ES AMACE
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
A diagram which shows the variations of the axial load for all sections in the span of a beam
Shear Force Diagram
States that the moment of a force about a point is equal to the sum of the moments of the force's components about the same point
Varignon's Theorem
What is the straight line from point o?
Proportional Limit
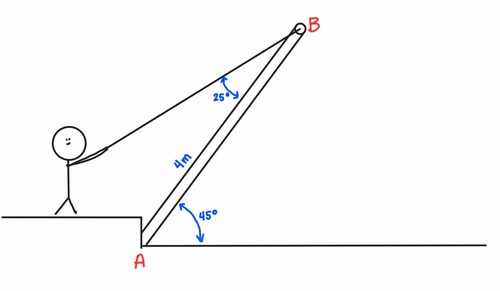
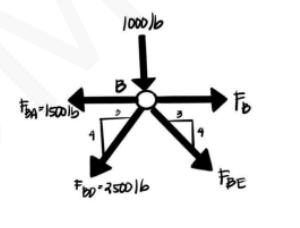
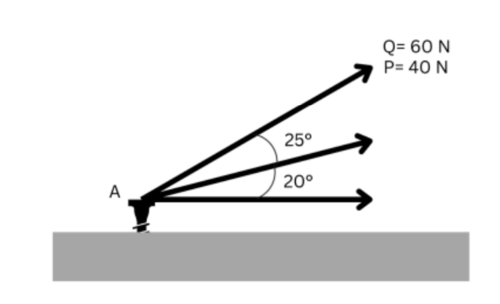
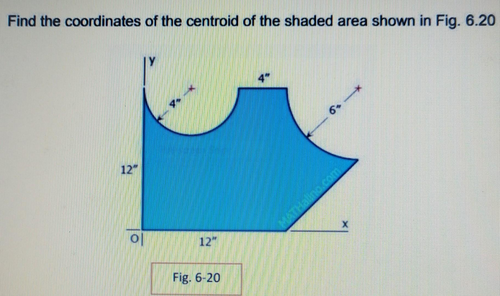
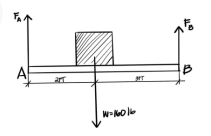
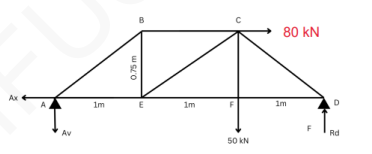
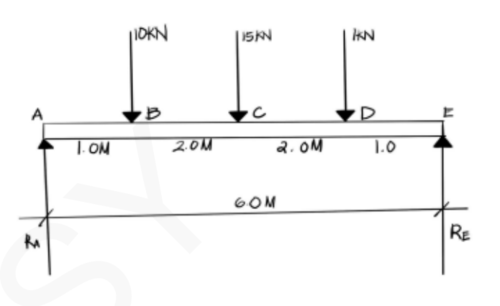
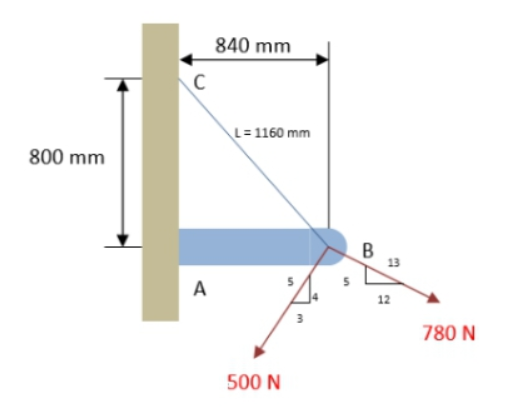
If the x- and y- components of the forces on the figure shown are -105 N and -200 N, respectively, what is the magnitude of the resultant force?
-225.90 N
Which of the is a “non-hookean” material?
Rubber
A kind of load that acts over a small distance that it can be assumed to act at a point
Concentrated Load
Force system whose lines of action pass through a common point
Concurrent
It is a structure made of two force members all pin is connected to each other
Truss
Force that inhibits change in the state of movement of a body
Reaction Force
The intensity of loading increases or decreases at a constant rate
Triangular Load
Deals with the relation between externally applied loads and internal effects.
Strength of Materials
A type of beam with at least three or more supports
Continuous Beam
An axis passing through the centroid of an area is known as a __________
Centroidal Axis
The action lines of all the forces are in the same plane and intersect a common point
Concurrent, Coplanar
Cantilevered beam is considered as:
Determinate Beam
Moment of Inertia is used for the stress calculations of________
Moment
The resultant of two forces which is the diagonal formed on the vectors of this force.
Parallelogram Law
Each action has a reaction equal in magnitude and opposite in direction
Newton’s 3rd Law
The measure of tendency of a force to make a rigid body rotate about a fixed axis
Moment
Two forces 3 N and 4N are perpendicular to each other the resultant of the two forces is
5 N
A 5cm-diameter 80cm long steel bar is restrained from moving. If its temperature is increased 100 deg. C, determine the induced compressive stress? For steel = 11.7 x 10.6 per degree C, E = 210 GP
246000kpa
The slope of the stress and strain
Modulus of Elasticity
Strain is deformation divided by _______
Length
This method uses the free body diagram of joints in the structure to determine the forces in each member
method of joints
Some members in the truss which cannot carry load
Zero Force member
Centroid is used to determine if the building is
Stable
A type of beam with either or both ends extending beyond the support
Overhanging Beam
What is the unit of stress?
Pascal
It is the intensity of the force.
Magnitude
Unit of force
Newton
Quantities having both magnitude and direction
Vector
When several forces act in a given situation
System of Forces
A beam that is simply supported at both ends is called
Simple Beam
What kind of curve is the Uniformly Distributed Load in the shear diagram?
Second Degree Curve
Strength of materials refers to the tendency of the structure not to _______
Break
It is a type of beam which is restrained at both ends
Fixed beam
What is the unit of torque?
kN-m
Centroid is also called the axis of ________
Zero Stress
The safe load the material can carry
Proportional Limit
Deformation is a measure of the material’s ______________
Rigidity
The external effect of a force in a rigid body is the same for all point along its line of action
Principle of Transmissibility
Can be calculated if we have a rectangular coordinate system, one can define the area moment of interial around the axis
Area Moment of Inertia
Bolt double shear is an example of what stress
Bearing
When a machine shaft is subjected to torque, the stress is _______
Torsional
If an area has one line of symmetry the centroid will
lie somewhere along the line of symmetry
What will be the minimum diameter of a steel wire, which is used to raise a load of 4000 N if the stress in the rod is not to exceed 95 MN/m^2?
7.32 mm
The quantity of matter in a body is its _____
Mass
The stress in a rod is 70N/mm2 and the modulus of elasticity is 200000 N/mm2. What will be the strain in the rod?
0.00035
The types of normal stresses are shear and bending.
False
What is the unit of compressive stress?
N/mm^2
Shear force is diagram is a/an _______ representation of shear force plotted as ordinate
Graphical
A tensile test was conducted on a steel bar. The load of elastic limit was 250 kN and the diameter of the steel bar was 3cm. What will be the value of stress?
35368 x 10^4N/m^2
The phenomenon of slow growth of a strain under a steady tensile stress is called __________.
Creeping