Module 8
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
advancement in information and communication technologies
allows for scalibility (lower transaction and search costs)
leveraging communities vs features of the product
community as the chief assset vs resource
→ no need to own assets
growing by the power of network effects
the larger the network, the better the matches
as more people join, the more valuable the network becomes
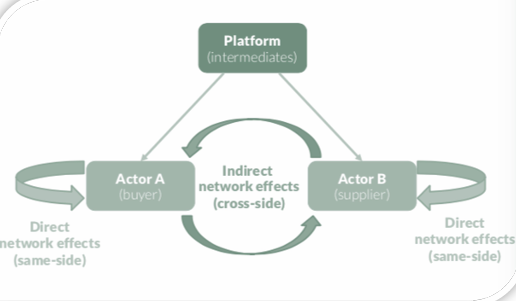
cross side vs same side network effects
Cross-side network effects occur in two-sided or multi-sided markets where an increase in the number of users on one side of the market affects the value for users on the other side. Typically, these markets involve two distinct user groups that interact through an intermediary platform.
Same-side network effects occur when an increase in the number of users on one side of the market affects the value for other users on the same side. This type of network effect is often seen in social networks, communication platforms, and other peer-to-peer systems.
network effects
explain how the value a user derives from a network relates to the number of user in the network
value of network is proportional to n^2 users of users: Matcalf’s Law
two network users can make 1 connection, 5 can make 10, 12 66…
number of possible connections between network users: n(n-1)
two types of network externalities
positive
an additional network user increases value to all other users
negative
an additional user decreases value to all others
a market perspective on networks
market - a medium that facilitates exchange (of goods and services)
one-sided market
two sided market
one sided market
large share of value is derived from a single class of users
eg: messaging services, telephone networks
two-sided market
value is derived from two categories of network users
more complex as the firm must consider interaction between the two sides
eg: payment services, video game consoles, Airbnb, uber
market perspective on networks
same side network effects
cross-side network effects
positive feedback loops
same side network effects
increasing value to a class of users resulting from an increase in the number of users from that class
eg: the added value from your friends joining WhatsApp
cross-side network effects
increasing value to a class of users resulting from an increase in the number of users from another class
eg: greater choice on airbnb : a vendor offering a certain payment option; video game players and developers
positive feedback loop
an increase in a leads to an increase in b which leads to an increase in a
two sided can have both types of exchange benefits
eg: user rating on airbnb
network effects and competition
industries with strong network effects lead to winner-takes all dynamics
may be strong competition when a new market emerges
once a leader emerges, positive feedback loop strenghen its position further
eg: mobile operator, social media
E commerce
use of Internet, web and mobile apps to transact
began in 1995 and grew exponentially (still 12 to 15 % a year)
move from desktop to smartphone
m commerce accounts for 2 third of the total e commer
three major segments of e commerce
retail goods
travel and services
online content
features of e commerce
social
collection of tech-based tools for communication with shoppers
conversation, engagement
leading social commerce platforms: facebook, insta, X, linkedin
mobile
from pcs to mobile phones
mobile marketing is 75% of all marketing
people are constantly connected to a cellphone
local:
local merchants can gain access to customers
personalized offers based on gps location
why is e-commerce different?
ubiquity
marketspace is virtual (allows customers to partake at any time)
transaction costs reduced (cost of participating in the market)
mobile devices extend services to local areas
global reach
transactions cross-cultural and national boudaries (global shipping possible)
universal standards
one set of technology standards: internet standards
lower market-entry costs (the costs merchants must pay to bring their goods to the market)
reduces search costs for customers
richness
supports video, audio, and text messages (allow for content diversification
interactivity
using a chat window to interact with technical support
information density
reduction in information costs (total amount and quality of information available to all market participants)
personalization/customization
technology permits modification of messages, goods (eg amazon adjusts to your preferences)
social technology
promotes user content generation and social networking (every user can be a marketer)
key concepts in e-commerce
information asymmetry
menu costs (merchants’ costs of changing prices)
dynamic pricing
switching costs
delayed gratification
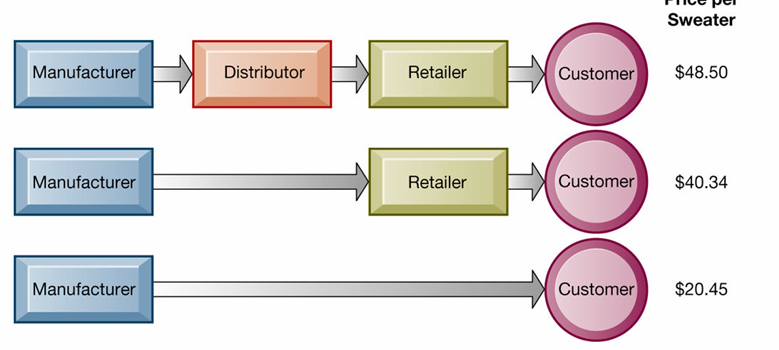
disintermediation
digital goods
goods that can be delivered over a digital network (music, videos…)
cost of producing first unit is almost entire cost of product
cost of delivery over the internt is very low
marketing costs remain the same: pricing highly variable
industries with digital goods are undergoing revolutionary changes
types of E commerce
business to consumer (B2C)
selling products and services to individual shoppers
Business to business (B2B)
involves sales of goods and services among businesses
consumer to consumer (C2C)
consumers selling directly to other conumers
e-commerce can be categorised by platform
Mobile commerce (m-commerce)
Business models
portal (search engine: eg google,, facebook)*
e-tailer (selling goods online: amazon)
transaction broker (eg paypal)
content rovider (netflix)
market creators (bringing two or more sides of the market togather (aibnb)
service provider (gmail)
community provider (instagram, linkedin)
revenue models
advertising revenue model
sales revenue model
subscription revenue model
free-freemium revenue model
transaction free revenue model
affiliate revenue model
advertising revenue model
revenue comes from displaying ads
most widely used revenue model in e-commerce
sales revenue model
sale of good, info or service
micropayment system (apple itunes store)
subscription revenue model
content or services for a subscription fee (spotify)
free-freemium model
basic services for free and premium for advanced (duolingo)
transaction fee revenue model
fee for enbaling or executing a transaction (uber)
affiliate revenue model
referring visitors to other websites for a free (skyscanner)
referral fees or lead generation fees
how e-commerce has transformed marketing
internet provides new ways to identify and communicate with cutomers
long-tail marketing
different marketing and advertising format (email, search, ads, video)
behavioral targeting
tracking the online behavior of individuals
on individual websites-apps and across advertising networks
programmatic ad buying
native advertising
has resulted in concerns about online privacy