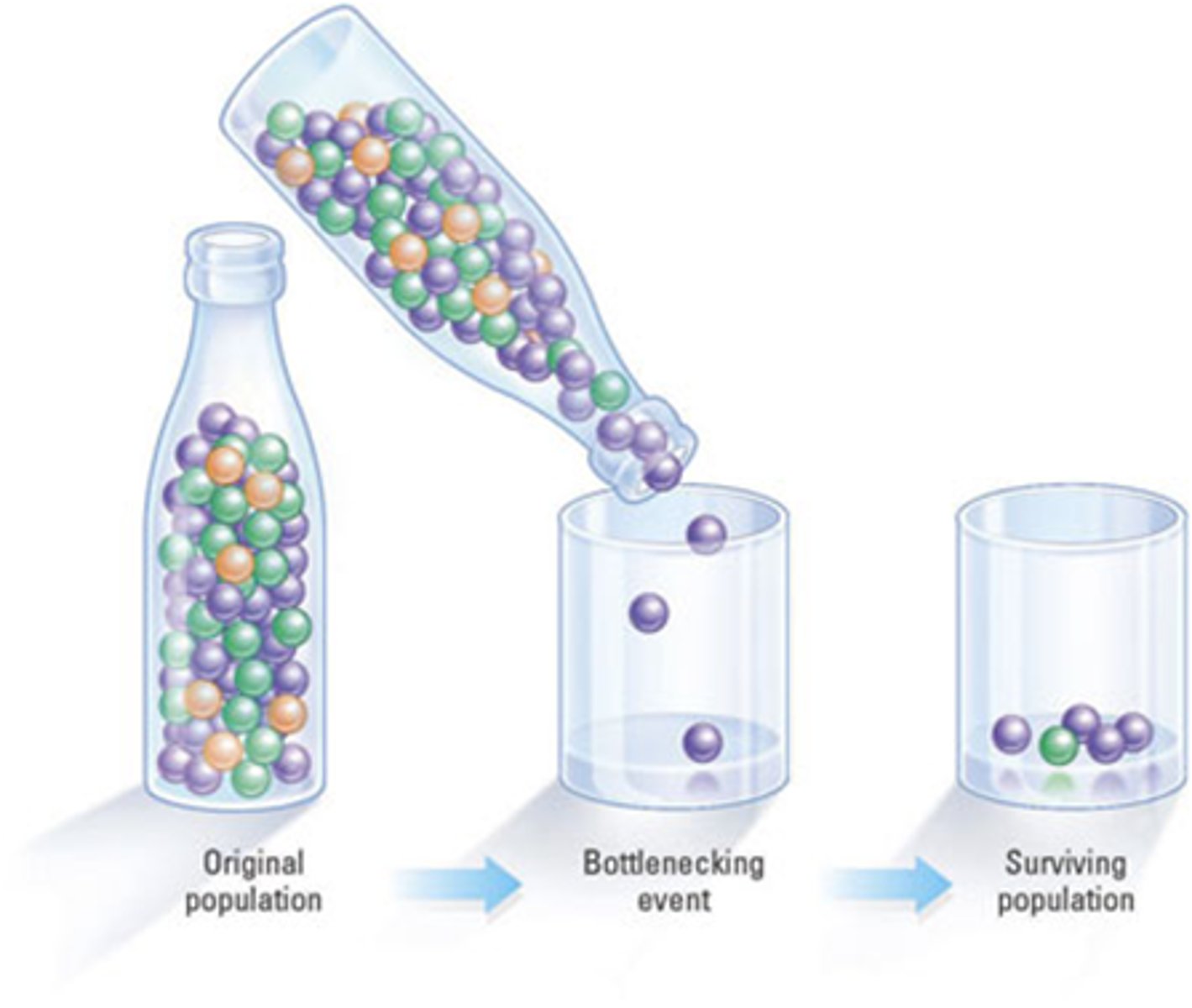
What is the bottleneck effect?
-Drastic reduction in pop. from natural disaster
-Gene pool changes (random chance)
What are the key points of genetic drift?
1. Significant in small populations
2. Allele frequencies CAN change at random
3. Pop. CAN lose genetic variation
4. Harmful alleles CAN become fixed
What is gene flow?
-Movement of alleles between populations
-> frequencies of alleles change
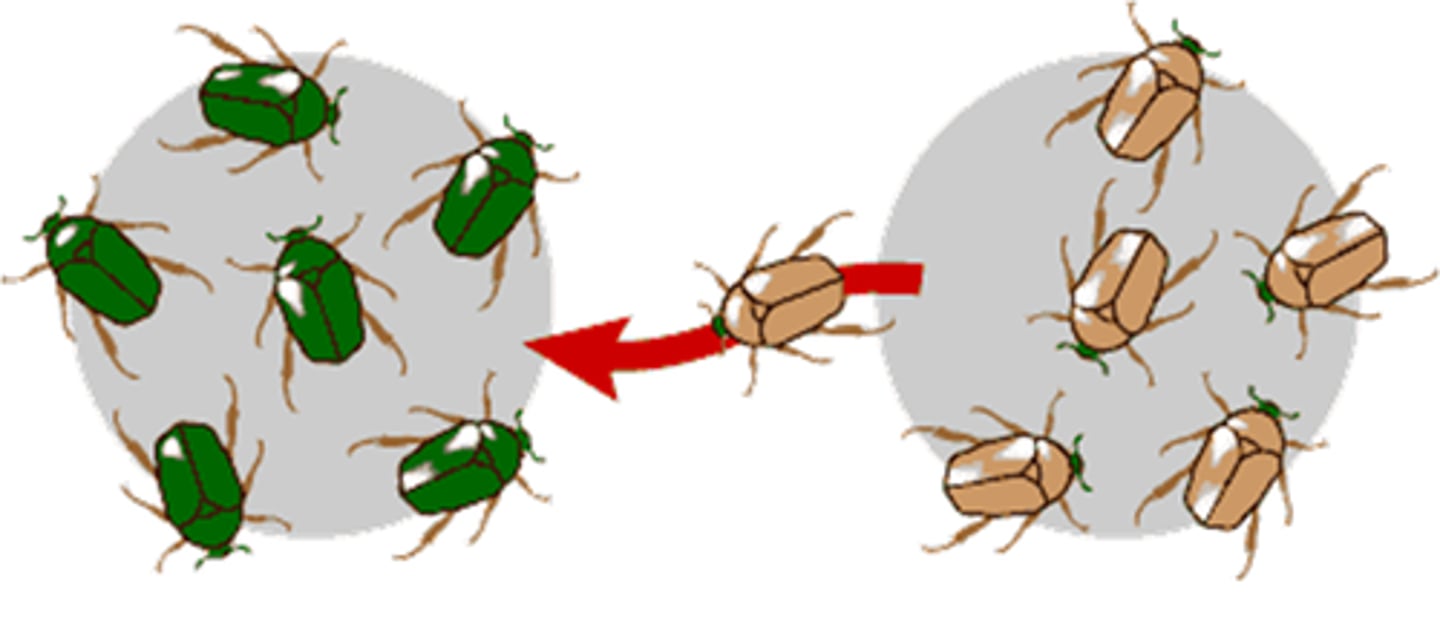
How does natural selection cause microevolution?
1. New genetic variation by chance
2. Beneficial alleles are favoured
**Adaptive evolution: ALWAYS an increase in advantageous alleles
How does natural selection indirectly effect frequencies?
-Natural selection acts directly on phenotype -> indirectly affects allele/genotype frequencies
**Heritable variation is essential for evolution!
What are the 2 sources of heritable variation?
1. Mutations = new types of alleles
2. Genetic shuffling (sexual reproduction) = more combinations of alleles
What are the 3 types of natural selection?
1. directional - favours one end
2. disruptive - favours extremes
3. stabilizing - favours middle, acts against extremes
What is a heterozygote advantage?
-Heterozygotes have a higher fitness than homozygotes
-> natural selection keeps both alleles in the pop.
What is sexual selection?
When certain adaptations increase mating success
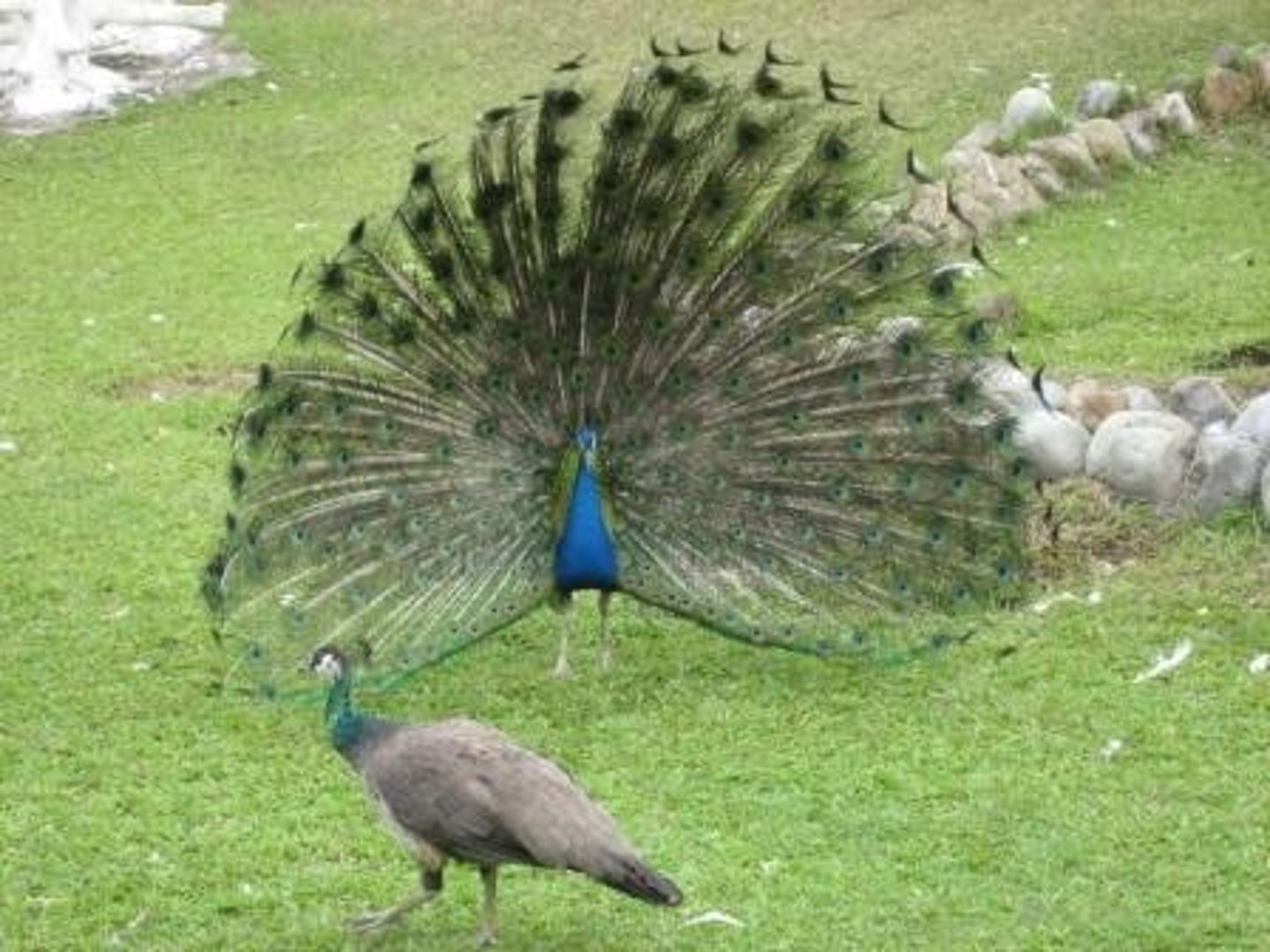

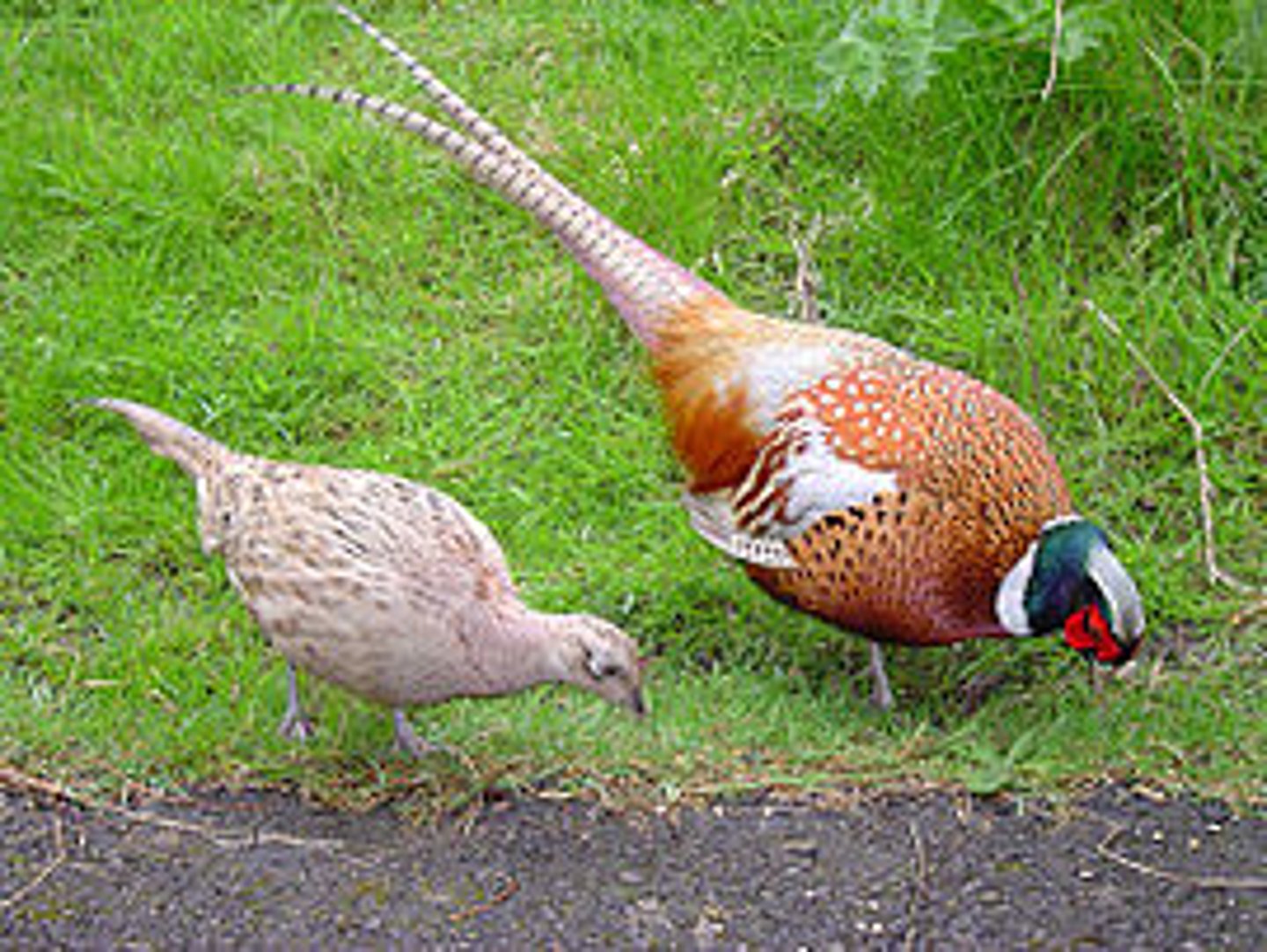
What is sexual dimorphism?
Male and females who differ in traits

What is the biological species concept, gene flow?
A species is a group of pops. whose members can breed normal offspring
** Gene flow keeps the populations together
What is reproductive isolation, types?
Biological barriers that prevent species from breeding
1. prezygotic
2. postzygotic
What are the types of prezygotic barriers?
1. Habitat (*no physical barriers)
2. Temporal - breed at different times
3. Behavioural (courtship rituals)
4. Mechanical
5. Gametic - do not recognize each other
What are the types of postzygotic barriers?
1. reduced hybrid viability - won't develop
2. reduced hybrid fertility - can't reproduce
3. hybrid breakdown - generations are weaker

What are the limitations of the biological species concept, alternatives?
-Don't apply to fossils/asexual organisms!
1. morphological,
2. ecological, and
3. phylogenetic species concepts
What is speciation, 2 types?
-Process where 1 species splits into 2+
-Explains features that are shared by inheritance
1. allopatric
2. sympatric
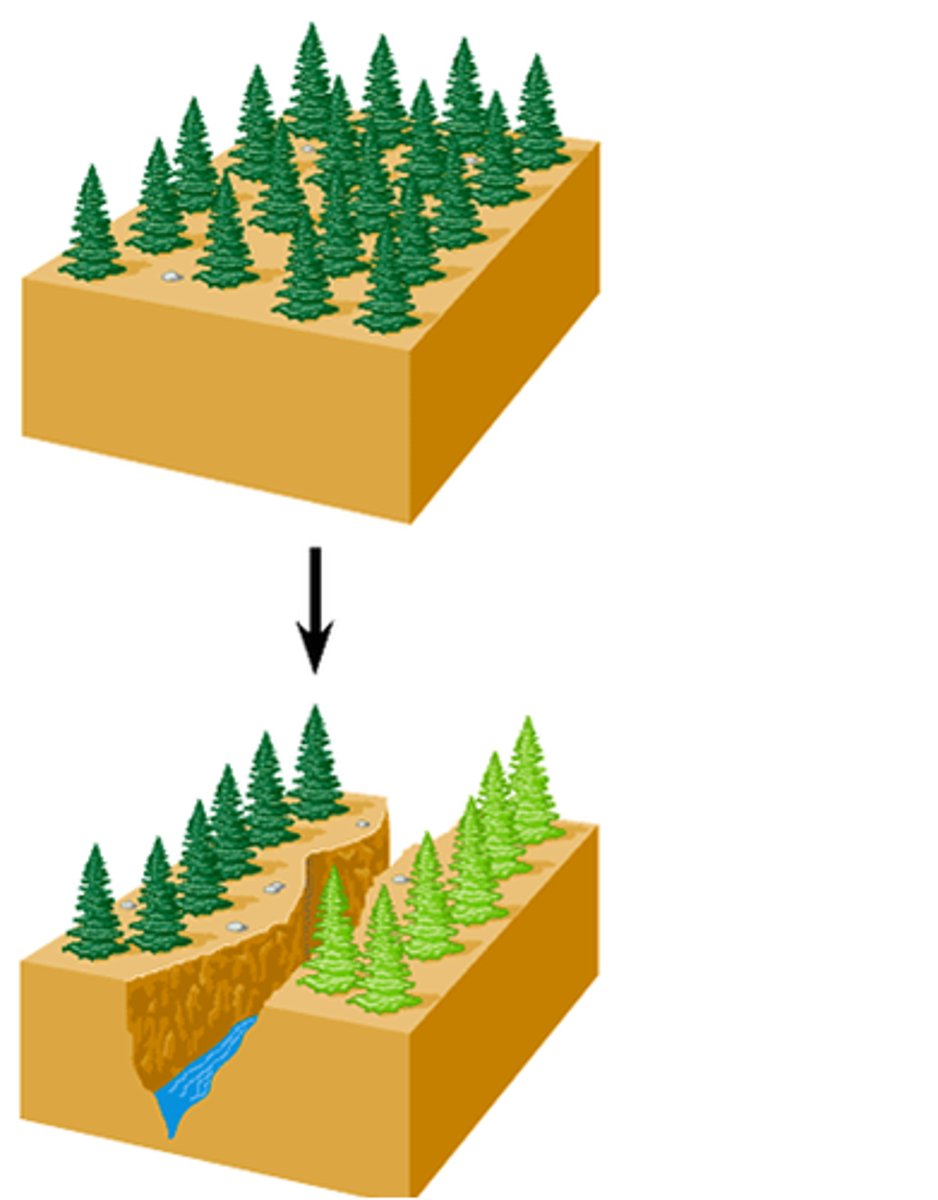
What is allopatric speciation, evidence?
Isolation between pops. causes independent evolution
-> may be reproductive barriers
What is sympatric speciation, 3 types?
Independent evolution without isolation
1. Polyploidy
2. Habitat differentiation
3. Sexual selection
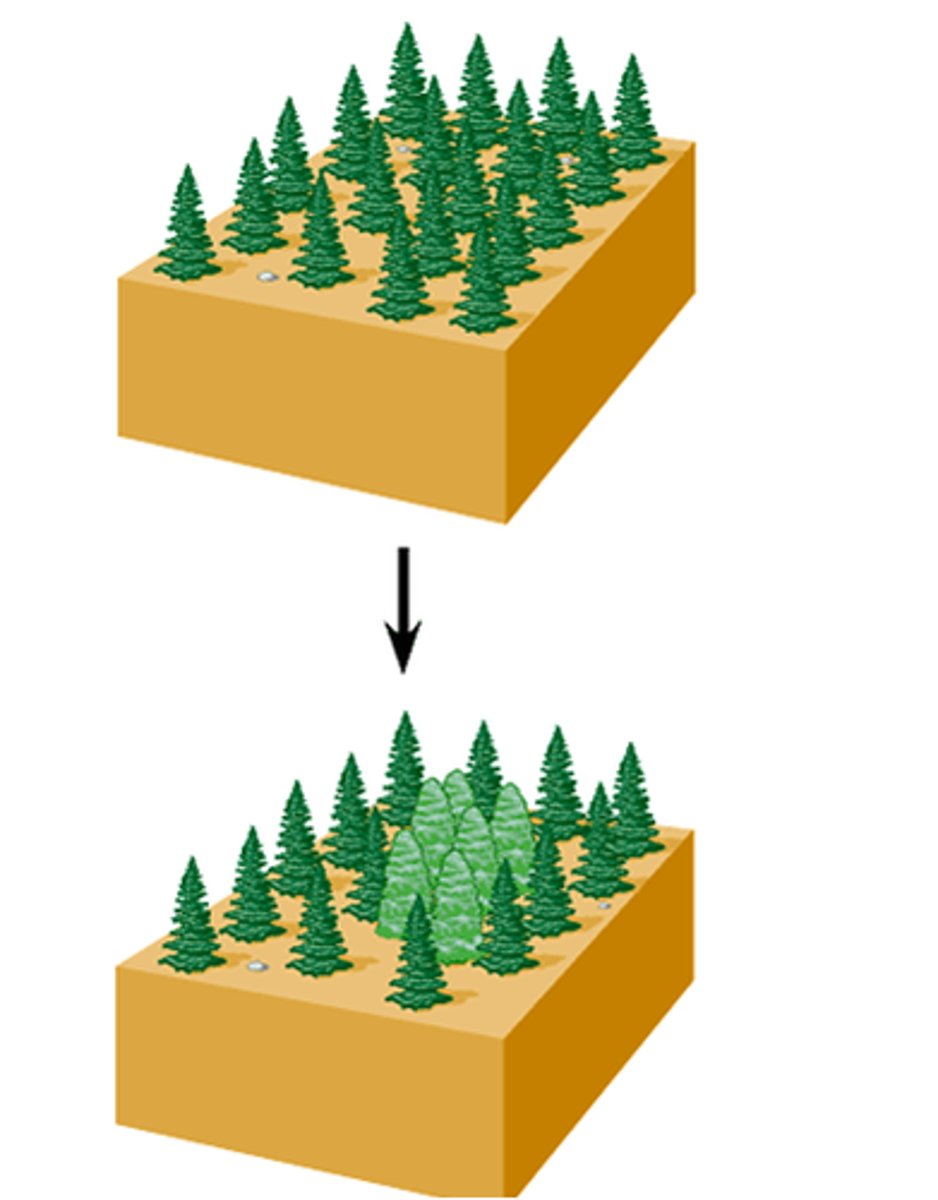
What is polyploidy, effect on speciation?
Extra sets of chromosomes accidentally -> offspring can only reproduce with one another
What is habitat differentiation, effect on speciation?
New ecological niches -> reduces gene flow
How does sexual selection affect speciation?
Groups may only mate with specific phenotypes-> reduces gene flow
How and when did the Earth form?
-4.6 b.y.a
-Earth cooled = early atmosphere changed which formed oceans

What were the stages for life to start on Earth?
1. Abiotic synthesis of small organic molecules
2. Joining the molecules into macromolecules
3. Packaging molecules into protocells
4. Origin of self-replicating molecules

1. What is the abiotic synthesis of molecules?
-Free energy from lightning/eruptions helps produce organic molecules
-MILLER/UREY EXPERIMENT
2. How were macromolecules constructed?
ORGANIC SOUP MODEL: Organic molecules accumulated, made solutions that sparked joining monomers
3. How were protocells formed? What are they?
-Organic molecules form vesicles (protocells) with a lipid bilayer in water
-Protocells can replicate and metabolize
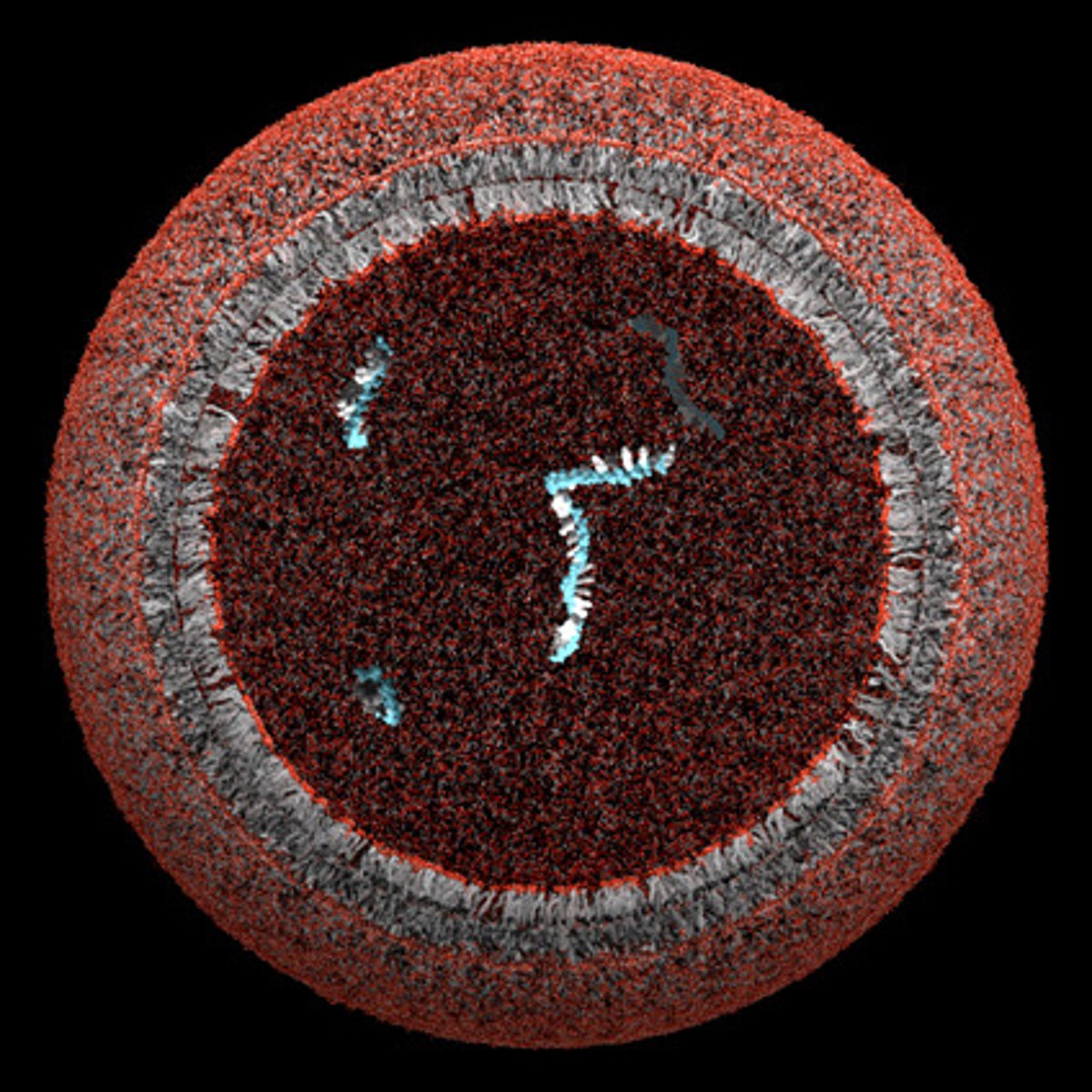
4. What is the origin of self-replicating molecules?
RNA WORLD HYPOTHESIS: RNA is the first genetic material
-Protocells with RNA can make a daughter vesicle
What is a geologic record?
Divides Earth's history into different measurements of time
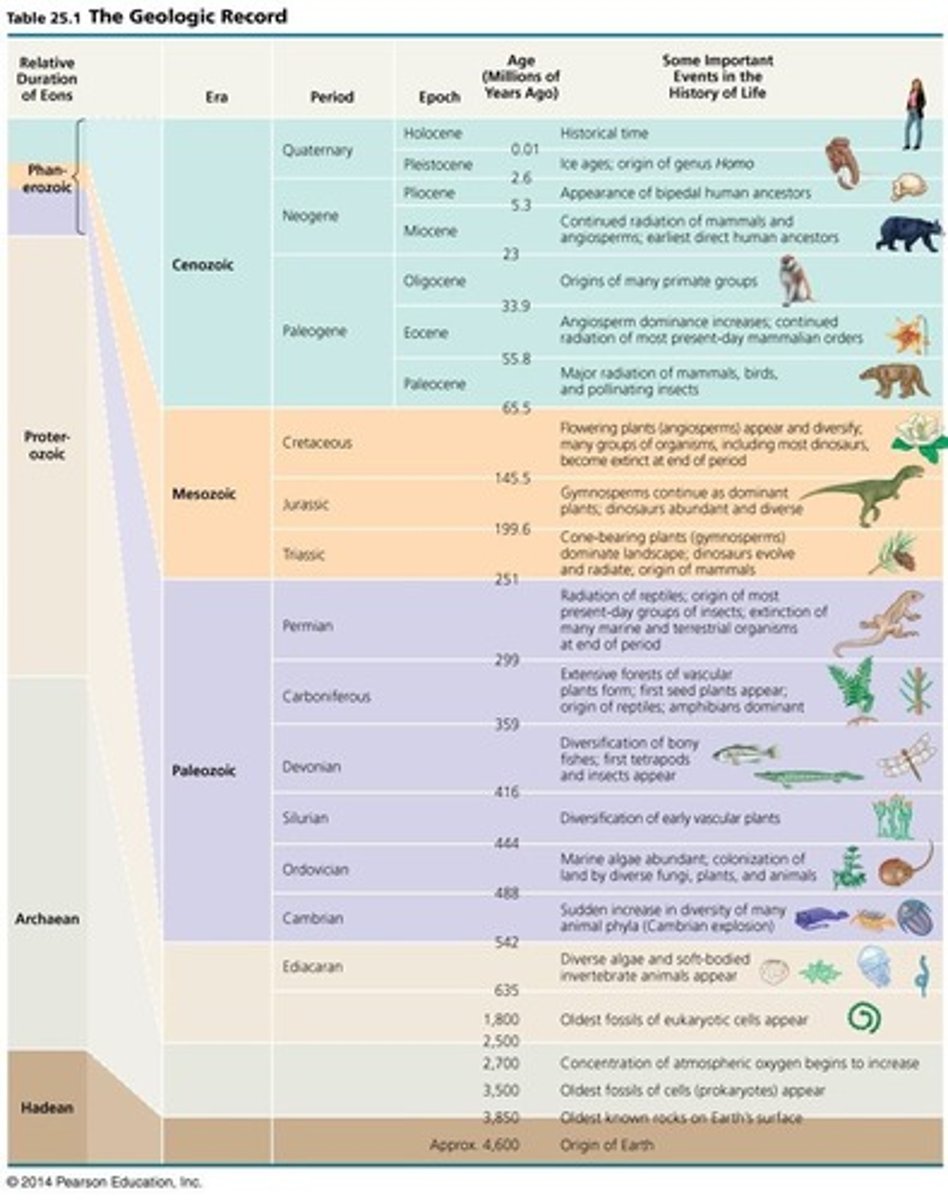
What was the rise, fall, and aftermath of anaerobic prokaryotes?
-3.5 b.y.a
-Grew when oxygen levels on Earth were low
-Declined when oxygen increased
-1.8 b.y.a. eukaryotic cells appeared (aerobic) and have evolved since
What are the 2 biggest mass extinctions?
1. Permian mass extinction - eruptions cause global warming/ocean acidification
2. Cretaceous mass extinction - asteroid debris blocked sunlight

Why is genetic diversity important?
More likely to have survivors and adapt
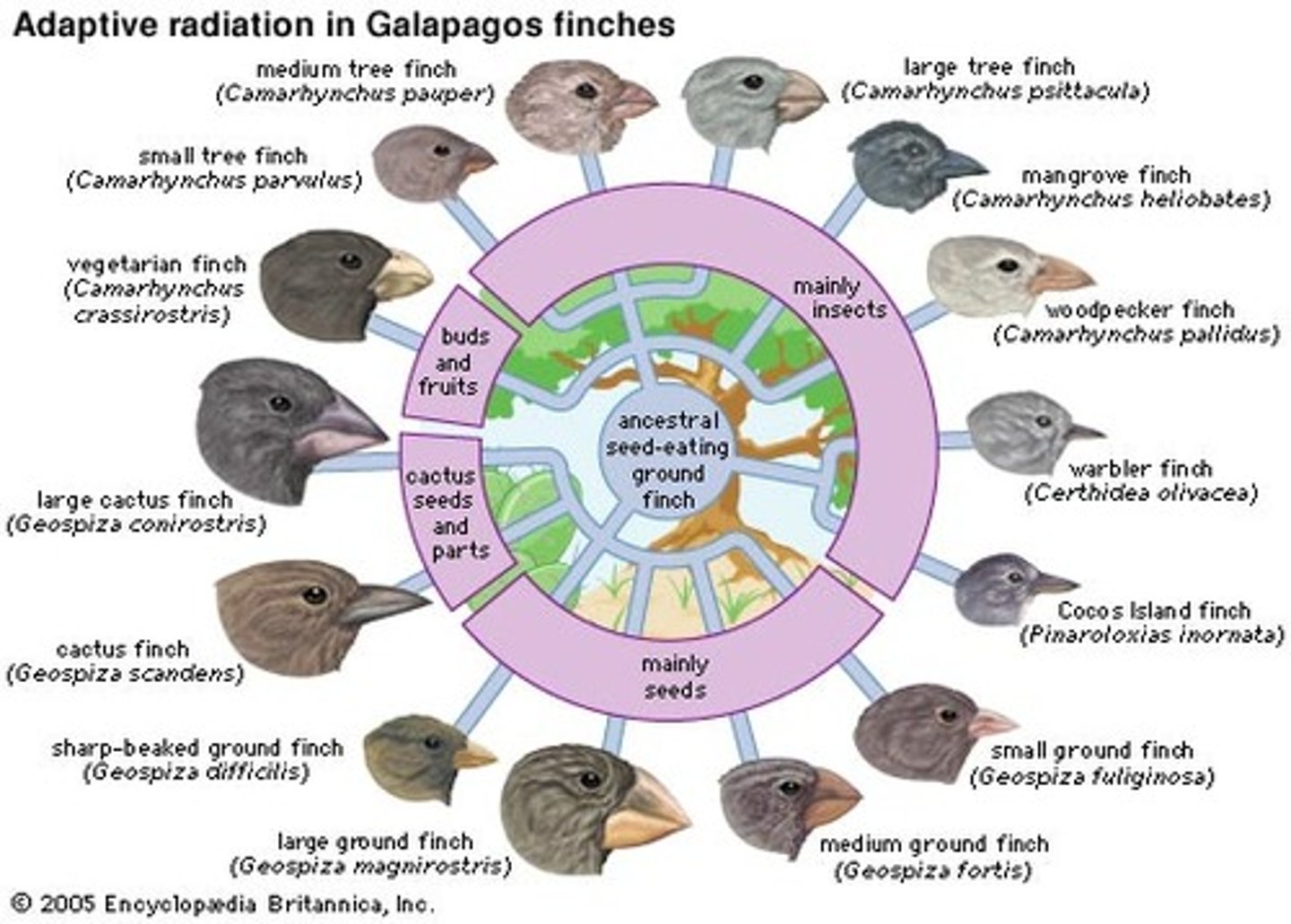
What is adaptive radiation, causes?
Rapid evolution of many species from a common ancestor
1. Mass extinction
2. Evolution of new traits
3. Colonization of new regions
What is maximum parsimony?
Way to build phylogenetic trees by choosing the simplest tree
What are the 2 types of adaptive radiation, examples?
1. Worldwide - e.g. mammals after dinosaurs
2. Regional -e.g. Galapagos finches