1.05 Progressive power lenses (PPLs)
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
How do PPLs work
Works by a change in radius of surface curvature between the distance portion and the near vision area
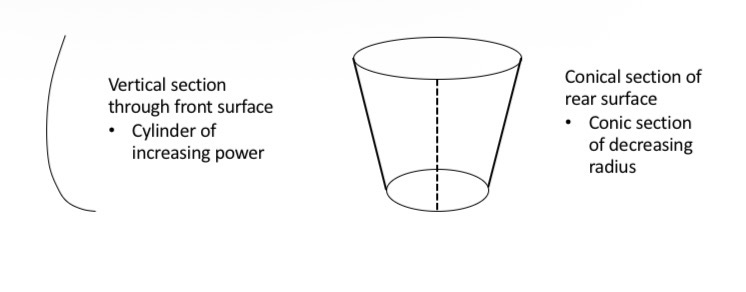
Aves design
The Aves design had a front surface with a cylindrical element that increased in power towards the bottom of the lens. The rear surface was a section of a cone with the cone apex below the lens
Volk and weinberg bennet
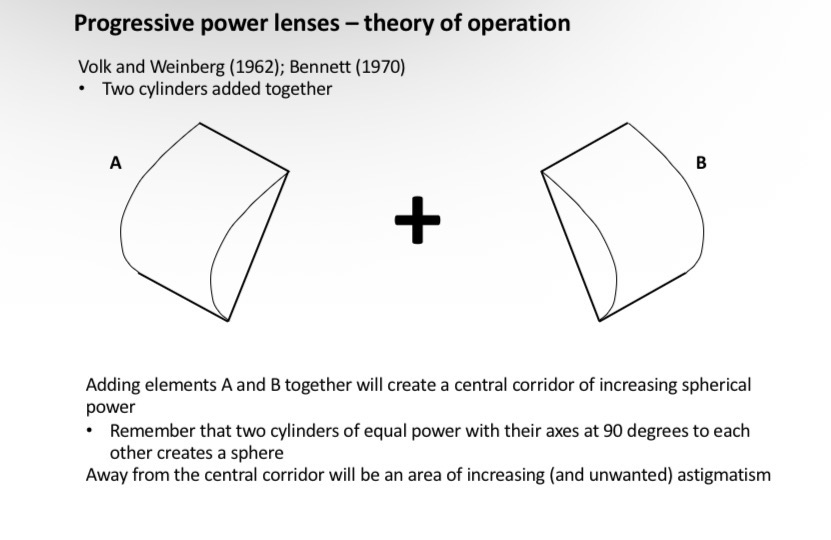
What is this showing
Cylinder 1 - increases in positive power as you go down and right
Cylinder 2 - increases in positive power as you go down and left
The two aspheric cylinders are added together
Increasing power as you go down the central corridor of the lens
It is spherical all the way down the centre (principle meridians are the same power)
Lots of surface astigmatism at the peripheral regions of the lens which causes distortion and bad vision
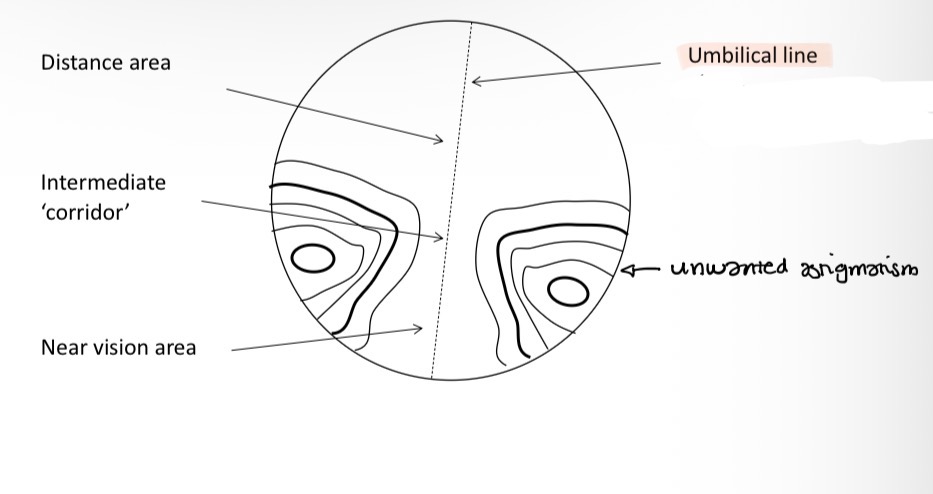
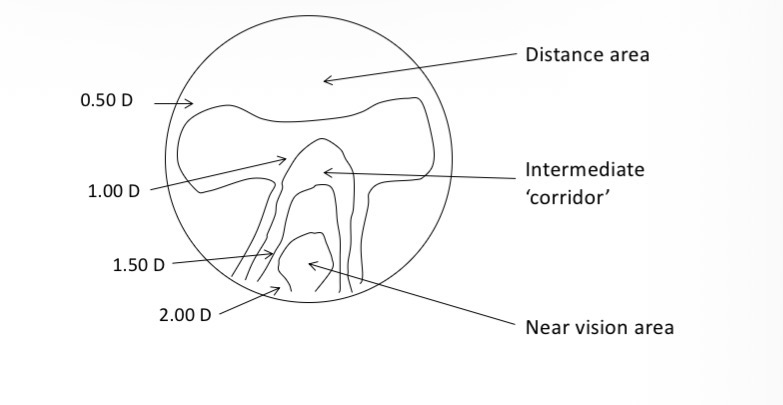
Label the parts of the PPL lens
Umbilical line
Unwanted astigmatism
Near vision area
Intermediate corridor
Distance area
How does the umbilical line tell you which lens it is
It always slopes inwards (nasally)
Using the umbilical line which eye is this lens for
Left eye
What is a hard design characterised by
A wide stable area for the distance prescription
A wide stable area for the near prescription
A relatively short and narrow progression corridor
Relatively high astigmatism either side of the progression corridor
What is a soft design characterised by
A narrower area for near where the prescription is ‘correct!
A more gradual change (ie longer) progression corridor
A wider progression corridor
Relatively low astigmastism either side of the progression corridor
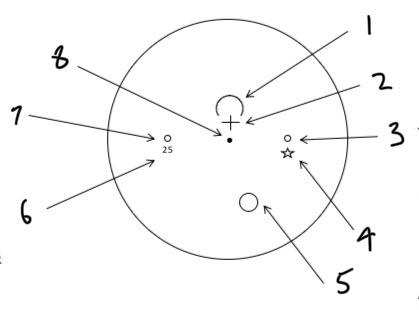
Label the markings and which ones are permenant
Distance checking point
Fitting cross
Engraved circle 34mm from the other engraved circle
Manufacturers logo
Near checking point Fitting cross
Abbreviated near addition marking placed on the temporal side
Engraved circle
Prism checking point
Permenant - 2 small circles, the abbreviated addition, manufacturers logo
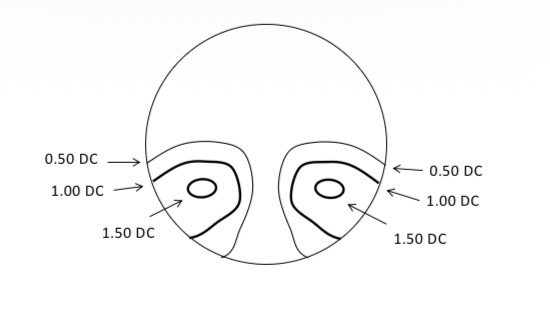
What is this plot called
Mean power plot
Shows the change in mean spherical power across a PPL
What is this plot called
Iso cylinder plot
A method of showing the distribution of ‘unwanted’ astigmatism across a PPL
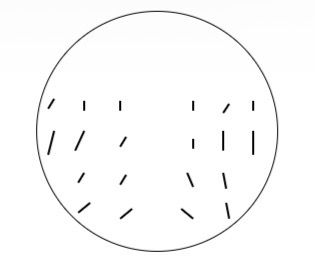
What is this plot called
Vector plot
Length and orientation of line shows the amount and direction of lens astigmatism
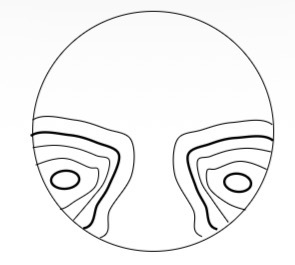
Is this a hard or soft PPL lens design and how do u know
Hard design
High surface astigmatism
Wider area of stable near vision power
Shorter progression corridor
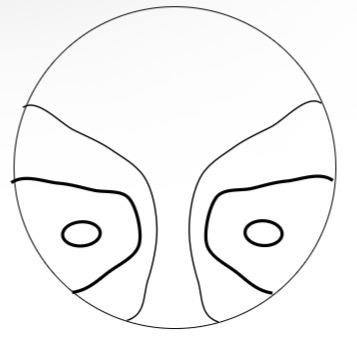
Is this a high or soft PPL lens design and how do u know
Soft design
Low surface astigmatism
narrower area where the near prescription is stable
Longer progression corridor
Disadvantages of a longer progression corridor
Pt has to move their head more to get to maximum near Rx
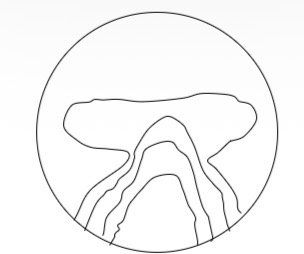
Is this a hard or soft PPL lens design and what plot is it
Hard design
Mean power plot
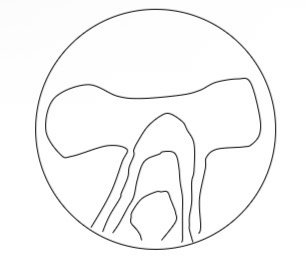
Is this a hard or soft PPL lens design and what plot is it
Soft design
Mean power plot
What is the effect of addition power on lens performance
As the addition increases the difference in lens surface power increases
The amount of surface astigmatism increases
Subjective distortion for the wearer will become more apparent
What should we keep in mind when prescribing PPLs for the first time
Prescribe these lenses earlier in life so they can get used to it and you can gradually increase near Rx as they get older
Instead of a high near Rx straight away as theyre not used to high levels of surface astigmatism
How can we account for convergence of the eyes for near vision
Symmetrical lenses can be rotated to allow for convergence (distortion equalled out on either side - more comfortable for pt)
Modern designs are asymmetrical with a specific design for right and left lenses
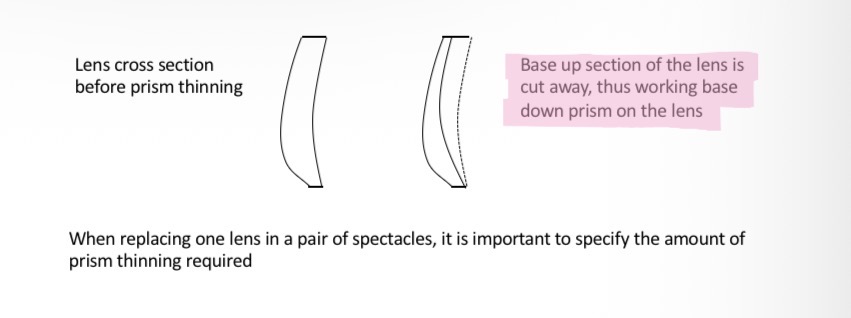
How to thin the lens to improve cosmetic appearance
Use a base down prism to reduce the thickness of the lens and make it lighter
Eg for a +2.25 D near addition a 1.5 dioptre base down prism could be worked on the lens
What is the progression corridor length
The distance between the stable distance vision area and the maximum addition power for near vision
What kind of frame is best for a shorter corridor
Shorter corridors allow a PPL to be fitted to a relatively shallow frame
Good for DV and NV
Why would putting a long corridor in a shallow frame be bad
Long corridor in a shallow frame = smaller near section
Why is a short corridor bad for pts with a high near addition
A shorter corridor means a greater rate of change in lens power for a given amount of eye/head movement - worse if pt has a high near add
So quite small movements can disrupt clear vision
What is the minimum fitting height of standard corridor length design
17 to 18mm
What is the minimum fitting height for a shorter corridor length
14mm
Which measurements should be considered when fitting a PPL
Horizontal positioning of the lens
Vertical positioning of the lens
Pantoscopic angle
Dihedral angle
What does horizontal positioning of the lens control
Controls the horizontal position on the lens with respect to the pupil position during distance vision, intermediate and near vision, fov and stability of vision
What does vertical positioning of the lens control
Controls relative position of vertical corridor relative to position of pts head
Head position must be comfortable and practical for the tasks that the wearer wishes to perform
What is the pantoscopic angle
Usually 5-10°
A smaller tilt can reduce the effective size of the reading angle
What is the dihedral angle
When looking at the lens from above
Can be considered when dispensing modern free form design
Can affect the power of the lens
How to determine the horizointal positioning of the lens
Measure monocular PDs (distance from centre of nose to each pupil)
Do not assume pts eyes are placed symmetrically either side of the nose
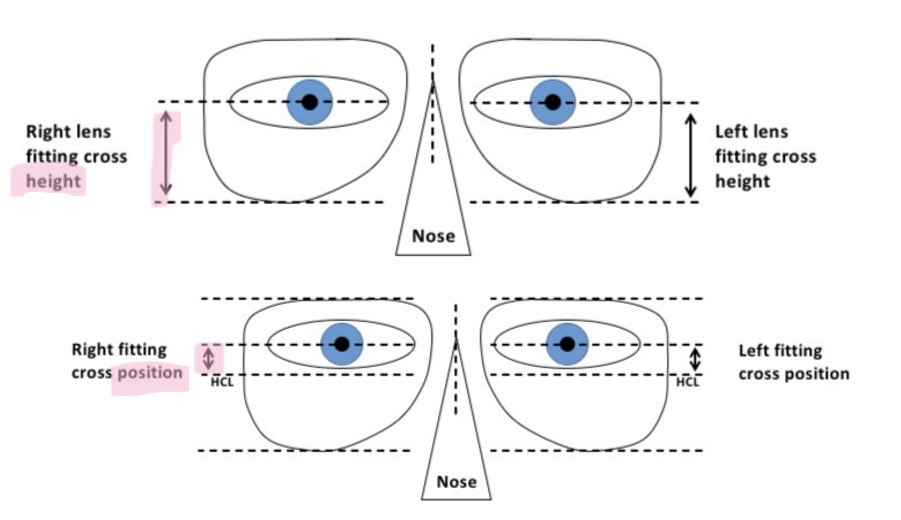
How to determine the vertical positioning of the lens
Make sure frame is sitting in the right place before taking measurements
2 methods of defining vertical positioning:
Fitting cross height - distance between pupil centre and a tangent to the lowest point of the lens
Fitting cross position - distance between pupil centre and the horizontal centre line of the frame
Measurement will need a sign to specify whether the fitting cross should be above or below the HCL
Above HCL = +
Below HCL = -
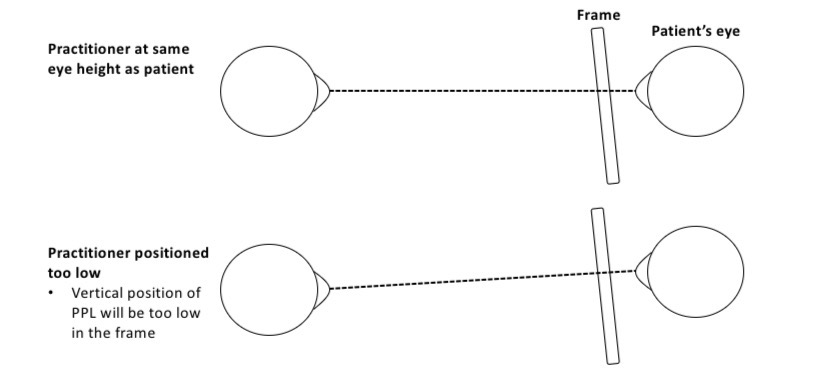
How to avoid parallax error
Sit infront of the pt and at the same eye level
Measurements were taken poorly - which measurements and what are the effects of this
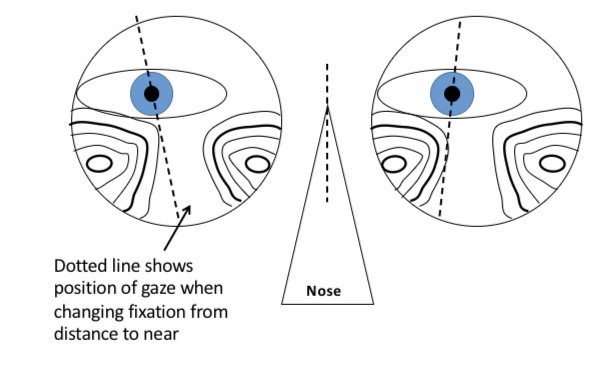
Pt has L mono PD smaller than R mono PD but lenses fitting assuming symmetrical PDs
Gaze is close to astigmatic area which causes distortion
Intermediate and near vision will be sub optimal
Pt will hold reading material to one side to find the clearest area (in this eg to the left)
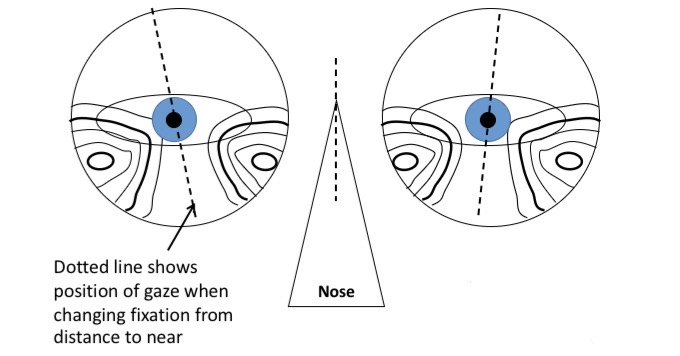
Measurements were taken poorly - which measurements and what are the effects of this
Heights too low
The eyes will be looking through the upper part of the progression corridor in primary gaze
They will have blurred distance vision
They will tilt their head downwards to compensate
Measurements were taken poorly - which measurements and what are the effects of this
Heights too high
The eyes will be looking through the upper portion of the distance vision portion
Distance vision will be ok
For near vision they will have to lift their chin upwards to read
High add power effect on progression corridor and reading area
With a high add power:
The progression corridor will be narrow
The reading area will be narrow
Which pts wont enjoy PPLs
Pts with neck problems - greater head movements can be needed to make best use of the reading area
Fussy pts may not cope with peripheral but after a while they may adapt