CVM 3221 - Final Study Guide
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/128
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Surgical Nursing and Anesthesia Management Lab
Last updated 6:53 PM on 8/2/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms
1
New cards
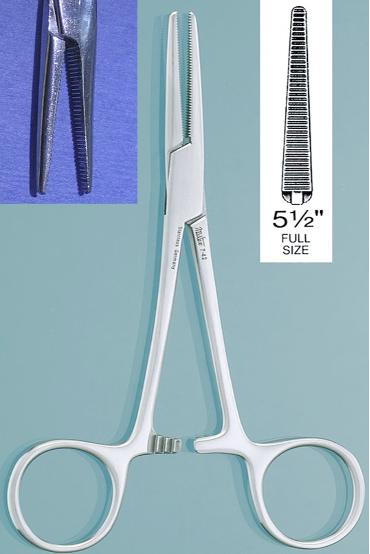
Identify this instrument.
It is used to occlude small uterine horns and medium blood vessels. It has transverse grooves on the entire jaw (“crile goes a mile”).
It is used to occlude small uterine horns and medium blood vessels. It has transverse grooves on the entire jaw (“crile goes a mile”).
Crile Forceps
2
New cards
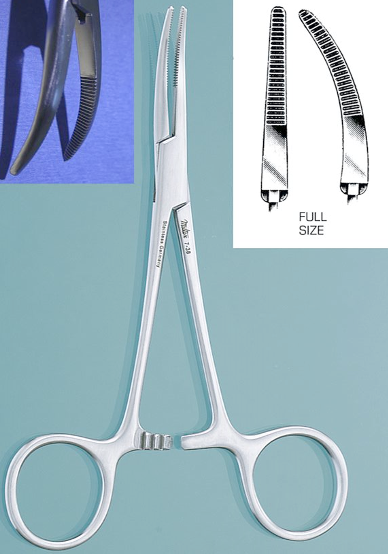
Identify this instrument.
It is used to occlude small to medium blood vessels. It has transverse grooves only on the top half of the jaws and the smooth area is used to clamp tubing.
It is used to occlude small to medium blood vessels. It has transverse grooves only on the top half of the jaws and the smooth area is used to clamp tubing.
Kelly Forceps
3
New cards
How does a Crile Forcep differ from a Kelly Forcep?
Crile forceps has transverse grooves on the entire jaw whereas Kelly Forceps has transverse grooves only on the top half of the jaws
4
New cards
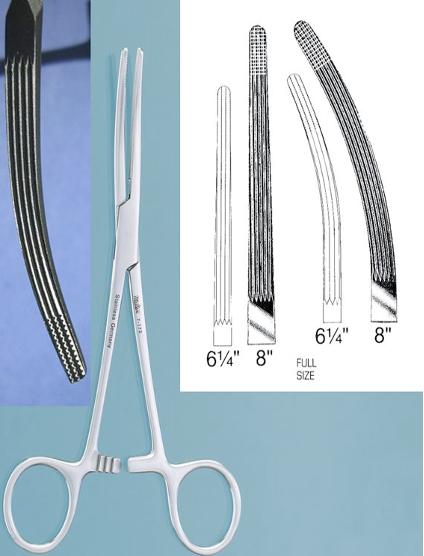
Identify this instrument.
It is used to occlude small to medium vessels. It has transverse grooves only on the top half of the jaws. The smooth area is used to clamp tubing.
It is used to occlude small to medium vessels. It has transverse grooves only on the top half of the jaws. The smooth area is used to clamp tubing.
Rochester-Carmalt Forceps
5
New cards
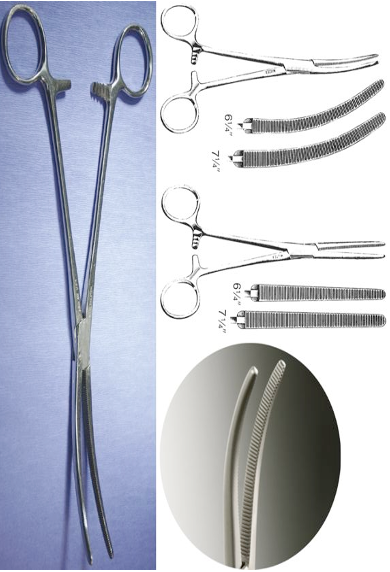
Identify this instrument.
It is used to clamp blood vessels or control large tissue bundles. The jaws have transverse grooves the entire length which has good crushing action.
It is used to clamp blood vessels or control large tissue bundles. The jaws have transverse grooves the entire length which has good crushing action.
Rochester-Pean Forceps
6
New cards
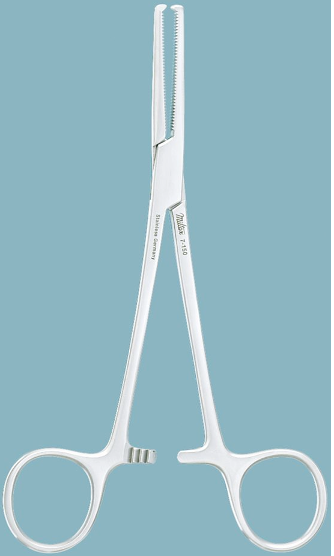
Identify this instrument.
It is used to clamp blood vessels and grasp tissue. It has transverse grooves and the tips of the jaws have teeth.
It is used to clamp blood vessels and grasp tissue. It has transverse grooves and the tips of the jaws have teeth.
Rochester-Ochsner Forceps
7
New cards
Atraumatic forceps include…
Debakey Forceps and Babcock Intestinal Forceps
8
New cards
Traumatic forceps include…
Allis Tissue Forceps and Dressing Forceps
9
New cards
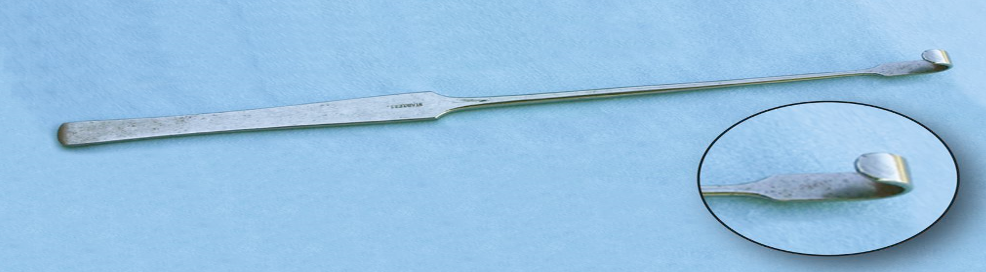
Identify this instrument.
It is used to retrieve the uterine horn.
It is used to retrieve the uterine horn.
Snook’s Ovariectomy Hook
10
New cards
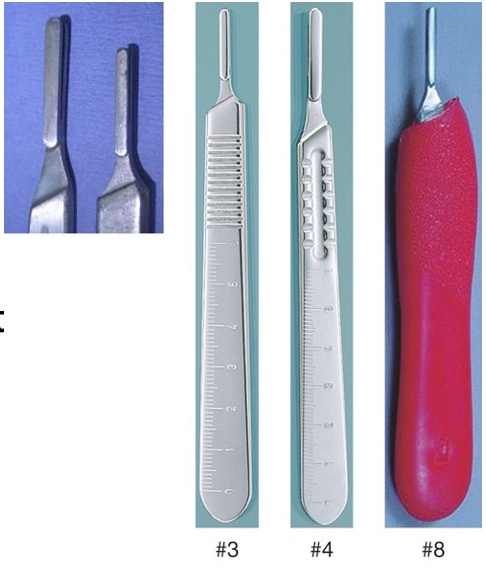
Identify this instrument.
Scalpel handle
11
New cards
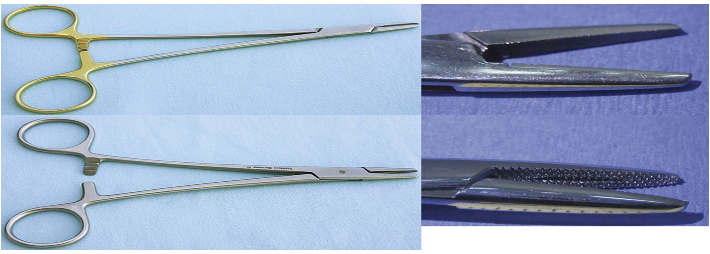
Identify this instrument.
It is used to drive suture needles through tissue and has short jaws with grooves that are cross-hatched.
It is used to drive suture needles through tissue and has short jaws with grooves that are cross-hatched.
Mayo-Hegar Needle Holders
12
New cards
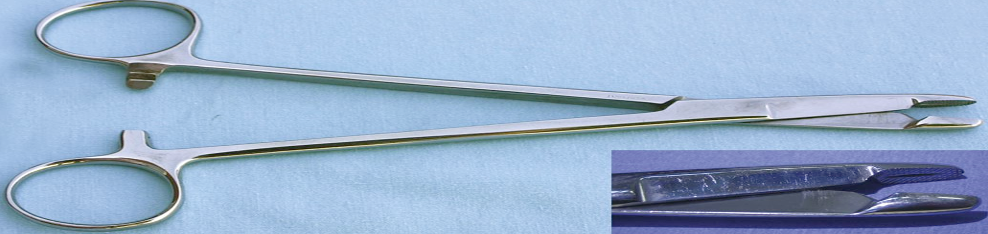
Identify this instrument.
It is used to drive suture needles through tissue and has scissor blades set behind the jaws.
It is used to drive suture needles through tissue and has scissor blades set behind the jaws.
Olson-Hegar Needle Holder-Scissors Combination
13
New cards
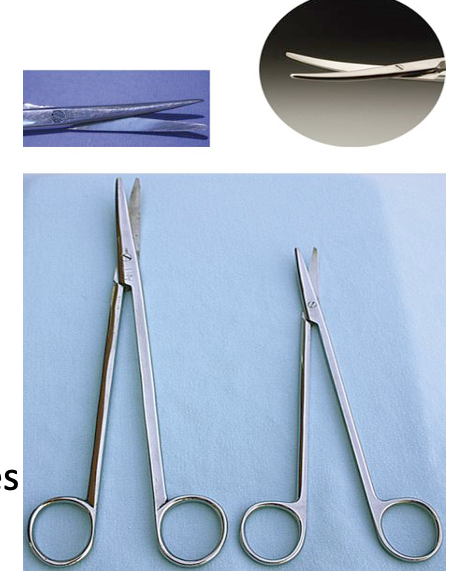
Identify this instrument.
It is used to blunt-disect or cut soft tissue. The blades can be straight or curved, smooth or serrated.
It is used to blunt-disect or cut soft tissue. The blades can be straight or curved, smooth or serrated.
Metzenbaum Scissors
14
New cards
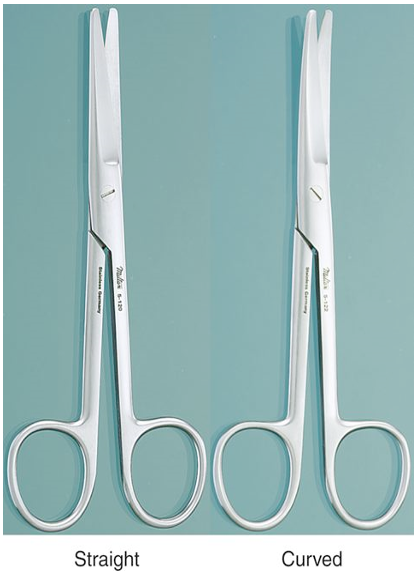
Identify this instrument.
It is used to perform blunt dissection and cut bulky connective tissue. It is commonly used in large animals. The blades can be straight or curved, smooth or serrated.
It is used to perform blunt dissection and cut bulky connective tissue. It is commonly used in large animals. The blades can be straight or curved, smooth or serrated.
Mayo Scissors
15
New cards
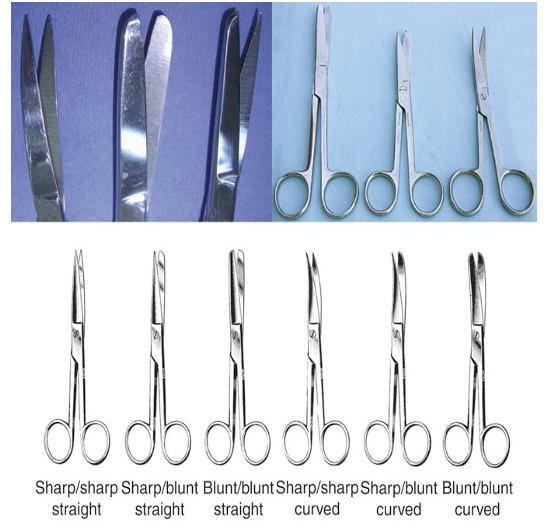
Identify this instrument.
It is used to cut suture material or other inanimate materials. The tips can be blunt-blunt, sharp-blunt or sharp-sharp.
It is used to cut suture material or other inanimate materials. The tips can be blunt-blunt, sharp-blunt or sharp-sharp.
General Operating Scissors
16
New cards

Identify this retractor.
It is used to hold open a wound or incision and works well with smaller incisions and wounds. It ends in three-pronged curve sharp or blunt points.
It is used to hold open a wound or incision and works well with smaller incisions and wounds. It ends in three-pronged curve sharp or blunt points.
Senn Rake Retractor
17
New cards
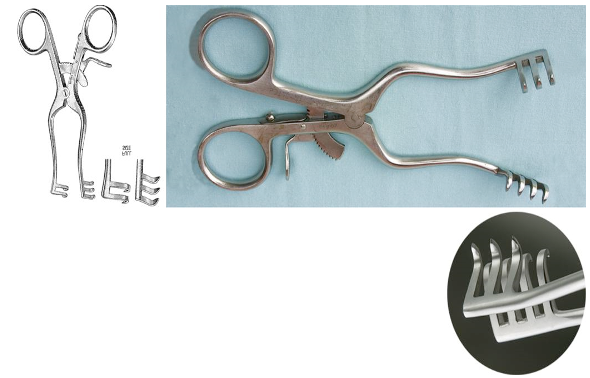
Identify this retractor.
It is used to maintain muscle retraction during orthopedic surgery.
It is used to maintain muscle retraction during orthopedic surgery.
Weitlaner Retractor
18
New cards
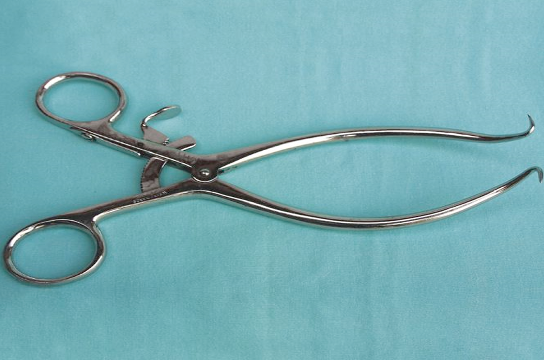
Identify this retractor.
It is used to maintain wound exposure during general surgery, orthopedic and neurosurgery. It can also have stops on the points.
It is used to maintain wound exposure during general surgery, orthopedic and neurosurgery. It can also have stops on the points.
Gelpi Retractor
19
New cards
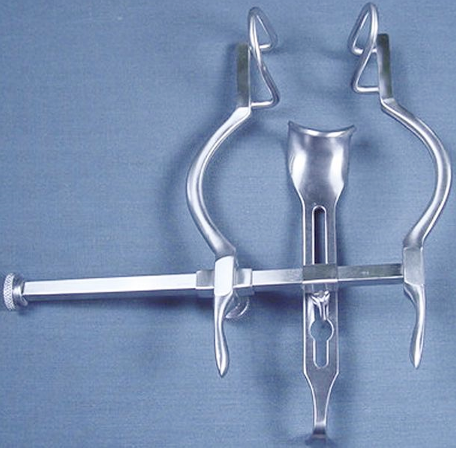
Identify this instrument.
It is used to hold the abdominal wall open for surgery.
It is used to hold the abdominal wall open for surgery.
Balfour Retractor
20
New cards
Which retractors are self-retaining?
Gelpi
Weitlaner
Balfour
Weitlaner
Balfour
21
New cards
Which retractors are manual?
U.S. Army
Senn
Senn
22
New cards
What is the correct way to hold needle holders?
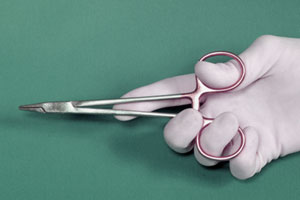
23
New cards
What is the correct way to load the needle drivers when grabbing a needle for suturing?
Grasp the needle in the curve; the middle to caudal 1/3 of the needle
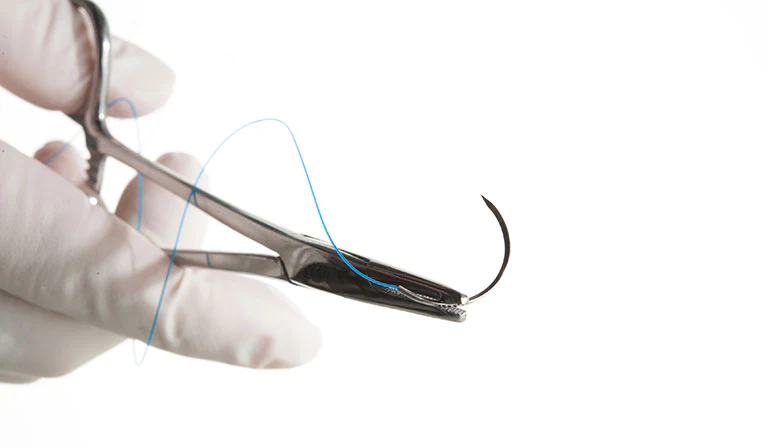
24
New cards
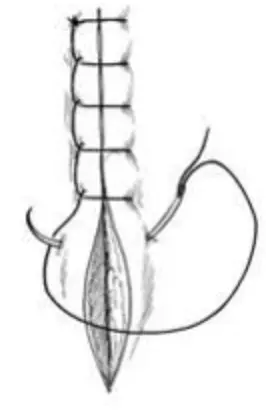
Identify this suture pattern.
Ford-Interlocking Pattern
25
New cards
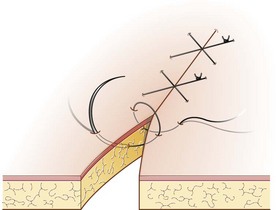
Identify this suture pattern.
Cruciate Pattern
26
New cards
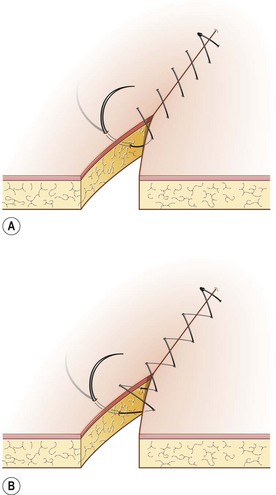
Identify this suture pattern.
Simple Continuous Pattern
27
New cards
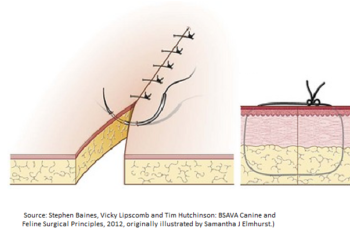
Identify this suture pattern.
Simple Interrupted Pattern
28
New cards
Which suture patterns are interrupted?
Cruciate Pattern
Simple Interrupted
Simple Interrupted
29
New cards
Which suture patterns are continuous?
Ford-Interlocking Pattern
Simple Continuous
Simple Continuous
30
New cards
Which image demonstrates proper technique for tying a knot that will hold and remain strong and secure without unraveling? Assume that the incision line runs horizontally from left of the image to right of the image.
(Know how to identify from an image)
(Know how to identify from an image)
Proper knot tying technique
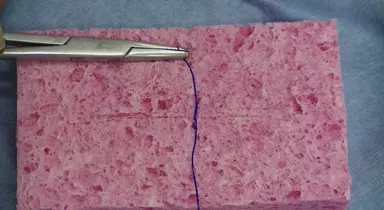
31
New cards
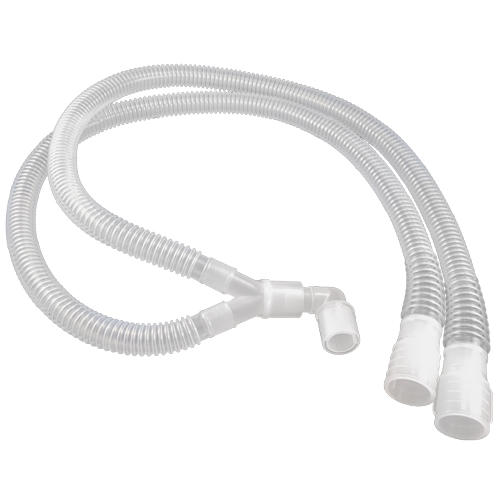

Identify this breathing circuit.
Rebreathing circuit
32
New cards
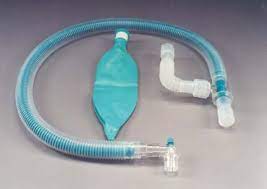
Identify this breathing circuit.
Universal F rebreathing circuit
33
New cards
When would you use a non-rebreathing circuit?
Patients weighing less than 5 kgs
34
New cards
What is the benefit of using a non-rebreathing circuit?
This is because patients weighing less than 5 kgs benefit the most from the low gas resistance.
35
New cards
What is the correct way to release the pressure from the circuit when ending your pressure test?
Open the pop-off valve
36
New cards

Identify this part of the anesthesia machine.
Flowmeter
37
New cards
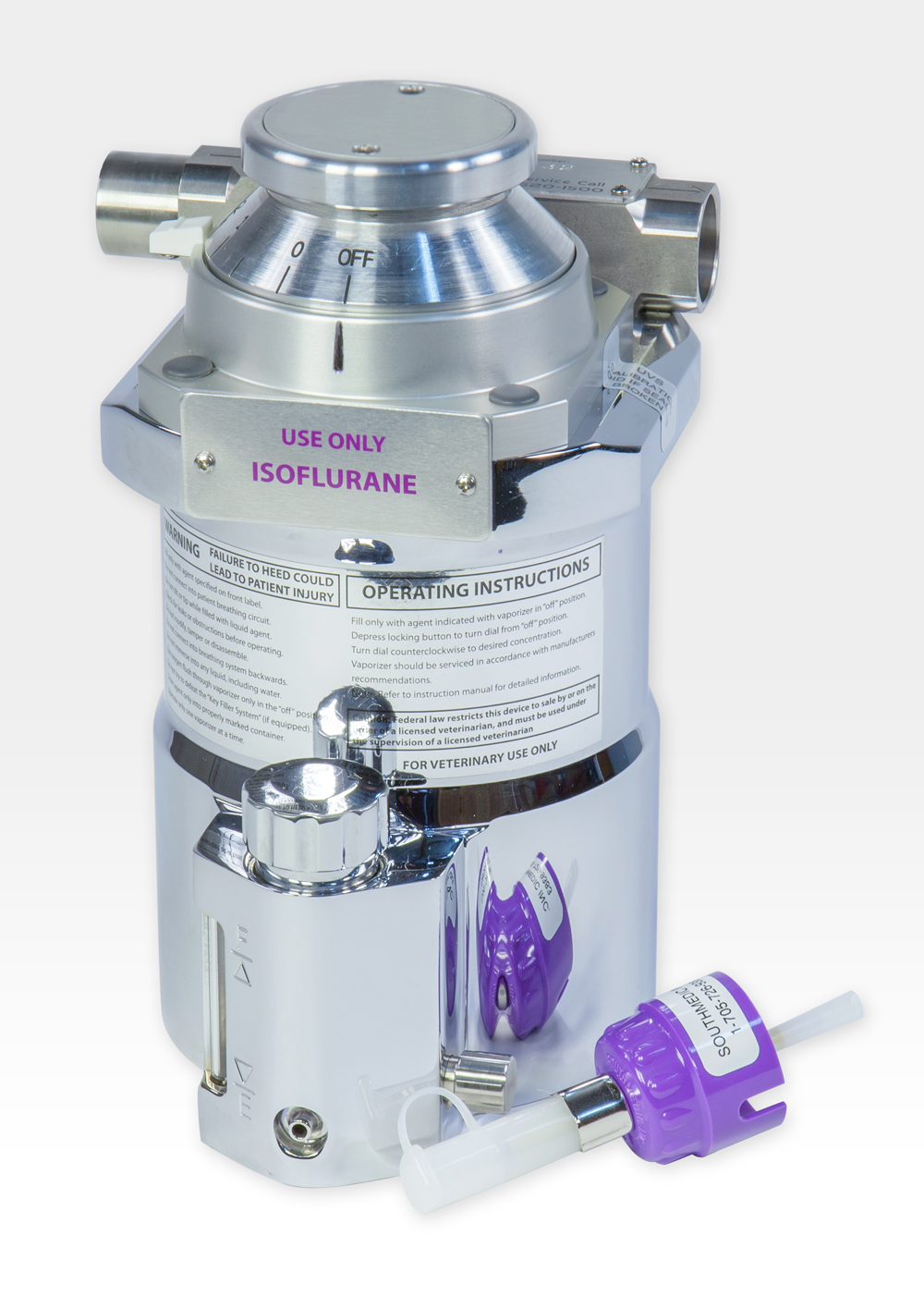

Identify this part of the anesthesia machine.
Vaporizer
38
New cards

Identify this part of the anesthesia machine.
Manometer
39
New cards

Identify this part of the anesthesia machine.
Sodasorb canister
40
New cards
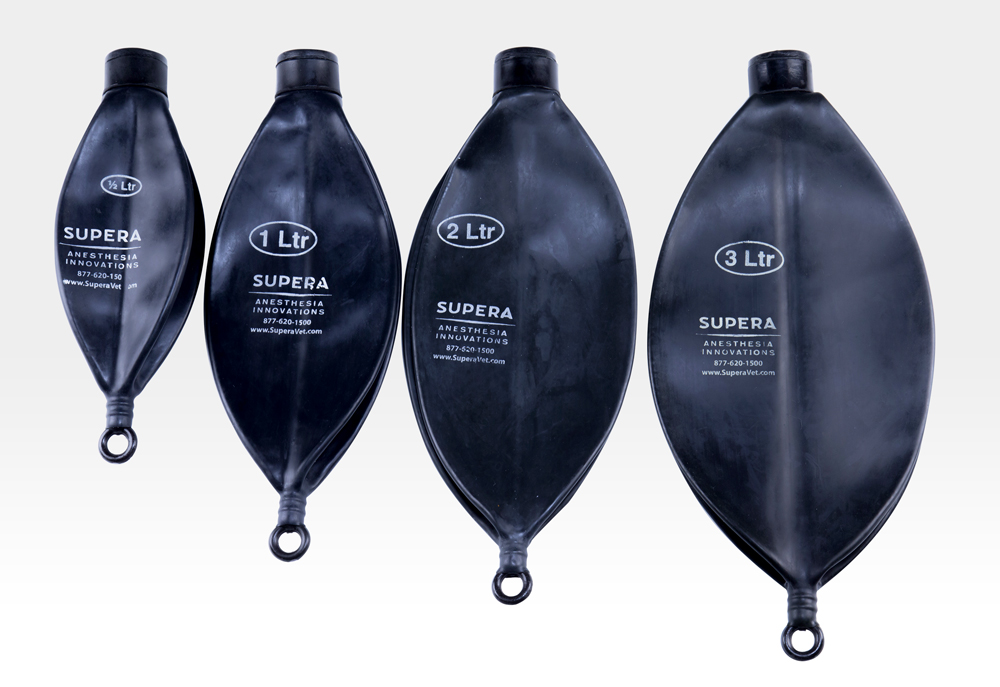

Identify this part of the anesthesia machine.
Reservoir Bag
41
New cards
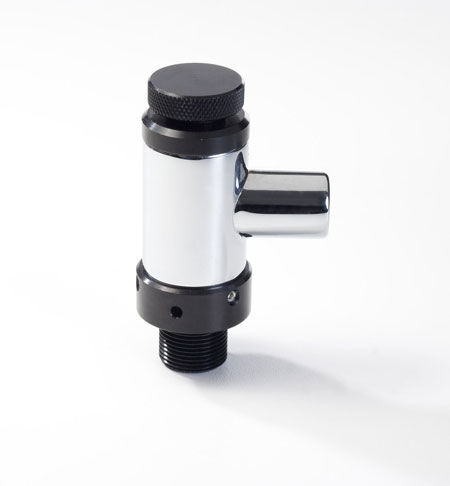

Identify this part of anesthesia machine.
Pop-off valve
42
New cards

Identify this part of the anesthesia machine.
Fresh gas outlet
43
New cards

Identify this part of the anesthesia machine.
Occlusion valve
44
New cards
If you turn your O2 flow to 200 mls/min and the leak stops, can you still use the machine?
Yes, it is an acceptable leak
45
New cards
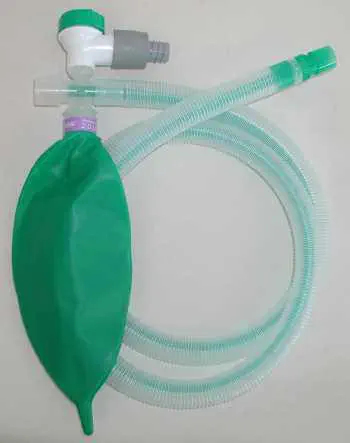
Identify this breathing circuit.
Non-rebreathing Bain Circuit
46
New cards
List the following steps for performing an anesthesia machine leak check.
1. Connect oxygen hose to oxygen source or turn on local oxygen source
2. Attach circuit to be used
3. Check vaporizer for adequate level of liquid anesthetic
4. Securely occlude patient end of circuit with thumb, palm in hand
5. Completely close pop-off valve
6. Depress fast flush valve until a pressure reading of 40 cm H2O registers on the manometer
7. Observe needle of manometer for declining movement, which would indicate a leak
8. If there is no leak, proceed to step 12
9. If there is a leak, turn to oxygen flow to 200 ml/min
10. If leak is corrected - indicated by a stable needle on the manometer - no further action is needed. Proceed to step 12
11. If leak is not corrected, perform machine maintenance to determine location of leak. Correct leak
12. Without removing the occlusion from the patient end of the circuit, open the pop-off valve. The rebreathing bag should deflate
13. Remove hand, thumb from circuit end
14. Check scavenging system to ensure that connections are intact
15. Completely open pop-off valve
47
New cards
What are the landmarks you use for measuring how far to pass the ET tube into the trachea?
Canine tooth to cranial to the thoracic inlet
48
New cards
How can you confirm correct placement of the ET tube into the trachea?
Coughing
Fogging of the tube
Blowing of gauze or hair
Air movement
Palpation
Fogging of the tube
Blowing of gauze or hair
Air movement
Palpation
49
New cards
What is the correct way to secure the ET tube to the patient after intubation?
Use gauze/tape and tie around the ET tube first and then on top of the maxilla in a bow behind the canine teeth
50
New cards
How do you determine the proper length of the laryngoscope blade to use?
Tip of the nose to the pharyngeal area
51
New cards
Where should you apply sterile lube to the ET tube?
Only on the cuff
52
New cards
Be able to describe the proper technique for your assistant to open the mouth for intubation?
1. The restrainer holds the patient in sternal recumbency.
2. The restrainer opens the mouth by holding the maxilla in one hand and the mandible in the other hand.
1. In a dog, the maxilla should be held caudal to the canine teeth
2. In a cat, the maxilla should be held just caudal to the ear pinna so that the skull is in the palm of the restrainer’s hand
3. The hand holding the mandible grasps the tongue and fully extends it over the mandibular incisors
4. The restrainer lifts the head and extends the neck to aid the intubator’s visualization
53
New cards
Where do you want the end of the ET tube to be for proper intubation and ventilation?
Cranial to the thoracic inlet
54
New cards
What is a cuff syringe used for?
It is needed to inflate the cuff of the ET tube
55
New cards
How do you check for a leak around the ET tube’s cuff after intubation?
1. Completely submerse the tube in a pan of clean water
2. Attach a syringe to the cuff indicator
3. Fully inflate the cuff and observe for any bubbles. Bubbles in the water, seen coming from any spot on the tube, indicate a leak in the tube
56
New cards
Where does the bain circuit connect to the anesthesia machine to deliver O2 and inhalant to the patient?
The common gas outlet
57
New cards
How do you seal the leak around the ET tube’s cuff after intubation if there is one?
It should be thrown way or kept and identified as a leaky tube
58
New cards
What is the very first thing you must do after you secure the ET tube to your patient after intubation?
Confirm its placement in the trachea and connect the ET tube to oxygen
59
New cards
If your patient did have a leak around the ET tube cuff, what might happen if you don’t fix it?
Their anesthetic depth may be hard to maintain and/or they may not be getting enough oxygen + expelling enough CO2
60
New cards
If you are in surgery, and you suspect your patient has a leak around the ET tube, how could you check?
Give a breath and listen just like when you are originally leak testing
61
New cards
Normal ETCO2 range for a dog and cat
35-45
62
New cards
Normal SPO2 range for dogs and cats
>95%
63
New cards
Normal NIBP (MAP) range in dogs and cats
70-90
64
New cards
Normal heart rate range in dogs and cats
Dogs: 60-120 bpm
Cats: 100-140 bpm
Cats: 100-140 bpm
65
New cards
Normal respiratory rate in a dog and cat
Dog: 15-34 bpm
Cat: 16-40 bpm
Cat: 16-40 bpm
66
New cards
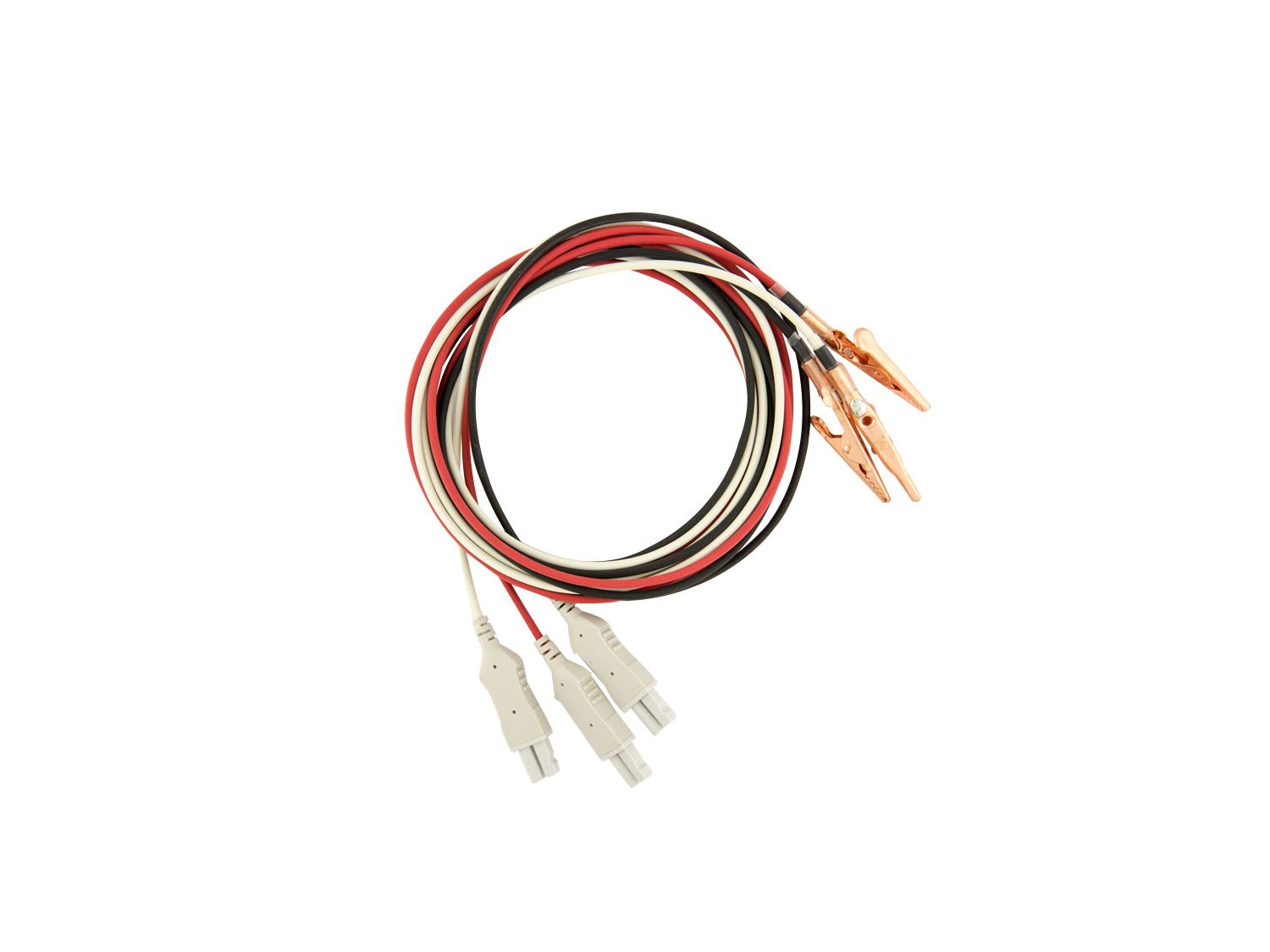

What are these? Where do you place them?
ECG leads
White on the right axillary region, black on the left axillary region and red on the left inguinal region
White on the right axillary region, black on the left axillary region and red on the left inguinal region
67
New cards

What is this? Where do you place it?
Non-Invasive Blood Pressure cuffs
Base of the tail, metatarsus, and metacarpus
Base of the tail, metatarsus, and metacarpus
68
New cards
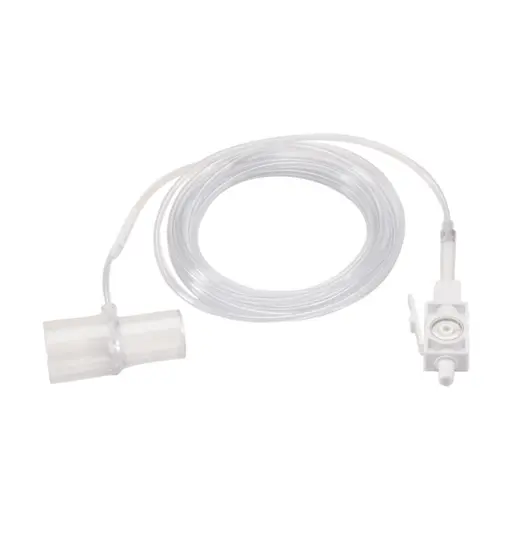

What is this? Where do you connect it?
Capnograph
Connect it at the end of the ET tube
Connect it at the end of the ET tube
69
New cards
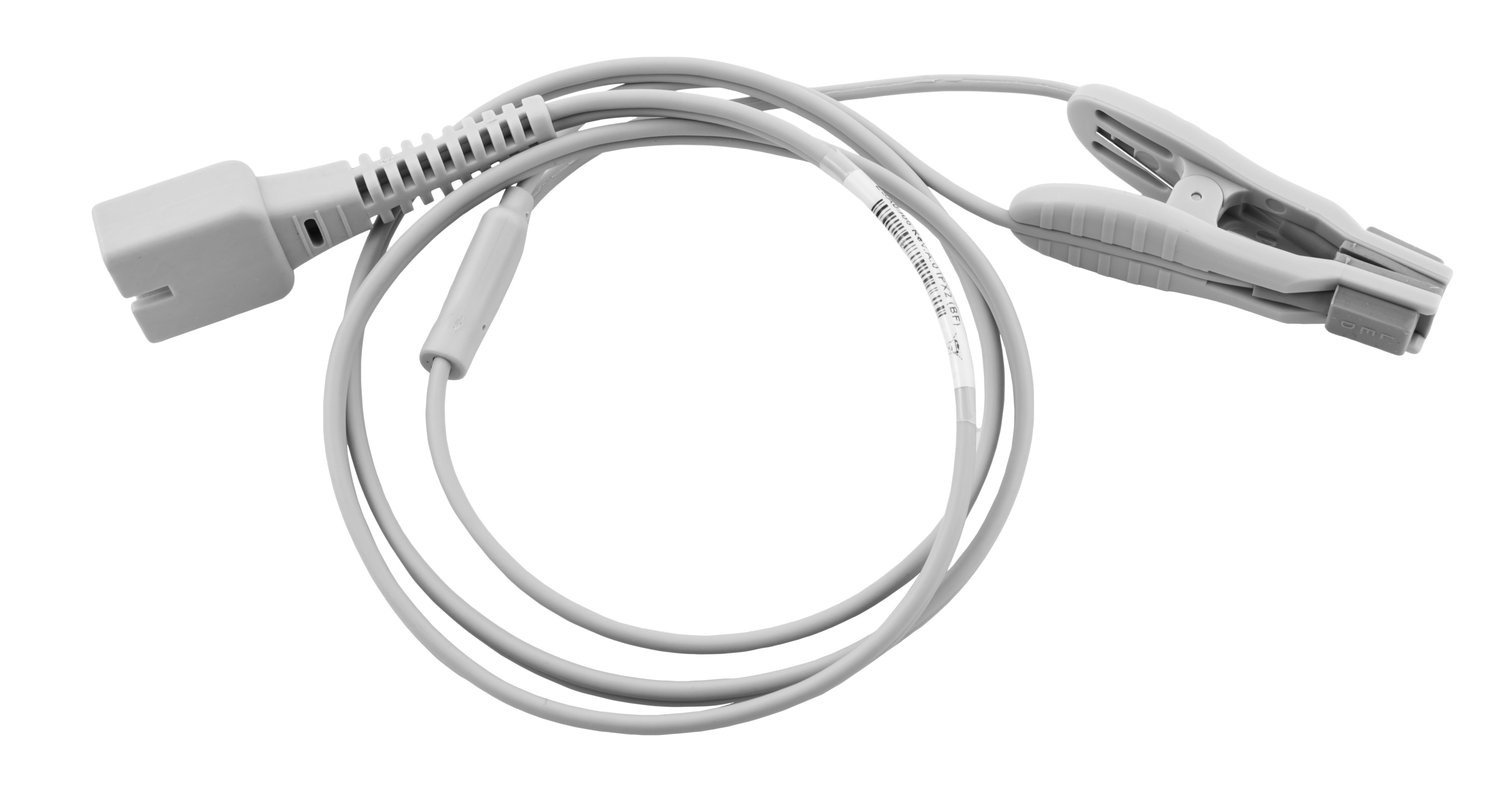

What is this? What positions can you place it?
Pulse oximetry
Tongue, toe webbing, external genitalia (prepuce or vulva)
Tongue, toe webbing, external genitalia (prepuce or vulva)
70
New cards
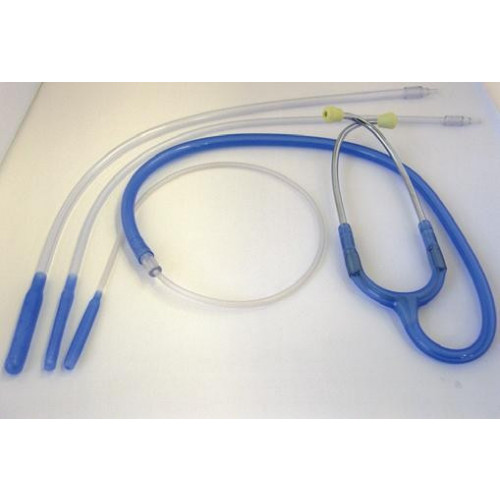
What is this?
Esophageal stethoscope
71
New cards
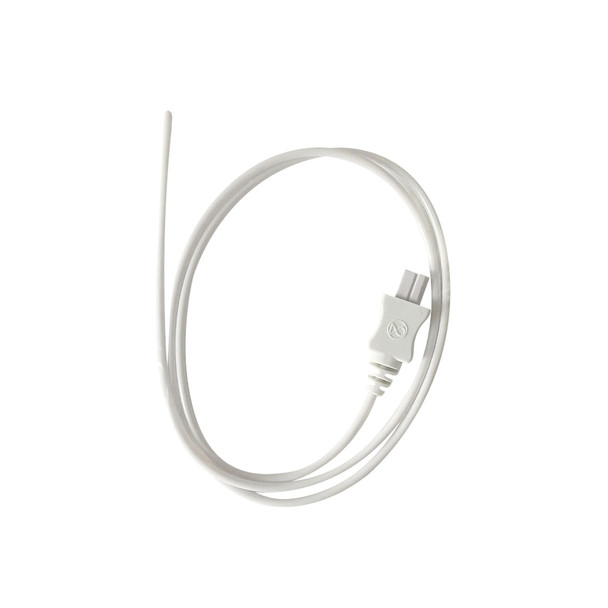

What is this? Where is it placed?
Thermometer probe
Down the throat or rectally
Down the throat or rectally
72
New cards
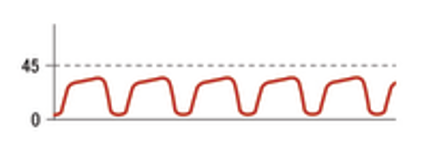
What is this called?
Hyperventilation
73
New cards
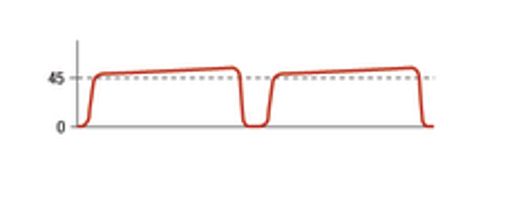
What is this called?
Hypoventilation
74
New cards
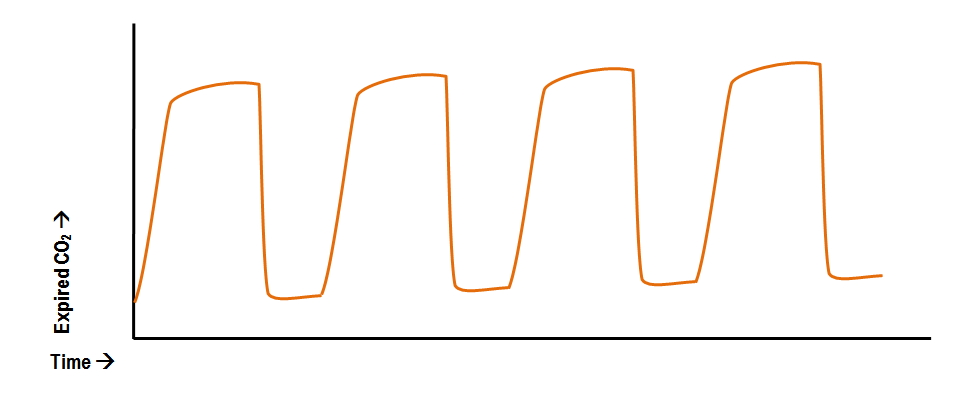
What is this called?
Rebreathing of CO2
75
New cards
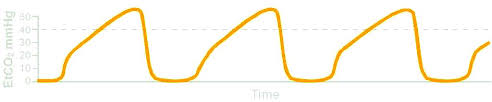
What is this called?
Airway obstruction
76
New cards
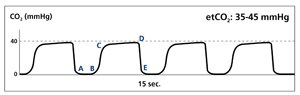
What is this called?
Normal ventilation
77
New cards
If you are monitoring your patient and see a reading you do not like, what should you do first before reaching for medications, notifying your surgical team, or adjusting the vaporizer/O2 settings?
Trouble shoot and make sure nothing is messed up with your leads/machinery and also get your hands on the patient to palpate pulse, respirations, etc. to see if your monitors are giving incorrect values
78
New cards
What is the purpose of the steam indicator strip and where is it placed?
To tell you whether or not the parameters for sterilization have been met
It is placed in the middle of the pack
It is placed in the middle of the pack
79
New cards
How can you tell if a surgical pack is properly sterilized?
The autoclave tape will have turned color
80
New cards
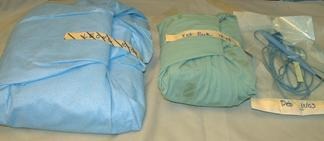
Is this pack properly autoclaved and sterilized?
Yes. It is properly labeled and taped.
81
New cards
What is closed gloving used for?
It provides assurance against contamination because no bare skin is exposed in the process. It is used for major surgical procedures.
82
New cards
What is open gloving used for?
It is a method that enables the scrubbed personnel to glove themselves and should not be used routinely for surgical gloving. It is used when only the hands need to be sterile and no gown is needed, such as for minor surgical procedures, bone marrow biopsies, or catherizations.
83
New cards
Which parts of the body are considered sterile when you are scrubbed, gowned, and gloved?
Fingertips to elbows and shoulders of the front of the gown to the waist/tabletop
84
New cards
Know how to maintain sterility when working with sterile fields.
Sterile field to sterile field
When passing another sterile personnel, pass front to front or back to back
When passing another sterile personnel, pass front to front or back to back
85
New cards
For how long should you scrub?
3-5 minutes per arm
86
New cards
What is assisted gloving?
It is used when a sterile team member helps another scrubbed-in team member glove. This usually happens when a glove is ripped or contaminated during surgery.
87
New cards
How would you reglove during surgery if you have no other sterile team member to assist you?
Use open gloving
88
New cards
How do you perform the open gloving technique?
With the left hand, pick up the right glove by grasping the cuff on the “future” inside surface (non-sterile surface) of the fold only. Gently guide the fingers into the glove, leaving the cuff well turned over the hand. Keep the thumb in the palm of the hand until it is well inside the glove. Do not adjust the cuff. Place the gloved fingers of the right hand under the everted left glove cuff, on the sterile side of the left glove. Slide the fingers of the left hand into the glove, keeping the thumb inside the palm of the hand, until inside the glove. Pull the glove on all the way. With the left hand, slide the fingers under the outside edge of the right cuff and unfold it by stretching it up the wrist. Avoid touching any bare, exposed skin.
89
New cards
What parts of the body are considered sterile when you are gloved using open gloving?
Only the hands
90
New cards
Know how to maintain sterility when performing final sterile prep.
Wear sterile gloves.
Use clean hand, dirty hand technique.
Use clean hand, dirty hand technique.
91
New cards
For how long should you scrub the patient to complete final sterile scrub?
You should scrub for at least 5 minutes.
92
New cards
What does the clean hand dirty hand technique mean?
Use one hand to grab scrub/rinse and pass it to the other hand which does the scrubbing; this keeps the bowl with gauze clean
93
New cards
What are Backhaus towel forceps used for when draping?
To secure the towels to each other and to the patient's skin
94
New cards
What is the correct order for placing each item when draping? Be able to recognize correct draping in a picture.
Huck towels
Backhaus towel drapes
Lap drapes
Fenestrated drape
Backhaus towel drapes
Lap drapes
Fenestrated drape
95
New cards
Which huck towel is placed first and which is placed second? Which is placed third and fourth?
The first and second huck towels are placed on the lateral aspect of your incision site; place on the side closest to you first and then walk around to the other side and repeat
96
New cards
What is the purpose of the laparotomy (lap) drape?
It covers areas of the patient that have not been sterilely prepped to avoid contamination of the sterile field.
97
New cards
When should you open the inner pack wrapper of the instrument pack?
When the circulating nurse opens the outer wrap
98
New cards
When should you perform your instrument, sharps, and sponge counts?
Before the surgery and before closing the incision
99
New cards
Where should you stand if you are also assisting the surgeon in surgery?
On the opposite side of the table as the surgeon
100
New cards
How do you pass an instrument that has a ringed handle?
The ringed handle should be placed firmly in the surgeon’s dominant hand. The box lock should be locked.