Aquatic and Wetland Plants Lecture
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
Why are aquatic ecosystems important?
habitat, refugia and food for aquatic organisms
Anthropocentric recreation
Environmental services: water filtration, algal control, erosion control
Economically important aquatic plants: rice, invasive aquatic plants
Definition of aquatic plants
Grow in/near water, evolved to exhibit various forms. Few are fully aquatic
Ephemeral aquatic areas
Are wet for only a portion of the year
How do we define aquatic community boundaries?
By using aquatic plants
Four types of aquatic plants
submerged, floating, emergent, shoreline
Submerged plants
Underwater for full life cycle, roots located in submerged soil at the bottom of water
Floating plants
Plants float on water’s surface, roots may float or be submerged in soil
Emerging plants
Plants with a large portion of their architecture elevated above water’s surface. Roots located in submerged soil
Shoreline plants
Found near the edge of a body of water. Tolerate periodic flooding, but their roots are not fully/continuously submerged
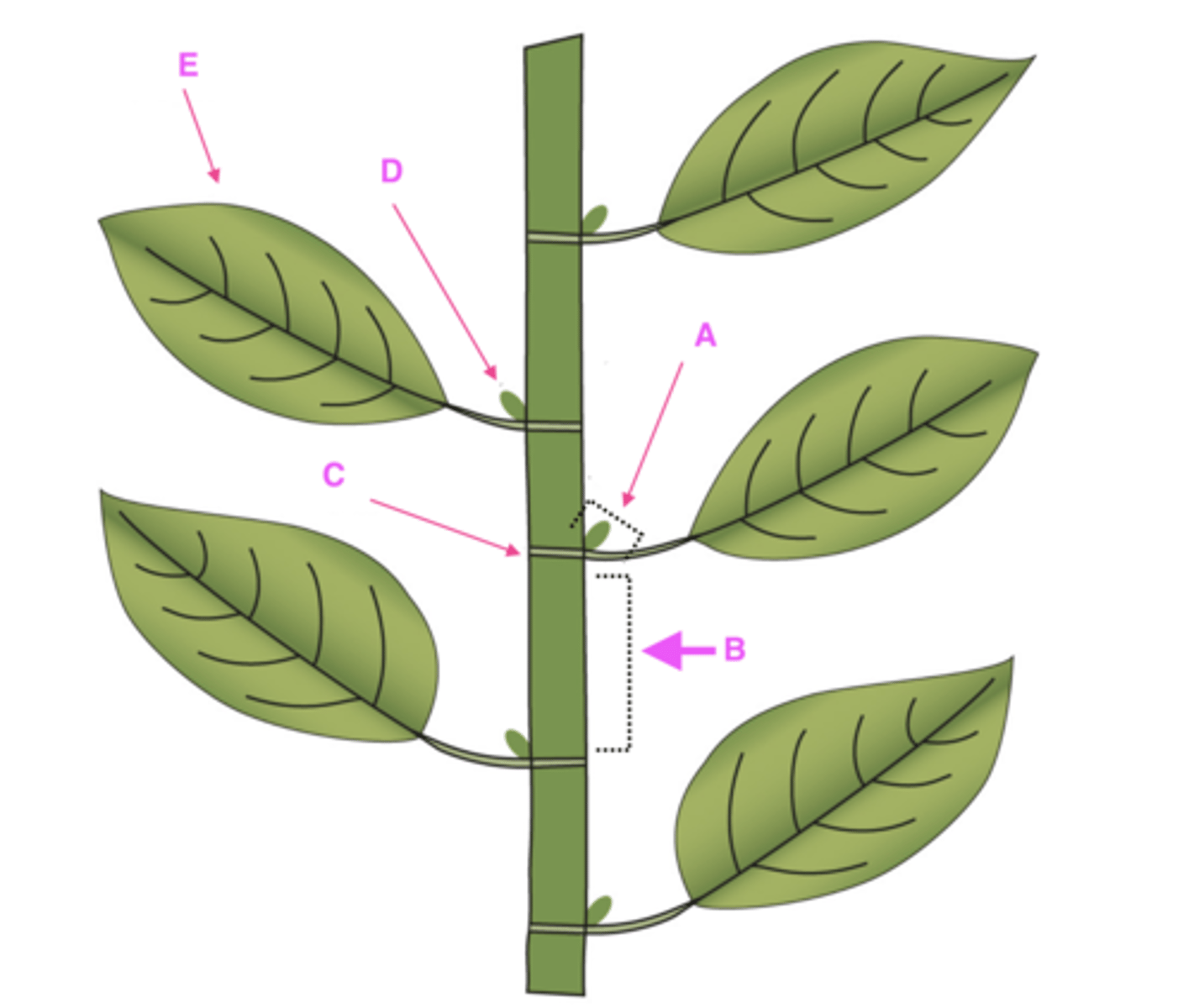
Label structures A-E with proper plant architecture terminology.
A. Leaf axil: point at which the leaf connects to stem or branch
B. Internode: area between nodes
C. Node: area of the stem where buds develop and form into stems/branches
D. Axillary bud
E. Leaf
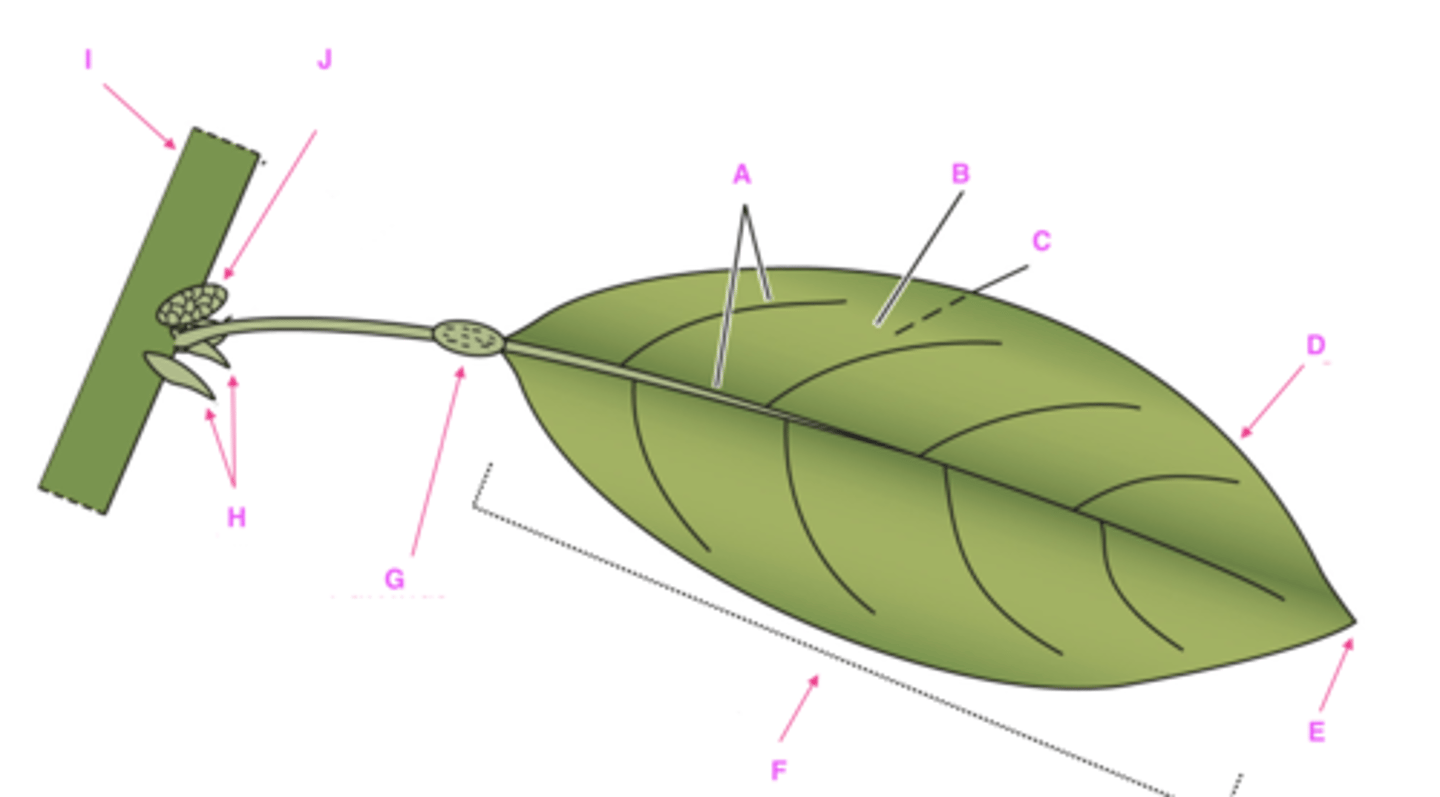
Label structures A-J with proper leaf components.
A. Veins
B. Adaxial surface (top, facing stem)
C. Abaxial surface (bottom, away from stem)
D. Margin (edge of leaf)
E. Apex (tip of leaf)
F. Blade
G. Pulvinus (joint-like thickening at base of leaf/leaflet, helps move the leaf)
H. Stipules
I. Stem
J. Bud

What shape is this leaf?
Acicular: needle shaped
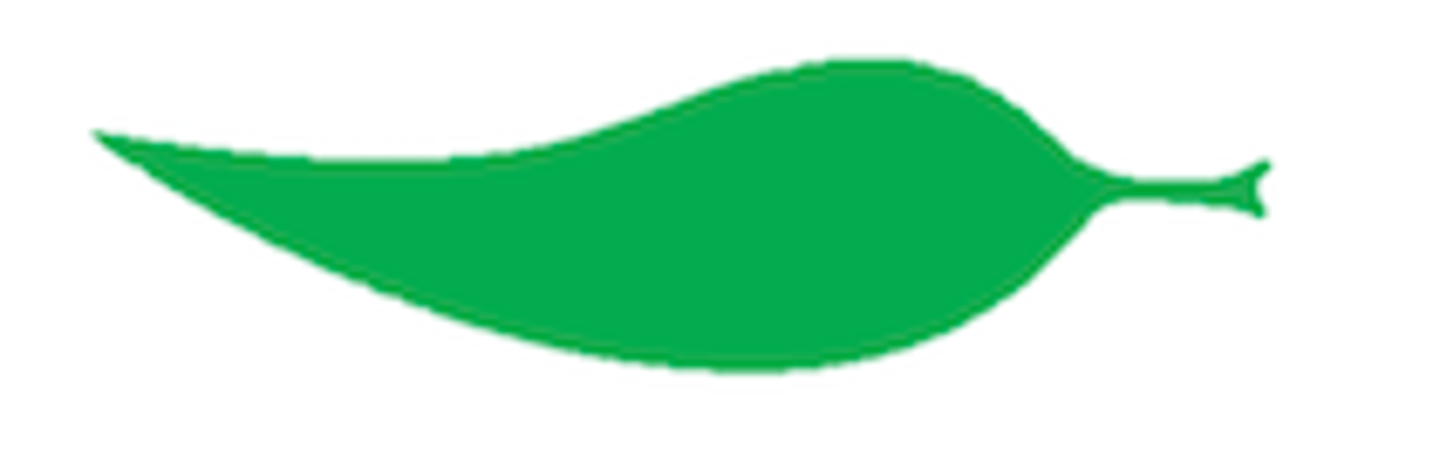

What shape is this leaf?
Falcate: sickle-shaped
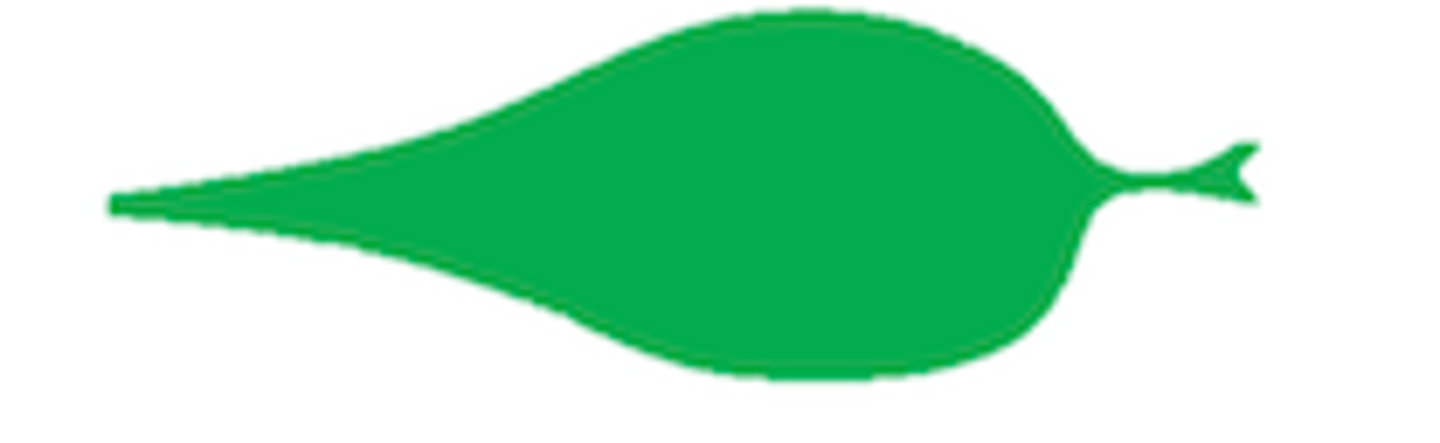

What shape is this leaf?
Acuminate: long with tapering point at tip

What shape is this leaf?
Ovate: egg-shaped and wide at base
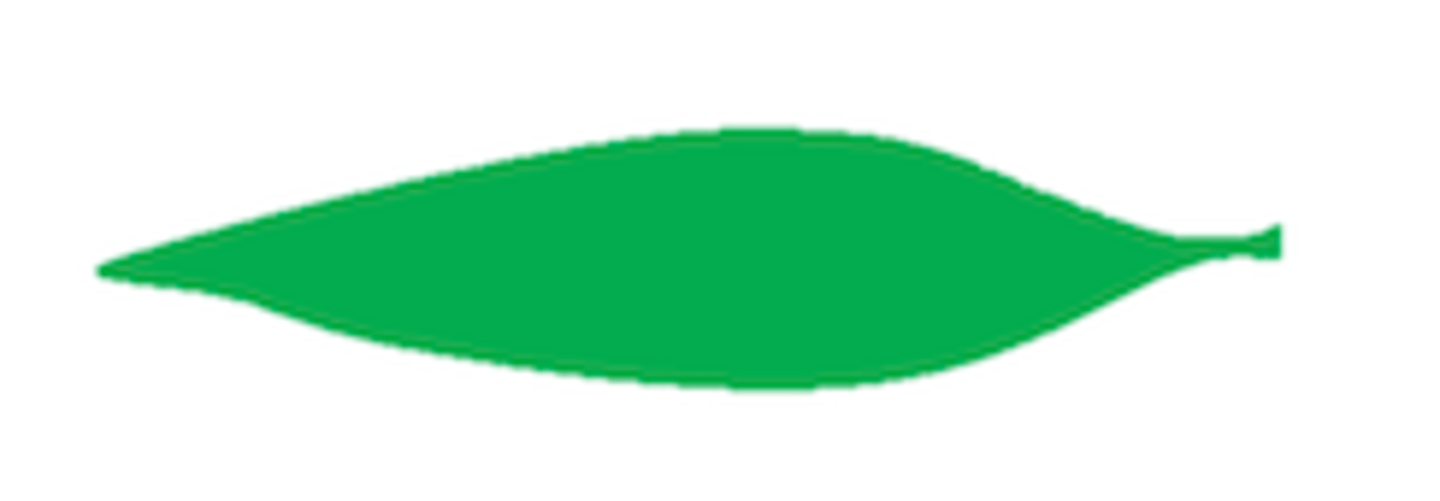

What shape is this leaf?
Lanceolate: pointed at base
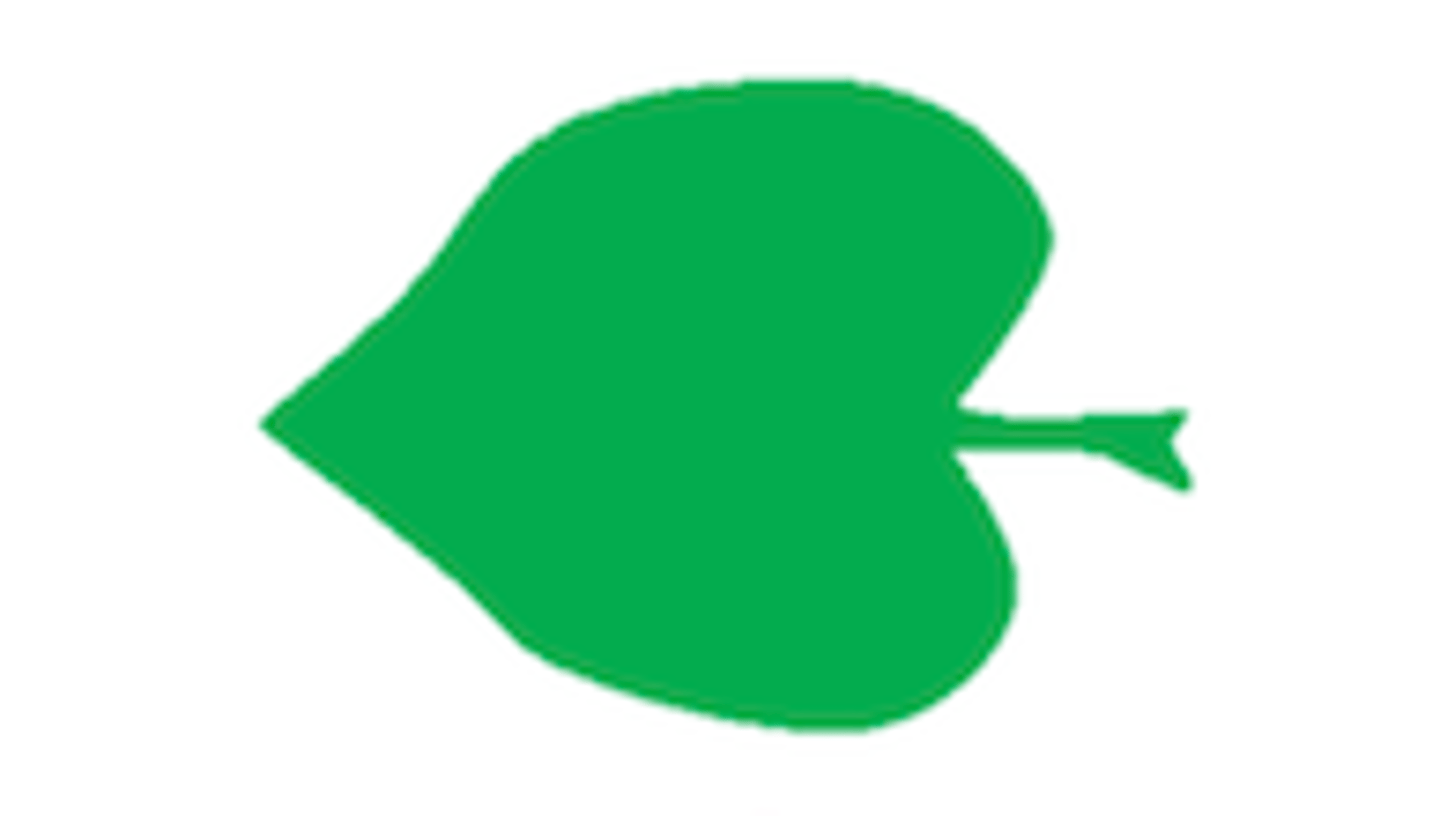

What shape is this leaf?
Cordate: heart-shaped

What shape is this leaf?
Lobed: indented margins
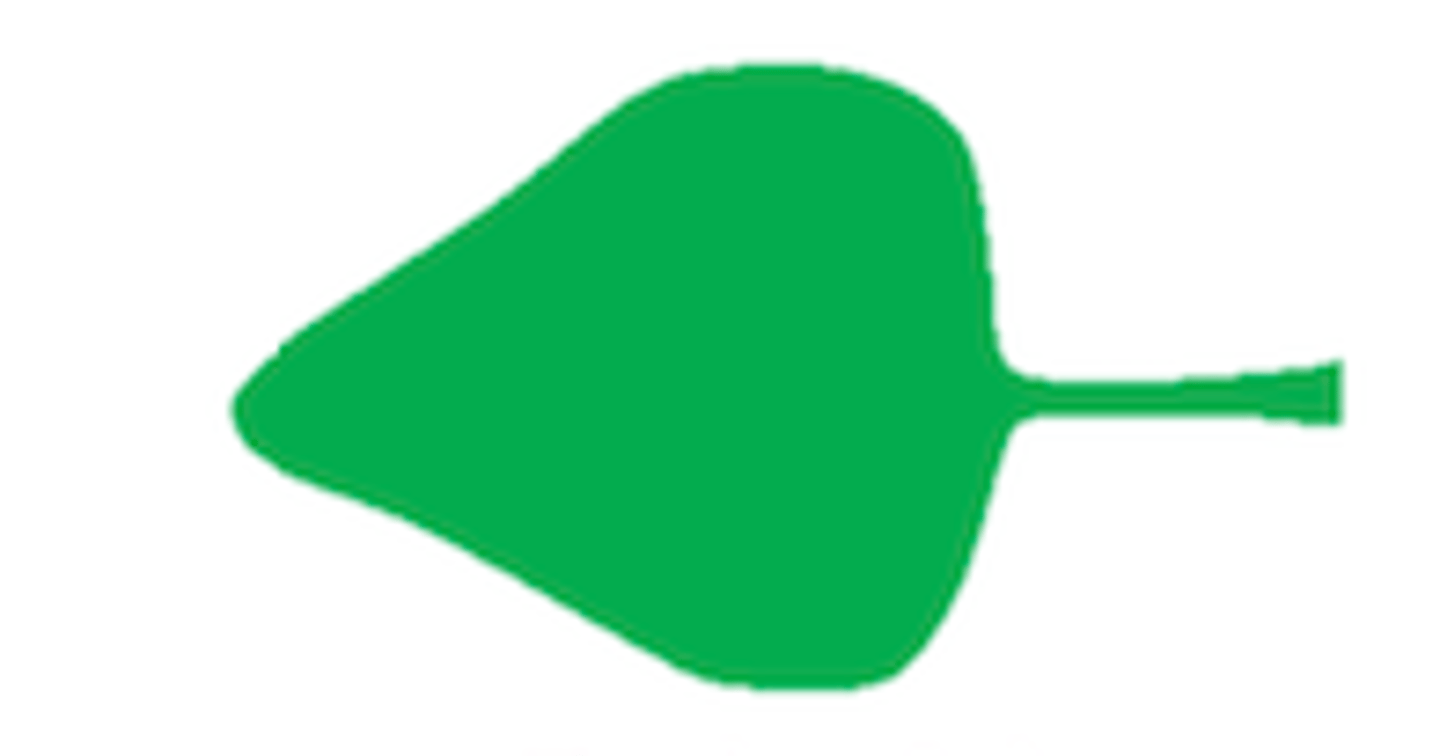
What shape is this leaf?
Deltoid: triangular
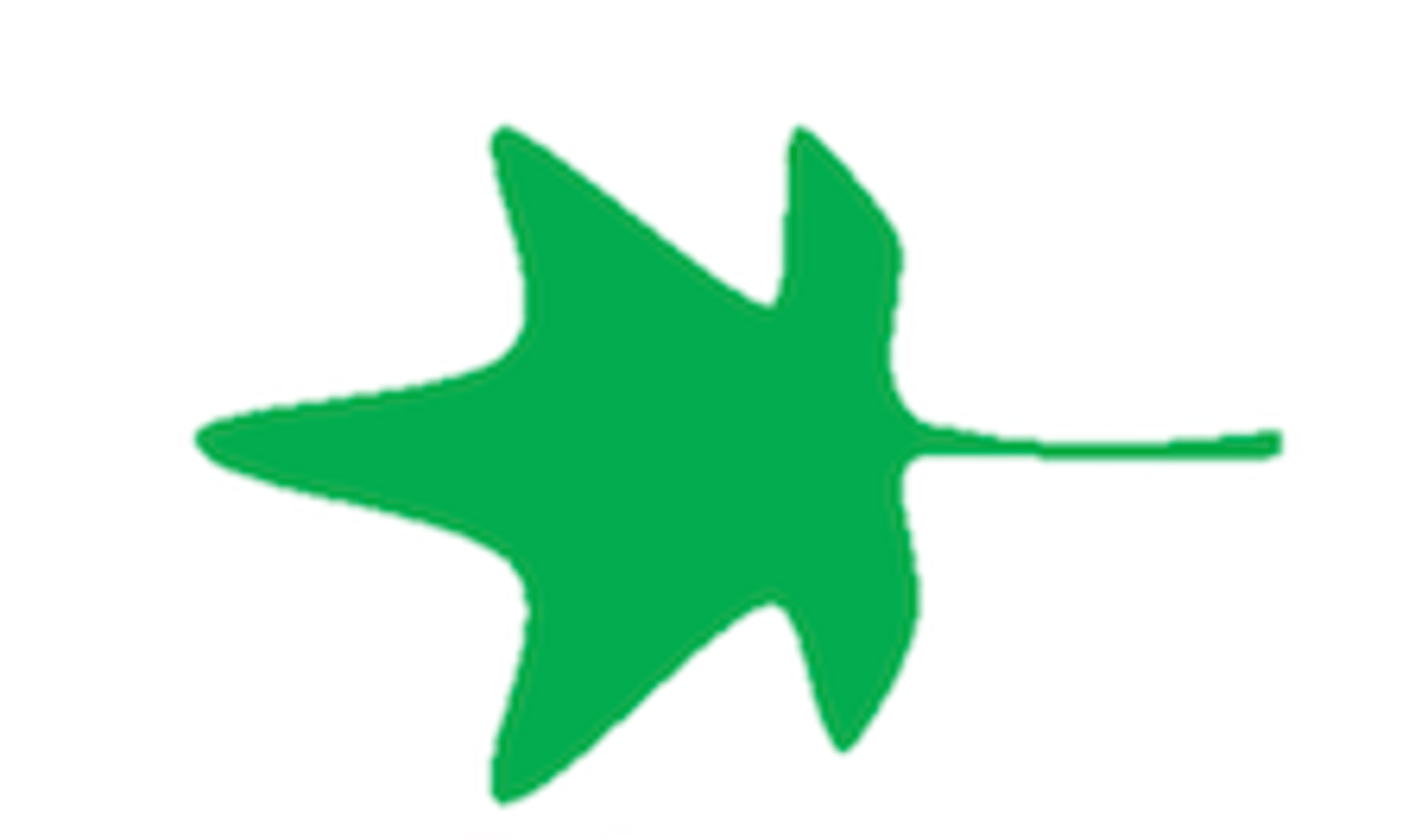

What shape is this leaf?
Palmate: hand-shaped
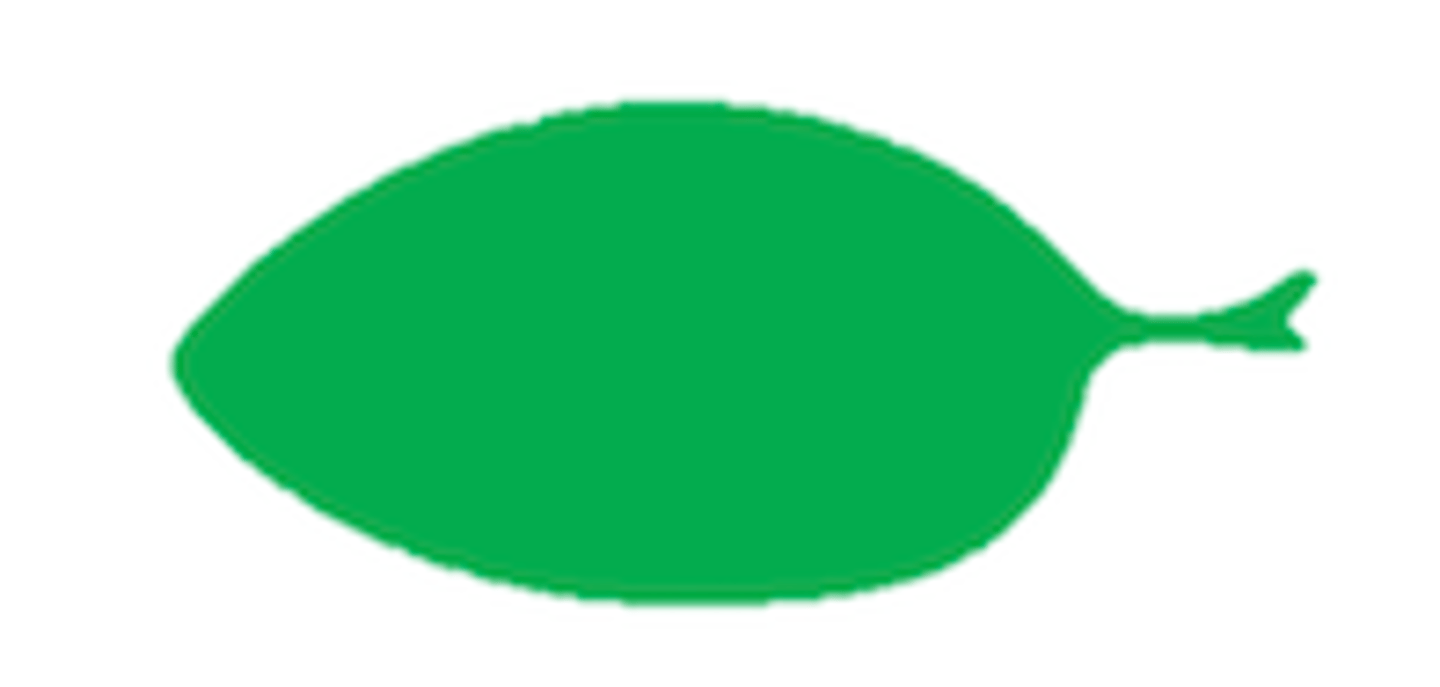

What shape is this leaf?
Elliptic: oval-shaped with little to no point at tip
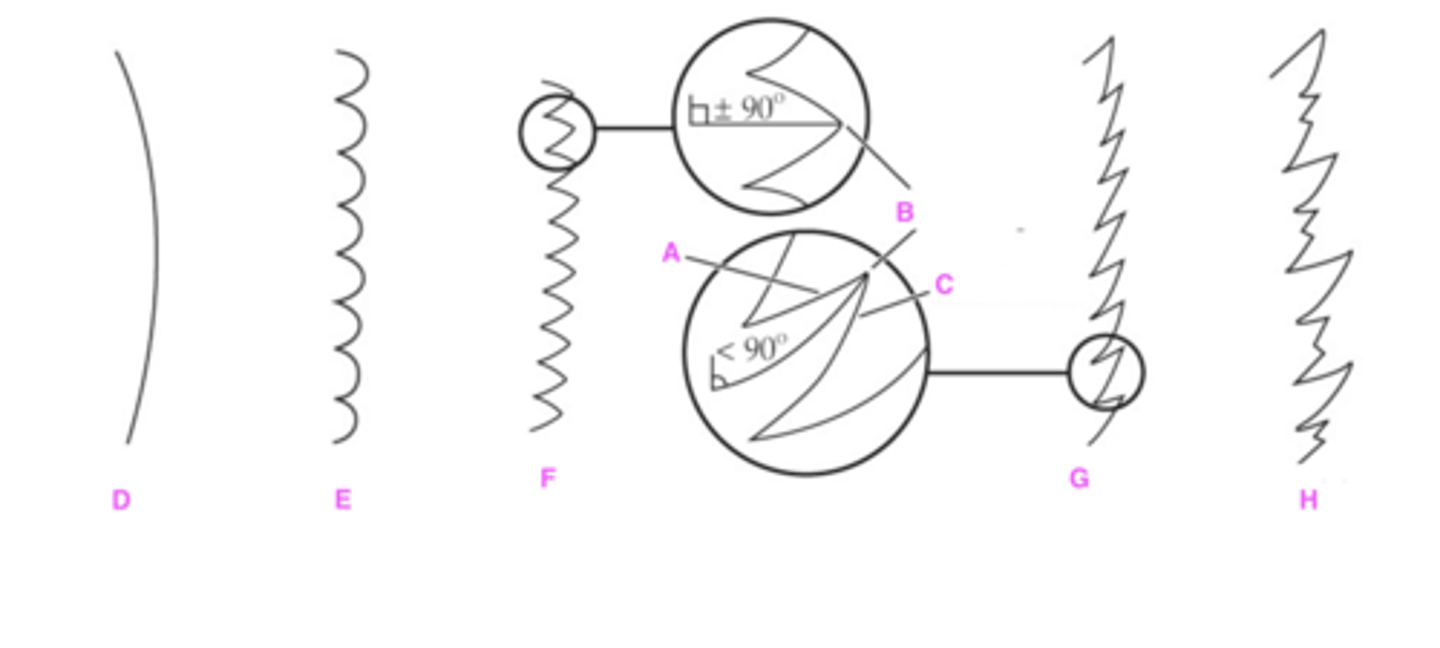
Label structures A-H with proper leaf margin terminology.
(hint: A & C are asking for the term for these sides)
A. Apical side
B. Tooth apex
C. Basal side
D. Entire: leaf margin is smooth
E. Crenate: leaf margin is wavy
F: Dentate: teeth on leaf margin at 90 degree angles
G: Serrate: teeth on leaf margin LESS than 90 degree angles
H: Doubly serrate: serrate with small sub-teeth
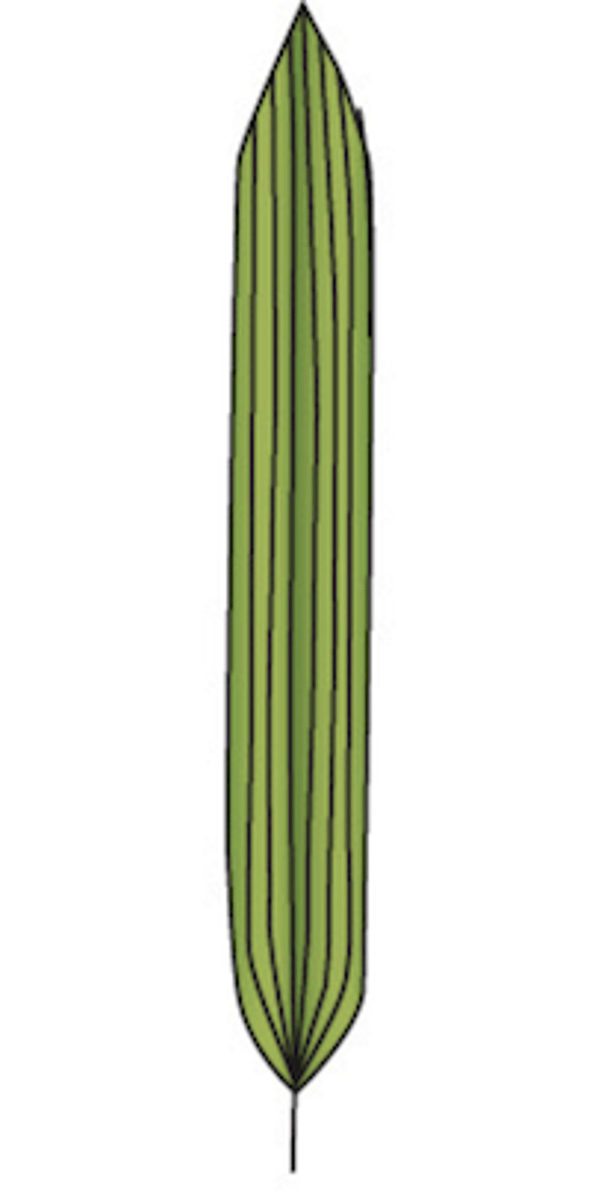
What type of venation does this leaf display?
parallel: veins run parallel to one another (monocots)
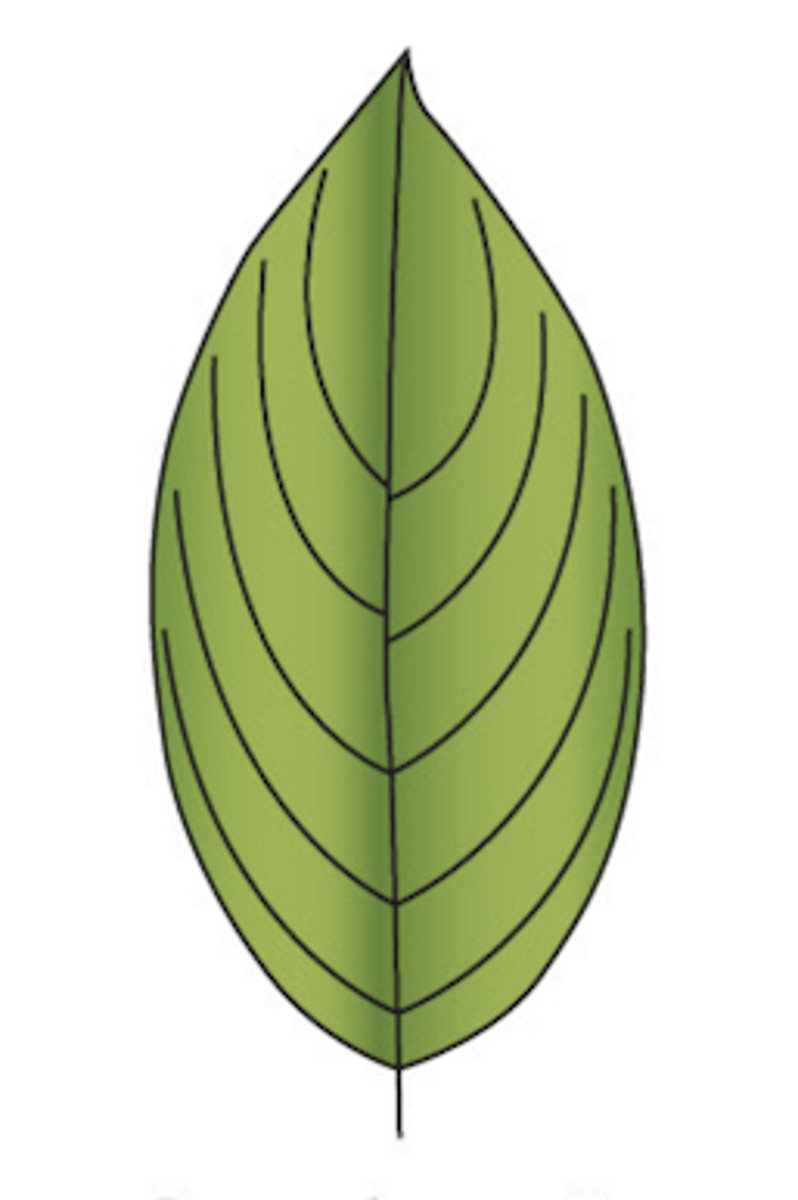
What type of venation does this leaf display?
arcuate (think that the veins are ARCING)
- veins arch to come into contact (or nearly) at the leaf apex
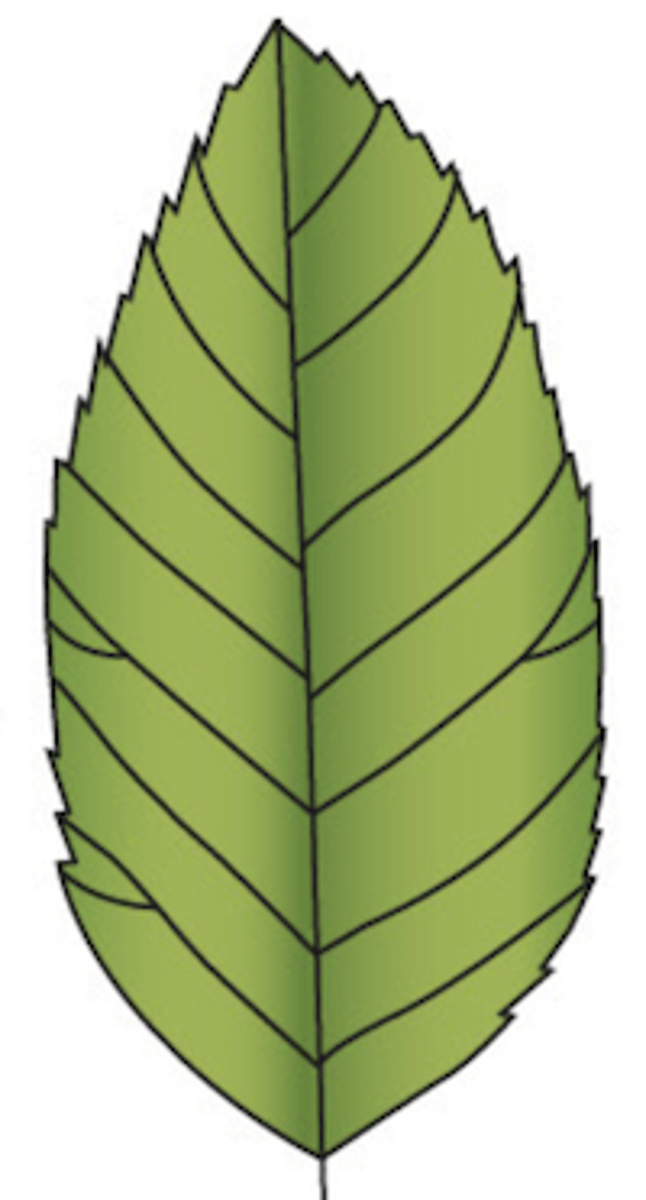
What type of venation does this leaf display?
dichotomous: veins branching in pairs, may or may not end in teeth
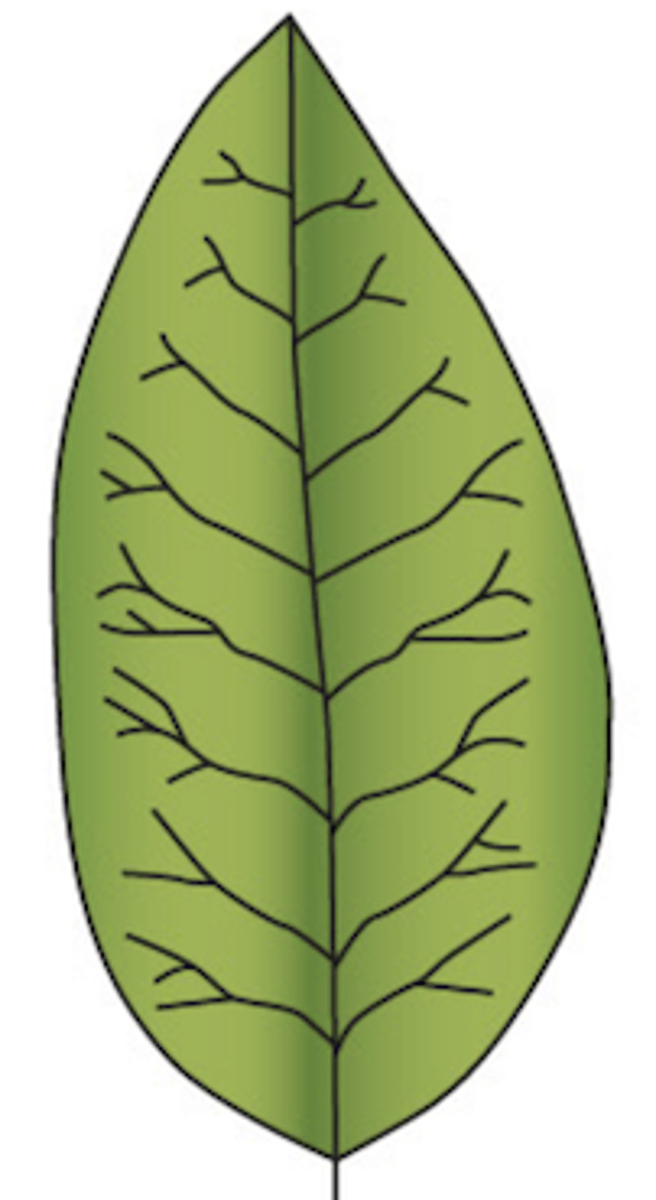
What type of venation does this leaf display?
dichotomous: veins branching in pairs, may or may not end in teeth
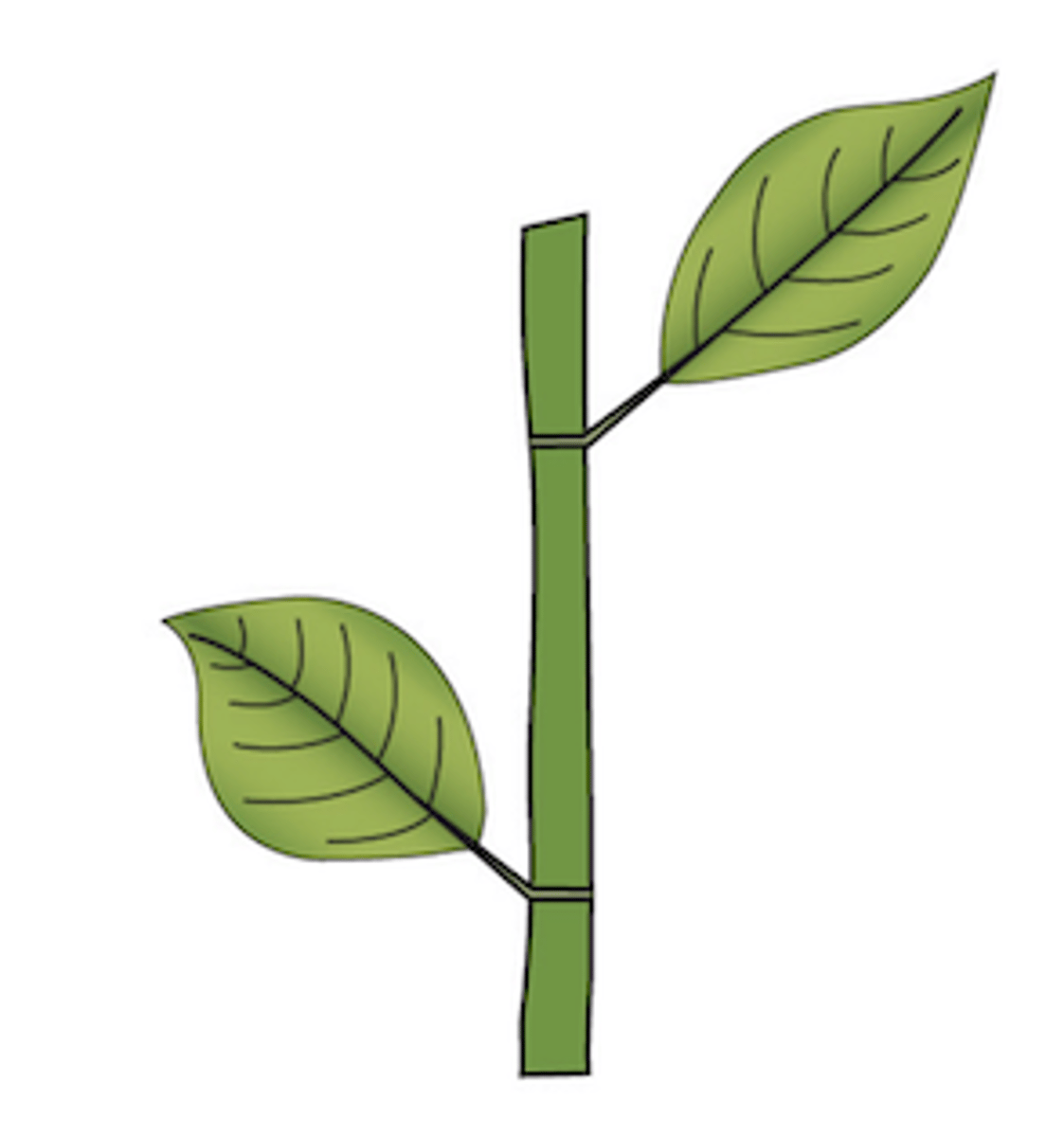

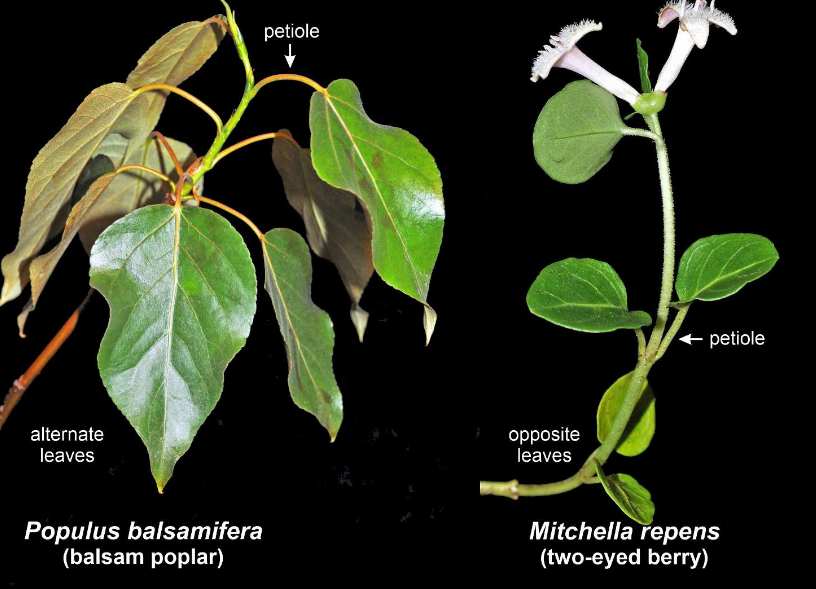
What type of leaf arrangement does this plant display?
alternate: 1 leaf per node
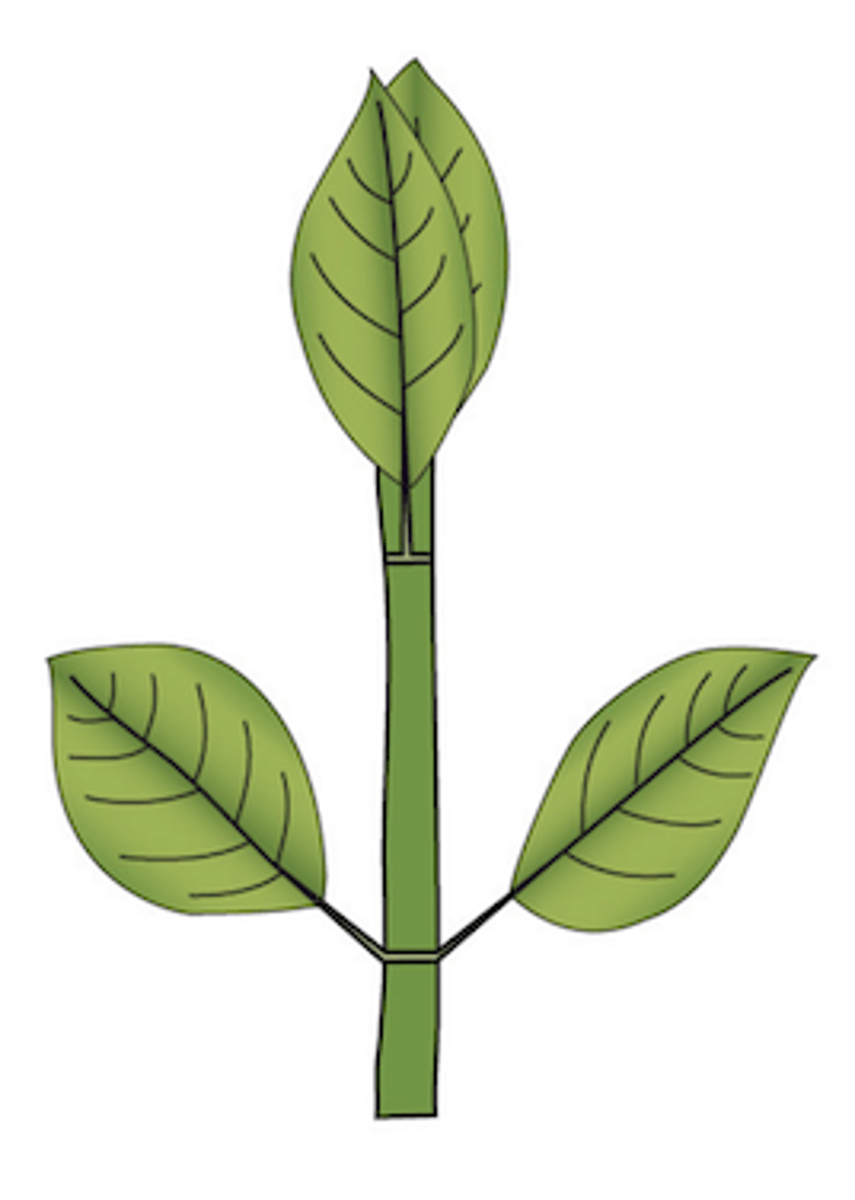

What type of leaf arrangement does this plant display?
opposite: 2 leaves per node opposite from one another on stem
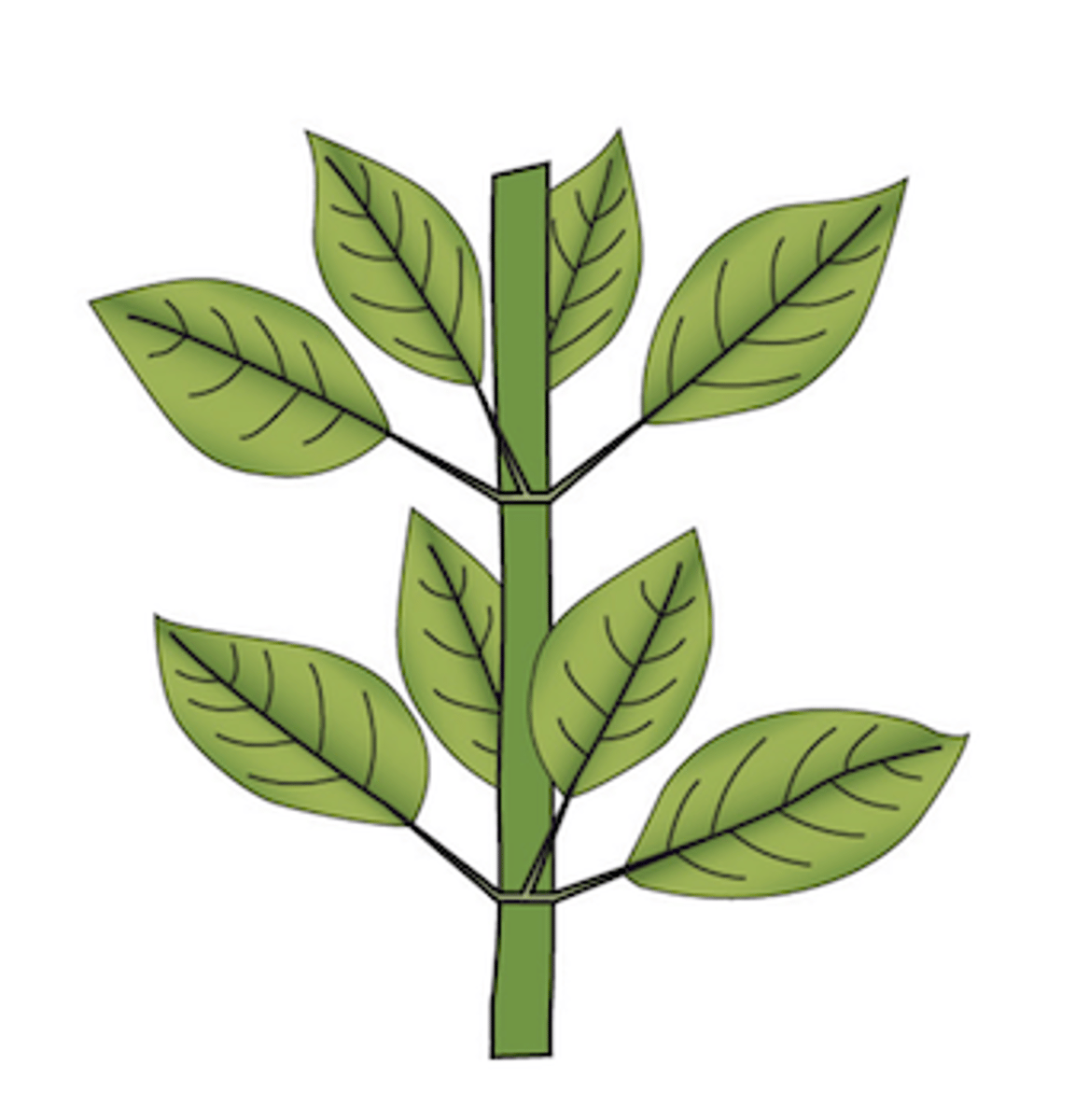

What type of leaf arrangement does this plant display?
whorled: 3 or more leaves per node
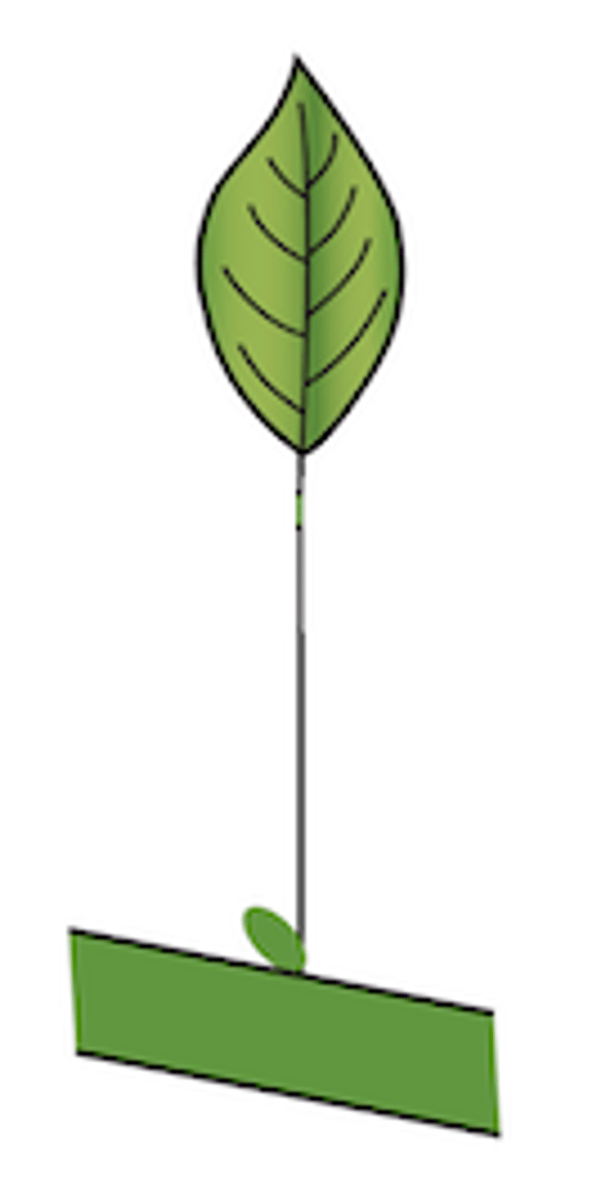

Explain the type of leaf complexity this leaf possesses (simple, compound, etc.)
Simple: single blade connected to a stem
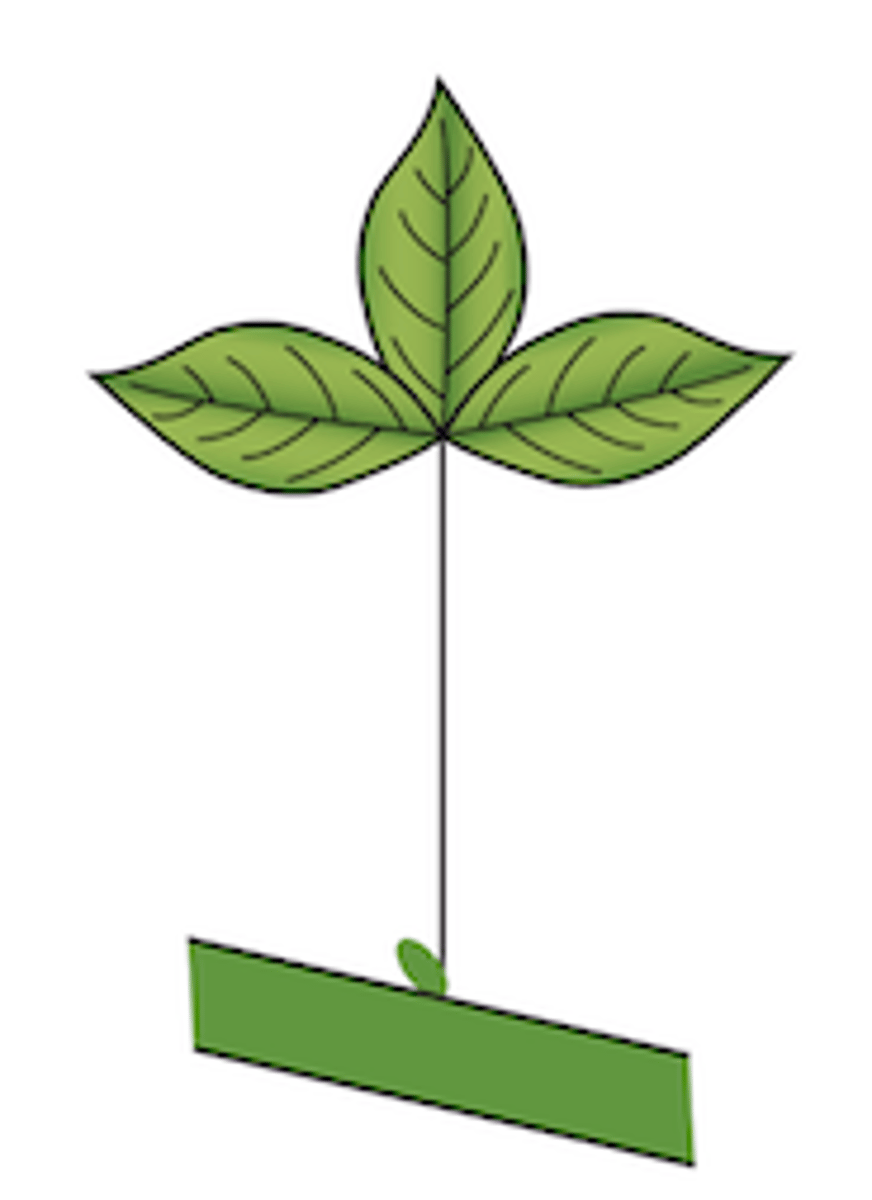

Explain the type of leaf complexity this leaf possesses (simple, compound, etc.)
Trifoliate: single blade with three lobes
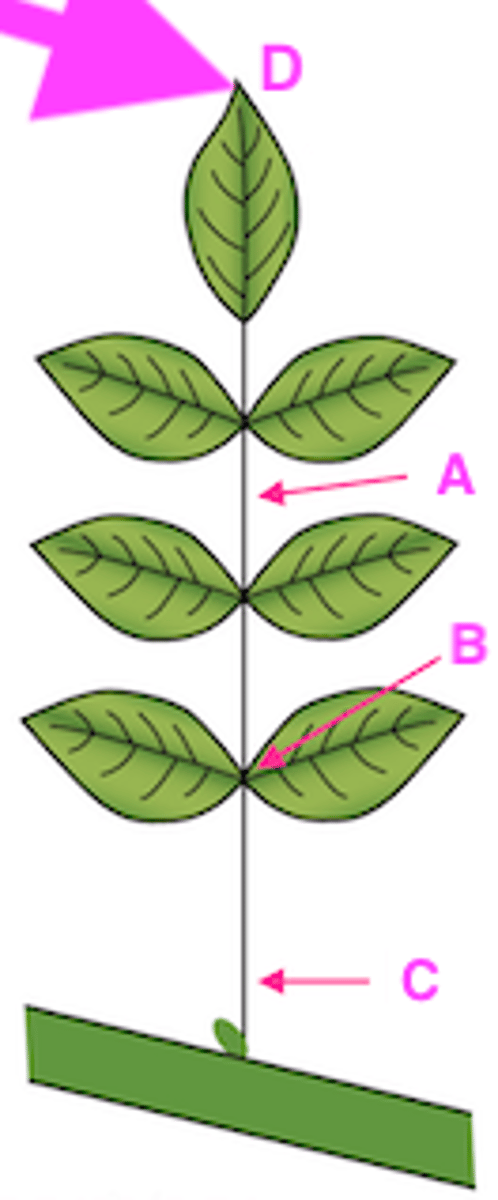
Explain the type of leaf complexity this leaf possesses (simple, compound, etc.) and label structures A-D.
Pinnately-compound: each leaf has multiple leaflets
A. Rachis (area of petiole between leaflets)
B. Petiolule (where leaflet meets rachis)
C. Petiole
D. Terminal leaflet
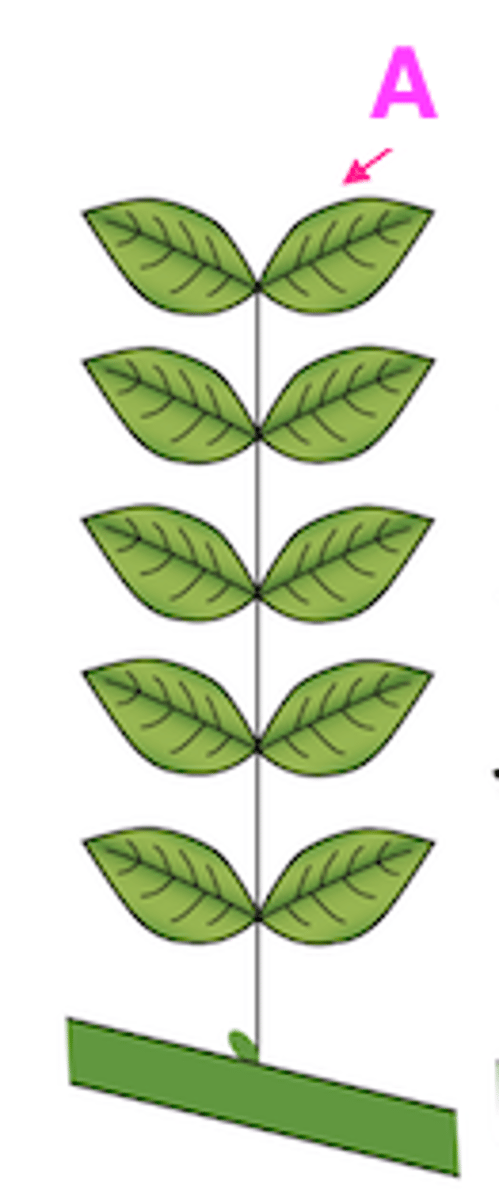
Explain the type of leaf complexity this leaf possesses (simple, compound, etc.) and label structure A.
Pinnately-compound: each leaf has multiple leaflets
A. Leaflet
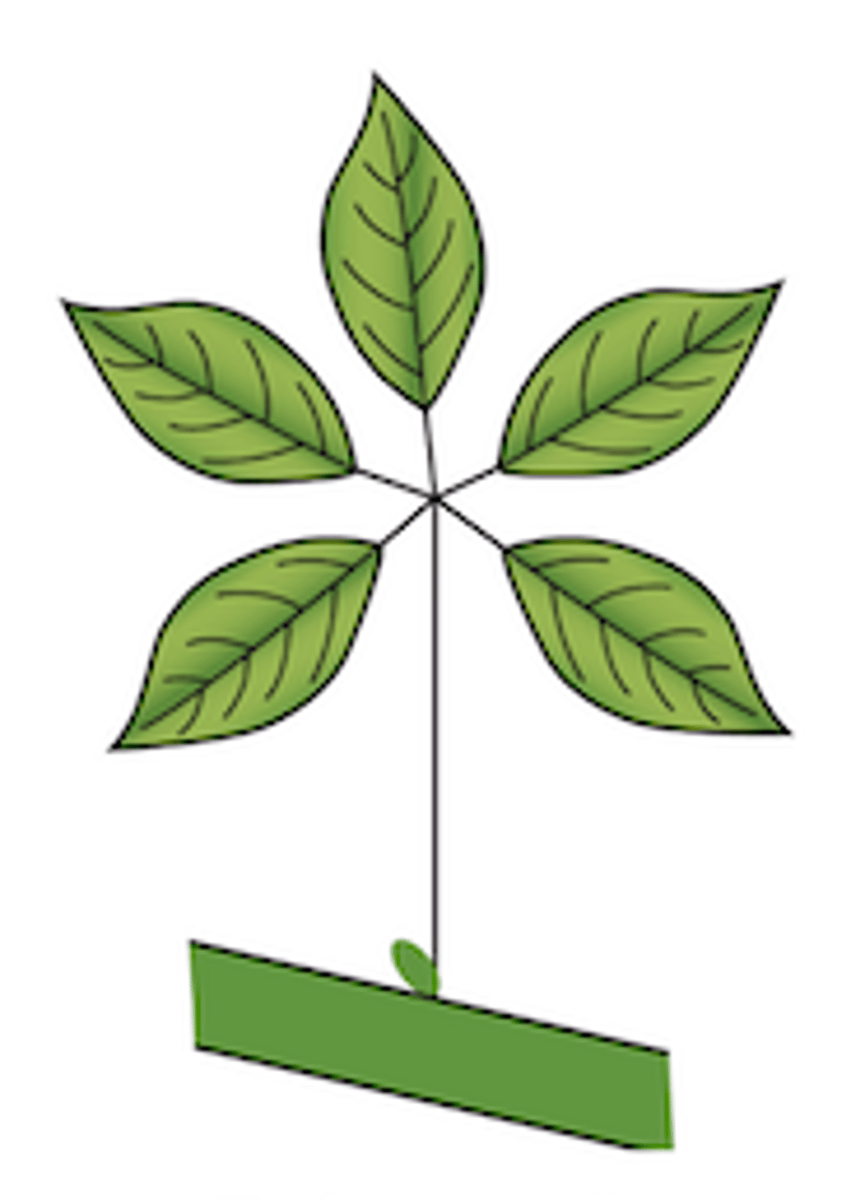

Explain the type of leaf complexity this leaf possesses (simple, compound, etc.)
Palmately-compound leaf: leaflets arranged to resemble a hand
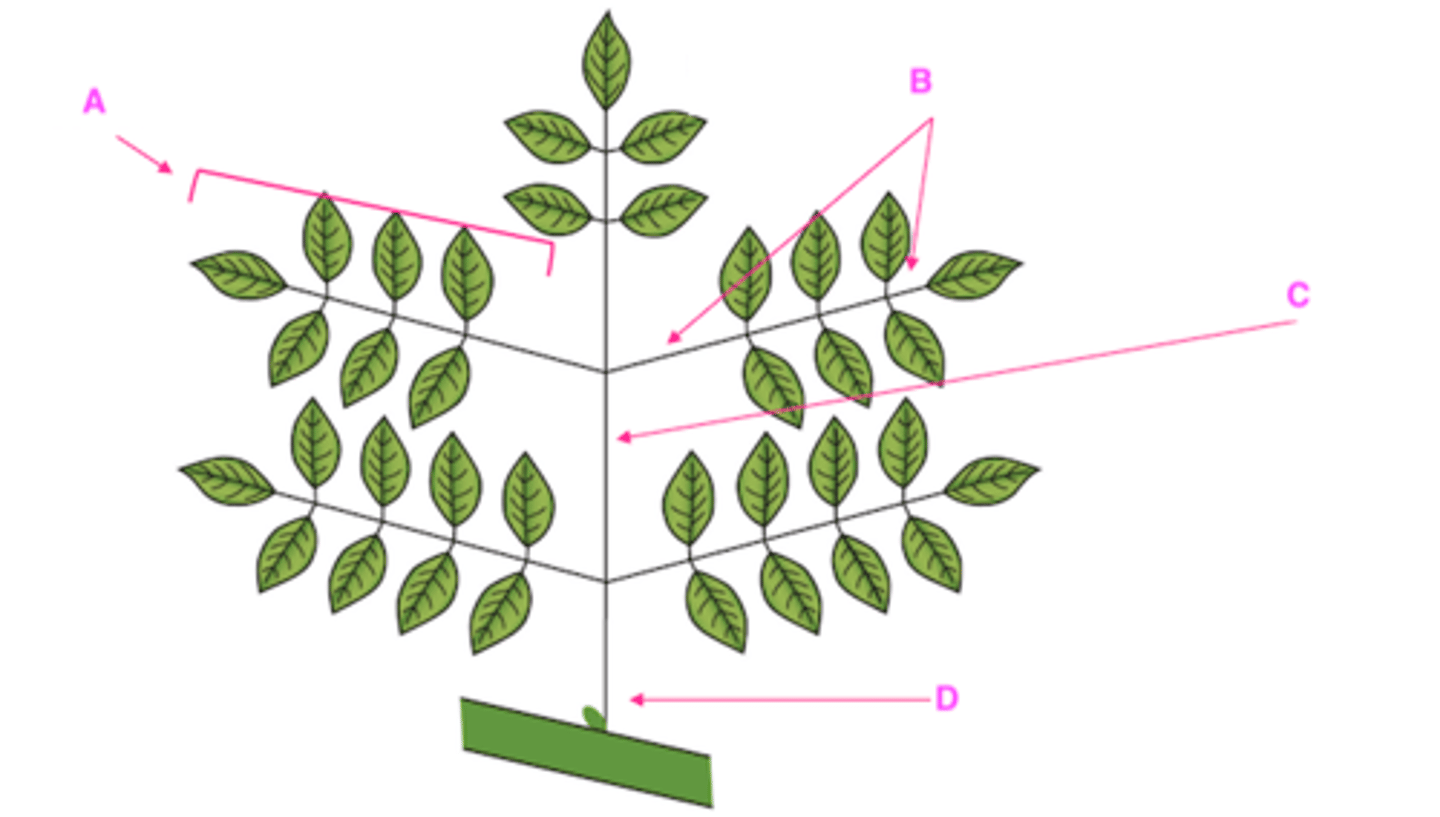
Bipinnately-compound: two levels of division
A. Leaflet
B. Petiolule (where leaflet meets rachis)
C. Rachis (think baby stem on compound leaves)
D. Petiole
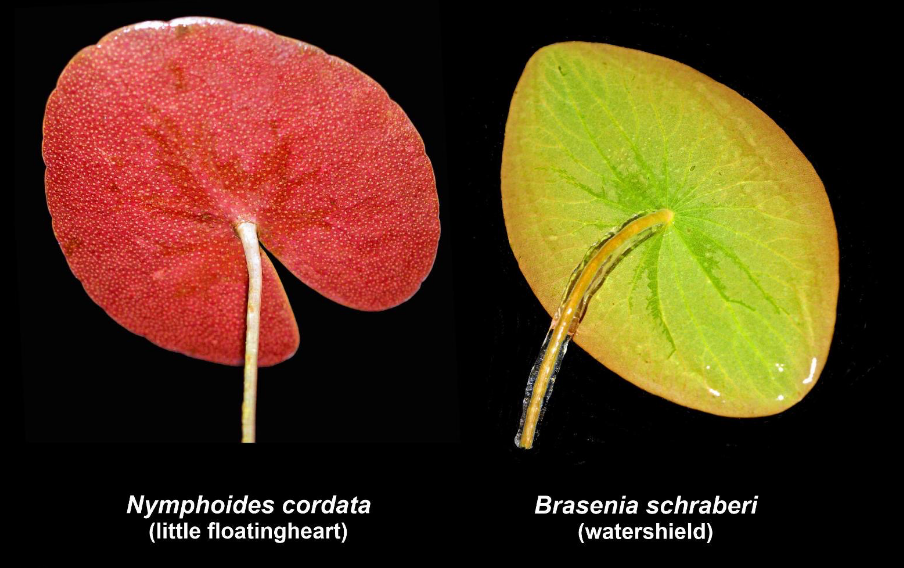
Explain the type of leaf complexity this leaf possesses (simple, compound, etc.) and label structures A-D.
Peltate leaves
Petiole attached to the abaxial (lower) leaf surface (umbrella shaped)

Petiolate leaves
attached to the stem by a petiole (leaf stalk)
Sheathing leaves
with the lower portion of a grass leaf enveloping, but not fused to the culm, except at a node
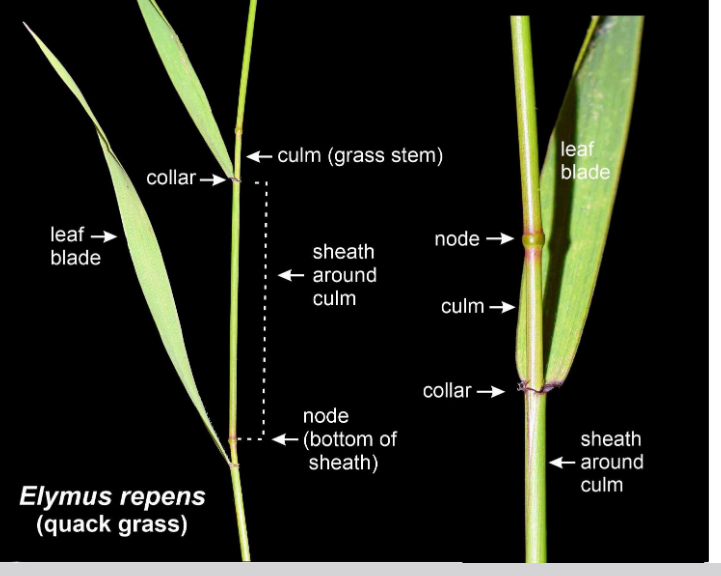
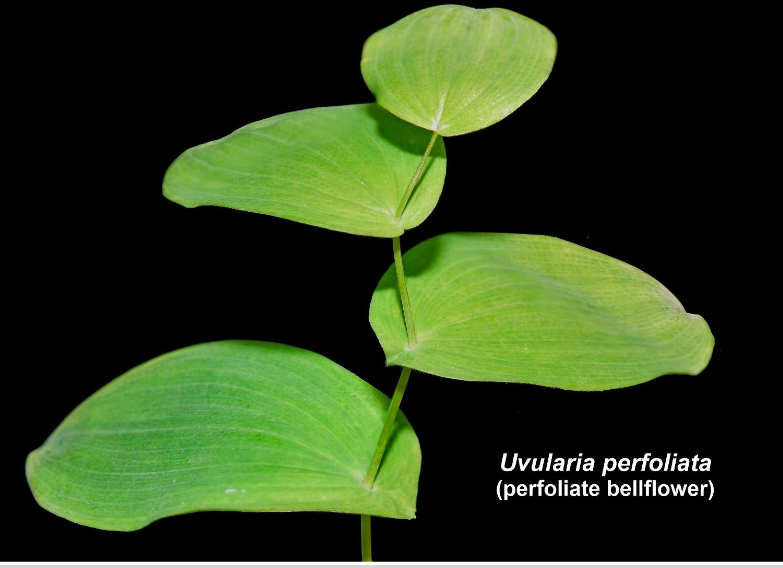
Perfoliate leaves
With basal lobes completely surrounding the stem, and fused (connate) around the stem

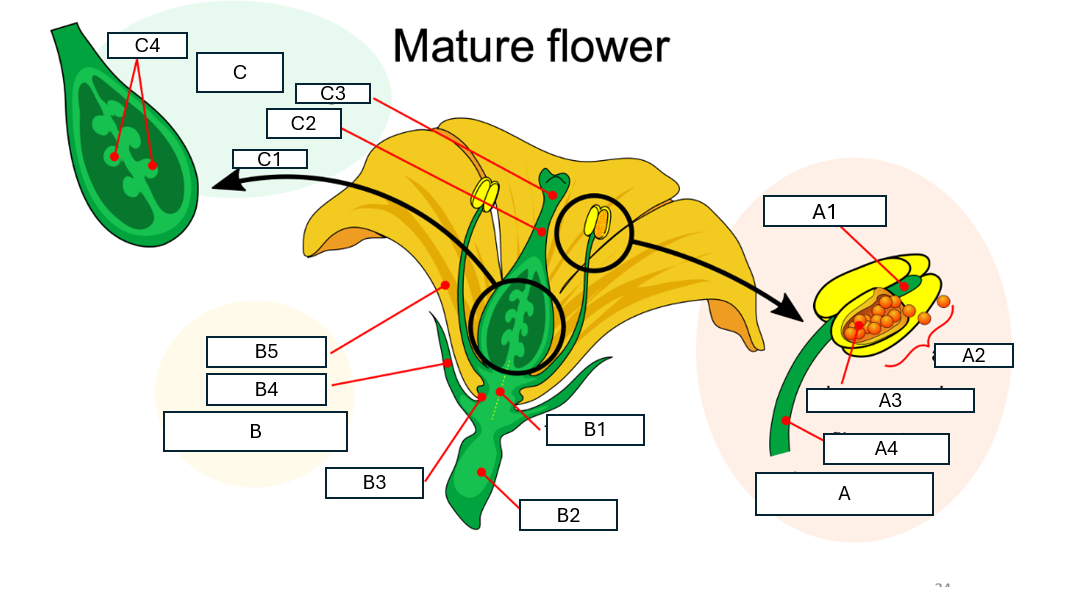
Name flower structure A and its component parts A1-A4
A: stamen
A1: connective
A2: anther
A3: microsporangium
A4: filament
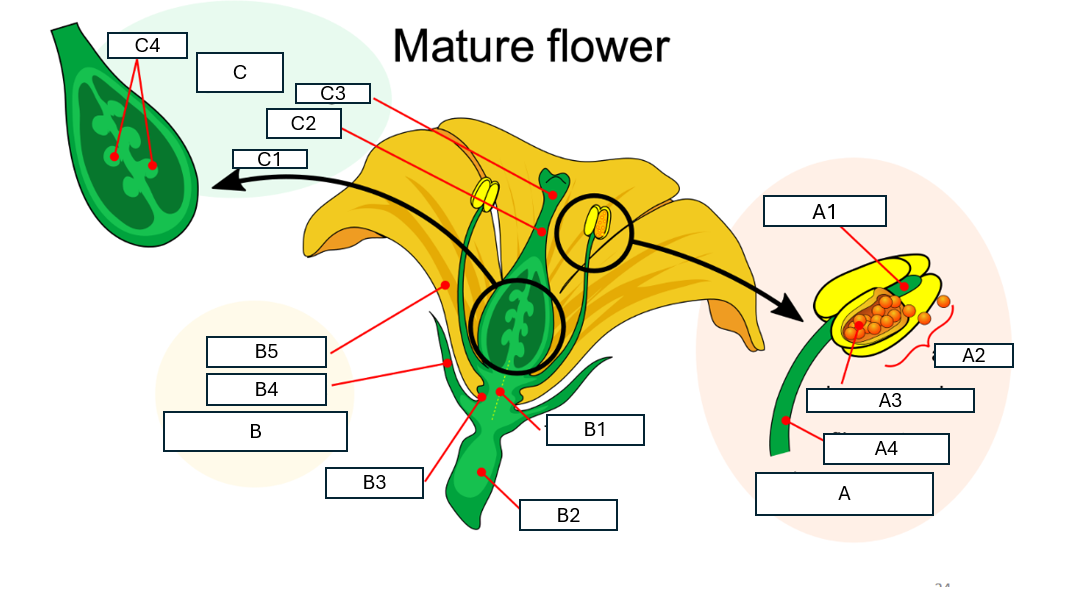
Name flower structure B and its component parts B1-B5
B: perianth
B1: floral axis
B2: pedical
B3: nectary
B4: sepal/calyx
B5: petal/corolla
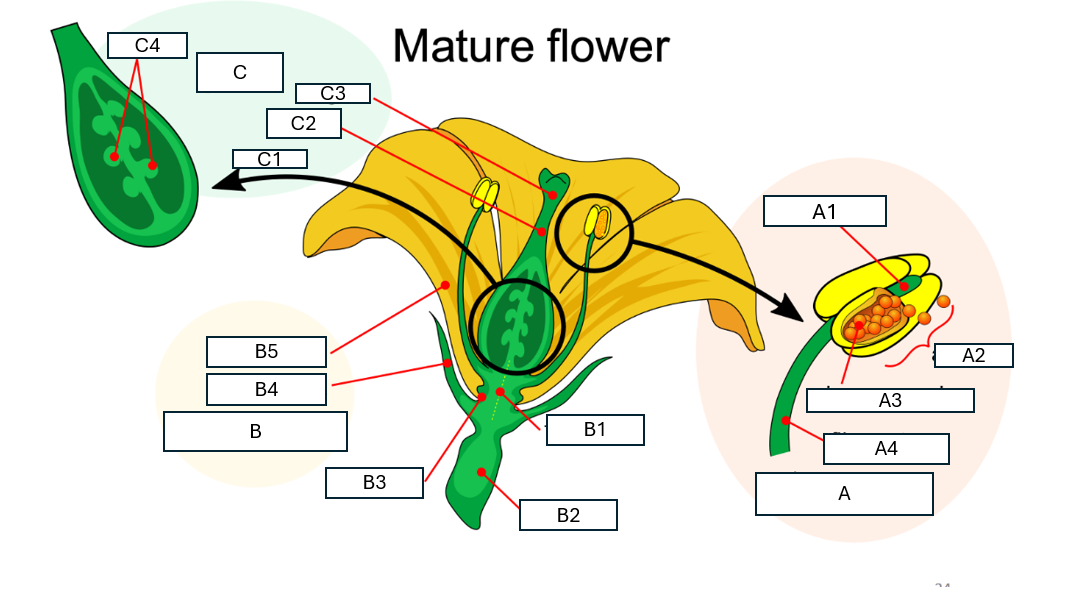
Name flower structure C and its component parts C1-C4
C: pistil
C1: stigmaa
C2: style
C3: ovary
C4: ovules (within ovary)
wetland indicator status OBL
99% occurrence in wetland
wetland indicator status FACW
67-99% occurrence in wetlands
wetland indicator status FAC
34-66% occurrence in wetland
wetland indicator status FACU
1-33% occurrence in wetland
wetland indicator status UPL
<1% occurrence in wetlands
Factors that make wetlands differ
salinity, temperature, depth, proximity to neighboring water bodies, soil types, aquatic plant community
Palustrine
inland, non-tidal wetland with less than .5 ppm marine salt
Riparian
wetlands adjacent to rivers and streams
Estuarine
brackish water with one or more rivers/streams meeting the sea: transition from river to maritime
Marine
oceanic/sea water
Ramsar convention on wetlands
includes areas of restored and man-made/impacted wetlands,. 10 categories accepted in the literature
Peatland (Palustrine)
Unique soils produced by waterlogged conditions that prevent plants from decomposing: organic matter exceeds its decomposition rate
Peatlands function
Cover about 2.84% of earth’s terrestrial surface, store and sequester and exceptional amount of carbon. When drained, carbon oxidizes to CO2. Overtime proper hydrology cannot be restored without soil amendments
Bogs
(peatlands) peat-accumulating wetlands that are hydrologically isolated from groundwater or surface flows, ph<6.
Bogs vegetation
Sphagnum mosses mixed with conifers or Ericaceae shrubs
Fens
Peatlands connected to ground/surface water, ph 6-8.
Fen vegetation
graminoids (grasses and sedges), various shrubs/trees
Pocosin
Temperate peat wetlands with deep, acidic sandy peat soils (Southeast VA, NC, SC) in higher elevations
Pocosin vegetation
woody evergreens
Seagrass beds
marine herbaceous non-peatland: near-shore aquatic habitats in coastal marine ecosystems
Seagrass bed vegetation
herbaceous aquatic angiosperms (Alismatales)
Salt marshes
estuarine herbaceous non-peatland: tidal zones of coastal ecosystems
Salt marsh vegetation
salt tolerant grasses (halophytes)
Littoral zone wetlands
lacustrine herbaceous non-peatland: margins of lake ecosystems, water no deeper than 2m, water can be fresh or brackish
Littoral zone vegetation
mixture of herbaceous plants
Marshes
palustrine herbaceous non-peatland:broad category of shallow freshwater wetlands
Marsh vegetation
variety of herbaceous species
wet meadow
palustrine herbaceous non-peatland: freshwater-shallower depth than marshes or short duration flood period
wet meadow vegetation
greater diversity than marshes, lots of graminoids
mangrove swamps
marine woody non-peatland: marine coastal wetlands dominated by mangrove trees or shrubs: tropical and subtropical regions. Exhibit ecological zonation/taxonomic differentiation with different depths
swamps
palustrine woody non-peatland: wetlands dominated by trees with occasional shrubs, fresh or marine waters
Wetlands present in KY
Swamps (Cypress/Tupelo swamps in Western KY), Bogs/seeps (high elevation Eastern KY and lower elevations in coastal plain region), marshes (spanning the state, common in low-lying areas), wet meadows (very degraded due to agriculture)
Four factors determining if a location can support a wetland ecosystem
water depth, duration, frequency, chemical composition
Water balance equation
ΔS = Pn ± Qo ± QS/G − ET (water storage equals net precipitation minus flow in/out of wetlands minus evapotranspiration)
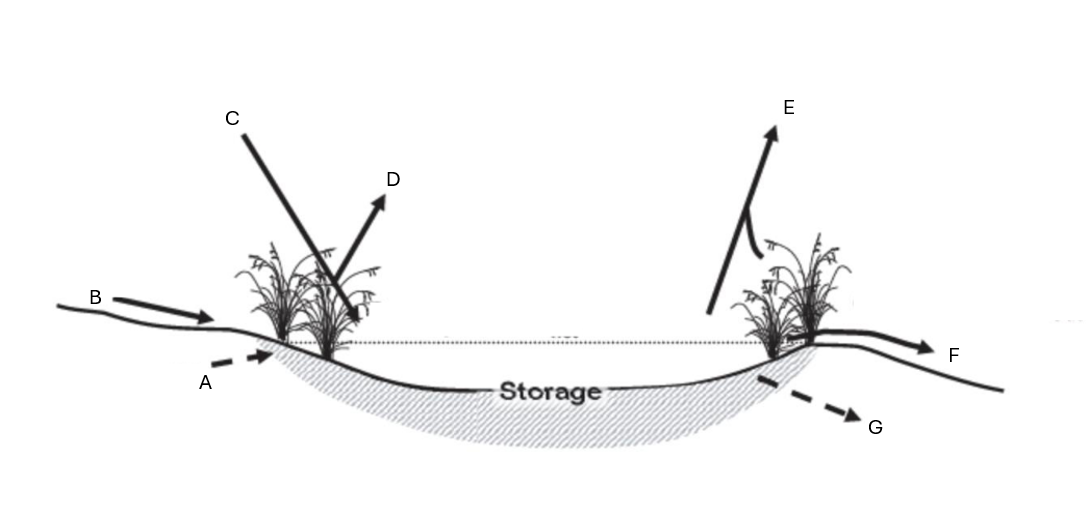
Label water sources in and out of wetland A-G
A: Qs/g in
B: Qo in
C: Pn
D : evaporation
E: ET
F:Qo out
G: Qs/g out
Pn
net precipitation: precip can be intercepted by plants
Qo
overland surface flow into and out of wetland, eg runoff
Qs/g
subsurface/groundwater flow in/out of wetland
Ways to measure water input/output
Rain gauge: tipping bucket gauges limit evaporation/splash
Ways to measure interception
Measure precipitation above/below canopy to get net precipitation. For stemflow, collars may be placed around a tree trunk. For fall through, rain gauges beneath the canopy
How to measure streamflow
Volume of water passing a selected point. Velocity will differ based on regions of the stream velocity of water and cross/sectional area at given point. Can use a weir or a flue, control water levels by calculating streamflow rates, but must be installed via stream manipulation
How to measure runoff
For true estimates collection troughs were installed on the base of a slope where water will accumulate so volume can be measure. Now can use electronic loggers to continuously measure water pressure/depth
How to measure soil/groundwater flow
Darcy’s law, soil cores, wells, pizeometer, lysimeter
Darcy’s law
Q = Ksat A*(Sh/Sx), hydraulic conductivity of soil times cross section of subsurface layer times hydraulic gradient across layer of interest
How to measure evapotranspiration
Water potential= free energy of a sample of water relative to a pure water and tendency of that water to move to a gradient. Becoming more negative with increasing mineral ions and sugar. Water will move from high to low potential. Water potentials approx 0 mPA for freshwater wetlands and -2.7 mPA for saltwater systems
Factors that may impact evapotranspiration
solar radiation, water vapor deficit, air temperature, wind speed in the tree canopy
Plant evolution
first from an aquatic environment then onto land: gained vascular systems, stomata and a cuticle
Photosynthetic components that may be obstructed in aquatic environments
Light: limited by mineral and organic matter which can absorb, reflect and scatter light as it passes through water. Carbon access: CO2 is soluble in water and gets into water via diffusion, some fully submerged plants may use bicarbonate from rocks/soils
components of respiration that may be obstructed in aquatic environments
carbohydrate produced, oxygen, water’s ability to hold oxygen deals with atmosphere and water pressure/water temp
Patterns of O2 availability
Daily fluctuations in DO2 because of photosynthesis in water column: consumption of O2 by aerobic microbial metabolism; Release of O2 into soil by plants; inputs of rainfall/overland surface flow into wetland; exposure of soil/sediment during drought
Carlton and Wetzel (1988) takeaways
Microbes rapidly consume oxygen: plant roots struggle to acquire O2 in deep soil, especially if no photosynthesis
Hypoxia
<2.5 mg/l in aqueous environments
Factors inducing hypoxia
Decomp of organic matter consumes O2: without enough O2, microbial community shifts from being aerobic to anaerobic
Hypoxia and denitrification
Microbes produce nitrogen from nitrate, use manganese, then iron, then sulfate, then start to generate methane: usable nitrogen leaves wetland and goes into atmosphere: reduced forms of Mn, Fe and S harm plants
How do plants deal with hypoxia?
Temporarily switch to anaerobic respiration: burn sugars produced during photosynthesis: lactic acid/ethanol are byproducts. Helps maintain energy production
Aerenchyma
Internal air passageways, allows for O2 diffusion within plants, occur predominantly in roots. Production enhanced in response to flooding. Allows O2 to diffuse into roots and ethylene out of roots
Lenticels
In woody plants: small area where bark is interrupted allowing for gas exchange
Pneumatophores
Specialized root structure growing out of water surface for aeration, common in mangroves and bald cypresses