Photosynthesis and Calvin Cycle: Key Concepts for Biology
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Photo
Convert solar energy to chemical energy (ATP)
Synthesis
Building organic molecules (glucose) from inorganic nutrients (CO2 + H20)
What is the formula for photosynthesis?
CO2 + H2O --> C6H12O6 + O2
Photo in photoautotroph's
Convert solar energy to chemical energy (ATP)
Autotroph in photoautotroph's
building organic molecules from inorganic nutrients (CO2 + H2O)
Marine Phytoplankton
algae, diatoms, photosynthetic bacteria, photosynthetic protists
What do marine phytoplankton do?
maintain our oxygen rich atmosphere as we know it
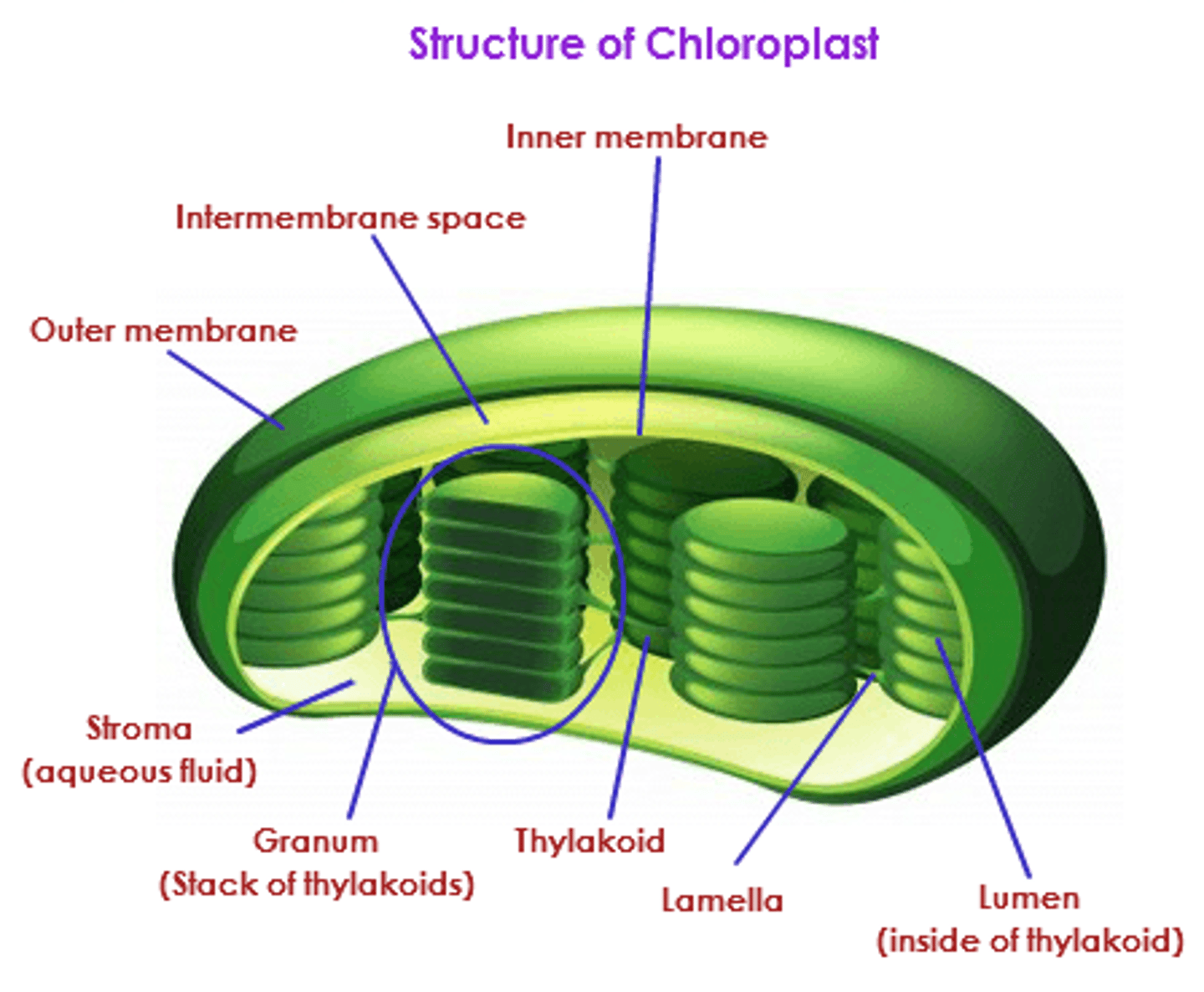
What is at the thylakoid membrane?
ETC
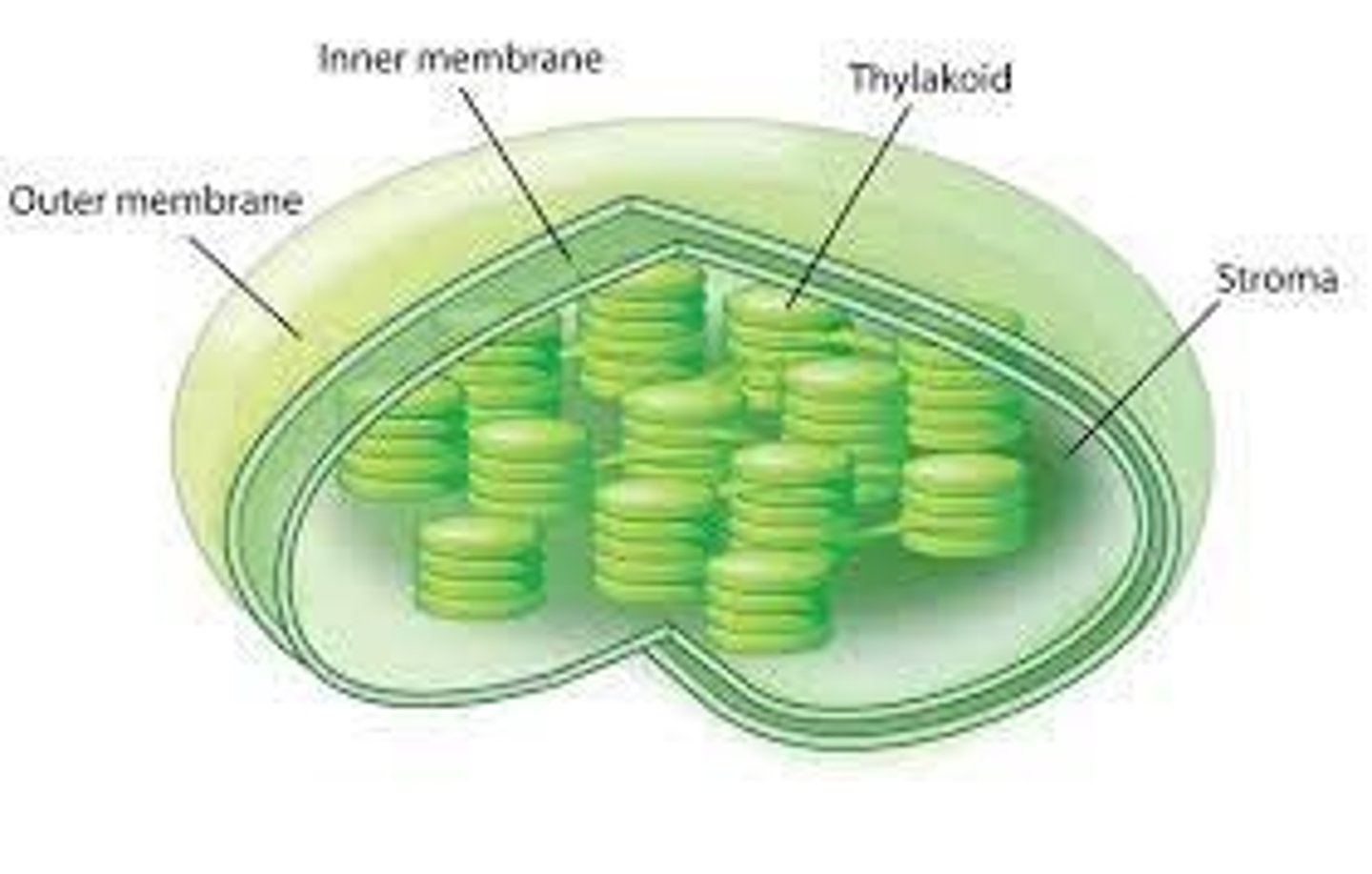
What is at the thylakoid space?
H+ gradient
What is at the stroma?
Calvin cycle
Visible light
a narrow range of electromagnetic radiation that we can detect
Why do molecules appear white?
because most molecules reflect all wavelengths of visible light
Pigments
molecules that absorb some wavelengths of light and reflect others so they appear the color of the wavelengths they reflect
Green plants use two pigments in photosynthesis called?
chlorophyll alpha (Ca) and chlorophyll beta (Cb)
What colors do Ca and Cb most effectively absorb?
red and blue light and reflect green light
What are carotenoids?
a class of pigment not used in photosynthesis
What is the function of carotenoids?
maybe absorb extra light to prevent sun damage reflecting yellow, orange, and red
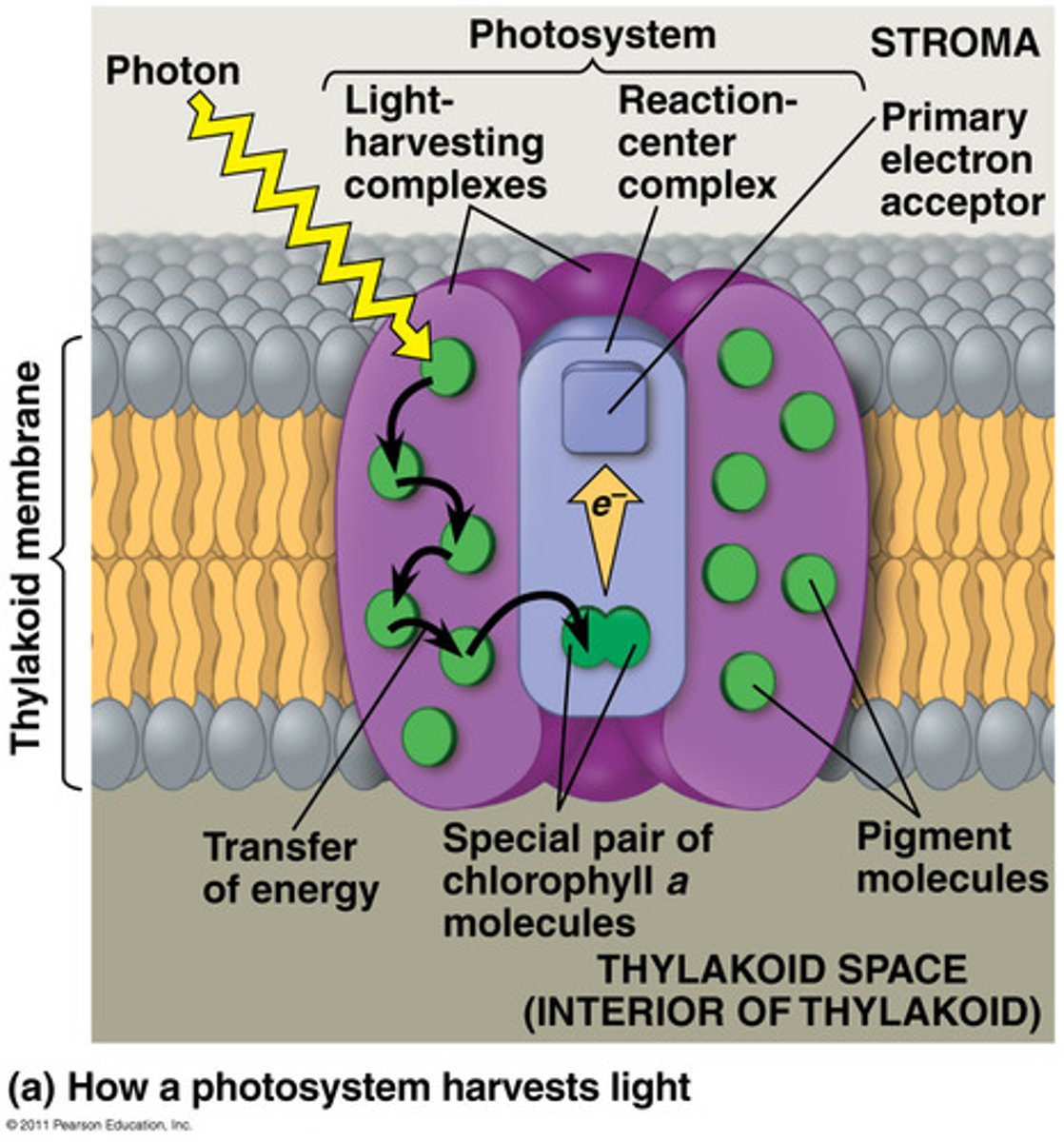
Where are photosystems located?
They are embedded in the thylakoid membrane
What is the Light Harvesting Complex?
Where the chlorophylls are, can be Ca and/or Cb
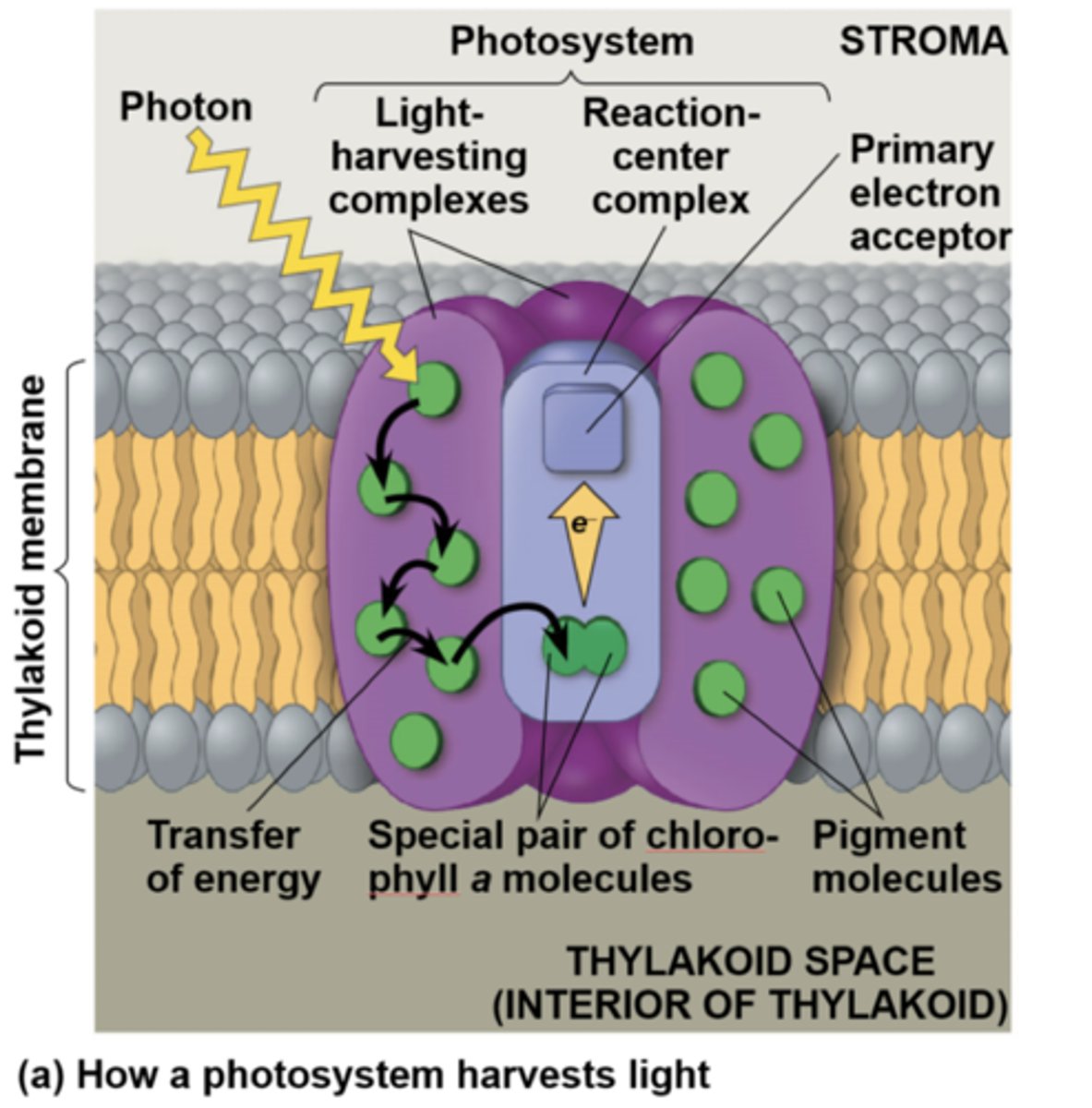
What happens at the LHC?
light strikes a chlorophyll and an e- jumps to a higher shell and immediately falls back
How is energy passed through the LHC?
Energy is passed laterally from one chloroplast to the next, until it reaches the special pair in the Reaction Center Complex
What does the Reaction Center Complex have?
It has a special pair of chlorophyll alphas bound together
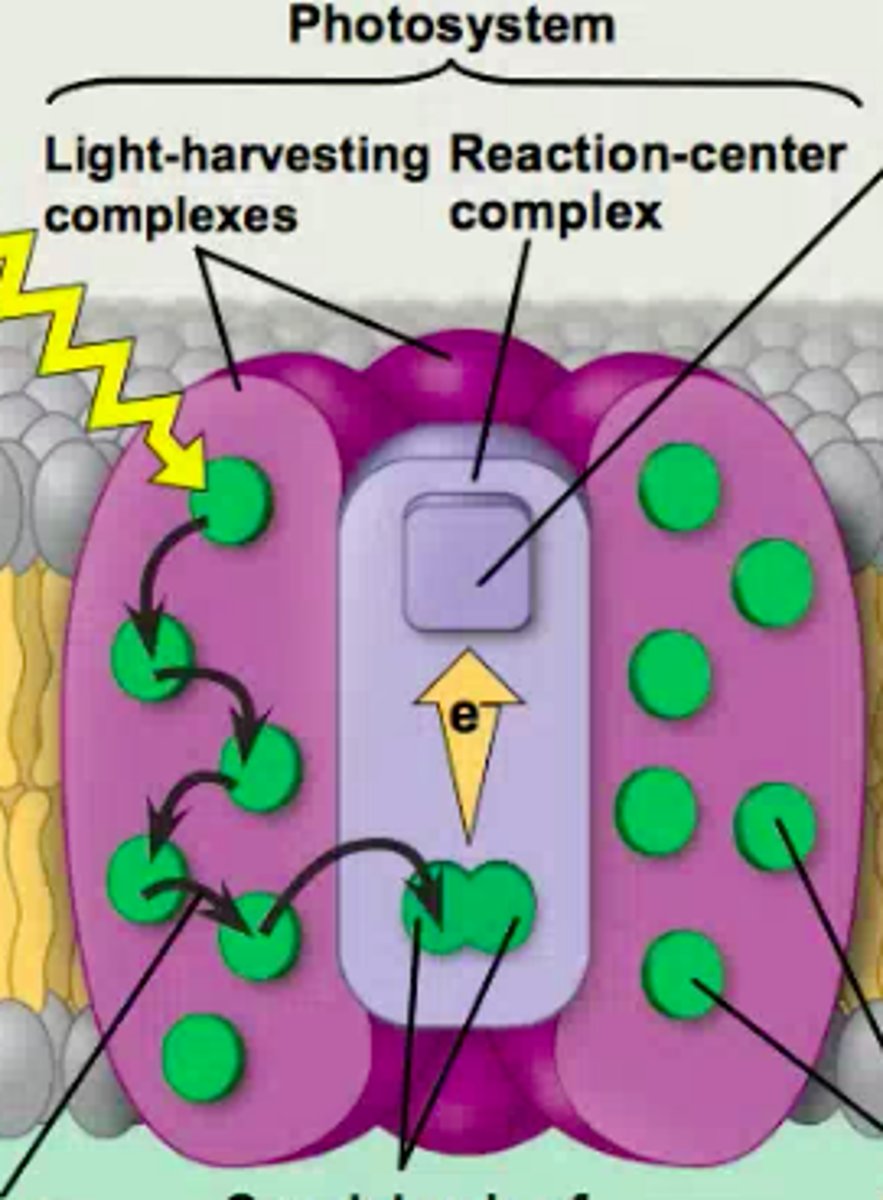
When the e- at the special pair jumps, what is it picked up by?
It is picked up by the primary e- acceptor
Which photosystem has a special pair of P680?
photosystem 2
What happens first in photosystem 2?
P680s e- goes down an ETC
After P680s e- goes down an ETC, what happens?
H+ are shuttled from the stroma into the thylakoid space.
From there, what is established in the thylakoid space?
A H+ gradient
What allows H+ in the thylakoid space to diffuse back into the stroma
ATP Synthase
What does having H+ in the thylakoid space to diffuse back into the stroma generate?
it generates ATP in the stroma, Photophosphorylation
How does P680 replace the lost e-?
by taking e- from H2O
When H2O breaks down, what do the oxygens that recombine form?
O2 gas
Which photosystem has a special pair of P700?
Photosystem 1
P700s e- are sent to e- carrier NADP+ to form what?
NADPH in the stroma, these e- are used in the Calvin cycle
P700 replaces lost e- by?
taking P680's e- from the ETC, takes e- from the ETC to replace lost e-
The calvin cycle uses more ATP than e-, so what occurs?
an imbalance is created, too much NADPH and too little ATP
What corrects the imbalance?
cyclical flow of e-, NADPH gives its e- back to the ETC to regenerate extra ATP
What is the "synthesis" part?
The calvin cycle
What is the first step in the calvin cycle?
carbon fixation
What happens in carbon fixation
converts CO2 gas to a solid by attaching it to another molecule as a carboxyl
In carbon fixation, it does this by attaching it to ribulose bis phosphate as a carboxyl with the help of enzyme rubisco, creating what?
an unstable 6 carbon molecule that splits into 2 PGAs
After carbon fixation converts CO2 gas to a solid by attaching it to another molecule as a carboxyl, what happens
you start with 3 ribulose bisphosphates, the enzyme rubisco then fixes 1 CO2 to each of the 3 RuBPs. This results in 6-C compound that is so unstable that it immediately breaks into two
When the unstable 6-C compound breaks into two it ends?
with 6 PGAs
What is the second step of the calvin cycle?
Reduction
What happens in reduction?
ATP transfers Phosphate to the PGAs which destablilizes PGA
After destabilizing the PGA, what happens
PGA accepts e- from NADPH and PGA expels extra Phosphate
At the end of reduction, what is left?
6 Glyceraldehyde-3 Phosphates ( 6 G3Ps)
What is the third step of the calvin cycle?
release
What happens in release?
one G3P molecule is released to other metabolic pathways
What is the fourth step of the calvin cycle?
regeneration
What happens in regeneration?
The remaining 5 G3Ps are turned back into 3 RuBPs
What is a stomata?
sites of gas exchange on the leaf, CO2 into the stomata, O2 and H2O out
The stomata can be...
opened and closed
In hot, dry weather the plant does what?
the plant closes the stomata to prevent water loss and photorespiration
When the stomata are closed, what happens
it prevents gas exchange from occuring in the leaf, CO2 levels fall and O2 levels rise, bad since photorespiration may occur
What is photorespiration?
Bad because Rubisco fixes O2 to RuBP instead of CO2, which causes RuBP to be broken down/lost
What mechanisms are there to prevent photorespiration?
C4 plants and CAM plants
What are C4 plants?
grasses like corn, wheat, oats, etc
What do C4 plants do?
has a second enzyme PEPco, which has no affinity for O2 (won't bind)
What are CAM plants?
succulents
What do CAM plants do?
only open stomata at night. CO2 is stored as an acid until day