Veterinary Dentistry Workbook
1/261
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
262 Terms
The tip of the tooth root
Apex
The study and treatment of the inside of the tooth and periapical tissues
Endodontics
The condition in which the mandible is abnormally short in relation to the maxilla
Brachygnathism
The area between the roots of a multirooted tooth
Furcation
Tooth decay that results from demineralization of hard tooth structures by acid-producing oral bacteria
Caries
Term for mammals that have two sets of teeth (primary and deciduous)
Diphyodont
The term used to indicate an upper jaw that is wider than the lower jaw (normal in most species)
Anisognathism
Having a wide skull and short maxilla
Brachycephalic
Light brown or yellow, raised, mineralized deposit adherent to the tooth and root surfaces
Calculus
Anatomic term describing the attachment structures of the teeth
Periodontium
Tooth structure that consists of nerves, blood vessels, lymphatics, and connective tissue
Pulp
Tooth type that has a large reserve crown and root structure that allows for continued growth over an animal’s lifetime
Hypsodont
Diffuse inflammation of the entire oral cavity
Stomatitis
Hard layer covering the surface of the root of a tooth
Cementum
Having a narrow skull and long maxilla
Dolichocaphalic
The extraction of diseased teeth
Exodontics
Gap between teeth seem normally in many species
Diastem
Tooth type in which the crown is relatively small compared with the size of the well-developed roots
Brachyodont
Inflammation of the gingiva
Gingivitis
Thin layer covering the crown that is the hardest tooth substance
Enamel
The most commonly used system of numbering teeth
Triadan System
Misalignment of the teeth or jaws
Malocclusion
Having a well-proportioned skull width and maxillary length
Masocephalic
Inflammation of the gingiva and other supporting tooth structure
Periodontitis
A white-tan film that collects on teeth and is composed of bacteria, exfoliated cells, food debris, and saliva
Plaque
The most rostral teeth in cats and dogs; used for gnawing and grooming
Incisors
Having two sets of teeth
Diphyodont
The type of teeth seen in horses, rodents, and lagomorphs
Hypsodont
Large teeth found caudally to premolars
Molars
Primary or “baby” teeth
Deciduous
Spatial relationship of teeth within the mouth
Occlusion
Adjective used to describe the largest shearing tooth of the upper and lower jaws in carnivres
Carnassial
Smooth convex bulge located on the palatal side of the gingival third of incisor teeth
Cingulum
Teeth used for prehending and holding
Canine
Describe the adjacent or near-adjacent surfaces of teeth
Masial, distal
Using the numeric Triadan system for tooth identification saves time when performing detailed dental charting. Match each canine or feline tooth listed with its corresponding Triadan number by writing the appropriate number in the space provided. Not all teeth are present in a normal adult cat. Write “not present” if the tooth listed is not present in a normal adult cat.
Canine Left Maxillary Second Incisor Tooth
#202
Using the numeric Triadan system for tooth identification saves time when performing detailed dental charting. Match each canine or feline tooth listed with its corresponding Triadan number by writing the appropriate number in the space provided. Not all teeth are present in a normal adult cat. Write “not present” if the tooth listed is not present in a normal adult cat.
Feline Right Mandibular Third Premolar Tooth
#407
Using the numeric Triadan system for tooth identification saves time when performing detailed dental charting. Match each canine or feline tooth listed with its corresponding Triadan number by writing the appropriate number in the space provided. Not all teeth are present in a normal adult cat. Write “not present” if the tooth listed is not present in a normal adult cat.
Canine Left Maxillary Second Molar Tooth
#210
Using the numeric Triadan system for tooth identification saves time when performing detailed dental charting. Match each canine or feline tooth listed with its corresponding Triadan number by writing the appropriate number in the space provided. Not all teeth are present in a normal adult cat. Write “not present” if the tooth listed is not present in a normal adult cat.
Canine Right Maxillary Canine Tooth
#104
Using the numeric Triadan system for tooth identification saves time when performing detailed dental charting. Match each canine or feline tooth listed with its corresponding Triadan number by writing the appropriate number in the space provided. Not all teeth are present in a normal adult cat. Write “not present” if the tooth listed is not present in a normal adult cat.
Feline Left Mandibular Second Premolar Tooth
Not Present
Using the numeric Triadan system for tooth identification saves time when performing detailed dental charting. Match each canine or feline tooth listed with its corresponding Triadan number by writing the appropriate number in the space provided. Not all teeth are present in a normal adult cat. Write “not present” if the tooth listed is not present in a normal adult cat.
Feline Right Mandibular Third Incisor Tooth
#403
Using the numeric Triadan system for tooth identification saves time when performing detailed dental charting. Match each canine or feline tooth listed with its corresponding Triadan number by writing the appropriate number in the space provided. Not all teeth are present in a normal adult cat. Write “not present” if the tooth listed is not present in a normal adult cat.
Canine RIght Maxillary Fourth Premolar Tooth
#108
Using the numeric Triadan system for tooth identification saves time when performing detailed dental charting. Match each canine or feline tooth listed with its corresponding Triadan number by writing the appropriate number in the space provided. Not all teeth are present in a normal adult cat. Write “not present” if the tooth listed is not present in a normal adult cat.
Feline Right Maxillary First Premolar Tooth
Not Present
Using the numeric Triadan system for tooth identification saves time when performing detailed dental charting. Match each canine or feline tooth listed with its corresponding Triadan number by writing the appropriate number in the space provided. Not all teeth are present in a normal adult cat. Write “not present” if the tooth listed is not present in a normal adult cat.
Canine RIght mandibular Third Molar Tooth
#411
Using the numeric Triadan system for tooth identification saves time when performing detailed dental charting. Match each canine or feline tooth listed with its corresponding Triadan number by writing the appropriate number in the space provided. Not all teeth are present in a normal adult cat. Write “not present” if the tooth listed is not present in a normal adult cat.
Feline Left Mandibular Fourth Premolar Tooth
#308
Using the numeric Triadan system for tooth identification saves time when performing detailed dental charting. Match each canine or feline tooth listed with its corresponding Triadan number by writing the appropriate number in the space provided. Not all teeth are present in a normal adult cat. Write “not present” if the tooth listed is not present in a normal adult cat.
Canine Deciduous Right Maxillary First Incisor Tooth
#501
Using the numeric Triadan system for tooth identification saves time when performing detailed dental charting. Match each canine or feline tooth listed with its corresponding Triadan number by writing the appropriate number in the space provided. Not all teeth are present in a normal adult cat. Write “not present” if the tooth listed is not present in a normal adult cat.
Feline DEciduous Left Mandibular Canine Tooth
#704
Root debridement, gingival curettage, and periodontal surgery are often required
Grade III periodontal disease
Inflammatory changes are confined to the gingiva (gingivitis)
Grade I periodontal disease
Root debridement or subgingival curettage may be required
Grade II periodontal disease
Periodontitis where 50% or more of the attachment structures of the tooth have been lost
Grade IV periodontal disease
Early form of periodontitis
Grade II periodontal disease
This grade is easily reversible with a routine dental cleaning
Grade I periodontal disease
Periodontitis where 35% to 50% of attachment structures of the tooth have been lost
Grade III periodontal disease
Early attachment loss is present
Grade II periodontal disease
Fair to guarded prognosis to save affected teeth
Grade III periodontal disease
Frequently, affected teeth cannot be saved
Grade IV periodontal disease
Toothbrush bristles are placed along the gingival margin and the sulcus
Bass brushing tachnique
A gentle sweeping motion of toothbrush bristles is directed apical to coronal
Modified Stillman brushing technique
Toothbrush bristles do not enter the sulcus
Modified Stillman brushing technique
The bristles are directed at a 45-degree angle toward the marginal gingiva
Bass brushing technique
Tooth bristles are placed apical to the gingival margin
Modified Stillman brushing technique
Toothbrush bristles enter the gingival sulcus
bass brushing technique
A mesial to distal motion of brushing is employed
Bass brushing technique
Sometimes used in areas of periodontal surgery
Modified Stillman brushing technique
Onset of effect in 6 to 10 minutes
Bupivacaine 0.5%
Onset of effect in 2 to 5 minutes
Lidocaine 2%
Duration of action 0.5 to 2 hours
Lidocaine 2%
Duration of action 4 to 8 hours
Bupivacaine 0.5%
Most commonly used local anesthetic in veterinary dentistry
Lidocaine 2%
For this block, the needle is inserted perpendicular to the soft palate just caudal to the molar approximately ½ cm deep in cats and 1 cm deep in dogs
Maxillary nerve block
The foramen for this block is located dorsal to the roots of the maxillary third premolar
Infraorbital nerve block
This block affects sensation of the soft tissue and bone of the entire ipsilateral mandible
Inferior alveolar nerve block
This block may cause numbness of the tongue and therefore self-inflicted trauma
Inferior alveolar nerve block
The foramen for this block is located below the mesial root of the mandibular second premolar
Middle mental nerve block
The foramen for this block is located caudal and ventral to the mandibular third molar in the dog and the mandibular first molar in the cat
Inferior alveolar nerve block
This block requires a needle that is bent 1 cm from the tip
Maxillary nerve block
This block is placed just caudal to the maxillary second molar in the dog or the maxillary first molar in the cat
Maxillary nerve block
This block helps prevent sensation to the ipsilateral mandible rostral to the labial frenulum
Middle mental nerve block
Lidocaine may be the preferred local anesthetic for this block
Inferior alveolar nerve block
This block causes a loss of sensation rostral only to the third premolar on the ipsilateral maxilla
Infrairbital nerve block
This block prevents sensation of the entire maxillary quadrant on the buccal and palatal sides of the teeth
Maxillary nerve block
This block has an intraoral and extraoral approach described
Inferior alveolar nareve block
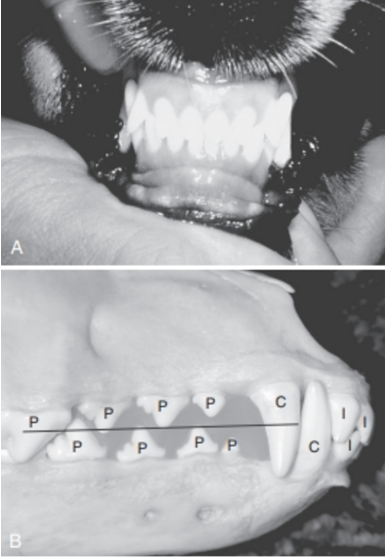
Identify this type of occlusion.
Normal Scissors Occlusion
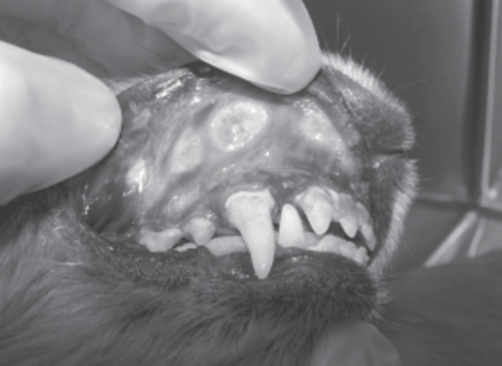
Identify this lesion in the dog.
Chronic Ulcerative Paradental Stomatitis
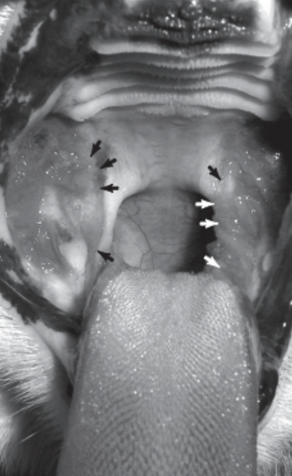
Identify this lesion in the cat that is lateral to the palatoglossus folds (see arrows)
Lymphocytic-Plasmocytic Stomatitis
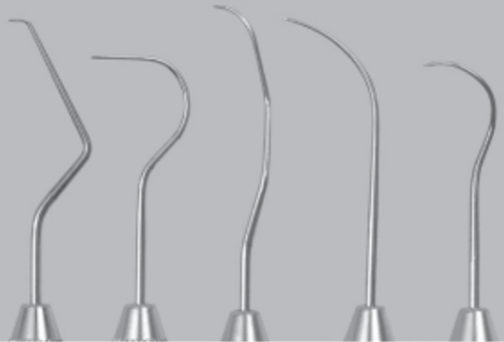
identify these instruments and their uses
Dental Explorers: used to determine the surface of topography of the tooth.
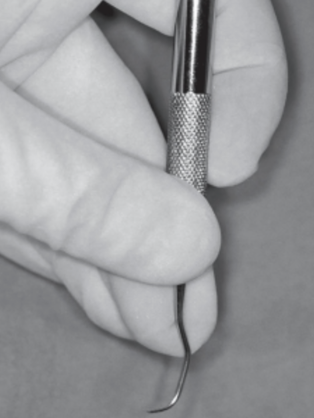
Identify this method of holding a dental instrument
Modified Pen Grasp
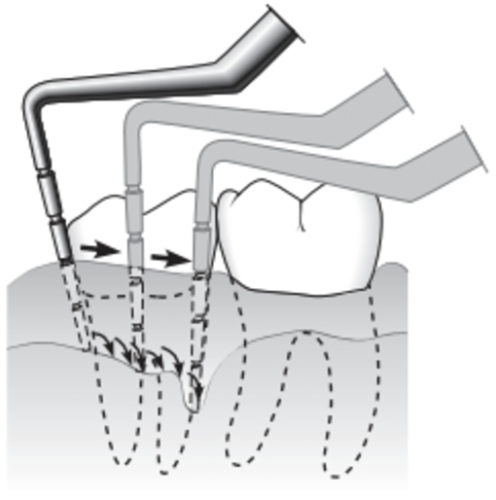
Identify this instrument and describe its proper use
The periodontal Probe; used to determine gingival sulcus depth. It is “walked” around the tooth circumference with short up and down strokes every few millimeters.
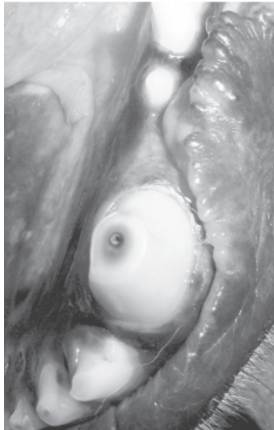
Identify this lesion. What instrument is used to confirm the diagnosis?
Pulp exposure caused by abrasion. An explorer is used to confirm access to the pulp chamber
Based on this picture, what is the measurement of the gingival sulcus of this patient?
3 mm
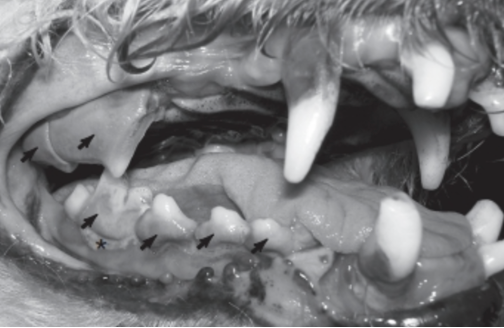
What accumulation is indicated by the asterisk in this picture? What subsequent formation is indicated by the arrows?
Plaque; Calculus
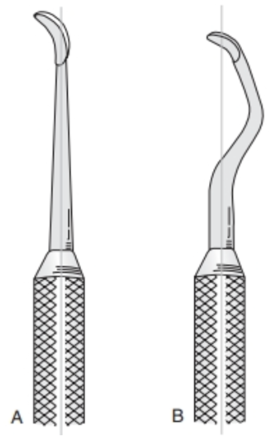
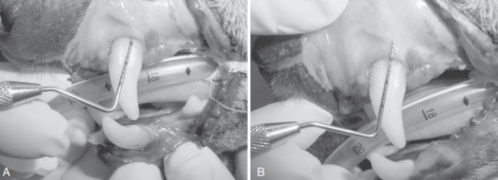
Which instrument (A or B) is better used for scaling the rostral portion of the mouth?
Instrument A
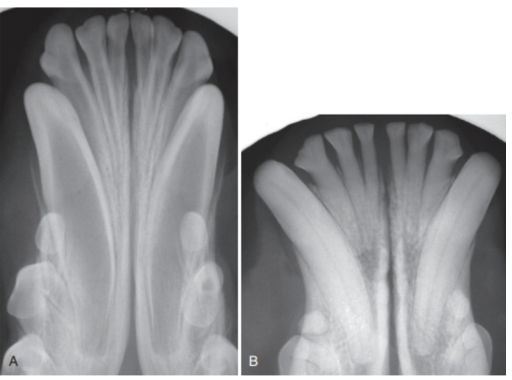
Which patient is older: A or B? How do you know this from looking at the radiographs?
Patient B is older based on the radiographic width of the pulp chamber. As an animal ages, the pulp chamber becomes narrower as a result of the continued playing down of secondary dentin
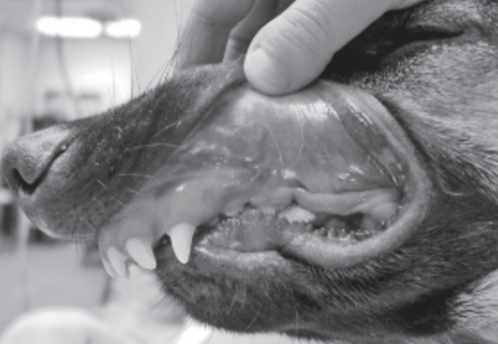
Identify this malocclusion by class
Class II
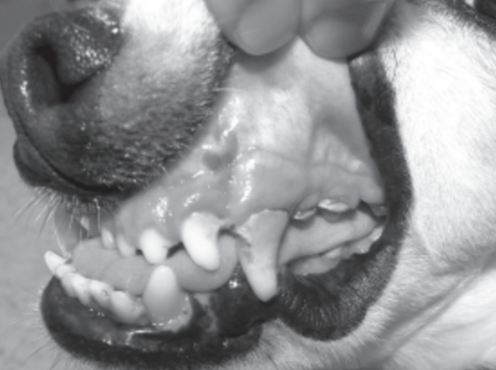
Identify this malocclusion by class.
Class III
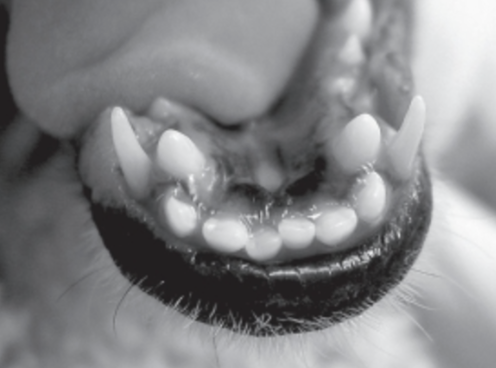
Identify the two malocclusions present in this patient.
a. Persistent Deciduous Canines
b. Lingually Displaced Mandibular Adult Canines
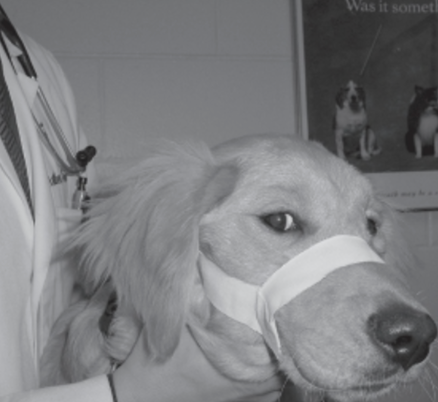

Describe this therapy and the most likely reason for its use.
a. Therapy
b. Reason for its use:
a. Tape Muzzle
b. Symphyseal (mandibular) fracture in a young growing dog

Identify these instruments, their use, and the species in which they are used.
a. Instruments:
b. What they used for:
b. Species:
a. Floats
b. Mechanical removal of raised areas/points from the occlusal surface of the teeth
c. Horse
Read the following statements and write “True” for true or “False” for false in the blanks provided. If a statement is false, correct the statement to make it true. Each dental or oral surgical procedure should begin with a comprehensive extraoral and intraoral examination.
True