Monomers, Polymers, and Macromolecules – Video Notes Review
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study flashcards covering carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, and key concepts like condensation vs. hydrolysis, enzyme characteristics, and base biology.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What are the monomer and polymer forms of carbohydrates?
Monosaccharide is the monomer; polysaccharide is the polymer.
What are the monomers of Lipids
Fatty acid
What are the Polymers of Lipids
Triglyceride
What is the monomer for proteins?
Amino acid (which forms proteins/polypeptides).
What is the Polymers for proteins?
Polypeptide
What are the monomers of nucleic acids?
Nucleotide
What are the Polymers of Nucleic acid
DNA,RNA
What is condensation reaction?
A reaction that fuses monomers together by removing a water molecule.
What is hydrolysis?
Uses water to split polymers into monomers.
What suffix do many enzymes have?
End in -ase (e.g., lactase, helicase, DNA polymerase).
What happens to enzymes if they are outside their optimal temperature or pH range?
They denature or break down.
Which elements make up proteins?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, and Nitrogen (C, H, O, N).
What functional groups are found in amino acids?
Amino group and carboxyl group.
What does DNA stand for?
Deoxyribonucleic acid.
What are the four bases in DNA?
Guanine (G), Cytosine (C), Adenine (A), Thymine (T).
Which bases are Purines and how many rings do they have?
Purines are Adenine and Guanine; they have two rings.
Which bases are Pyrimidines and how many rings do they have?
Pyrimidines are Cytosine and Thymine (and Uracil in RNA); they have one ring.
What is the general carbohydrate formula and its typical ring structure?
Formula C:H:O in a 1:2:1 ratio (e.g., C6H12O6); often drawn as a hexagon or pentagon ring.
How do carbohydrate names typically end and give examples?
End in -ose; examples include glucose, dextrose, maltose.
What roles do carbohydrates play in biology?
Short-term energy; signals in cells; form plant cell walls (cellulose).
What are the main roles of lipids?
Long-term energy storage; insulation; most hormones are lipids; cell membranes are phospholipid bilayers; nonpolar and water-insoluble.
What do proteins do in the body besides making up structures?
They act as enzymes (natural catalysts) to accelerate reactions.
What is the basic unit of nucleic acids and its role?
Nucleotides; they form DNA/RNA, carrying genetic material and code.
What is the DNA base pairing rule?
Guanine pairs with Cytosine; Adenine pairs with Thymine.
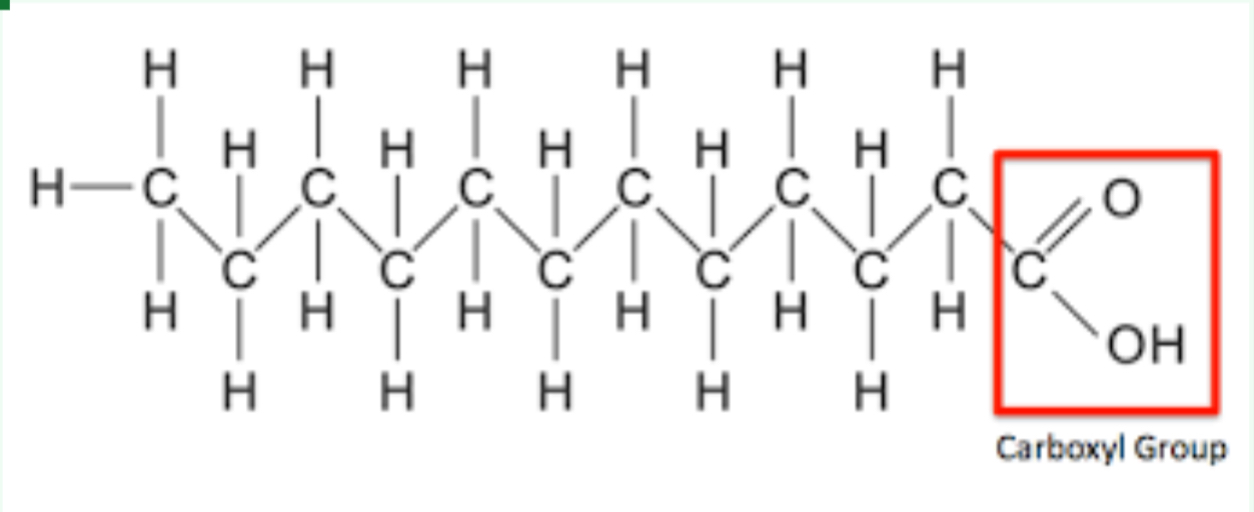
What molecule structure is this
Lipids
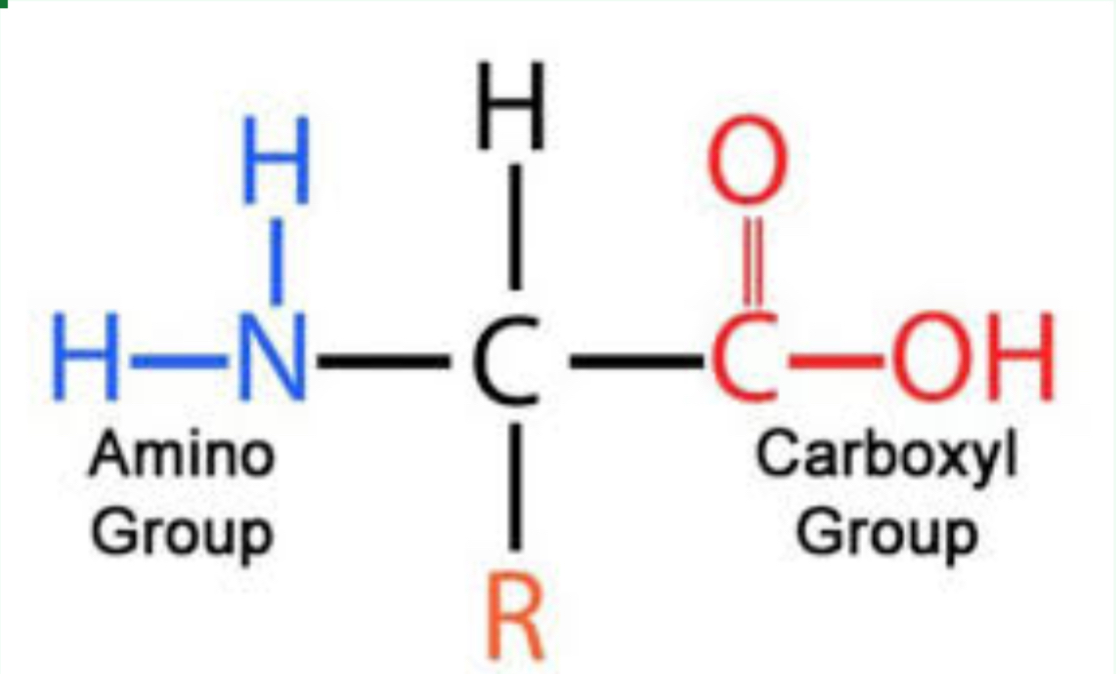
What molecule structure is this
Proteins
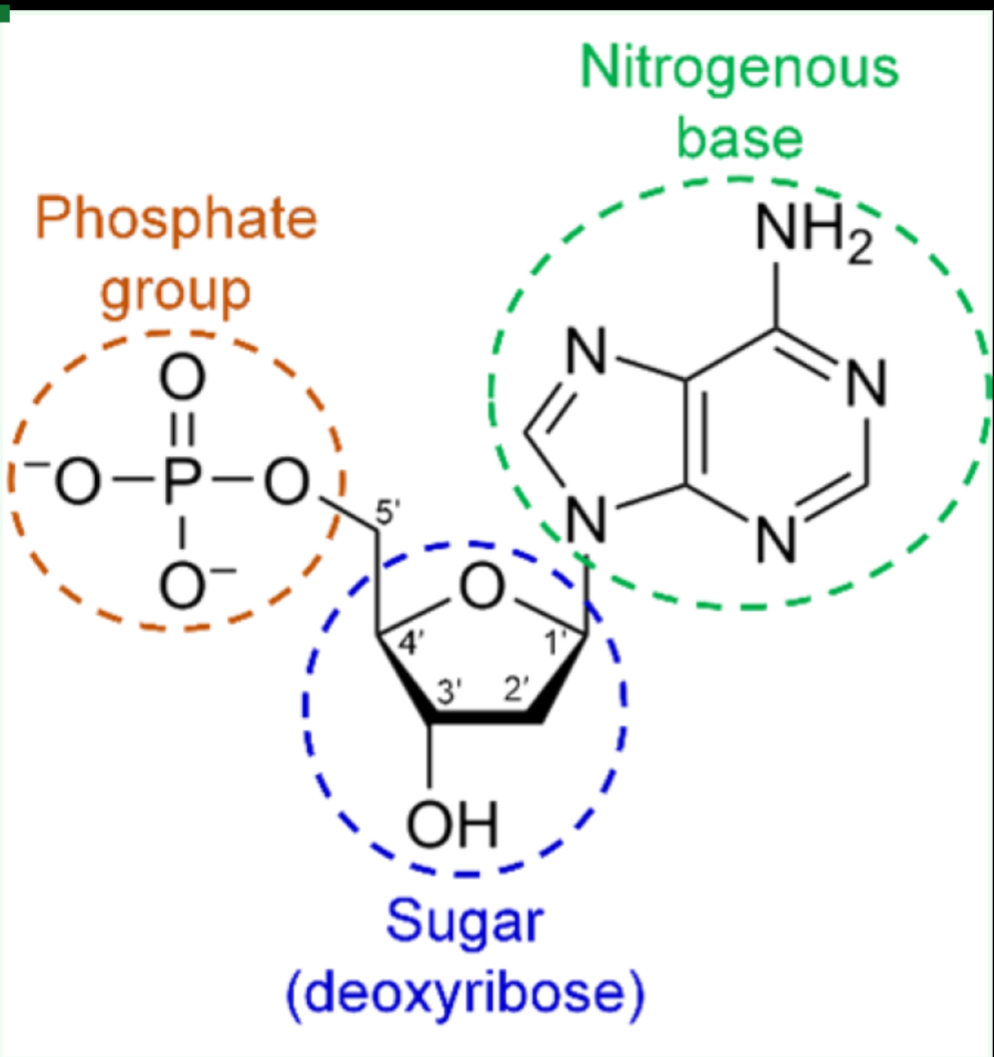
What molecule structure is this
Nucleic Acids
“What is Cohesion in water”
Cohesion in water refers to the attraction between water molecules due to hydrogen bonding, which allows them to stick together. This property contributes to phenomena such as surface tension.
“What is Adhesion in water”
Water molecules sticks to other substances, The Charged end of the water molecules are attracted to charged surfaces.
What is Surface tension in water
The layer on the surface of water that resists breaking
“What is High specific heat in water”
High specific heat in water refers to its ability to absorb and retain heat without a significant change in temperature, which is crucial for regulating climate and supporting life.
“What is Heat of vaporization in water”
Heat of vaporization in water refers to the amount of energy required to convert water from a liquid to a gas at its boiling point, which plays a significant role in temperature regulation and water cycling in the environment.
“What is Evaporative cooling in water”
As water evaporates the heat is removed cooling the surface, The molecules with the highest kinetic energy break hydrogen bonds down lowering the average temperature.