Science 8 - Intro to Cells
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
Characteristics of lens made in the 1600's?
curved, glass, bigger
What kind of microscope was made in 1630-1640s?
‘crap’, 1 lens, 4x-10x
What are the three kinds of modern day microscopes
Compound light, transmission electron, and scanning electron
What does a compound light microscope do?
Stacks lenses (10x/4x =40x)
Which microscope is a minimum of 60ft
Transmission electron microscope
How much does the transmission electron microscope multiply?
1,000,000 x
Who was the first person to see a cell?
Robert hooke
What was the first cell seen?
Cork
What do dead cells look like?
Empty monastery rooms
Who takes credit for the early microscope development?
Anton von Leeuwenhoek
Who saw the first living cell?
Anton von Leeuwenhoek
What kind of cell was the first living cell seen?
Pond water (protists)
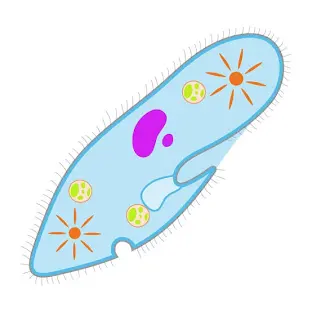
What is this?
Paramecium
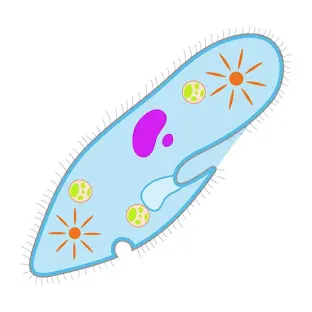
What are the hairs on the paramecium called?
cilia
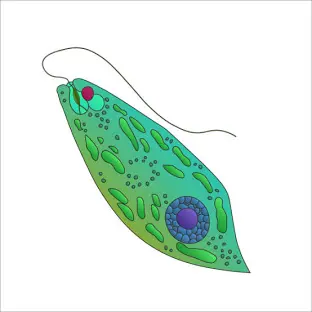
What is this?
euglena
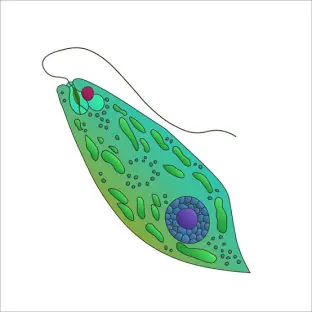
What is the tail on the Euglena called?
Flagellum
What is Matthias Schneiden’s profession
Botanist
What is Theodore Schwann’s profession
Zoology
What is Rudolf Virchows profession
Physician
Theory - All life is composed of cells
Matthias
Theory - The cell is the basic functioning unit of life
Theordore
Theory - Cells can only come from pre-existing cells
Rudolf
What is the average size of a cell
10-50 microns
How big is the largest cell?
3 meters (9 feet)
What is the biggest cell?
nerve cell of a giraffe
How big is the smallest cell?
0.2 microns
What is a microns size?
1,000,000th
What is the average shape of a cell?
Roughly cuboidal (not all cells are cuboidal)
What is an example of a special shaped cell? (not a blood cell)
neuron (nerve cells)
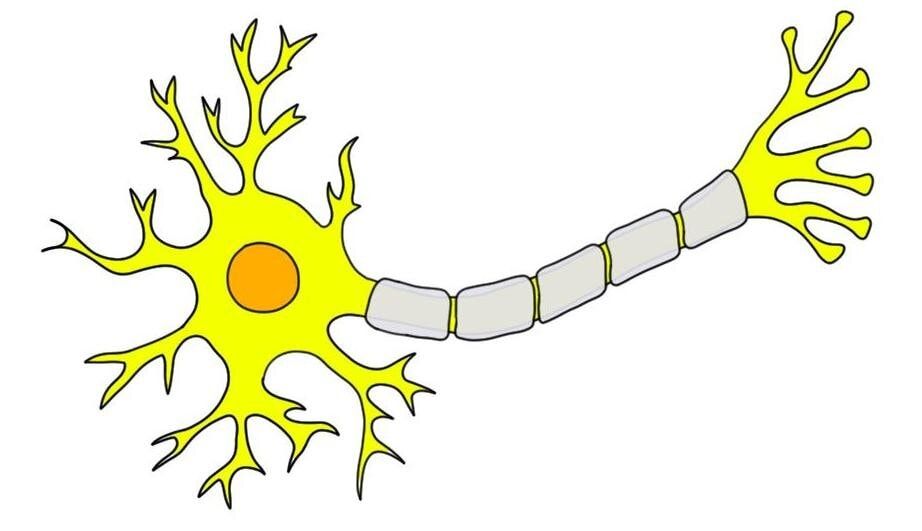
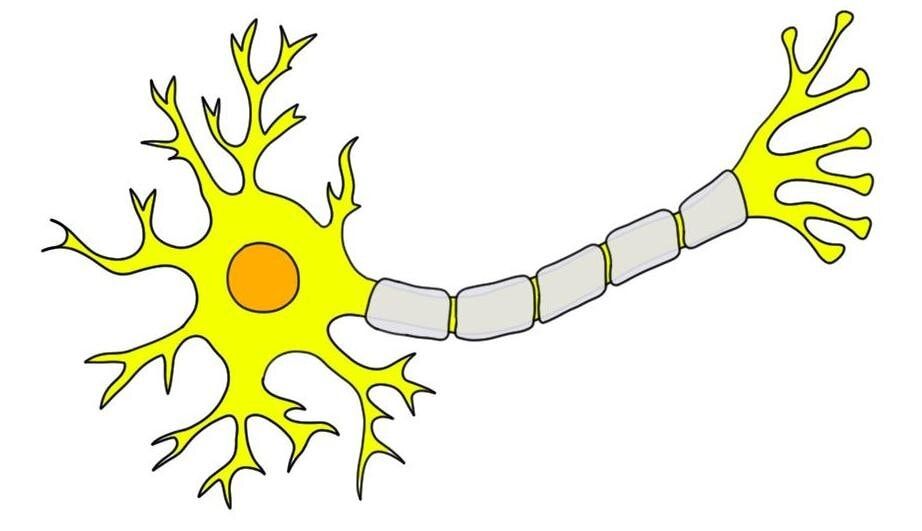
What is this?
neuron
What are the hair like features?
dendrites
Where are the dendrites and what do they do?
hair like, receive information
Where/what is the soma?
The center cell body
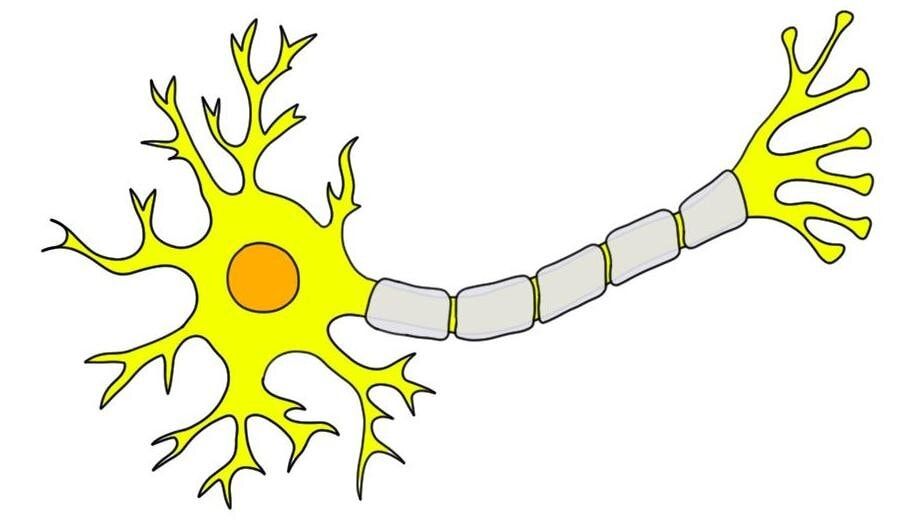
Where is the axon?
The long straight line
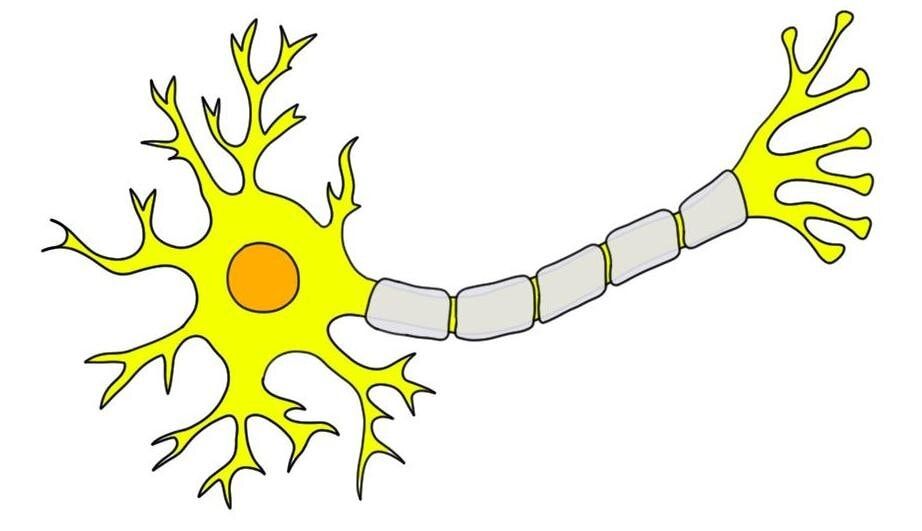
What does the axon do?
Send electricity
What is a Synapse?
the squiggly line (cells don’t touch) (idk bro)
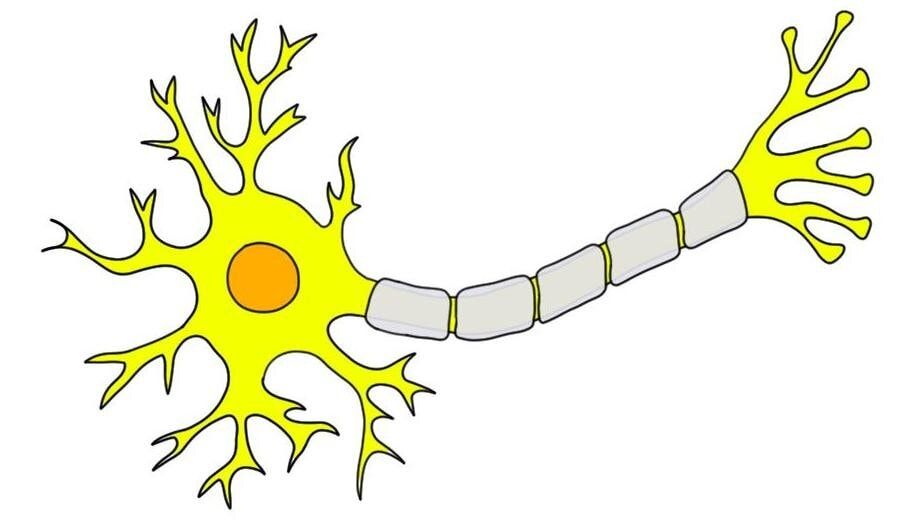
What is at the end of the of the “tree branches”
Synaptic end blubs
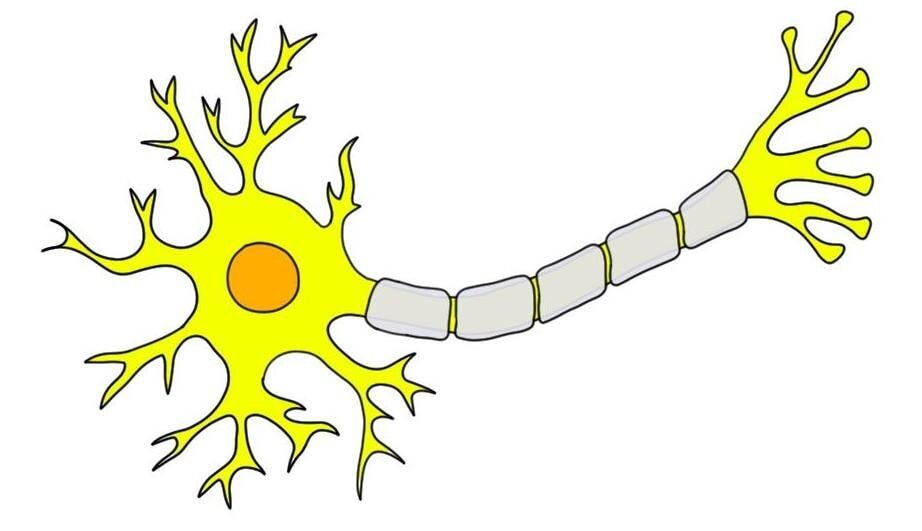
What are the “tree branches'“
teledendria
What determines the function of a cell?
shape
What is a function?
sends/receives electrical information
What are special shapes?
Rbc, Wbc, and neurons (nerve cells)
What is a prokaryote?
A cell with no nucleus
Where is the DNA in a prokaryote
cytoplasm
___ is only a prokaryote
bacteria
What is a eukaryote?
A cell with a nucleus
Where is the DNA in a eukaryote?
The nucleus
Four examples of a eukaryote
Protists, fungi, plants, animals
Why are all cells microscopic?
there is a mathematicial limit to cell size
How complex are prokaryotes?
Simple
How complex are eukaryotes?
Complex
What is the mathmaticial limit to a cell?
Surface area:Volume
How to find the volume of a cube?
L × W × L (S×S×S)
How to find the surface area of a cube?
L×W - (S×S)6
How to find the ratio of a cube?
Small number divided by itself, large number divied by small number.
EX: 24:8 = 3:1
SA:V is equivalent to what?
Food window:people
What is the shape of a white blood cell?
No shape, they transform
What is the job of a WBC
Killing pathogen
What is another term for RBC?
erythrocyte
What is the shape of a RBC
biconcave disc
What does the shape of the RBC (biconcave disc) do?
create more surface area, meaning more efficiency with carrying O2/CO2
What does the shape of the RBC (biconcave disc) do?
create more surface area, meaning more efficiency with carrying O2/CO2
How does a curved line effect surface area
It increases
The higher the unit of volume the more —-——
O2 carried
What kind of line is ALWAYS better in nature?
curved over straight
What are a cells two options as it approaches the size limit?
divide or die
What is the size limit of a cell?
1:1 (death)
Why does a cell have a size limit?
Volume in a cell grows faster then surface area
What happens to a cell as it gets smaller?
the ratio gets bigger
What is an advantage of having a large surface area?
the larger the surface area the more food (surface)
What is a disadvantage of having a large volume?
The larger the volume the less food/surface