Alcohols Reactions TO Various Things
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Type of reaction alcohol to alkene
E1 or E2 dehydration
Type of reaction alcohol to alyl halide
substitution (S1 or S2)
Type of reaction alcohol to ehter
Substitution
alcohol reaction to alkenes
Remember dehydration, taking away a water (OH and H). Can be done under basic conditions or acidic conditions. Either OH- or H3O under heat.
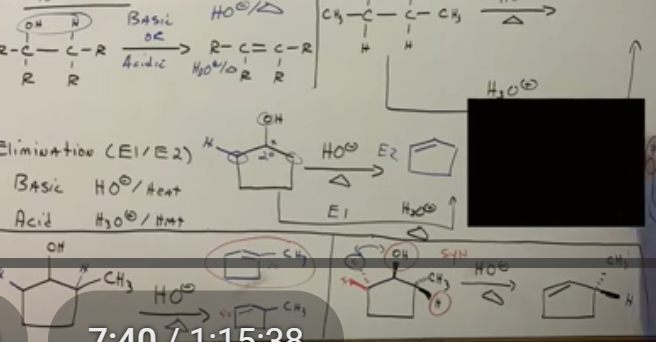
Beta hydrogens number meaning alcohols to alkenes
The number of beta hydrogens = number of products.
When E2 reactions occur
When you have a beta hydrogen ANTI to the leaving group. E2 reactions usually happen more often. The anti one leaves
Primary alcohol to alkenes under acidic conditions
Happens under E2 ONLY. The elimination occurs at the beta protons and bond forns between main and beta carbon.
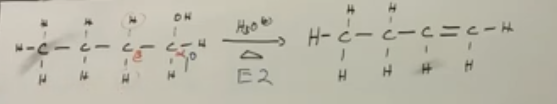
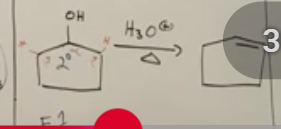
Secondary and tertiary alcohols to alkenes under acidic conditions
E1 is the primary way to dehydrate.
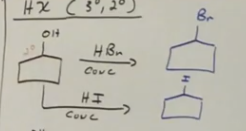
Alochol to alkyl halides reagents of HCl HBr or HI conc
Limited to secondary and tertiary alcohols. There tend to have multiple products (inversion OR retention of config).
Alcohol to alkyl halides reagents of SOCl2 in presence of pyr, PBr3 (sometimes the PCl3 or PCl5 but don’t need to remember that)
Mainly primary as well as secondary alcohols. These tend to have retention of configuration
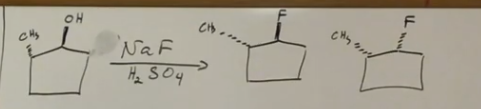
Using salts for alcohols to alkyl halides
NaBr, NaCl, NaI, or NaF, adds the halide to the alkyl halide.
simple alc to alkyl halide
Can use mineral acids because second degree (or 3rd)
What about in alcohol to alkyl halide when it shows two products? inversion of config and retention of config.
inversion of config and retention of config. The inversion gives us two different products.
alcohol to alkyl halide with salt
two products!! using the salts and mineral acids will give two products.
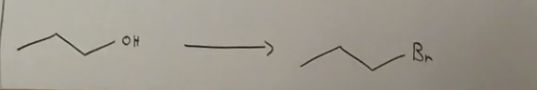
What reagent used here?
PBr3 because it is a primary alcohol!! the HBr is only for secondary and tertiary alcohols.
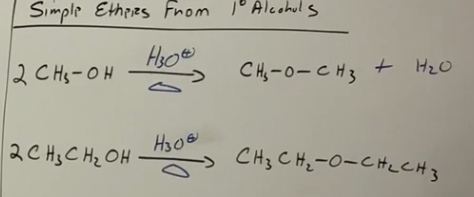
primary alcohols to ethers
Acidic reagents with heat. this is known as SIMPLE ether formation, because if you use H3O+ and heat with a secondary or tertiary alcohol, you can make an alkene. Makes symmetrical ethers. By product is water or alkene in given case.
Secondary or tertiary alcohol to ether - and the process name
This makes more complex and asymmetric ethers. The Williamson ethie synthesis. The first step is a base and the second step is whatever the SECOND R group is.
Bases used for synthesis of ethers from alcohols reaction (Williamson ethie synthesis)
NaOH followed by an alkylating reagent like CH3I, or NAH (more selective aggressive base) followed by CH3Cl