Mineral Groups
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What is the fundamental building block of silicate minerals? What is its chemical formula?
The basic building block is the silica tetrahedron, with the chemical formula SiO4
How are silicate minerals classified?
Silicate minerals are classified based on the arrangement of silica tetrahedra and their silicon to oxygen (Si:O) ratio
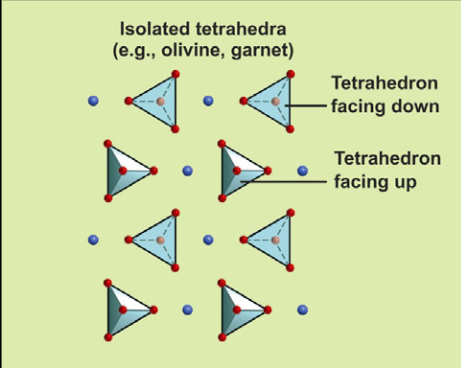
Describe the structure of independent tetrahedra (nesosilicates) and their Si:O ratio
Independent tetrahedra have no shared oxygen atoms. Their Si:O ratio is 1:4
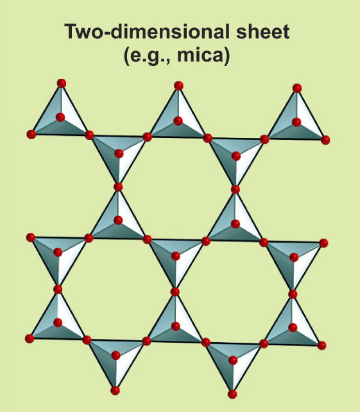
Describe the structure of sheet silicates and their Si:O ratio
Sheet silicates have all three basal oxygen atoms shared, forming sheets. Their Si:O ratio is 2:5

Describe the structure of framework silicates (tectosilicates) and their Si:O ratio.
Framework silicates have all four oxygen atoms shared, forming a 3-D framework. Their Si:O ratio is 1:2
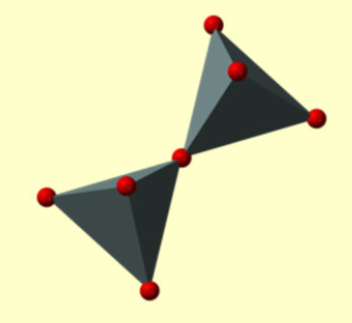
Describe the structure of Paired tetrahedra (sorosilicates) and their Si:O ratio.
One oxygen atom shared, Si:O ratio is 2:7.
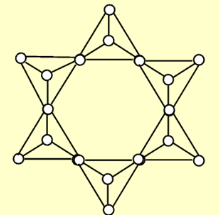
Describe the structure of Ring silicates (cyclosilicates)
and their Si:O ratio.
Ring silicates have two oxygen atoms shared in a six-tetrahedra ring, forming closed rings. Their Si:O ratio is 1:3 (6:18)
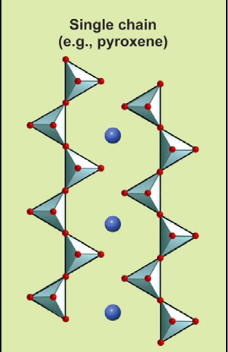
Describe the structure of single chains and their Si:O ratio.
Two oxygens shared: Si:O ratio is 1:3 (3:9)
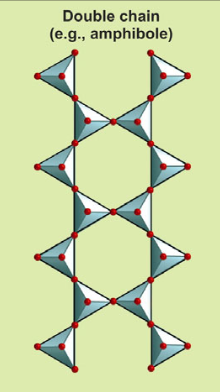
Describe the structure of double chains and their Si:O ratio.
Two or three oxygens shared between tetrahedra; Si:O ratio is 4:11.
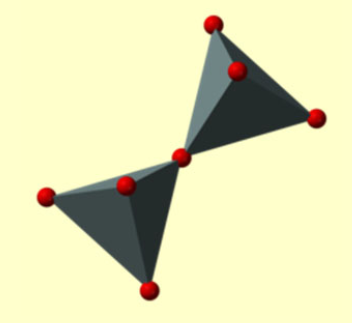
What is the silicon to oxygen ratio of the silicate structure below
2:7
Define a rock. How does it differ from a mineral?
A rock is a coherent, naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals (or, less commonly, glass) Unlike minerals, rocks are composed of one or more minerals
What are three ways that rocks can be held together?
Rocks are held together by cement (mineral precipitation), compaction (grains squeezed together), and crystalline structure (interlocking crystals
What are the three main types of rocks and how do they form?
The three main types are Igneous, Sedimentary, and Metamorphic
Igneous rocks:
Form from the solidification (freezing) of a liquid melt (magma or lava)
Sedimentary rocks
Form from grains of pre-existing rock that are compacted and cemented, or from minerals that precipitate out of solution
Metamorphic rocks
Form when preexisting rocks undergo changes due to heat and pressure without melting
How is sediment formed?
Sediment is formed by the weathering of solid rock
What are the two main categories of weathering that produce sediment?
The two main categories are physical weathering and chemical weathering
Briefly describe physical (mechanical) weathering
Physical weathering is the breakage of intact rock into clasts (pieces) through physical or mechanical processes