Ch 1: Chromosomes
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
In eukaryotic cells, nuclear DNA is present as ____ chromosomes inside of the nucleus
linear
What is the distinguishing feature of eukaryotic cells?
the nuclear envelope
In eukaryotic cells, organelle DNA is present as ____ chromosomes inside of the _____ and, in plants and algae,_______
circular, mitochondria, chloroplast
What are the two major phases of cell division?
- M phase (mitosis + cytokinesis)
- interphase
Mitosis
division of the nucleus
cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm
interphase
- G1 (cell growth) +S (DNA replication) +G2 (cell growth)
- non-divisional phases of cell division cycle
G0
- cell may exit cell division cycle during G1 and go into G0 to become non-dividing cell (quiescence)
- intestinal epithelium, neurons, etc (stay in G0 until death)
-if part of liver is cut, G0 cells will enter diving phase again to replace tissues
G1/S checkpoint
- cell makes sure dna molecule is intact, if not it fixes it and moves on
- once cell undergoes s phase the cell must divide
G2/M checkpoint
- makes sure all molecules replicated and size is large enough
end of mitosis and during G1/G0
each chromosome consists of a single dna molecule
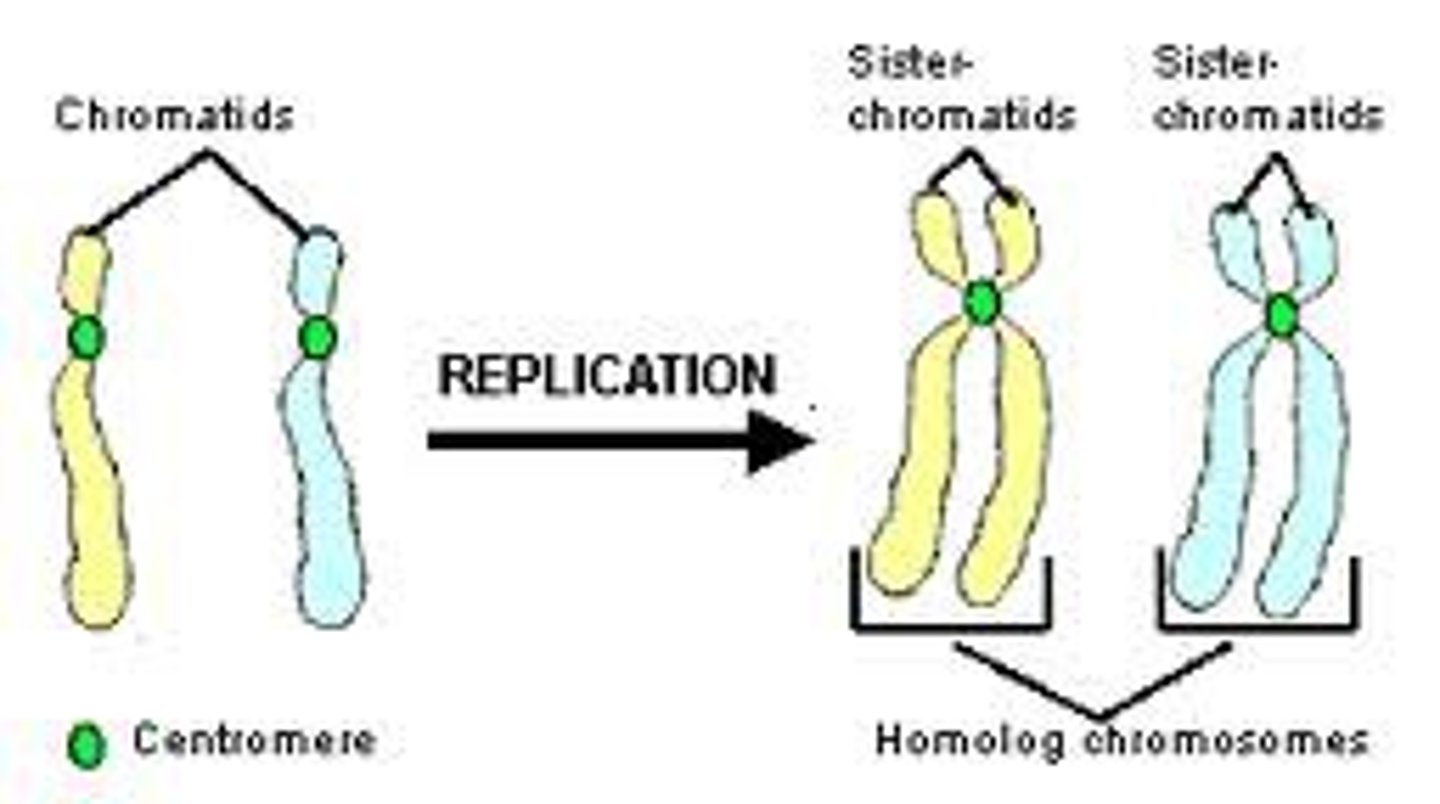
after S-phase and during G2
each chromosome consist of two DNA molecules (two identical sister chromatids)
telomeres
- stable ends of linear chromosomes
- bacteria are circular and do not have telomeres
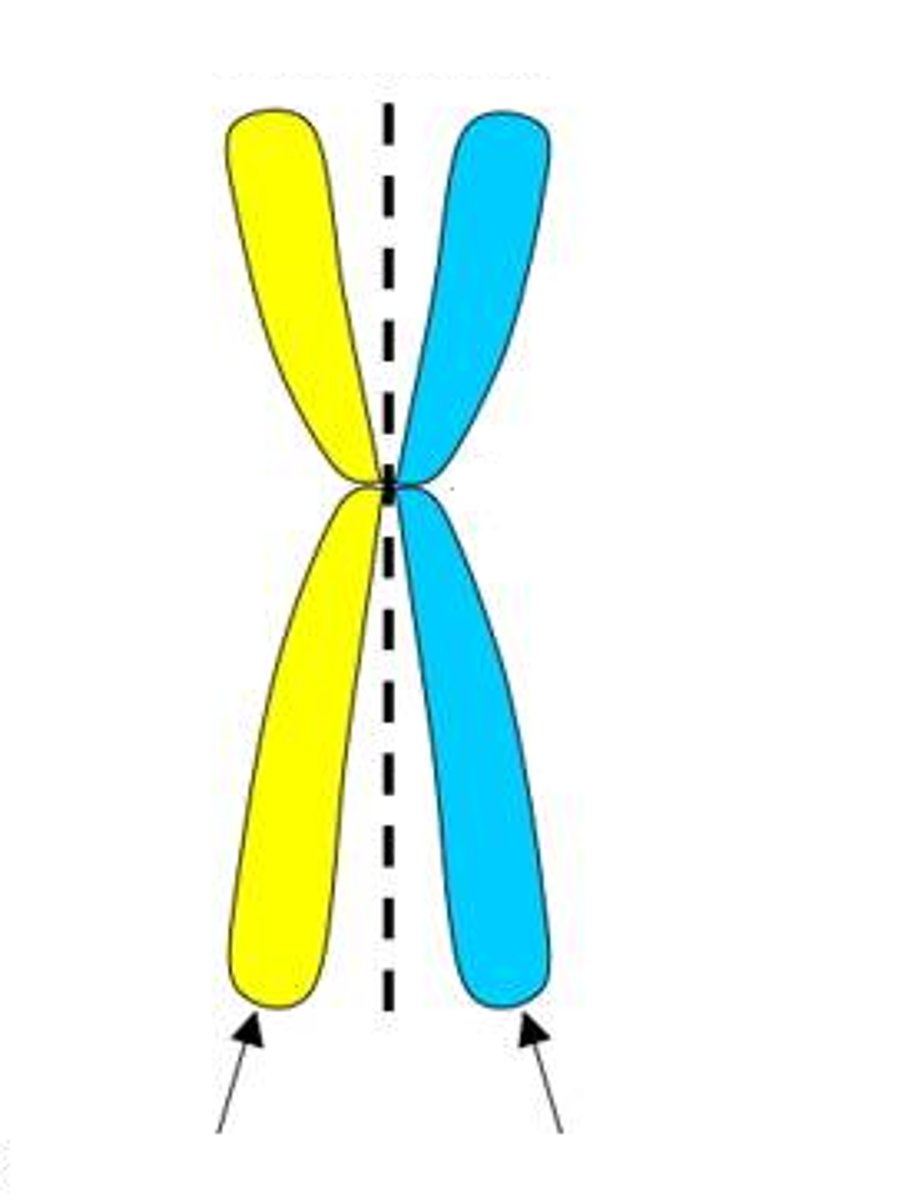
centromere
- defined region of a chromosome at which sister chromatids are joined following dna replication
interphase vs prophase
interphase:
- chromatin is decondensed and unidentifiable
- bowl of noodles (own distinct territories- don't like to mix, gaps for enzymes to travel)
prophase:
- chromatin is condensed into visible chromosomes by tightening interactions between dna and chromatin proteins (histones- wraps around inside particle twice and held in place by outside histone)
nucleosome
- basic unit of organization of dna in nucleus
- dna wrapped around 2x + 2 histones
chromatin
- dna+histones but loose/decondensed
- occurs during non-divisional phases of cell cycle
chromosomes
- before rep: single molecule of dna
- after rep: chromosomes consist of 2 sister chromatids, which contain identical dna sequences
chromosomes classified based on centromere location
- metacentric: center
- submetacentric: near center
- acrocentric: near telomere
- telocentric: at the telomere
- point of junction rarely at the center of the chromosome
locus
- specific point in chromosome
- p arm: petite/short arm
- q arm: long arm, below centromere usually
- Chromosome #, arm, designation
- all genes are in loci, but not all loci contain genes
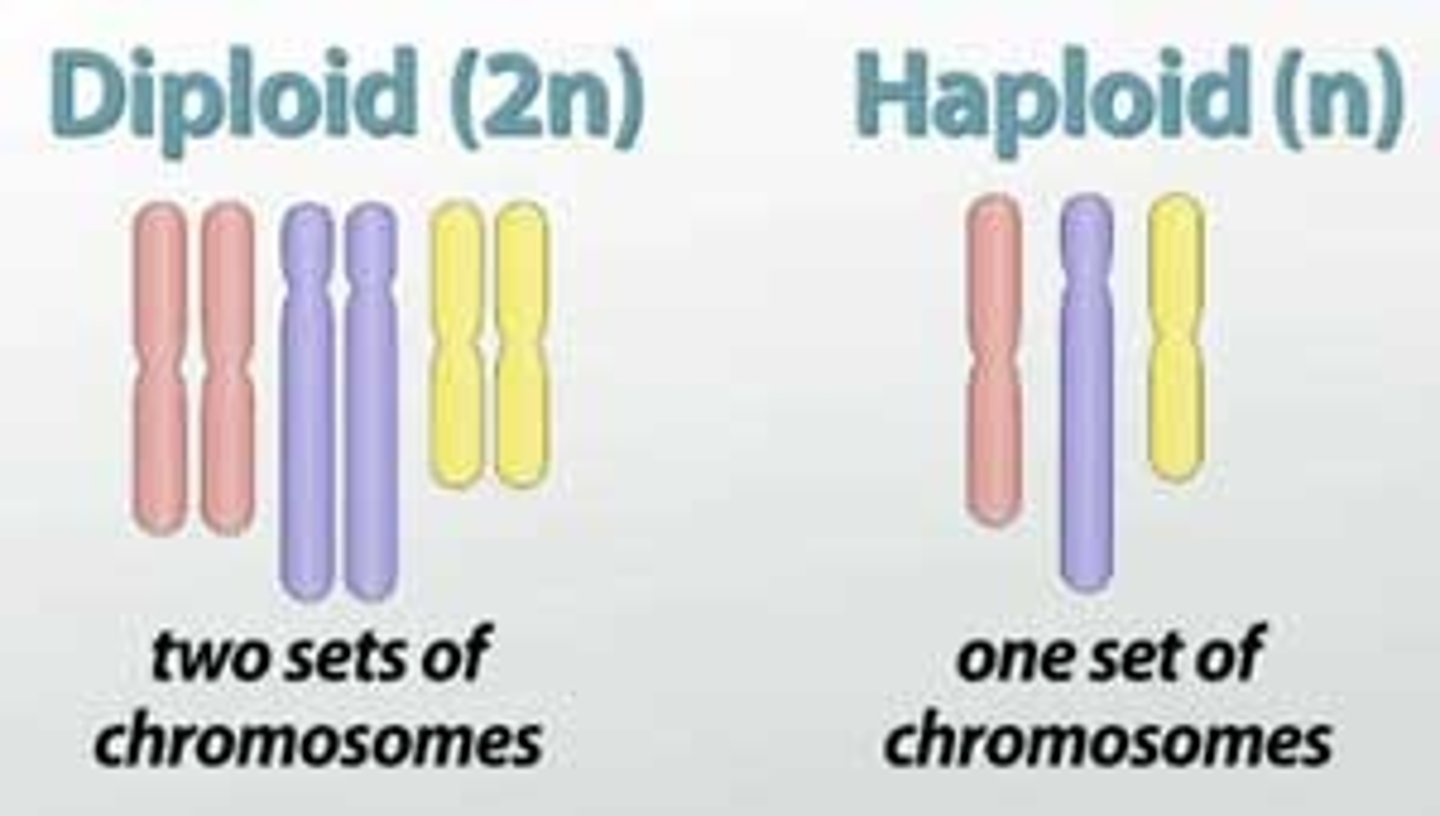
haploid
-N
- one copy of genetic material subdivided into chromosomes
- unpaired chromosomes
- humans= 23, gametes only
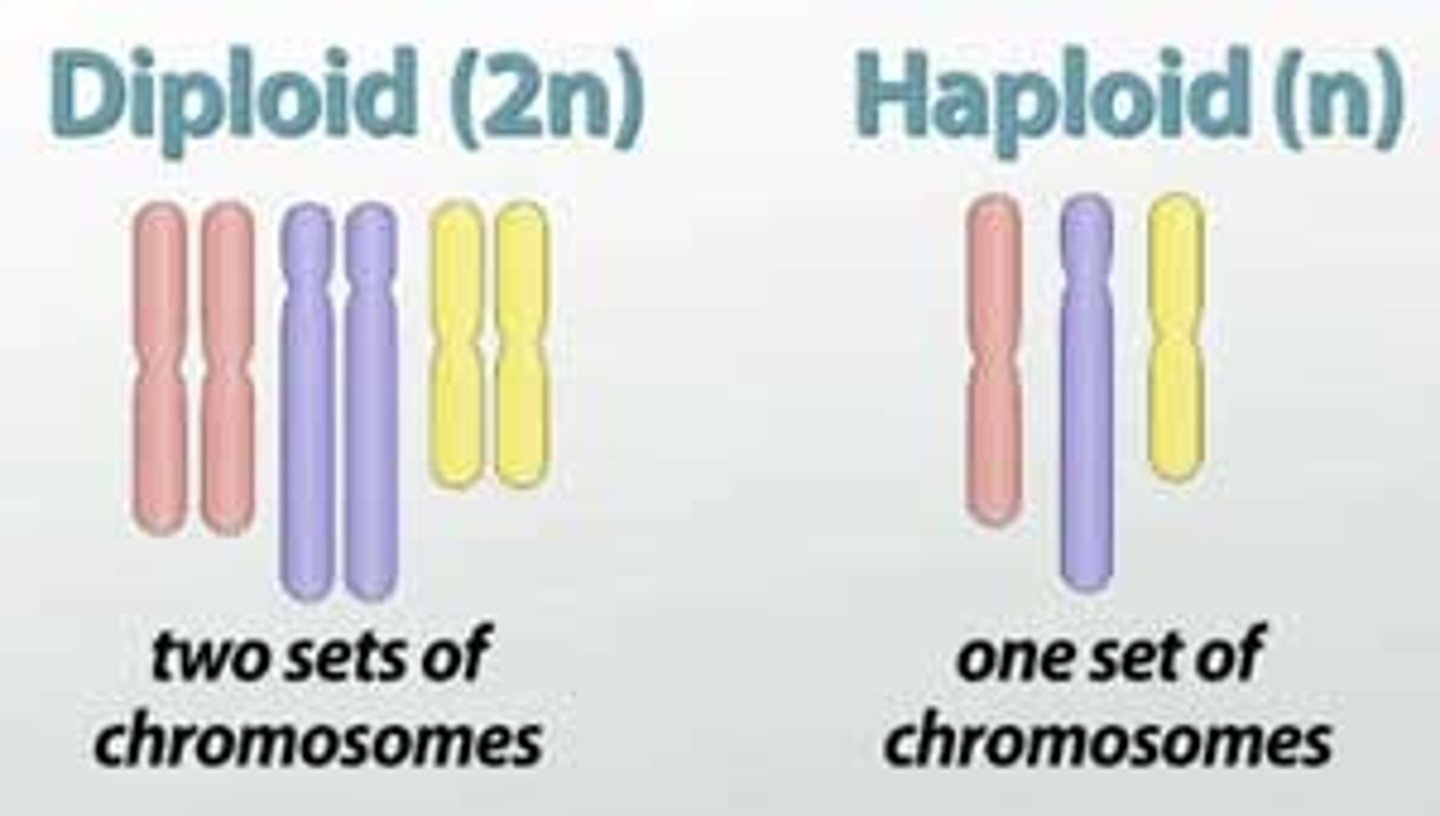
Diploid
- 2N
- two copies of genetic material subdivided into chromosomes
- diploid organism has 2 sets of chromosomes organized as homologous pairs
alleles
alternative forms of gene found at same position (locus) of homologous chromosome
homologous chromosomes
- chromosomes with same length and centromere location but not necessarily identical dna sequences. some of their genes may be allelic
- not sister chromatids because not the product of replication of one chromosome, not joined, and not identical
gene (transmission genetics)
a unit of heredity that is transferred from a parent to offspring and is held to determine some characteristic of the offspring.
gene (molecular genetics)
a region of a chromosome that codes for a functional product
karyotype
- Visual representation of an organism's complete set of chromosomes.
- humans- 22 homologous autosomal and pair of sex determining chromosome
Ploidy
the number of sets of chromosomes in an organism
polyploid
3n,4n,5n, etc
aneuploid
- Abnormal number of chromosomes.
- humans, having any number of chromosomes that is not 46
kinetochore
- protein structure that is assembled on centromere
- during mitosis, spindle microtubules attach to it and mediate the disjunction of sister chromatids
centrosome
- pair of centrioles
- it is the microtubule-organizing center of animal cells
- it is replicated before the beginning of mitosis, becoming a pole for spindles
prophase
- chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes
- centrosomes move away from each other to become poles of mitotic spindles made from microtubules
prometphase/metaphase
- nuclear envelope breaks down, mitotic spindles attach to kinetochores at the centromeres of chromosomes, and chromosomes line up at metaphase plate
anaphase
- chromatids are pulled apart by spindles and are disjoined
- are now individual chromosomes
- transient 4n cell (4 chromosomes becomes 8/ humans 23->92)
telophase
- chromosomes are segregated and their dna decondenses
- they become the chromosomes of the daughter cells
- nuclear envelope reassembles
- 2 diploid (2n) cells, each chromosome consist of single dna molecule
defining feature of mitosis
- all chromosomes go to metaphase plate individually
- homologous chromosomes at metaphase plate is not a requirement (haploids can undergo mitosis)
meiosis
- a special type of eukaryotic cell division cycle that occurs during generation of gametes in animals (sperm/eggs), or spores in plants and single-cell eukaryotes
- occurs in germ cells
- 2 rounds of division-> 4 haploid (1n cells)
tetrads
- 2 homologous chromosomes together (23 tetrads in humans)
meiosis 1
- reduction division
- tetrads are disjoined
- separated homologous chromosomes, still with 2 chromatids each, are segregated to daughter cells
- number of chromosomes in two daughter cells is half of that of the original cell
crossing over
-exchange of fragments of DNA between paired homologous chromosomes, occurs during pachytene
- pairing of chromosomes mediated by synaptonemal complex (ordered protein structure formed between homologous chromosomes during meiotic prophase 1)
- complex facilitates crossing over between non-sister chromatids and disappears during late meiotic prophase 1
5 substages of meiotic prophase 1
- leptotene: DNA begins to partially condense
- zygotene: homologous chromosomes pair to form tetrads (bivalents)
- pachytene: condensation continues and the individual chromatids become more visible. Crossing over occurs: the exchange of fragments of DNA between the paired homologous chromosomes
- diplotene: the homologous chromosomes begin to partially separate. The chiasmata become visible: points at which crossing over already occurred
- diakinesis: the homologous chromosomes pull further apart (but they remain together). Further condensation occurs in preparation for metaphase
following pachytene
- sister chromatids are no longer identical dna molecules due to crossing over and recombination between non-sister chromatids
middle prophase 1
chromosomes begin to condense and the spindle forms
late prophase 1
Homologous chromosomes pair, crossing over takes place, nuclear membrane breaks down
metaphase 1
Paired homologous chromosomes line up along the metaphase plate, mitotic spindles attach at kinetochores
anaphase 1
homologous chromosomes separate and are pulled to opposite ends of the cell
telophase 1
- 2 haploid (1n) cells
- chromosomes arrive at spindle poles and cytoplasm divides
meiosis 2
- equational division
- chromatids are disjoined and become individual chromosomes
- they are segregated to daughter cells
prophase 2
- may or may not decondense
- chromosomes recondense
metaphase 2
-individual chromosomes line up on the equatorial plate
anaphase 2
sister chromatids separate and move toward opposite poles
telophase 2
- chromosomes arrive at spindle pole and cytoplasm divides -> outcome is 4 haploid cells
- need diploid or even number for meiosis to be able to occur
spermatogenesis
- equal cytokinesis
- 4 gametes (sperm=haploid)
oogenesis
- unequal cytokinesis- one cell receives all the cytoplasms
- rest become polar bodies
- 1 gamete (egg=haploid)
fertilization
produces a zygote (diploid)
nondisjunction
- occurs if chromosomes or chromatids do not separate during anaphase 1 or anaphase 2 of meiosis
- both chromosomes/chromatids migrate to same gamete
- after fusion with normal gamete, trisomic and monosomic aneuploidies may occur
down syndrome
- trisomy 21 aneuploidy
- trisome-x viable but 13 and 18 not usually
turner syndrome
- monosomy x aneuploidy
- female features with webbed neck, shield chest, underdeveloped breast, rudimentary ovaries, brown nevi
cri-du-chat syndrome
- loss of piece of one of two copies of a chromosome, partial monosomy of 5p
- complete autosomal monosomies not viable in humans