Cell injury
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
What are the 4 mechanisms of cell injury? Give possible causes of each.
ATP depletion (hypoxia/anoxia, some toxins)
Permeabilisation of cell membranes (hypoxia/anoxia, ROS, infective agents)
Disrupted biochemical pathways (hypoxia/anoxia, ROS, fatty change in liver)
DNA damage (ROS, replication errors; UV rays, X-ray, gamma ray, some plant toxins, viruses)
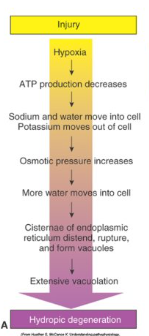
Describe hydroptic degeneration and its cause. What cells are most prone.
Acute cell swelling
Causes cytoplasm swelling with extensive vacuolisation
Due to hypoxia
Reversible change
Hepatocytes, pancreatic acinar cells and renal tubular epithelial cells
(Ballooning degeneration is what occurs in other cell types, like keratinocytes)
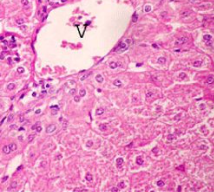
What are the 3 histopathological features of acute (early and reversible) cell injury
Cell swelling
Cytoplasmic vacuolation (caused by distended endoplasmic reticulum, due to excess fluid intake by the organelle)
Hypereosinophilia
What are the three ways hepatocytes react to injury (vacuolisation)
Hydropic degeneration
Fatty change
Glycogen accumulation
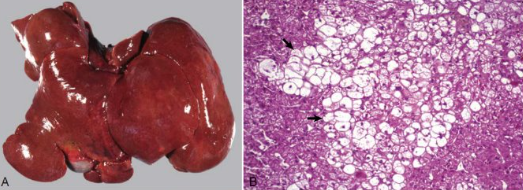
What change does this liver show? Give cause
Glycogen accumulation
Gross = hepatic swelling and pallor
Cause - glucocorticoid administration
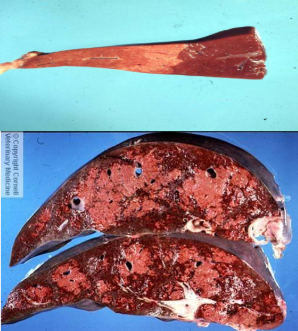
What are these liver changes? State the distributions
Hepatic lipidosis
Top = focal - tension lipidosis in a horse
Bottom = zonal - chronic passive congestion in a cow
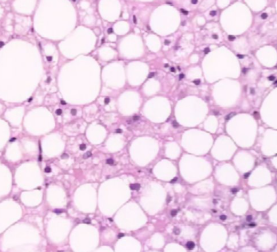
What are the 5 possible outcomes of cell injury
Repair
Adapt
Senescence
Death/necrosis
Dysplasia → neoplasia
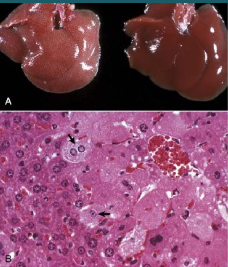
How is this liver reacting to injury? Describe the pathophysiology
Hydropic degeneraton
Excess fluid transferred to endoplasmic reticulum, causing vasuolisation.