Metabotropic Receptors: Second Messengers Systems
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
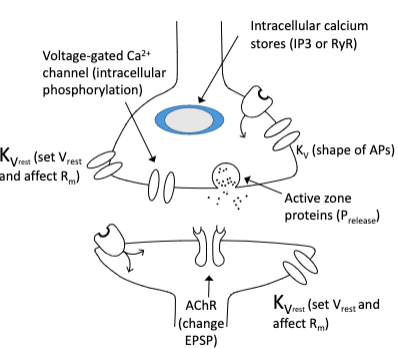
How do metabotrophic receptors affect neuronal activity
Altering Ca2+ channel function
Altering K+ Channel Function
Releasing Ca2+ from intracellular stores
Altering presynaptic active zone protein function (probability of release)
Alterations in postsynaptic receptor sensitivity
True or False: Metabotropic Receptors are activated by multiple NT which activate numerous pathways
True
External Signal(First Messenger)
Neurotransmitter
Transducer
G-proteins(a,B, y- molecular switch)
Primary Effector
First Protein that a-GTP or B-y dimers bind to
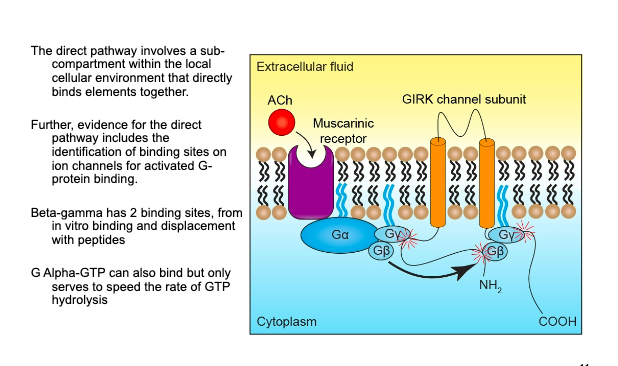
Describe the Direct Pathway
NT Acteylcholine—>binds to mACHr—>activates G b-y protein which acts on K+ Channels
Describe the cAMP Pathway
NT Norepinehphrine—>binds to B-adrenergic receptor—>activates Gs protein which acts on Adenyl Cyclase which activates cAMP to activate PKA
Describe the Phosphinositol Pathway
NT Acetycholine—>binds to Muscarinic Ach receptor—>activates Gq protein which acts on PLC which cleaves PIP2 to make IP3(responsible for Ca2+) and DAG(combined with Ca2+ activates PKC)
Describe the Arachidonic Acid Pathway
NT Histamine—>binds to Histamine receptor—>activates Gi/o protein which acts on PLA2 which activates the arachidonic acid to activate (5-Lipoxygenase,12-Lipoxygenase,Cyclooxygenase)
How did experimenters show which G-protein is involved in modulating GIRK channels
Experimenters put different G-protein constituents and tested for current
-A-B-y: no GTP
a-B-y+GTP-y-S: curret occured but don’t know which it is
a-GTP: no current occured
B-y(no GTP): Current occurred
What was a second way that experimenters determined which G-protein stimulated GIRK channels
They injected mRNA for GIRK Channels and G-proteins,waited 2 days for protein expression,a and recorded current from GIRK+ B,y proteins
IDK=FIX
How did experimenters prove that PKA increases calcium current by increasing the probability of channel opening
Blocked by PKA inhibitors
Mimicked by activators of PKA, adding catalytic subunit of PKA or cAMP itself
Purified channels in lipid bilayer to record single channel events
Add PKA/ATP show increased p(open), then run gel to show phosphorylation of channel
Evidence demonstrating indirect pathway involvement in G-protein mediated effects FIx
Use a PKC activator(oleoylacetylglycerol OAG) inhibits N-type calcium current\
Look for additive or occlusve effects= Effect of NE is blocked by PKC inhibitor(PKCl 19-31)
So, NE likely works through PKC pathway
How can GPCR exhibit specificity
Signaling Cascades can be spatially restricted,
Whole cell dialysis does not affect inhibition
Cell attached recordings don’t show inhibition when transmitter is added to the outside