Evidence Based Practice
1/163
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
164 Terms
what is evidence based practice?
the integration of best research evidence, clinical expertise, and patient values and circumstances used to make clinical decisions
what can influence EBP?
evidence can be influenced by the funding of research while patient preferences can be influenced by the culture, affordability, transportation, etc.
why are the benefits of EBP to the profession and patient care?
provides high quality care
decreasing unwarranted variation in practice
helps to deliver the best health outcome
enhance the value of our profession in order to increase health care quality, decrease medical errors, and decrease the consequences of unproven practices
what is the 5 step process for EBP?
1. Ask: specific questions
2. Find: evidence available
3. Appraise: identify strengths and weaknesses of article and be able to apply to the patient
4. Incorporate: how to use the evidence on patients
5. Self-evaluation: does it lead to another question
what are the barriers to EBP in clinical practice?
1. lack of time
2. decreased access to current research
3. lack of research skills/knowledge of research
4. poor quality evidence
5. confilicting evidence
6. barriers to application of evidence
7. remaining flexible and changing habits/attitude
8. lack of learning climate
what is evidence based practice NOT?
1. NOT a market-based practice: its not trying to create a lot of income or products
2. NOT a "cookbook" medicine: its not just taking the evidence and executing it. it involves taking your clinical expertise and patient preferences to adapt and figure out how to incorporate the evidence
what are the key points to consider when incorporating the evidence into clinical practice?
-is your patient similar to the participants in the study
-are the outcomes of the study consistent with your patients goals
-does the treatment align with your patients values and preferences
-is the treatment feasible in your setting?
-how does the treatmient fit into a comprehensive rehab program?
what are the two general approaches to how we ask a question in evidence based therapy?
1. Background: this is looking for information on the internet or in a textook about a certain topic, the diagnosis or medical information
2. foreground: looking for something direct or comparative or asking a more targeted question such as "what is the best intervention for my patient
What is PICO?
Patient or Problem: How would you describe the patient or their primary problem
Intervention: what main intervention are you considering
Comparison: what is the main alternatie to compare with the intervention; another treatment, control, placebo, etc
Outcomes: what are you trying to accomplish, improve or affect?
t/f questions may need to be redesigned multiple times to get an ideal amount of evidence
true
what is the evidence heirarchy?
From less to more bias

depending on the type of question, what is the best evidence?
-diagnosis: prospective, blind comaprison to a gold standard
-therapy/treatment: RCT>cohort>case control>case series
-prognosis: cohort study>case control>case series
-harm/etiology: RCT>cohort>case control>case series
-prevention: RCT>cohort study>case control>case series
-clinical exam: prospective, blind comaprison to a gold standard
what is the PICO 2.0 extension?
Patient or Problem: How would you describe the patient or their primary problem
Intervention: what main intervention are you considering
Comparison: what is the main alternatie to compare with the intervention; another treatment, control, placebo, etc
Outcomes: what are you trying to accomplish, improve or affect?
Type of question: is this a diagnosis, therapy, prognosis, etiology/harm, or prevention question
Type of study design: what study design would best answer this question?
what is research and why is it important?
research is a process of gathering proof of the truth
it’s important because clinicians rely on research as evidence for informing and supporting our clinical decisions. they pick a study design to best answer their specific question
discuss Clinical Practice Guidlines
systematically developed statements to assist practitioners and patient decisions about appropriate health care for specific circumstances
their goal is to provide clinicians with direct recommendations that they can use to make decisions based on available evidence grades
dicuss systematic reviews and meta-analyses.
systematic reviews: answer questions by systematically reviweing and describing ALL relevant available evidence. it attempts to synthesize available evidence to state what is known at this time
meta-analysis: synthesize findings from multipe studies to generate summary statistics. pools study samples together to create a larger sample and stronger evidence
discuss randomized control trials.
participants are randomly assigned to groups to compare interventions
pros: randomization helps isolate the effect of the intervention and reduce bias
cons: very specific focus and volunteer biasesd
discuss observational studies.
cohort studies: retrospective or prospective study of exposures and outcomes
case-control study: observation study design where cases have condition of interest.
these study designs do not show cause and effect, rather they attempt to understand correlations
discuss case studies or case series
typically have a smaller participant number from studying a rare condition
can provide detailed explanations of clinical intervention descriptions
provide evidence when there are barriers to other study design
con: limited generalizability of results
discuss narrative reviews and expert opinions
they provide clinical expertise, vision casting or calls to action when there is/are:
little available research or evidence on a topic
new or emerging events
a need to highlight/bring attention to
raise awareness for a new philosophy of thought
research is a systematic process for answering a question. what is this process?
develop a question
create a hypothesis
select a study design and collect data
test the hypothesis
interpret the findings
what is the null hypothesis vs alternative hypothesis?
null: there is no difference between two treatments
alternative: there is a significant difference between two treatments
what is the goal of research regarding the null hypothesis?
to reject the null— we first have to assume there is no difference until we can prove there is
what are the two ways to test a hypothesis?
one sided (or 1 tailed) test: these are directional. for example intervention A> intervention B. however the limitation here is that you can only test in one direction
two-sided (or 2 tailed) test: does not specify direction so intervention A ≠ intervention B. the limitation here is that further examination is then needed to determine “effect” of treatment
researchers want to provide evidence taht something is true (or works) for a certain population. this population is referred to as…
the target population
what is a sample?
a representative subset of the population
how do researchers use samples?
to make inferences about the target. the closer the sample matches the target population the more generalizable the results
what are the limitations of samples?
samples are always approximations. therefore researchers need to be mindful of…
the methods they use to select a sample
statistical plan to maintain a samples ability to make inferences about the target population
what is a variable?
characteristics of individuals, objects, or the environment
what are the types of variables?
independent: predector or explanatory; X variable; intervention tested
dependent: response; y variable; outcome of interested
measurements can be measured with increasing levels of measurement complexity to give different types of data. what are these ways?
from least complex to most complex:
nominal: categories
ordinal: order
interval: distance between has meaning
ratio: absolute zero
discuss nominal data
this is categorical data and categories have no mathemetical properties, rank or value
can be described as frequences and summarized with a mode statistic
ex: sex, eye color, marital status, medical diagnosis, race, geographic location
describe ordinal data
this is categorical but they have a rank, order, or value BUT there is no set distance between them.
can be described as frequences and summarized with a mode statistic
ex: manual muscle tests, level of assistance (min, mod, max), survey responses
discuss interval data
this is continuous data that has numerical values on a scale that have equal distances between them. but there is no zero point (values can be negative or positive.
described as mean, median, and mode
ex: temperature, calender year
describe ratio data
this is continuous data that has numerical values on a scale that have equal distances between them. but there there IS a zero point (values cannot be negative)
described as mean, median, and mode
ex: height, walking speed, walking distance, time to complete task
________ data is the first step to understanding it.
visualizing
what is central tendency?
used to describe measures that tell us about the center of a distribution of data
what are the central tendencies"?
mean, median, mode
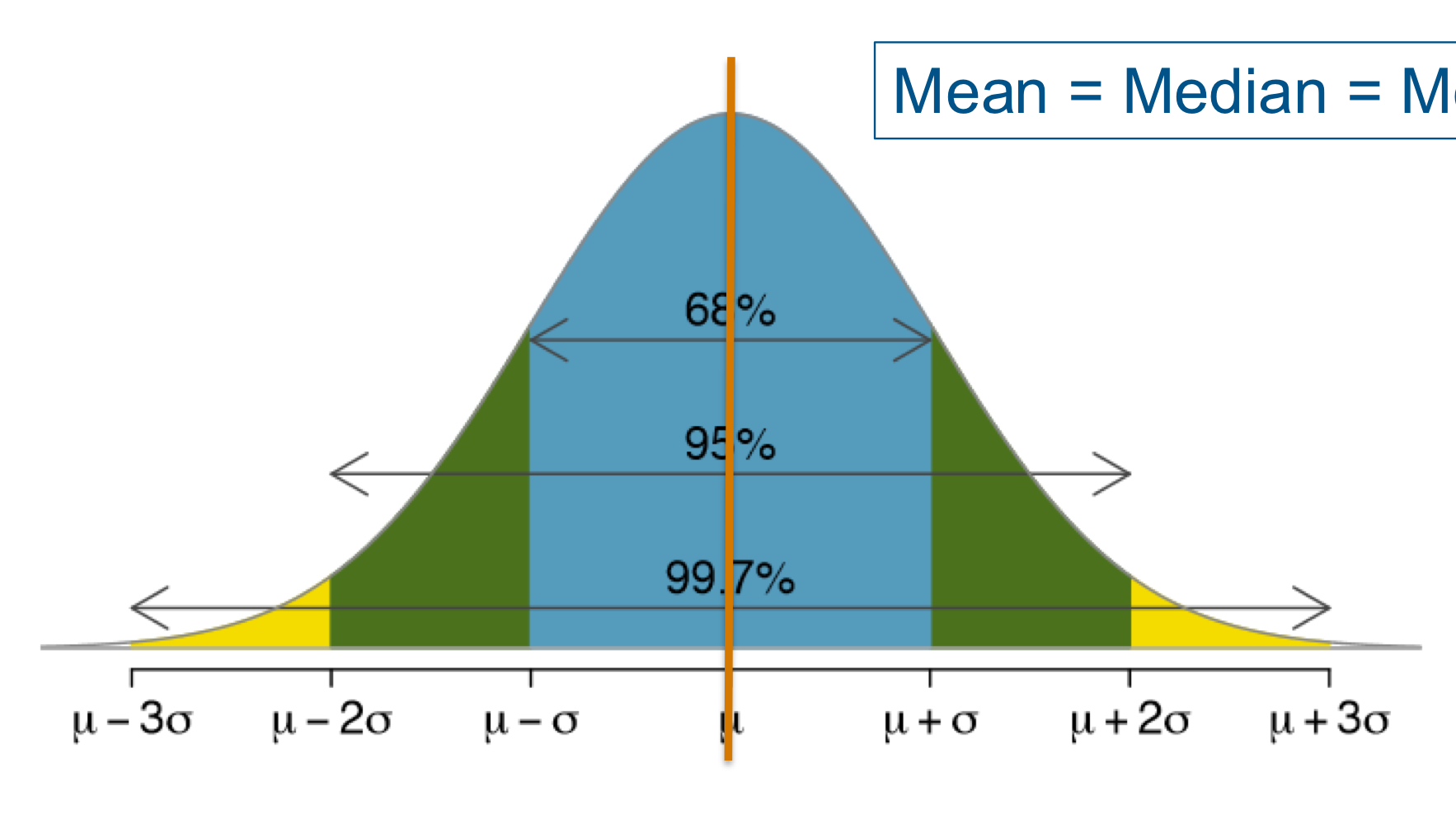
what is special about a normal distribution or parametric data?
the mean, median, and mode are all equal
it is representative of the variation in a population for a given characteristics
is is an assumption for many statistical tests
what is special about non-normal or non-parametric data?
the mean follows the tail while the mode is at the most frequent variable. the median is between these and best used to see the central portion of what most people demonstrate in a non-normal curve
non-normal distribution ≠ bad data— many variables in PT are not normally distributed and thats ok
what are the two types of skewed distributions?
left or negatively skewed: asymmetrical with mean shifted to the left
right or positively skewed: asymmetrical with the mean shifted to the right

_________ and _________ combine to better describe how data is distributed
measures of variability and measures of central tendency
what are the measures of variability?
range
standard deviation
coefficient of variation
z scores
standard error of the mean
confidence intervals
discuss range
the maximum value-the minumum value
its the simplist way to understand the spread of the data
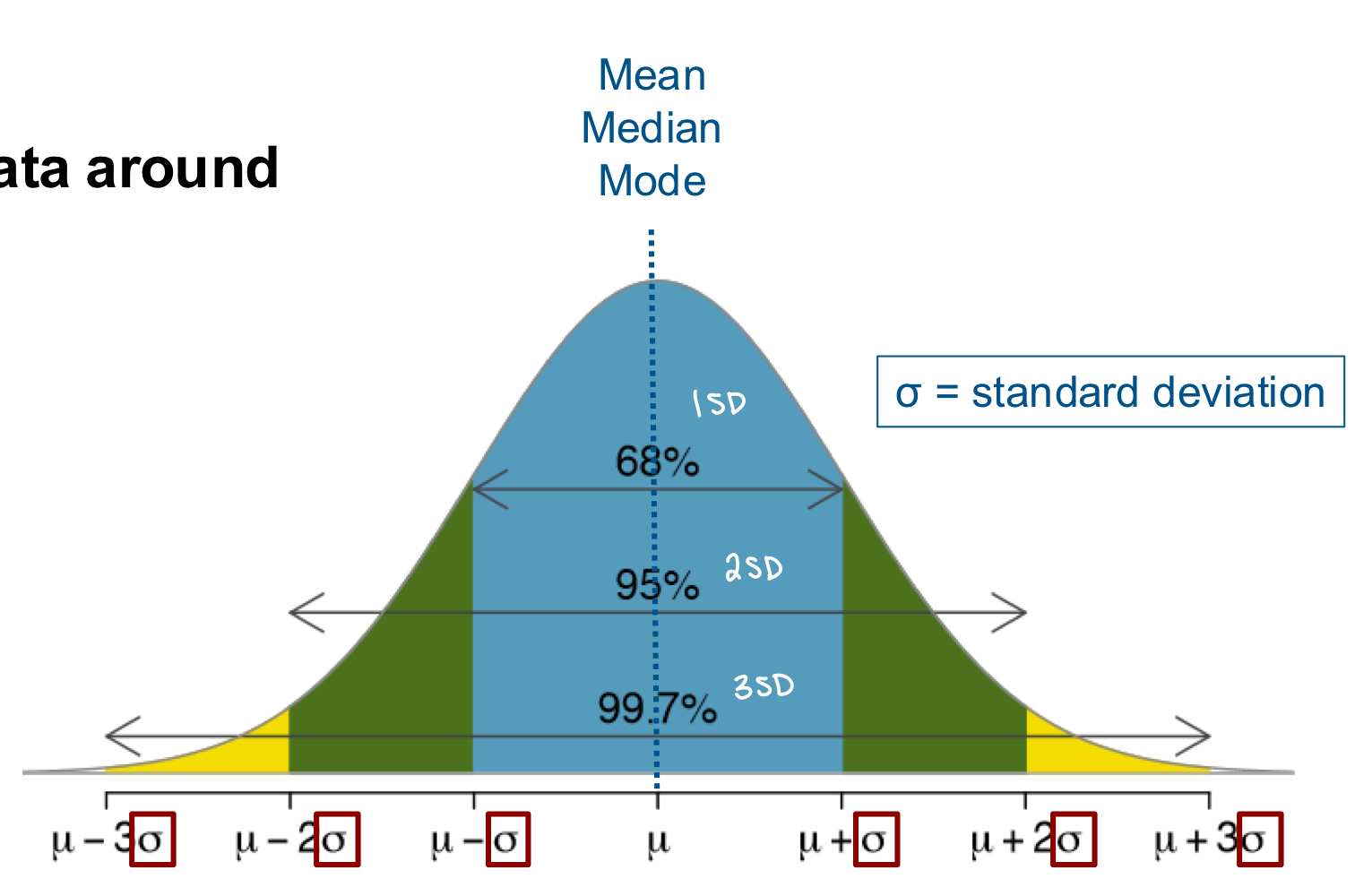
discuss standard deviation
it describes the spread of the data around the mean value
small SD: very little variance in the sample so all values are close to the mean
large SD: a lot of variance in the sample so all values are spread out over a wide range
dicsuss coefficient of variation
the amount of variablility expressed as a percentage of the mean
advantages
unit-less
compare variablility between different measures of the same thing
compare variability between 2 different samples on the same measure
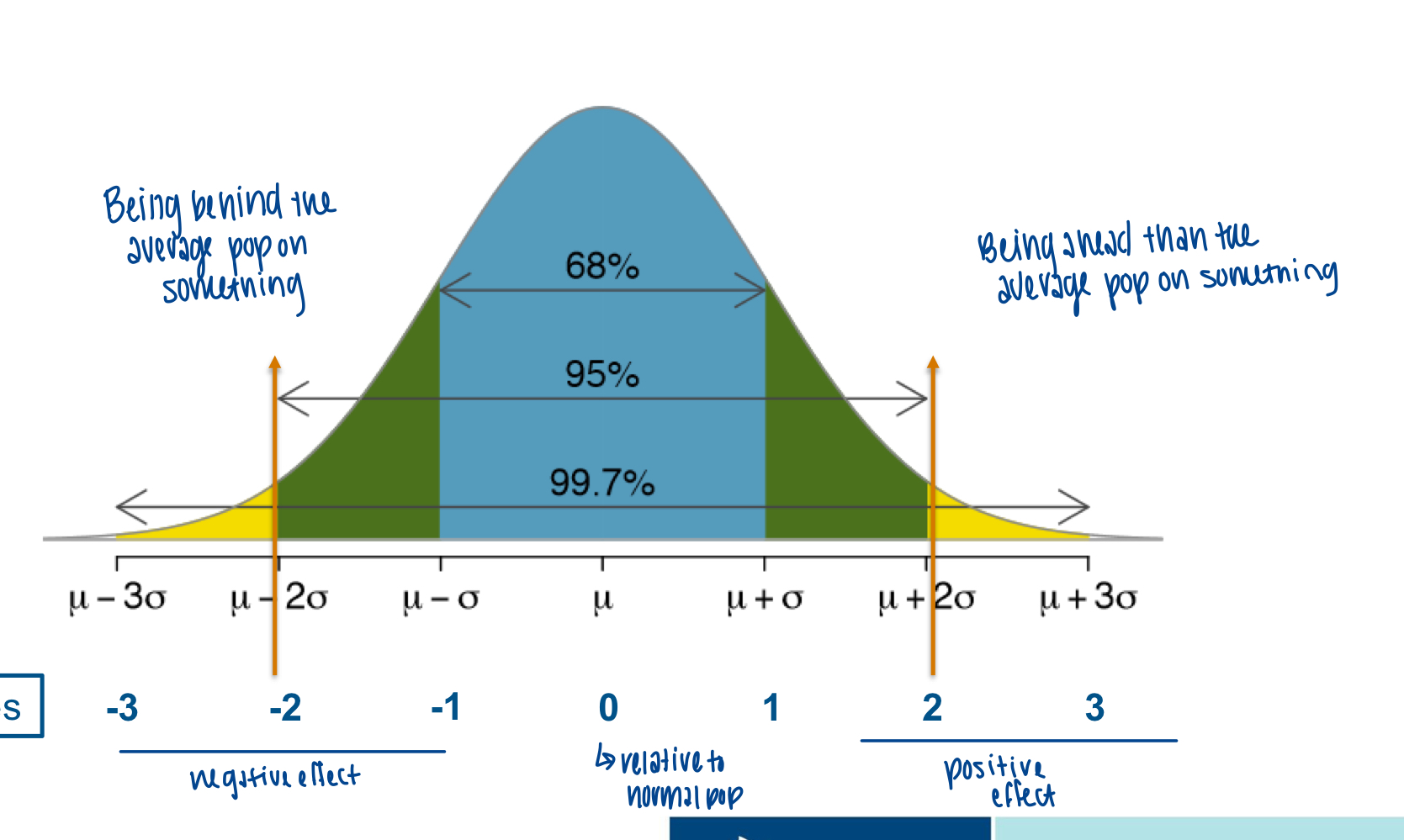
discuss z-score
the number of standard deviations a data point is from the mean of the sample or the population
informative for a singel data point or a group
allows comparison of data points across datasets
95% of z scores between the values of -2 and +2
discuss standard error of the mean
a measure of precision of the sample mean
it tells us how well your sample represents the population
smaller values are better bc it indicates the sample mean is more precise
the larger the sample, the smaller the standard error
discuss confidence intervals
a range of values that contain the true value with a given probability (95%)
a smaller interval is better bc we can be more confident that the mean shown is close to the target population mean for that measure
what is the purpose of measurement?
to provide a way to quantify something that is abstract in a meaningful way
what makes the perfect measurement tool and why do we need them?
standardized
sample free
equal distance between items or scores, providing a known distance
this allows for efficient and accurate understanding of how much exists
also provides knowledge for how much change is real, meaningful, and attainable
what are the measurement benefits?
a well selected measure will let you…
predict
diagnose
discriminate
assess change
measures increase the efficienty of your examination and improve communications
measured values should drive clinical decision making
what is a measured value?
true value + random error + systematic error
what are sources of error when measuring that could make a measured value change?
patient
examiner
environment
instrument
what is primary variance?
consistent changes in the measured value related to the primary effect
changes due to things like amount, duration, and quality of the independent variable
what is secondary variance?
consistent changes in the measured value due to factors other than the primary effect
changes due to things like environment, aspets of the participants, aspects of the raters
what is error variance?
inconsistent changes in the measured value due to things like measurement error or using incorrect statistics
what does it look like to control variance?
Maximize primary variance
control secondary variance
minimize error
what is measurement validity?
test/instrument measures what it is supposed t omeasure
a measure cannot be valid if it is not reliable but reliability does not imply validity
what are the types of validity?
face
content
criterion
construct
discuss face validity
“does the test instrument seem to be a good choice to measure this contstruct?”
clinical judgement, subjective, does it make sense
ex: pain scale
discuss content validity
used for outcome measures often
instrument covers all elements of the construct being measured but not does include irrelevant effects
ex: a balance questionare will not include questions about the wrist
discuss criterion validity
how a measure is related to an outcome
predictive: measure predicts an outcome of interest
concurrent: comparison with a gold standard at the same time. measure of interest and a measure with established validity are administered at the same time point and produce consistent results. Most common- orthopedic tests compared to medical imaging
discuss construct validity
degree to which a test measures the theoretical construct that it claims/intends to measure
ex: berg balance scale, patient reported outcomes
what is reliability?
repeated measures that are consistent
reproducibility, repeatability, consistency, dependability
______ tests/measures allow you to be more confident that a true change has occured between measurements
reliable
what are the types of reliability?
test-retest: measure is consistent when performed multiple times on same patient and construct has not changed. used in short time periods
intra-rater: measurements obtained by the same assessor are consistent
inter-rater: measurements obtained by 2 or more assessors are consistent with each other
What are the two types of validity in research?
Internal and External Validity
What are the types of research questions?
Does intervention A improve an outcome measure mroe than intervention B?
Does intervention A improve an outcome measure
Is variable C associated with Variable D?
Can the values of Variable C (and D, etc) predict the value of Variable E?
Is population F different from population G in terms of some characteristic or outcome measure?
none of the above (this is rare)
What is internal validity?
the degree to which the results of the study can be attributed to the study intervenention and not extraneous factors.
“how confident are you that the results truthfully answer the research question?”
what is internal validity dependent on?
study design
care with measurements
care with intervention delivery
what is the most important property of any study?
internal validity bc problems with internal validity can limit or discredit the findings of a study
what are the threats to internal validity?
selection bias
insufficient sample size
participant attrition
history
maturation
testing
assessor bias
conflict of interest
instrumentation
regression to the mean
multiple comparisons
diffusion of imitation of treatment
compensatory rivalry/resentful demoralization
multiple comparisons
what is selection bias?
the process of selecting subjects leads to a sample that is not representative of the target population
theprocess of placing subjects into groups leads to groups with different baseline characteristics
what is the potential problem with selection bias?
the samples characteristics could influence or mask the effect of the dependent variable
what are the potential solutions to selection bias?
randomization of subjects
matching of subjects
account for statistical analysis
what is insufficient sample size bias?
the sample size is determined by a calculation to detect an estimated effect while balancing the risk of error
what are the potential problems of an insufficient sample size bias?
increasing the sample size drastically increases the possilibyt of finding a significant difference
if the sample size is too low, a study is underpowered and researchers are at a higher risk of making a false negative (type II) finding
what is the solution to insufficient sample size bias?
sample size justification
what is participant attrition bias?
participants drop out of (or do not complete) a study due to injury, illness, death, family, transportation
what are the potetial problems with participant attrition bias?
can create bias, especially if non-random as the gruops may no longer by similar
influence study power
may be reflective or problems with the study such as intervention, timing, or burden
should be reported
what are the potential solutions of participant attrition bias?
enroll additional subjects
account for in statistical analysis
document drop-outs and reasons
what is history bias?
events that occur outside the study but influence the results of the study such as concurrent events with the study that are out of the control of the investigator and that woul likely increase the length of the study
what is the potential problem with history bias?
the outside event could influence of mask the effect of the dependent variable
what are the potential solutions to history bias?
random assignement with a control group
plan/schedule as able to avoid any known events
account for in statistical analysi
what is maturation bias?
changes over time that are internal to participants. not related to the study but may impact results
what is the potential problem with maturation bias?
the course of recovery or decline could influence or mask the effects of the dependent variable
what are the potential solutions to maturation?
random assignement with the control group
multiple baseline testing
what is testing bias?
the subjects become familiar with the test or there is inconsistent administration of testing procedures by the study team
what are the potential problems with testing bias?
something about the test could influence or mask the effect of the dependent variable
bas measurement gives unreliable results
what are the potential solutions to testing bias?
provide practice sessions with test
standardize protocols for test administration
what is assessor bias?
the person testing the participants has a particular bias or opinion about how the outcome of the study should look
what is the potential problems of assessor bias?
soemthing about the bias influences or masks the effect of the dependent variable
bad measurement gives unreliable results
what are the potential solutions of assessor bias?
blind the assessor to the group assignment
use a third party or technology to conduct testing
what is confluct of interest bias?
the persons involved in the study have an invested (apparent to them or not) interest in the outcome
what are the potential problems with conflict of interest bias?
something about the bias influences or masks the effect of the dependent variable
could result in ethical problems
what are the potential solutions of conflict of interest bias?
researchers declare conflict of interest
an independent team develops a plant to manage the conflict of interest
IRB approval and Data Safety Monitoring Boards can help prevent ethical concerns
what is instrumentation bias?
problems with measuring tools regarding selection, application, and calibration
what are the potential problems with instrumentation bias?
bad measurement gives unreliable results
what are the potential solutions with instrumentation bias?
select best, most appropriate measures
train study personnel on standardized testing procedures
calibrate equipment