Chapter 4 Plutonic field relationships
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Plutonic Rocks
Intrusive – non-specific types commonly called plutons or intrusions
Typically thought of as solidified magma bodies formed at depth within Earth that intrude “country rock”
Remnants of:
crystallized magma-chambers, magma lenses
magma conduits /feeders
volcanic plugs
deep zones of crustal melt
Also late-stage intrusions of granitic veins and pegmatites
Multiple: All phases of injection are of the same composition
Composite: More than one rock type is represented.
Plutonic rocks classified by:
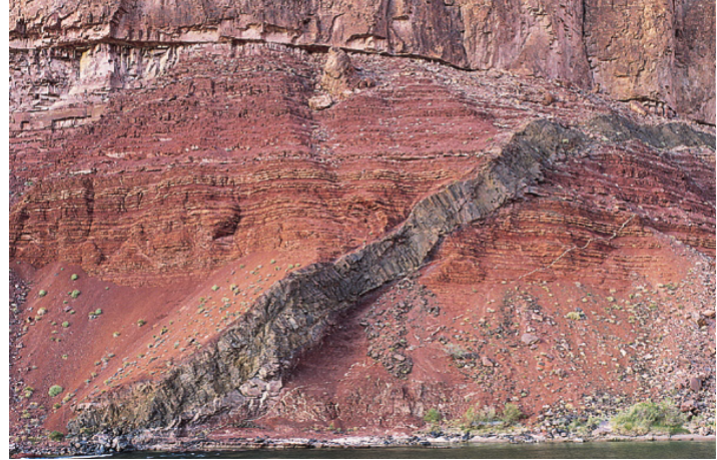
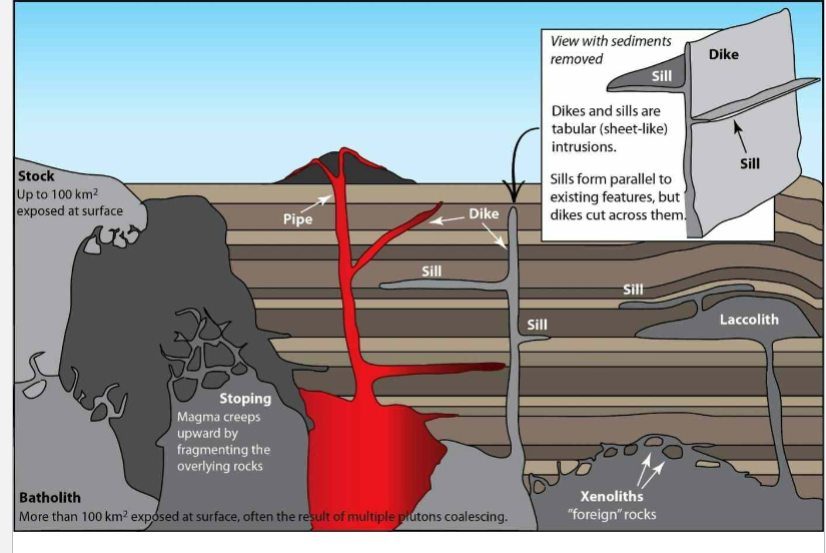
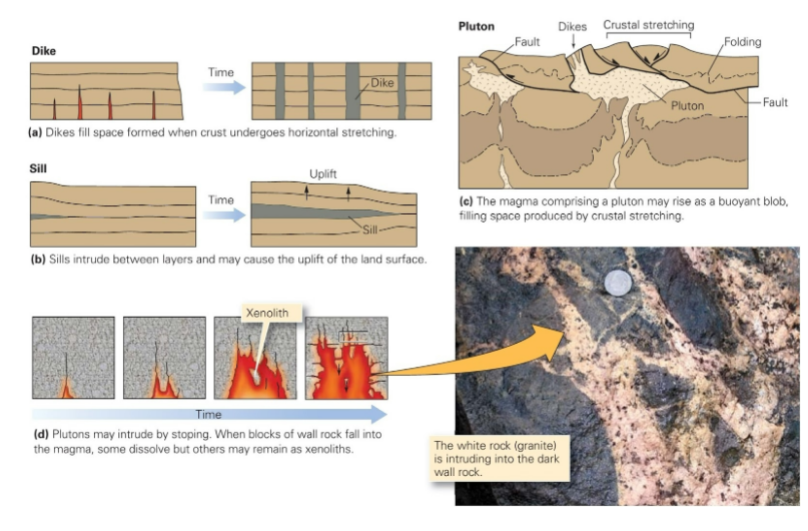
Tabular - injected along planes of weakness (fractures) sheet-like dikes (discordant) and sills (concordant)
Discordant: Cross cutting the country rock body
Concordant: parallel to the country rock structure
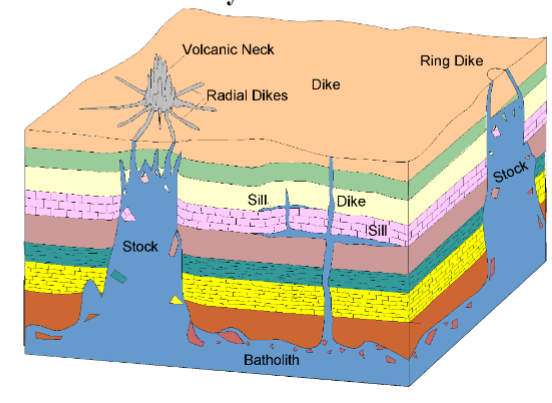
Vast majority of dikes and sills form by injection and dilation
Types of tabular igneous bodies in bedded strata based on method of emplacement.
a. Simple dilation (arrows) associated with injection.
b. No dilation associated with replacement or stoping.
Dike discordant -crosscutting

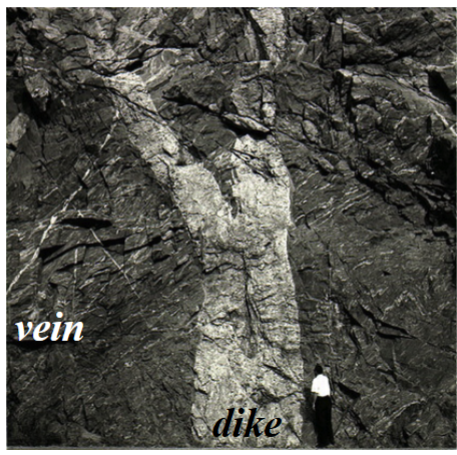
Vein
Vein refers to a small tabular body, whether or not it is discordant or concordant

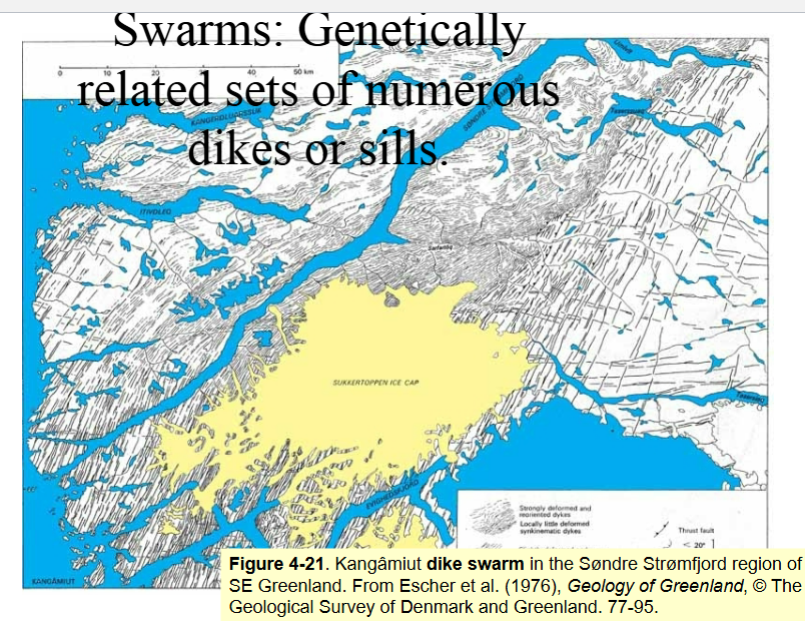
Swarms
Genetically related sets of numerous dikes or sills
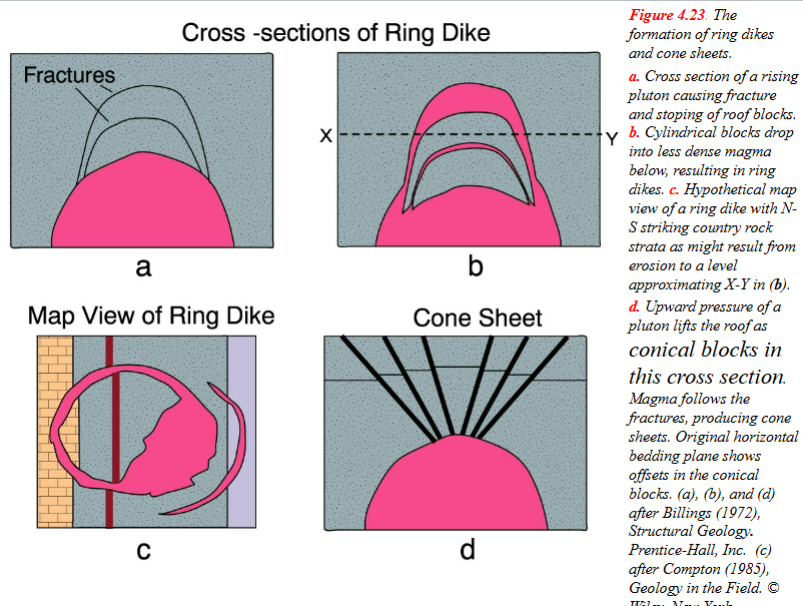
Yhe
formation of ring dikes
and cone sheets.
Cross section of a rising pluton causing fracture and stoping of roof blocks.
b. Cylindrical blocks drop into less dense magma below, resulting in ring dikes.
c. Hypothetical map view of a ring dike with N- S striking country rock strata as might result from erosion to a level approximating X-Y in (b).
d. Upward pressure of a pluton lifts the roof as conical blocks in this cross section.
Magma follows the fractures, producing cone sheets. Original horizontal bedding plane shows offsets in the conical blocks.
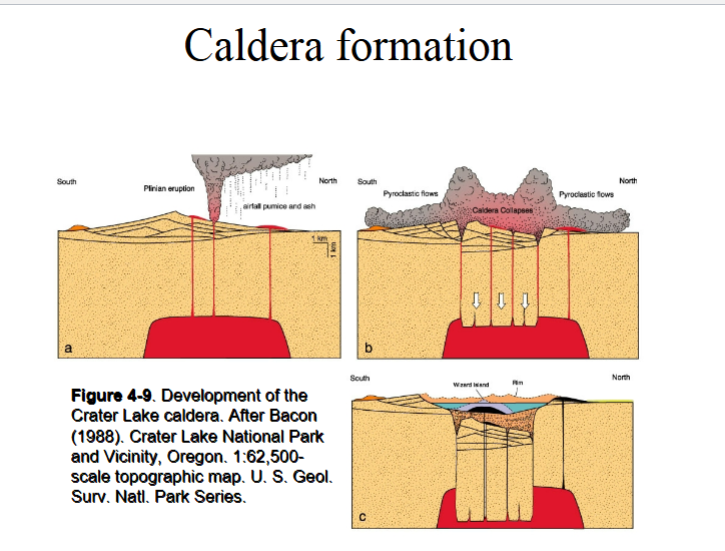
Caldera formation
Plutonic rocks classified by: Non-tabular
Non-tabular – detailed form depends on depth, density, ductility of country rock
various shapes
stocks (< 100 km2): plugs, necks –often volcanic conduits
Batholiths- ( >100km2; often composite): Mostly discordant but some more conformable to regional structures
laccolith (arched roof)
lopolith (cone shaped basin)
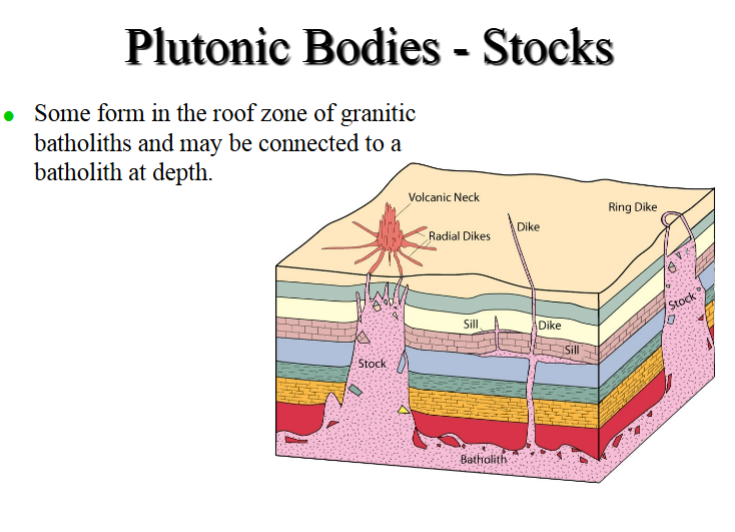
Plutonic Bodies - Stocks
Smaller igneous bodies, generally steep sided (roughly cylindrical).
Many unrelated to larger batholiths
-These associated with alkaline mantle derived magmatism at continental rifts and hotspots
Not limited to being granitic
Some form in the roof zone of granitic batholiths and may be connected to a batholith at depth
Plutonic Bodies - Batholiths
-Largest plutonic rock body (>100km2).
-Smaller bodies called stocks
-Broadly granitic in composition.
-Typically form in orogenic belts
-Deep roots. For some debate exists about the 3- shape/deeper structure
-Magmas ascend at depth via plastic deformation of surroundings. At shallower depths ascend by stoping.
-Probably rise as diapir
-Amount thermal energy to form and maintain batholith as it rises is high.
-Most cases heat source is mantle-derived basaltic melts.
-Form in orogenic belts and some in continental hotspots & rifts
Volcanic plugs
A volcanic plug: Stocks representing the cylindrical conduit and magma chamber
beneath volcanoes.
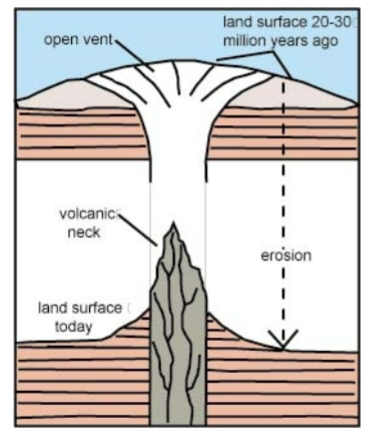
Volcanic plugs
volcanic neck: exposed portion of a plug, commonly remaining after the more easily eroded volcanics of the cone removed
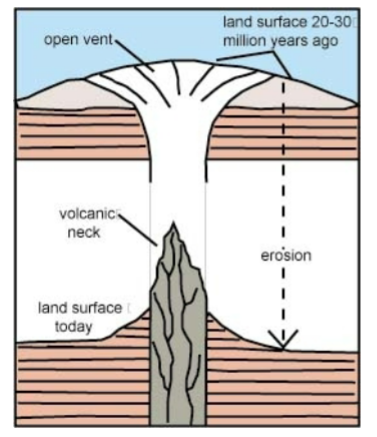
Ship Rock NM
Ship Rock NM the central feeder pipe of larger volcanic landform which has since
eroded away.
Concordant Plutons: Laccoliths and Lopoliths
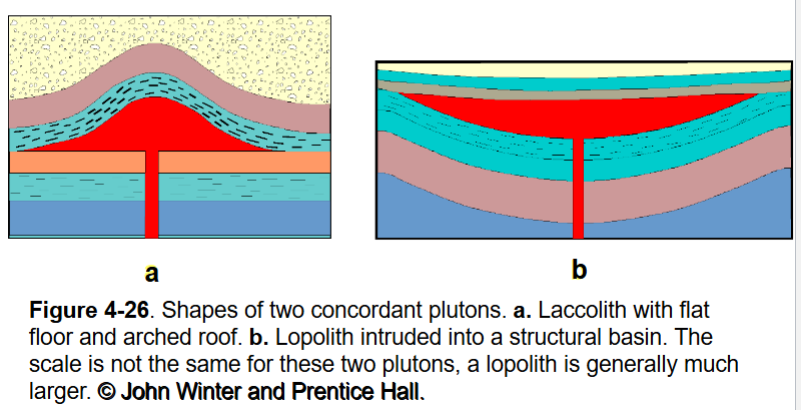
Plutonic Bodies - Laccolith
-Sufficiently viscous (silicic) to limit magma flow along the horizon plane
-Shallow enough to lift the roof rock
-Much smaller than lopolith
Plutonic Bodies - Lopoliths
-Down warped (saucer-shaped) concordant mafic intrusion.
-Almost all Precambrian
-Much larger than laccolith
Bushveld complex in S. Africa largest at 300 km diameter and 8 km thick)
Took 200,000 years to cool
-Some associated with meteorite impact
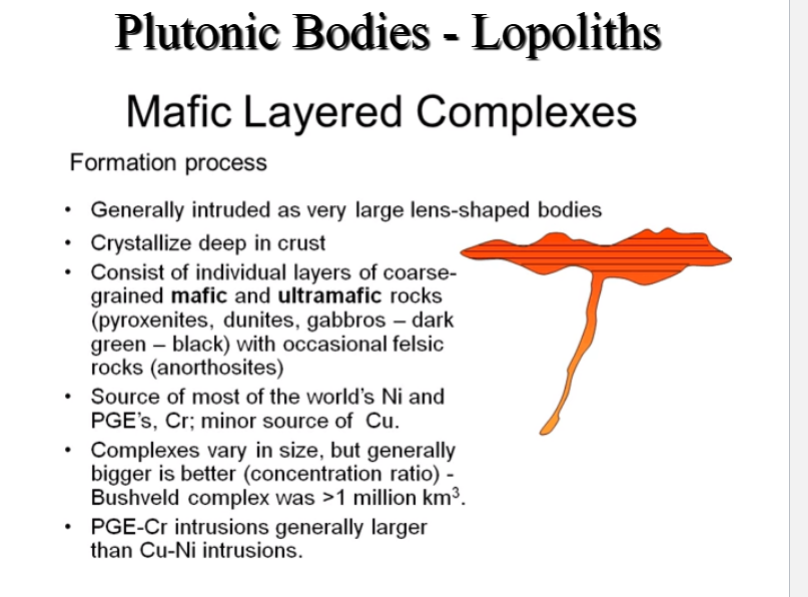
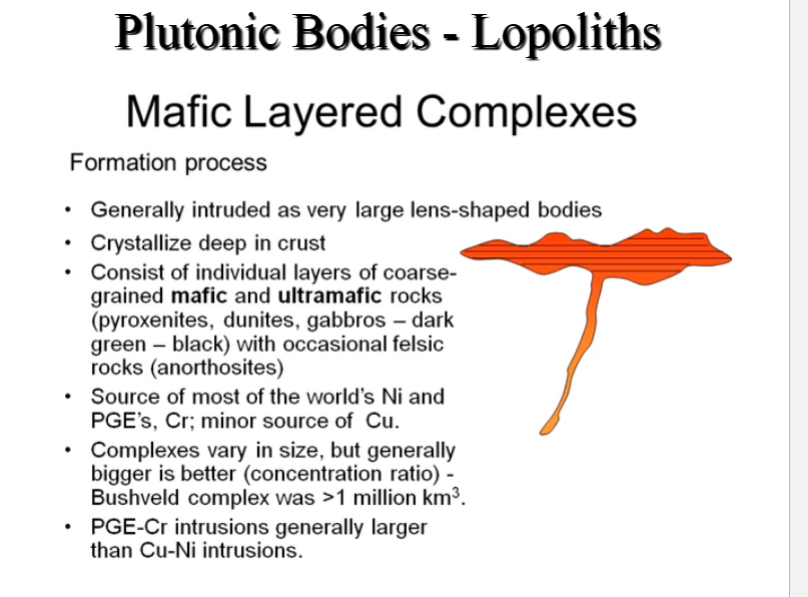
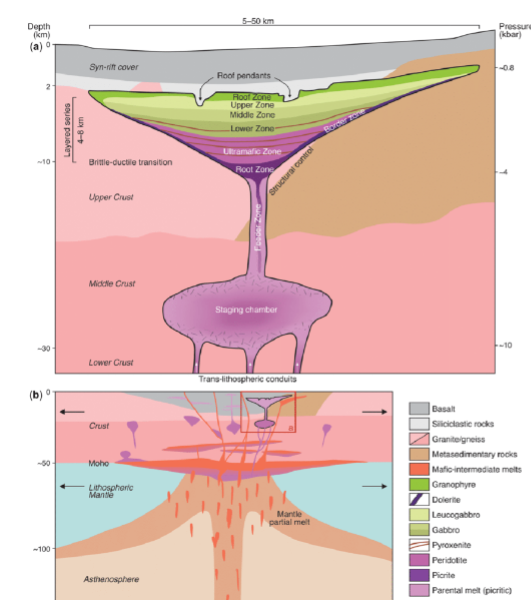
Layered Mafic Intrusions: LMI form in regions of extensive magmatism
Characterized by igneous layering distinguishable by shifts in mineralogy, texture, or
composition
Many emplaced during the Precambrian, predominantly at the margins of ancient cratons during intervals of supercontinent accretion and destruction
Contacts of Plutons: Chilled margins:
Chilled margins: A margin of finer grain size resulting from rapid solidification of the pluton at the contact with wall rock (thermal effects)
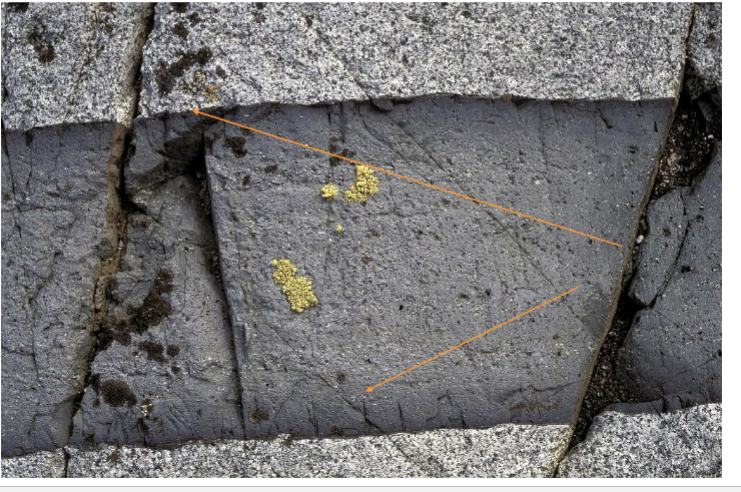

Contacts of Plutons

Schelieren
Schelieren: Elongated or flattened mineral aggregates or ductile
heated xenoliths that produce disc-shaped mass
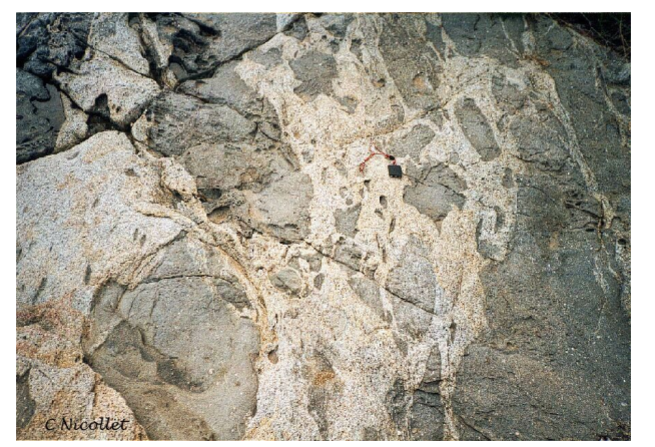

Marginal foliations
Marginal foliations developed within a pluton as a result of differential motion across the contact.
If the intruding magma is sufficiently viscous and the country rock hot enough, the contact shear can also affect the country rock, rotating the foliation outside the pluton
into parallelism with the contact.
Discordant to Concordant

Classification related to tectonic timing of intrusion
Related to Orogenic / subduction processes
Post-tectonic
After a metamorphic event, cross-cut deformation (lack deformational features ass. w/ met event) and overprint metamorphism
Syn-tectonic
During orogenic event.
Related to regional metamorphism foliation,continuous w/ emplacement
True granites associated with migmatites and gneiss
Pre-tectonic (rare)
Emplacement prior to an orogenic event. Imprinted by met.
MOR or Arc-related volcanism/plutonism
Additional Classification related to depth of intrusion
Pressure and Temperature of country rock
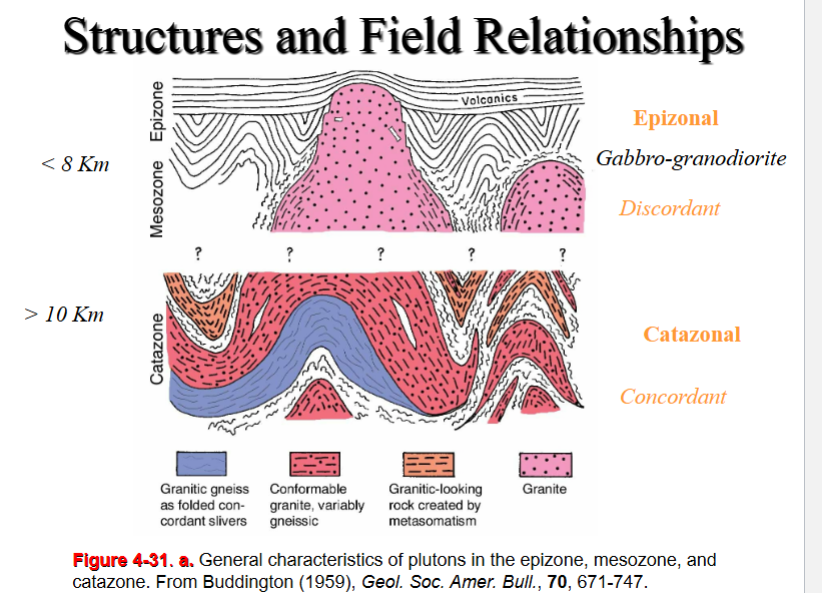
Epizonal : Brittle and Cool country rock
Shallow level < 8 Km (~3 kb, 0.3 Gpa)
Low T - <300 °C
Post-tectonic
Discordant – sharp contacts, tend to be smaller surface exposure
Contact metamorphic zone (high T low P)
Mesozonal – Low grade regional metamorphic rocks
Transitional (5-15 km, 300-500 °C)
Sharp-gradational contact; discordant or concordant
syn- or post- tectonics
Catazonal: Regional Metamorphism, hi-P and T (migmatites)
Deep Crustal levels >10 km
High T (> 400 -600°C)
Syn-tectonic, gradational contacts with no chilling margins
Conformable, deformation common
Magma Ascent and emplacement
Diapir
Diapir: a mobile mass that rises andmpierces the layers above it.
Diapiric Rise Model: Rising through ductile country rocks or rely on fractures or other weaknesses in the rocks
